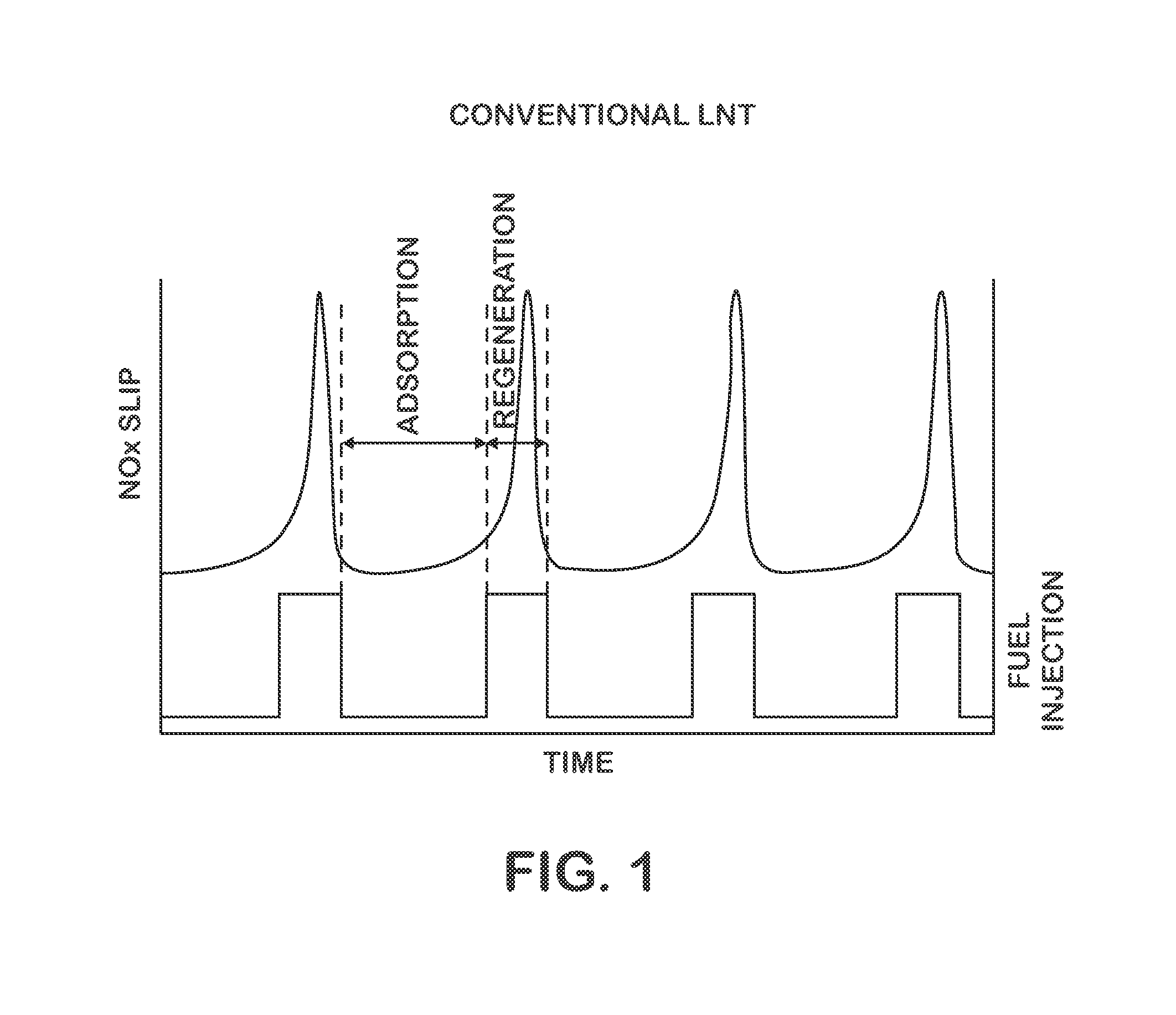
Diesel Engine Nox Reduction
a technology for diesel engines and nox reduction, which is applied in the direction of machines/engines, mechanical equipment, and non-fuel substance addition to fuel, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the storage capacity of nosub>x /sub>, putting such responsibility on the end-user to monitor and maintain the scr in working condition, and reducing the nosub>x /sub>. , to achieve the effect of minor fuel penalty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
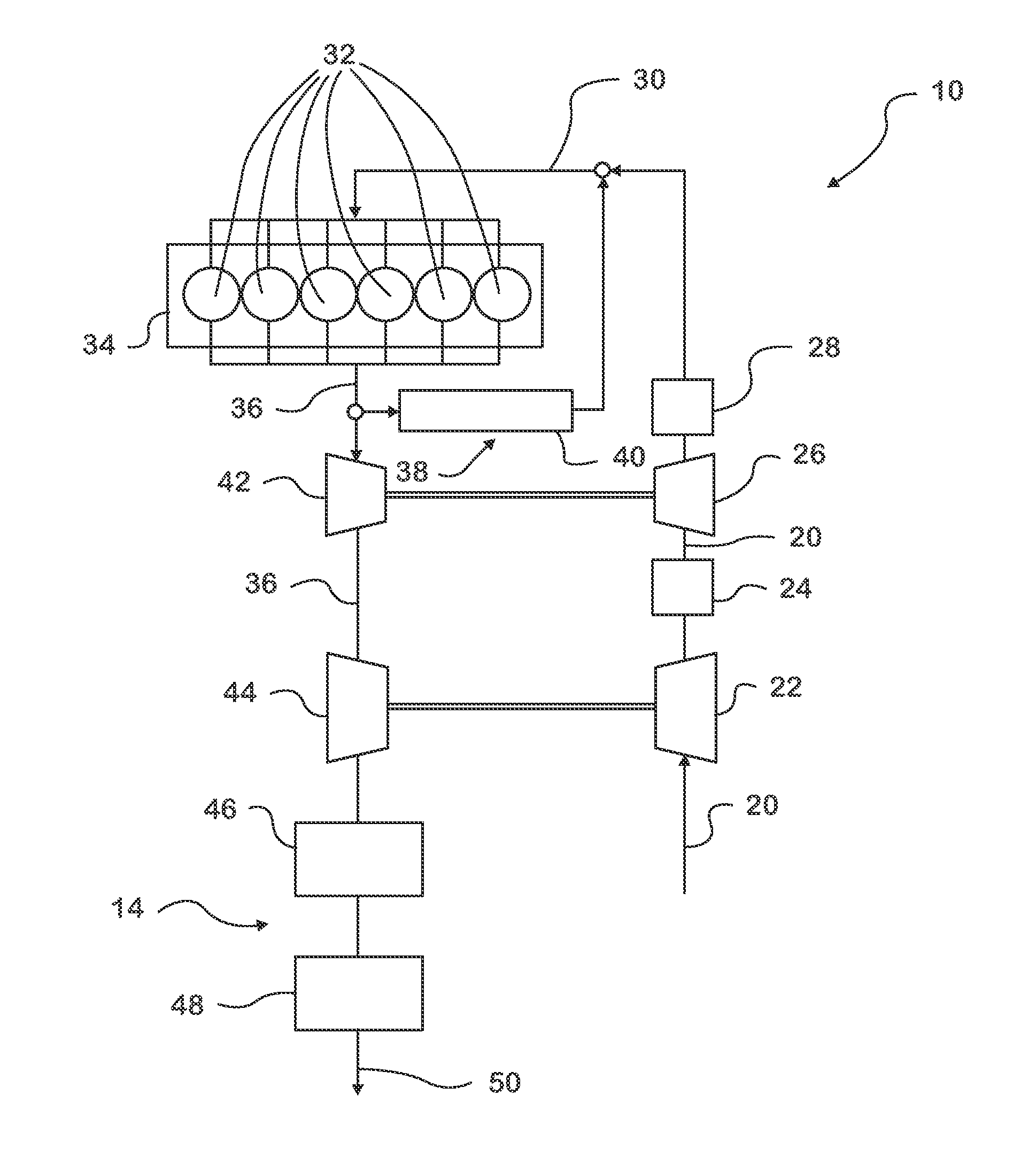
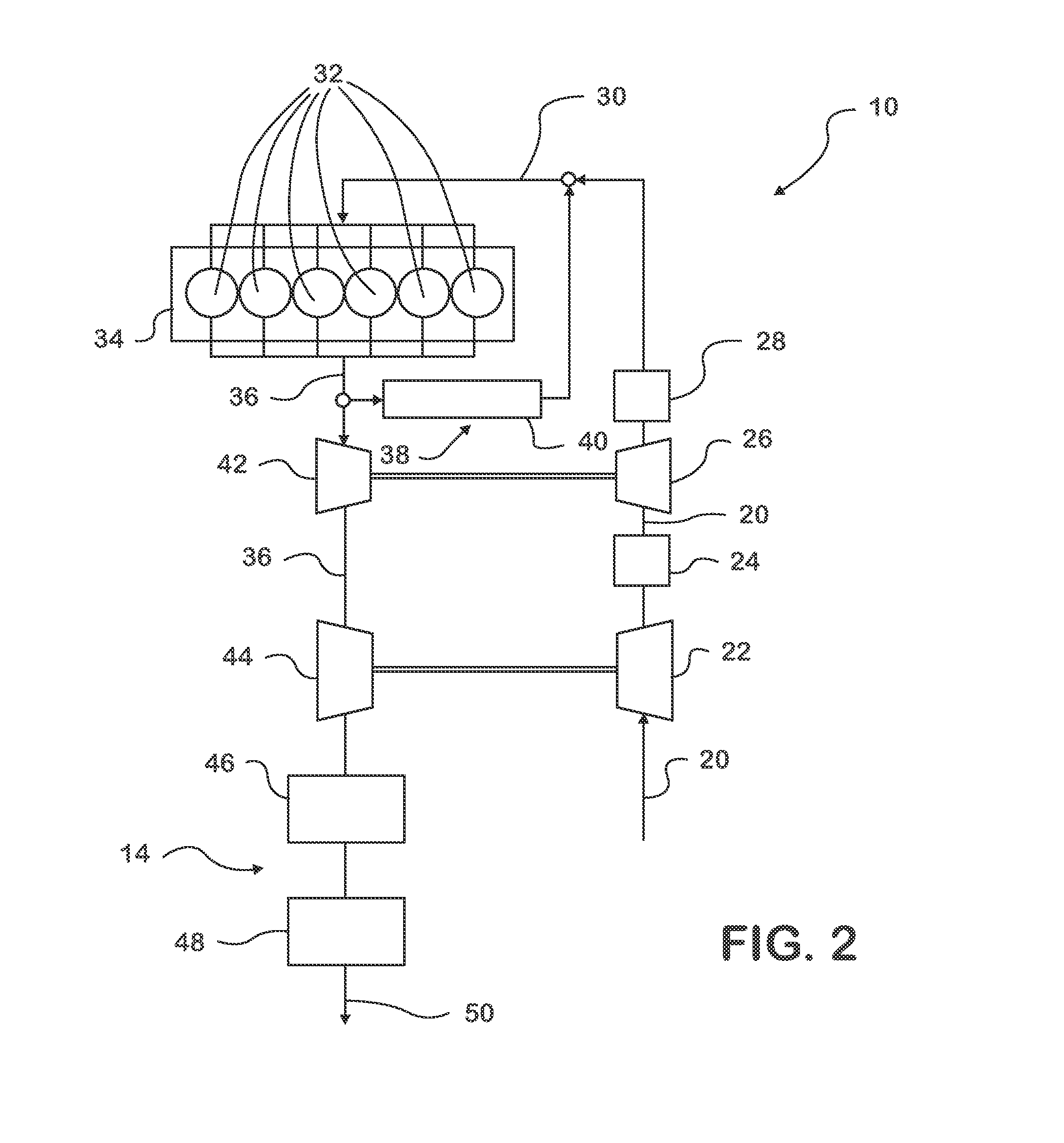
[0015]FIG. 2 illustrates a diesel engine system 10 that includes an exhaust gas after-treatment system 14 having a long-breathing LNT 46. As shown, air for use in the operation of the engine system 10, such as, for example, for use during an internal combustion process, may flow along an intake line 20 that includes various hoses and / or tubes. For example, air passes along a first portion of the intake line 20 and into a low pressure compressor 22 before flowing along a second portion of the intake line 20 to the interstage cooler 24. The air then flows through a high pressure compressor 26 and high pressure charged air cooler 28 before flowing through another portion of the intake line 20 to an intake manifold 30.
[0016]The air may flow through the intake manifold 30 and to cylinders 32 of the engine 34, where the air may be used in a combustion event(s) that is used to displace the pistons of the engine 34, thereby transmitting the force of the combustion event(s) into mechanical p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com