Method for enhanced oil recovery by in situ carbon dioxide generation
a carbon dioxide and in situ technology, applied in the field of enhanced oil recovery, can solve the problems of reducing sweep efficiency, affecting oil recovery, and affecting oil recovery, etc., and achieve the effect of maximizing oil extraction and enhancing oil recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
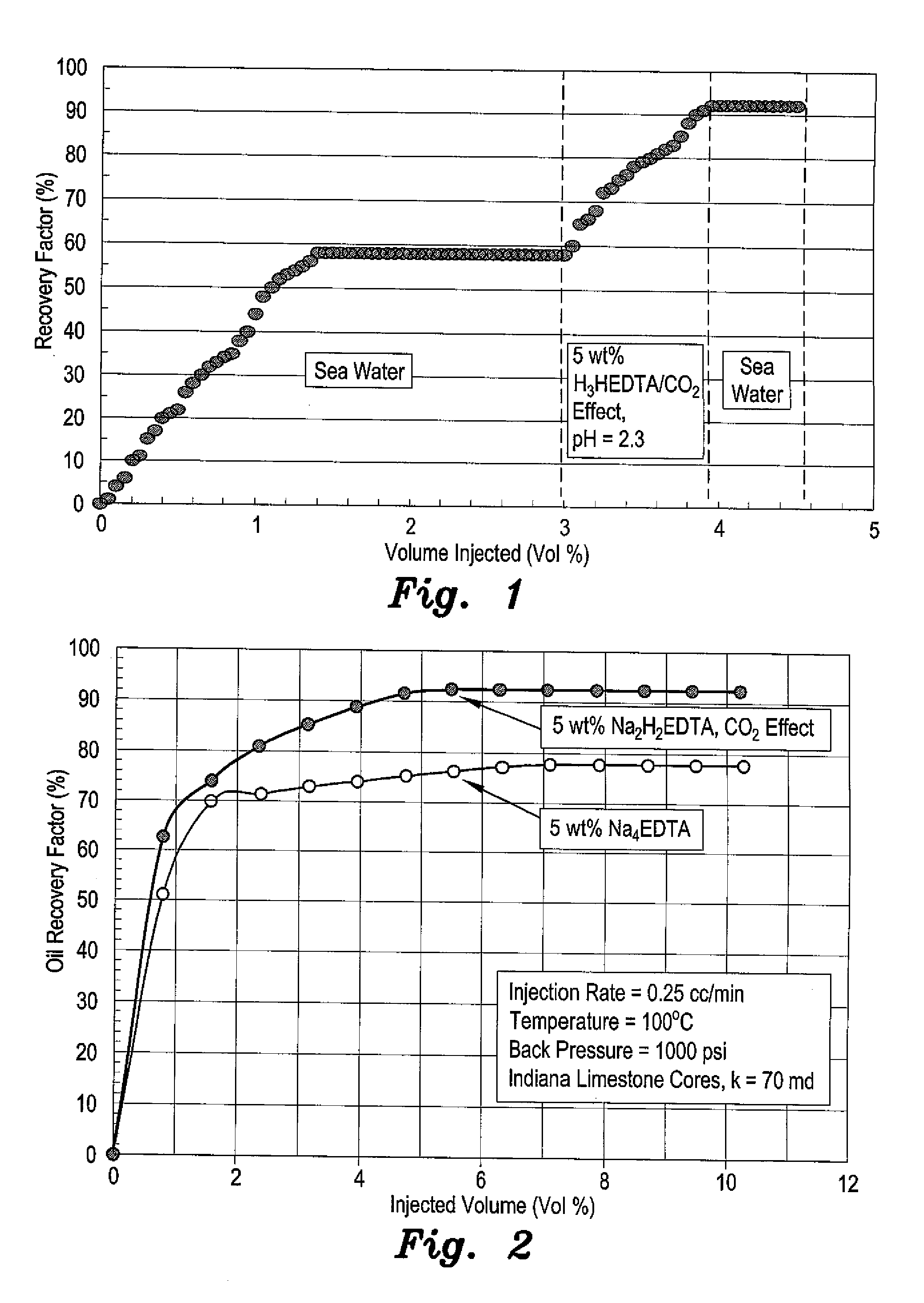
[0016]The method for enhanced oil recovery by in situ carbon dioxide generation utilizes a chelating fluid injected into an oil reservoir through a fluid injection system. The chelating fluid is a low pH solution of a polyamino carboxylic acid chelating agent. The polyamino carboxylic acid chelating agent may have a concentration of about 5 wt %. The polyamino carboxylic acid chelating agent is preferably either an aqueous solution of H2Na2-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (pH 4.5), H3-hydroxyethyl ethylenediamine triacetic acid (pH 2.5), or an aqueous solution of H2NaHEDTA (pH 4). The chelating fluid may be injected at a rate of approximately 0.25 mL / min. The injection of the chelating fluid may be preceded by flooding the core with seawater, and is followed by injection of either seawater, a high pH chelating agent, or low salinity water to ensure maximal extraction of oil from the reservoir. The method is particularly for use in formations where the core of the reservoir has a car...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com