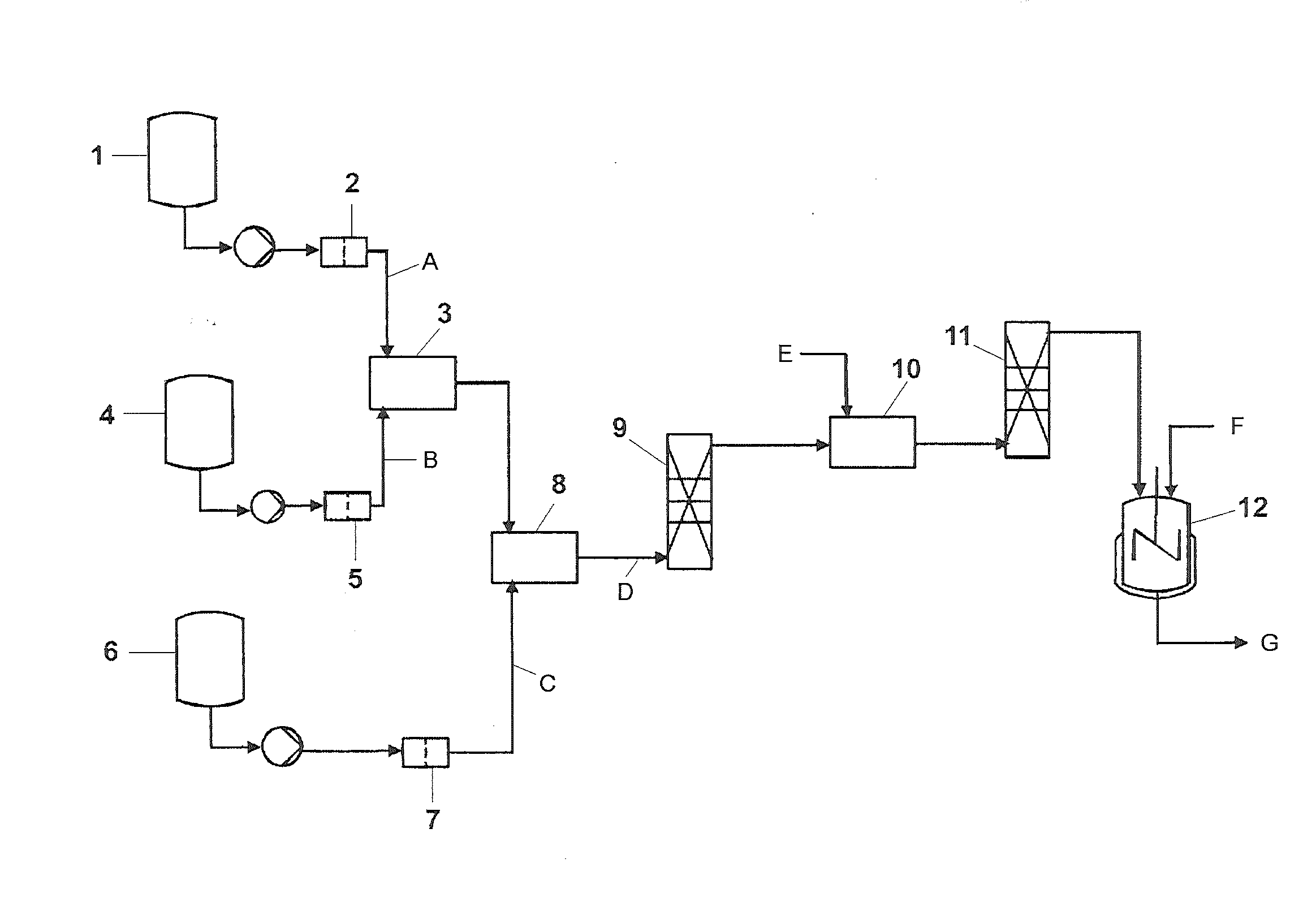
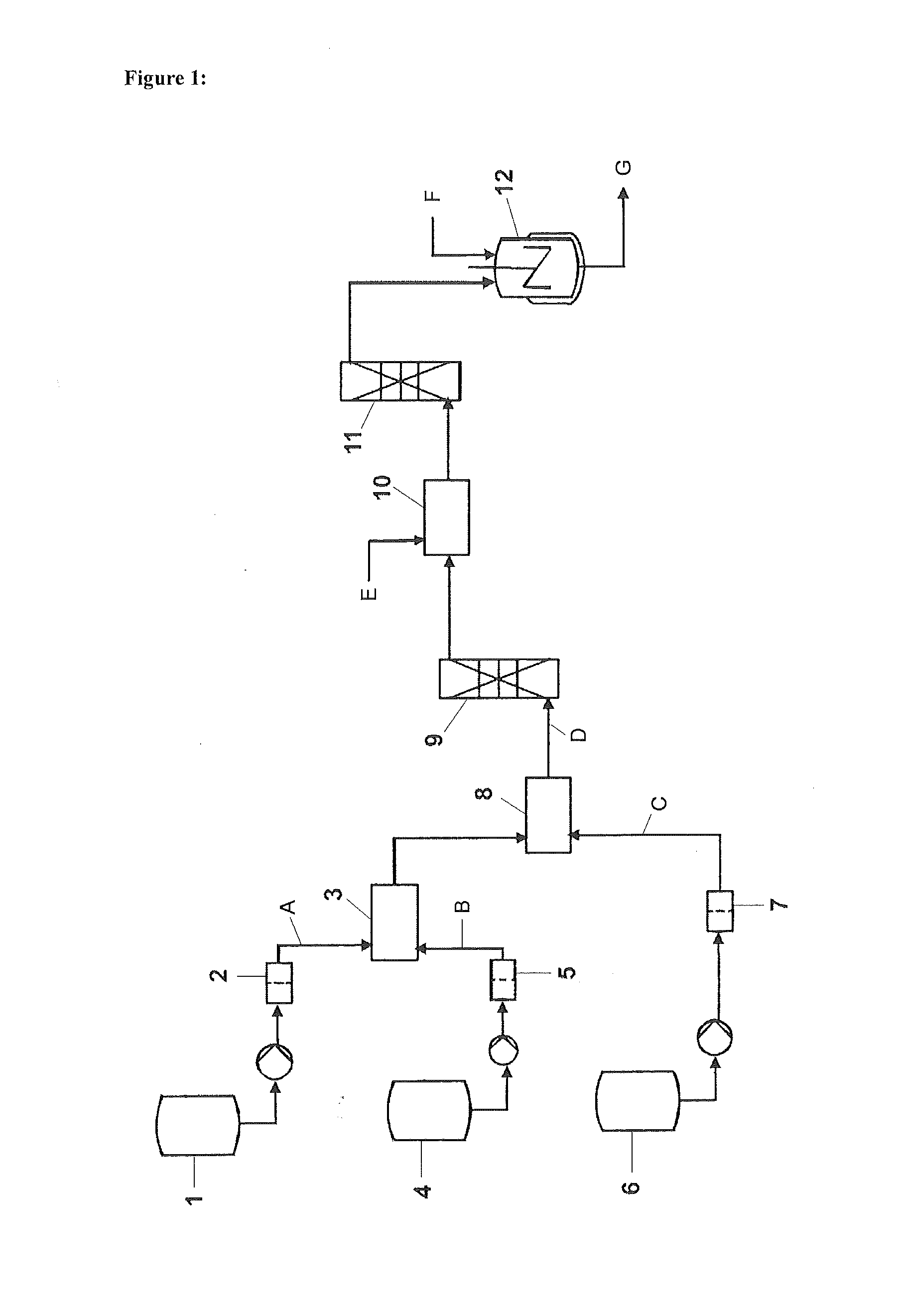
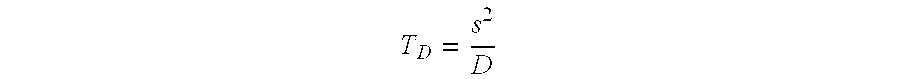Method and Device for the Continuous Production of Polymers by Radical Polymerization
a technology of radical polymerization and polymerization method, which is applied in the direction of liquid-liquid reaction process, transportation and packaging, chemical/physical/physico-chemical process, etc., can solve the problem that special materials that are extremely expensive should be dispensed, and achieve the desired activity of polymerization, and reduce the effect of molar mass distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
process example 1
[0227]An aqueous acrylic acid solution (50% by weight) was mixed at room temperature homogeneously with an aqueous sodium persulfate solution (2% by weight) by means of a micromixer and then homogeneously with an aqueous solution of 2-mercapto-ethanol (10% by weight) by means of a second micromixer. The resulting reaction solution was pumped in each case through a preheated reaction capillary whose temperature was controlled in an oil bath with a constant flow rate, and the reaction capillaries had different temperatures, materials, diameters and lengths according to table 1 (all feeds by means of laboratory HPLC pumps, from Bischoff).
[0228]In example 4, in a departure therefrom, an aqueous 7% by weight sodium persulfate solution and an aqueous 50% by weight solution of 2-mercaptoethanol were used.
[0229]In example 5, in a departure therefrom, an aqeuous 3% by weight 2,2′-azobis[2-(2-imidazolin-2-yl)propane] dihydrochloride solution (obtainable, for example, under the VA044 name from...
process example 2
[0231]The aqueous solution of acrylic acid and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid
[0232](35:15% by weight) was fed to a micromixer continuously and homogeneously with an aqueous sodium persulfate solution (4% by weight), mixed therein and then mixed homogeneously at room temperature with an aqueous solution of sodium hypophosphite (10% by weight) in a second micromixer. The resulting reaction solution was pumped continuously with a defined flow rate through a reaction capillary whose temperature was controlled in an oil bath, and the reaction capillaries had different temperatures, materials, diameters and lengths according to table 3.
TABLE 3FlowInitiatorRegulatorInternalØLengthrate[% by[% byTemperatureExampleMaterial[mm]1)[m]1)[g / h]wt.]2)wt.]2)*[° C.]1stainless1.6 + 3.010 + 107302580steel1.45712stainless1.6 + 3.010 + 108302580steel1.45711.1)x + y means: In the first capillary, the internal diameter was x mm or the length was x m and, in the directly connected second capillary...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com