Transcutaneous Implant for Skeletal Attachment of External Prosthetic Devices
a prosthetic device and implant technology, applied in the field of transcutaneous implant for skeletal attachment of external prosthetic devices, can solve the problems of poor proprioception of users, inability to adapt to the prosthetic interface, so as to facilitate the extraction of bone components, facilitate the connection of the prosthetic interface to the bone anchorage, and facilitate the effect of extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Two-Piece Transcutaneous Device
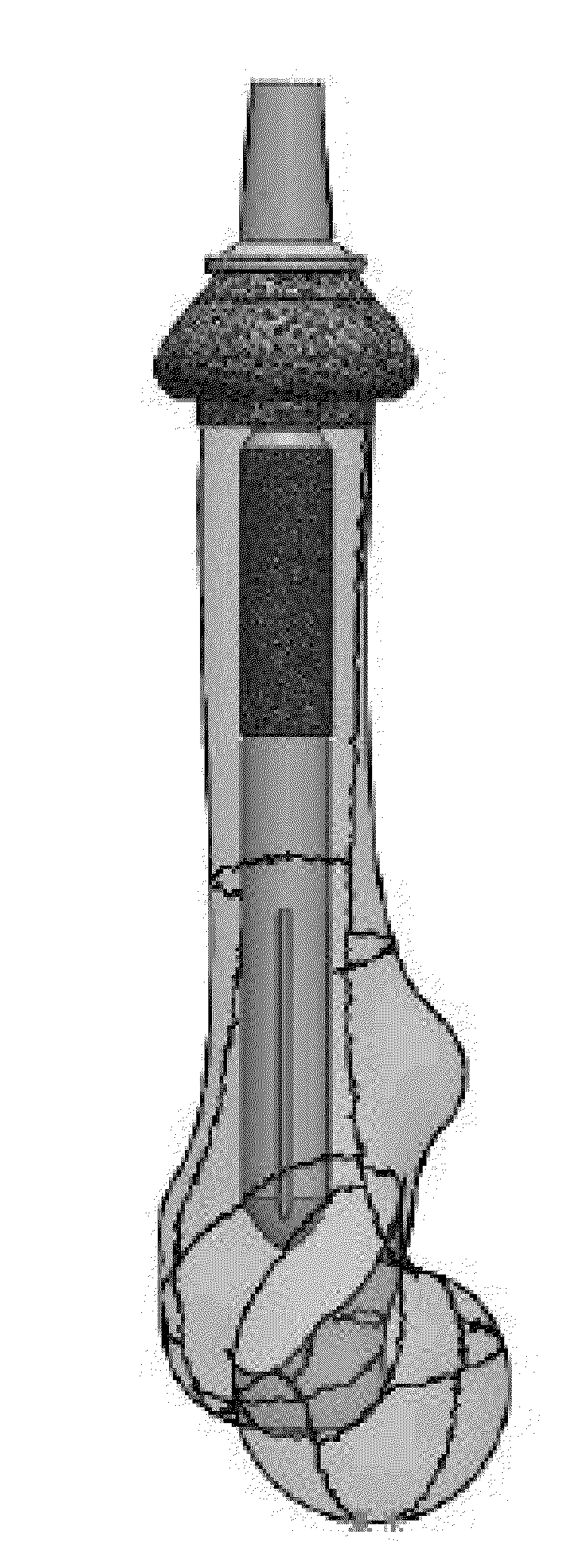
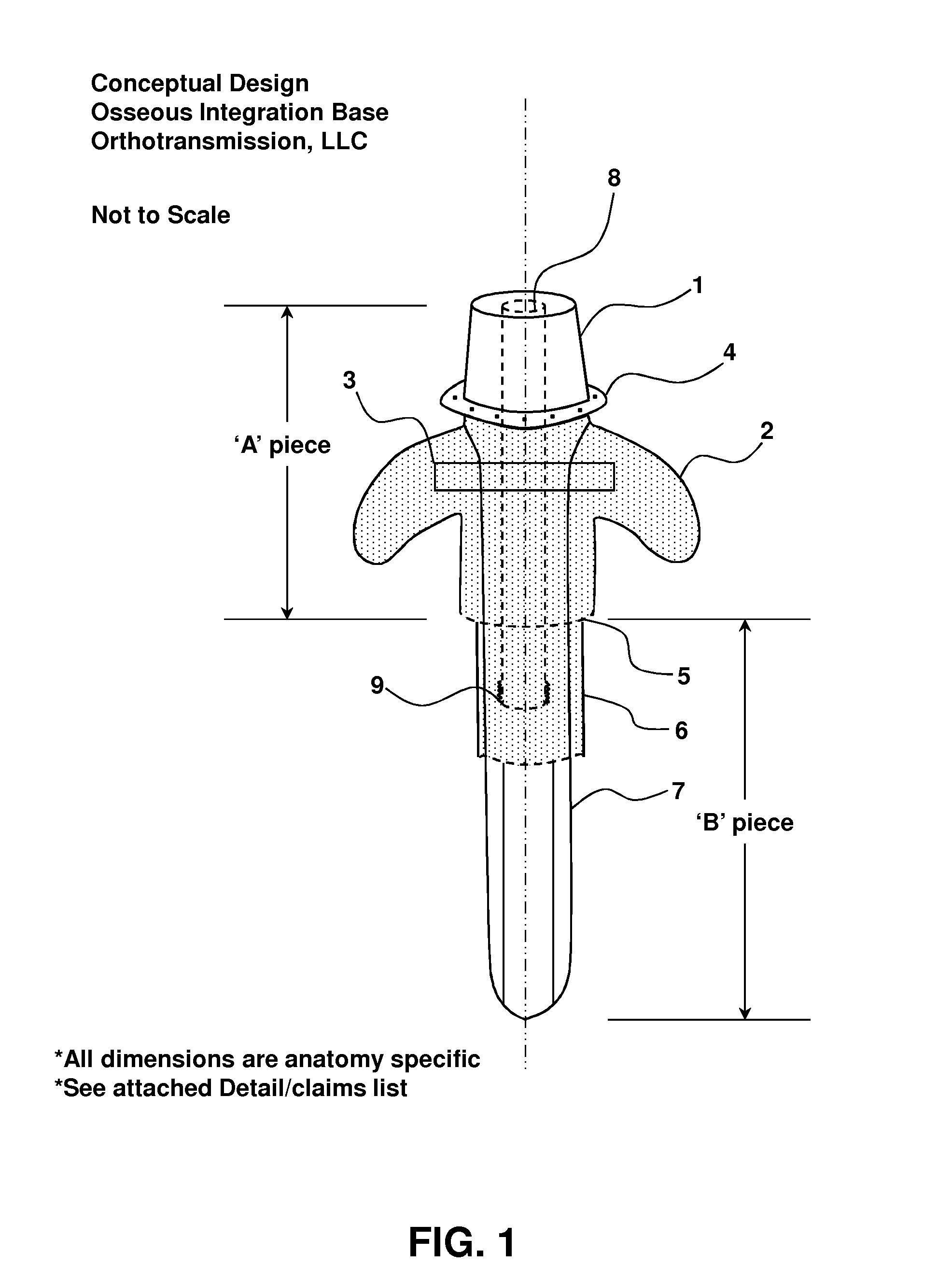
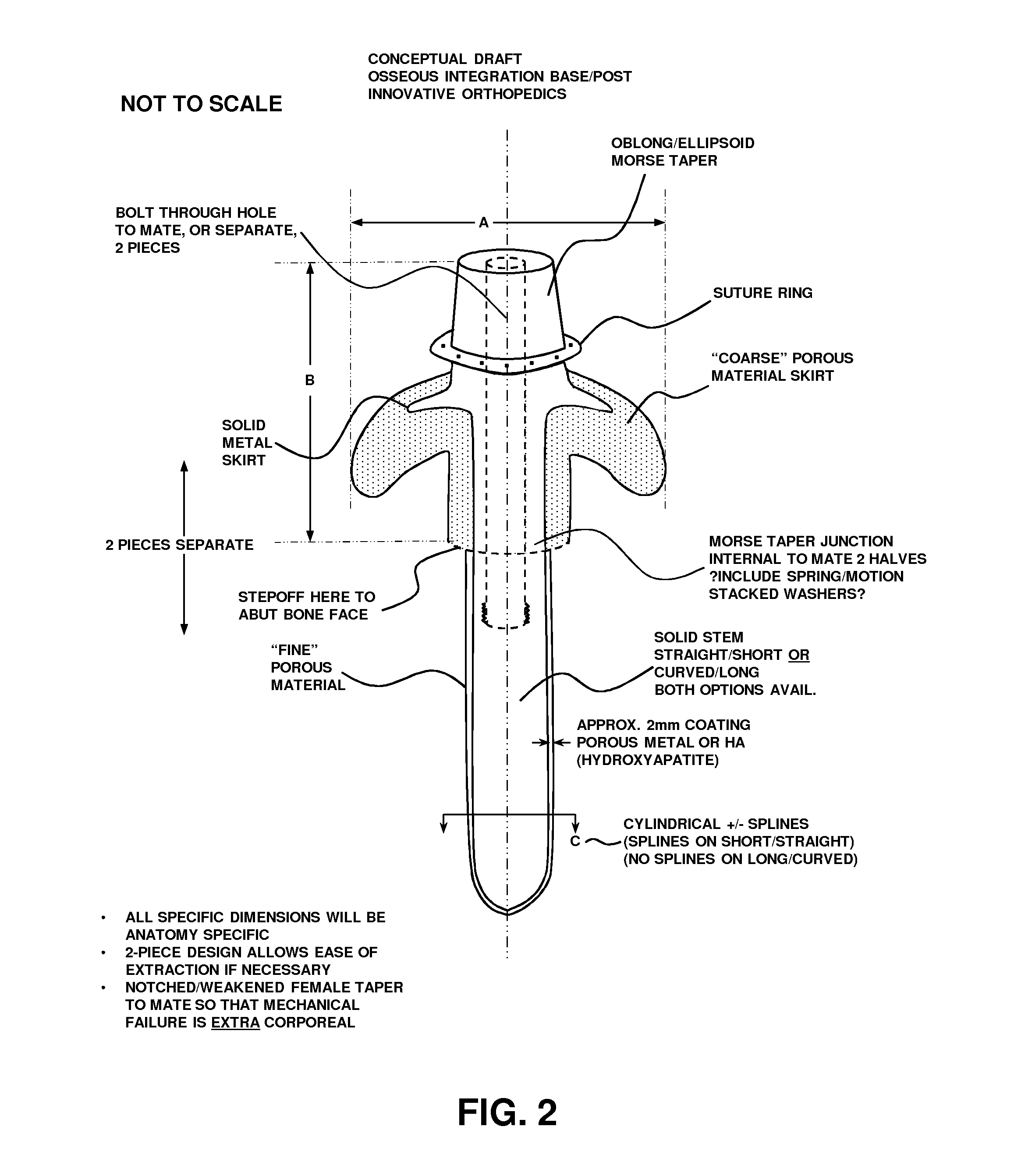
[0077]FIGS. 1-2 illustrate a two-piece transcutaneous device designed to provide a bone anchor in the bone of a residual limb or digit in an animal (human or non-human) for direct skeletal attachment of an external prosthetic device. The device uses highly porous coating along the majority of its length to act as a matrix for biologic ingrowth of various tissues.
[0078]The biologic ingrowth at the bone interface (in and around 5 of FIG. 1) is bony and facilitates rigid, stable, and durable fixation of the implant to the bone. The biologic ingrowth in the soft tissues in and around 2 (skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle) provides an effective barrier against infection at the bone / implant interface due to its vascularity—making available white blood cells and antibiotic delivery via blood vessels if necessary to ward off advancing bacteria.
[0079]The device is illustrated as two separate pieces, ‘A’ Piece (“prosthetic interface”) and ‘B’ Piece (“bone anchor”...
example 2
Prosthesis for Transfemoral Amputees
[0090]An example of a prosthesis for use by transfemoral amputees is illustrated in FIG. 3. The overall system can be characterized into different subsystems: the patient 10 (residual limb), implant 20, prosthesis 40 and, optionally, a failsafe 30 that operably connects the prosthesis 40 to the implant 20, including any of the two-piece transcutaneous devices disclosed herein. The failsafe functions as an interface between the prosthesis and the implant and, therefore, the patient; in particular the bone that surrounds the bone-implanted portion of the implant. As further discussed below, system load is empirically measured by force or pressure transducers, computationally determined such as by finite element analysis, and / or obtained from the literature. In this manner, the loads exerted on bone by the implant in various settings are determined. With such loads known, as well as the strength of patient's tissue such as bone strength and bone fail...
example 3
Failsafe
[0117]Examples of a failsafe 30 (see FIG. 3) for use between the prosthesis and the implant is provided in FIGS. 20 and 32. The failsafe, also referred to as failsafe mechanism or failsafe element, is designed to ensure that dangerous loads are not transmitted to the body, thereby avoiding possible harm such as bone fracture and / or bone anchor damage requiring surgical removal and replacement. Another example is provided in U.S. Pat. Pub. No. 2008 / 0058957. The implant provided herein may use any failsafe. The failsafe is preferably reliable, simple and easy to use. FIG. 20A shows one option for a failsafe based on controlled material properties, such as a shear pin and two notches. The shear pin 2000 is designed to fail in torsion while the notches 2010 are designed to fail in bending, in this case posterior / anterior and / or medial / lateral directions. Another failsafe option is provided in FIG. 20B that relies on a mechanical system having a plurality of springs 2020 connecte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com