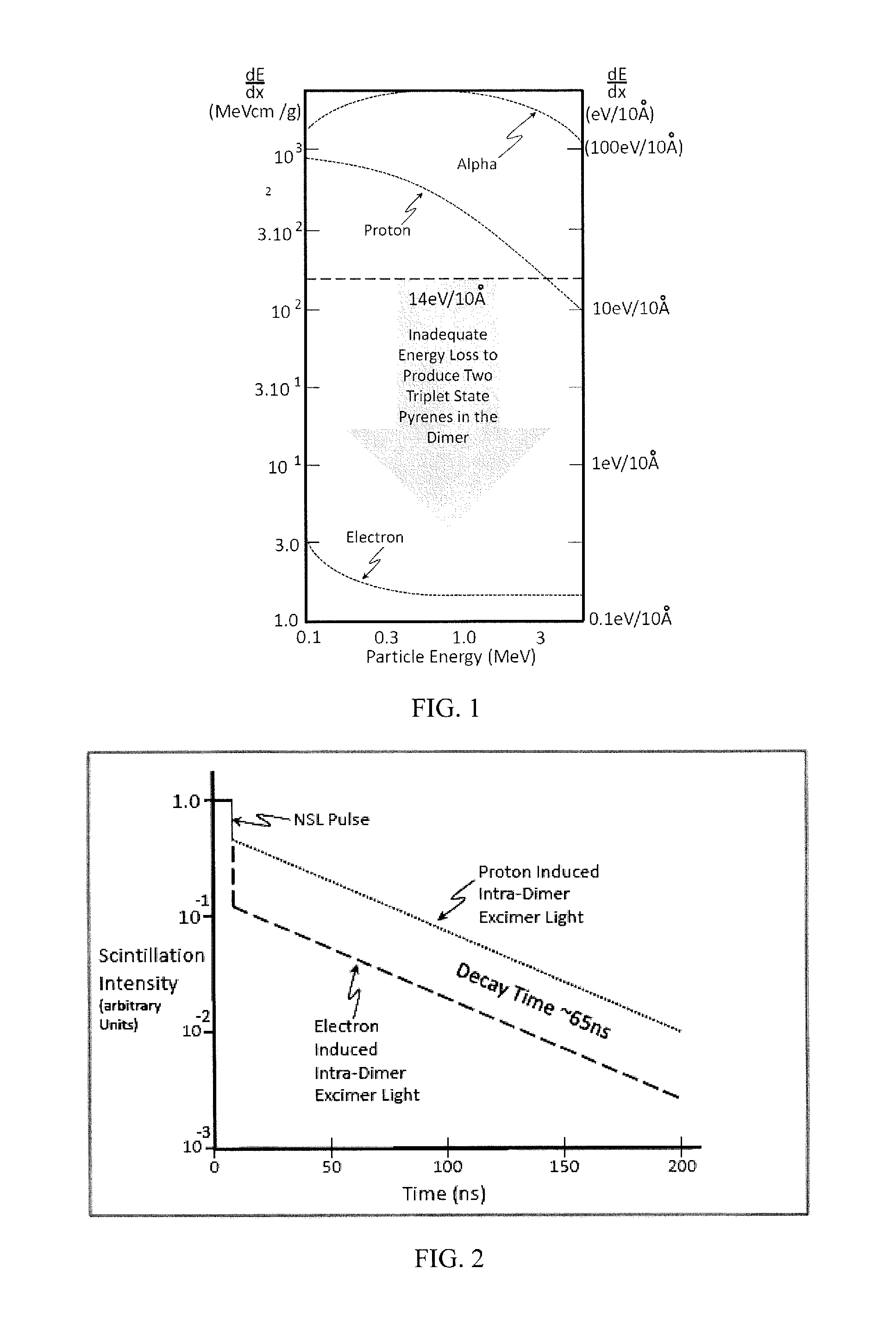
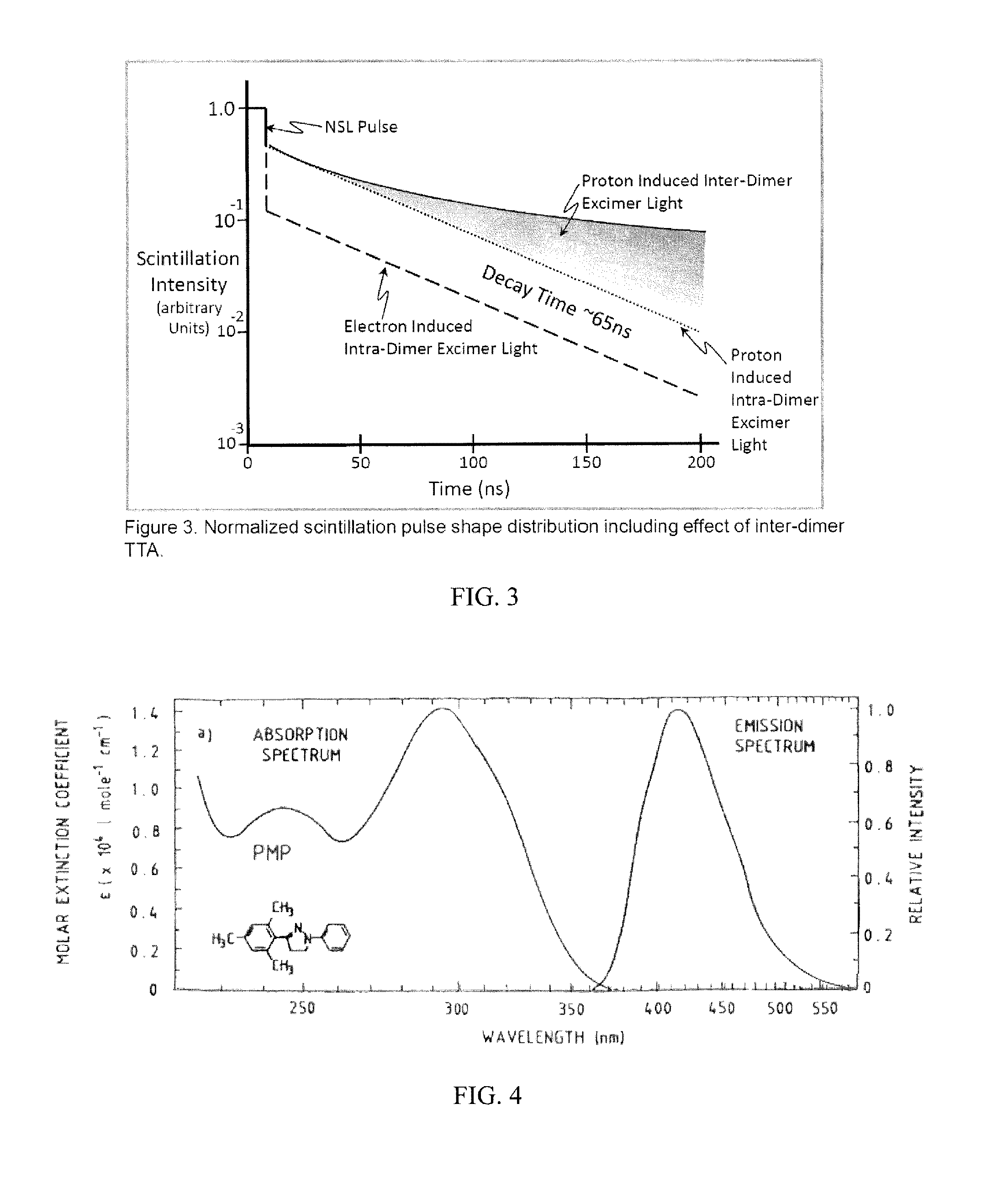
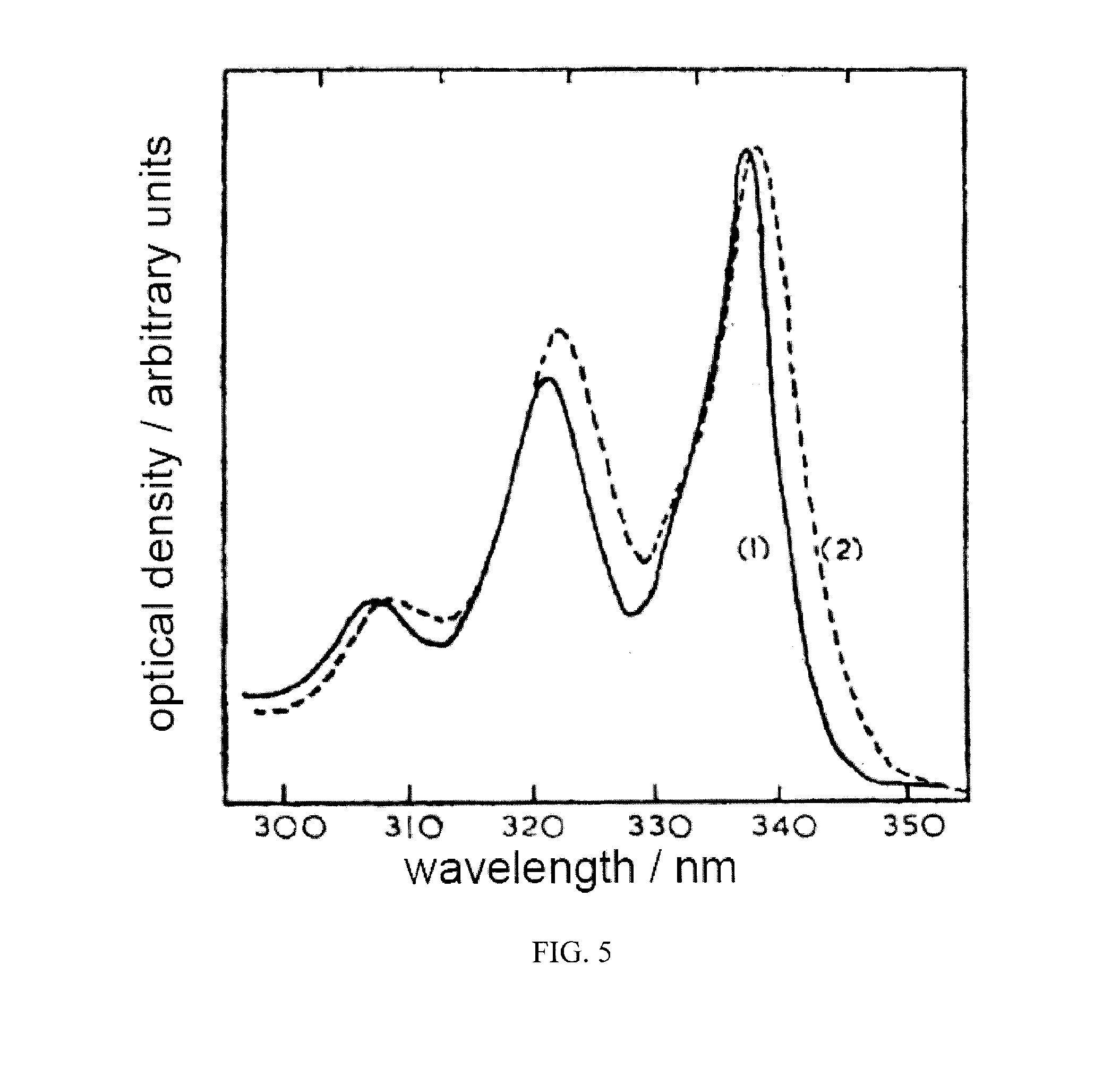
Method and apparatus for neutron detection utilizing pulse height discrimination and pulse shape discrimination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiments
Embodiment 1
[0094]A scintillation system for detecting incident radiation, comprising:
[0095]a scintillation composition, wherein the scintillation composition comprises:[0096]a matrix material; and[0097]chromophore dye molecules dissolved in the matrix material, wherein the chromophore dye molecules self-assemble to form dimeric chromophores, wherein a concentration of the dimeric chromophores is such that the dimeric chromophores have an average nearest neighbor distance in the range 2 to 15 Angstroms,[0098]wherein the dimeric chromophores produce excimer scintillation light upon excitation,[0099]wherein the excimer scintillation light has a prompt component and a delayed component, wherein the delayed time component is excimer scintillation light that is produced a delay period of time after excimer scintillation light of the prompt component is produced,
[0100]wherein an intensity of the prompt component and an intensity of the delayed component provide information so as to allow ...
embodiment 2
[0101]The system according to Embodiment 1, wherein the excimer scintillation light decay time constant is in the range 5 to 100 ns.
embodiment 3
[0102]The system according to Embodiment 1, wherein the delay period of time is in the range 20 to 200 ns.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com