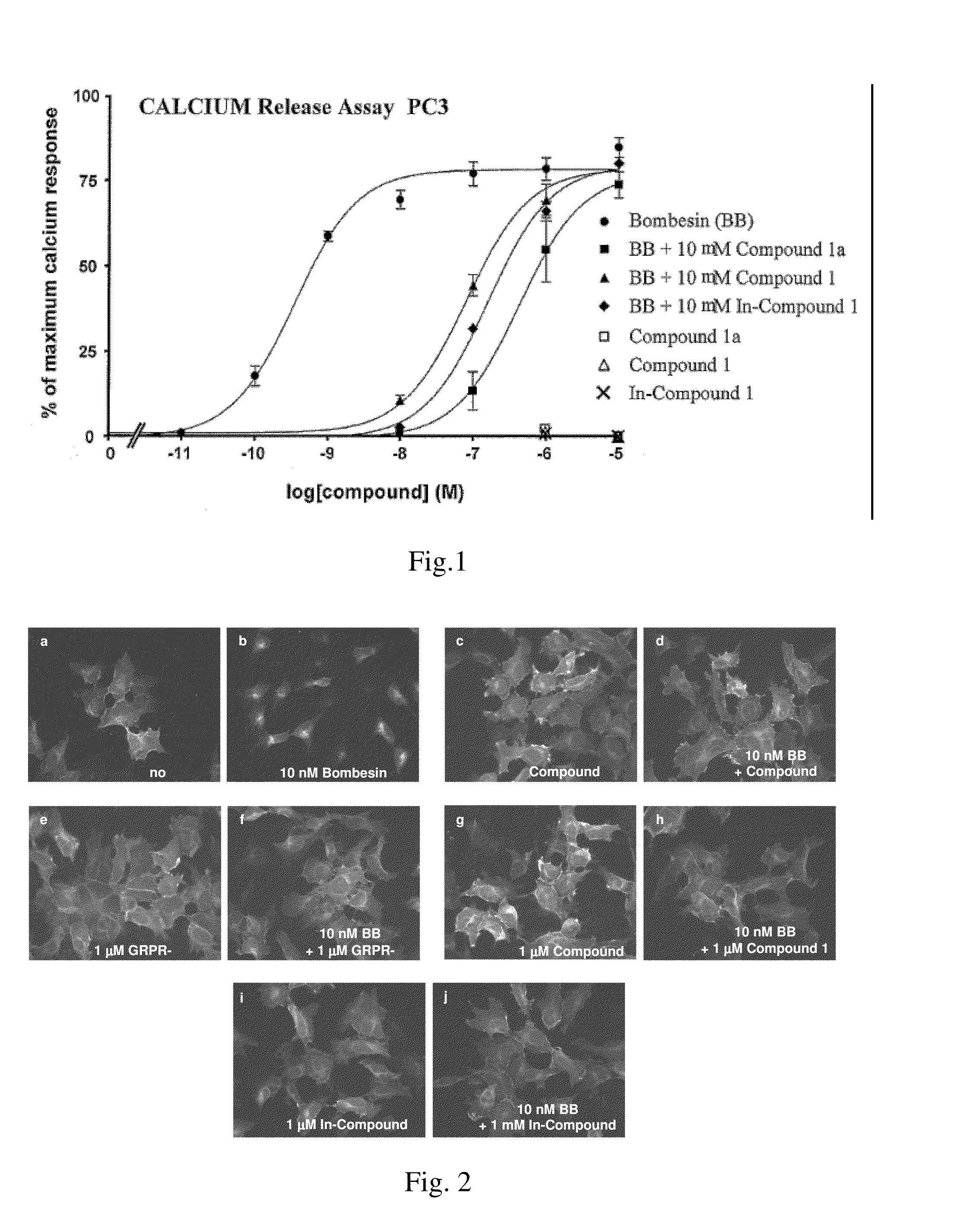
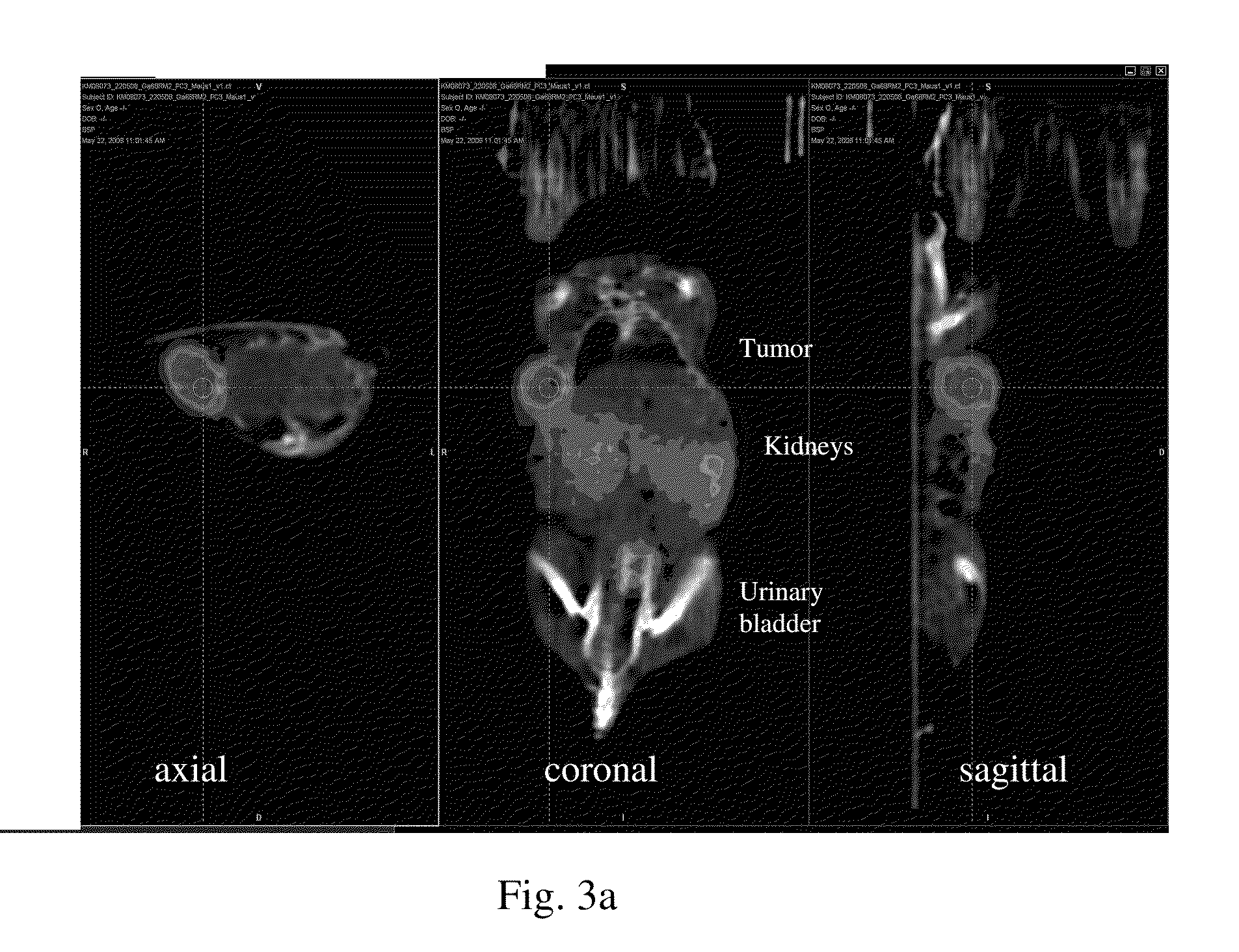
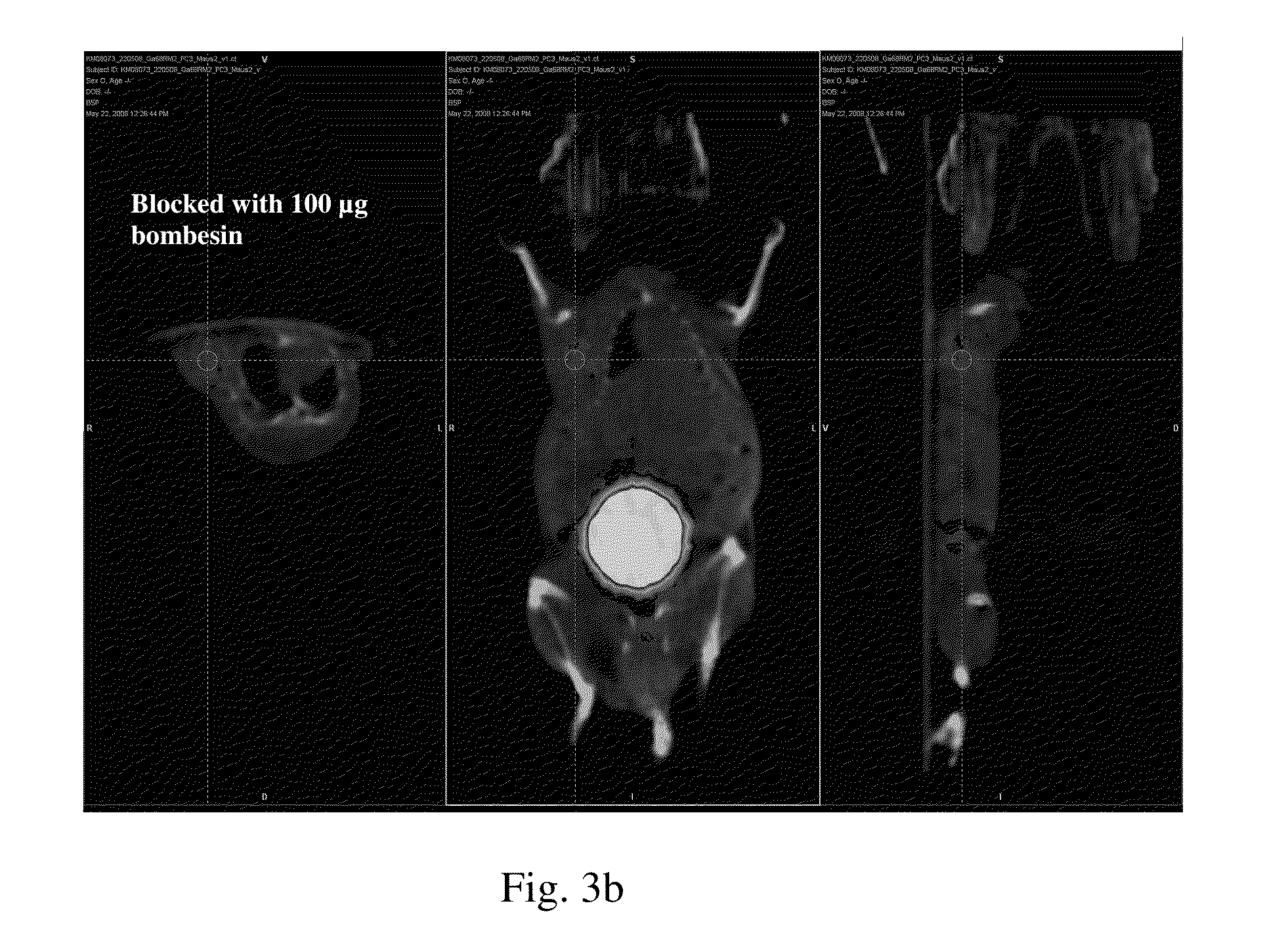
Bombesin analog peptide antagonist conjugates
a technology of analog peptides and conjugates, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, and therapeutics, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory radioscintigraphic imaging and radiotherapeutic purposes, unsatisfactory uptake, and need to be improved. to achieve the effect of inhibiting the effect of the agonis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1 (
A-B-C)
[0343]wherein A has the meaning of A but also A′ as appropriate for all examples disclosed below.
[0344]a) Synthesis of bombesin peptide antagonist conjugates with general sequence (A=DOTA, B=Spacer B1-B2, C=Peptide with N-terminal amide Z[Z═NH])
[0345]DOTA-Spacer-Xaa16-Gln7-Trp8-Ala9-Val10-Xaa211-His12-Sta13-Leu14-NH2 Peptides were synthesized manually on solid phase using Fmoc-strategy. To obtain N-terminal amides, Rink amide MBHA resin LL (100-200 mesh) ( 4-(2′,4′-Dimethoxyphenyl-Fmoc-aminomethyl)-phenoxyacetamido-norleucyl-4-Methylbenzhydrylamine resin) was used. In general, Rink amide MBHA resin with a theoretical loading of 0.34 mmole / g resin was given to the reactor, N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) was added to the reactor and was shaken for 30 minutes to allow swelling of the resin. After removing the solvent, a solution of 20% piperidine in DMF was added and the resin was shaken for 15 minutes to remove the 9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) protecting group. This step was r...
example 2 (
A-B-C)
[0374]a) Synthesis of bombesin peptide antagonist conjugates with general sequence (A=N-triazoles-dPEG1-azido, B=Spacer B1-B2, C=Peptide with N-terminal amide Z [Z=NH2])
[0375]N4-triazoles-dPEG1-Xaa16-Gln7-Trp8-Ala9-Val10-Xaa211-His12-Sta13-Leu14-NH2
[0376]a) Synthesis of the peptides: Fmoc-Xaa16-Gln7-Trp8-Ala9-Val10-Xaa211-His12-Sta13-Leu14-NH2
[0377]Peptides were synthesized manually on solid phase using Fmoc-strategy. To obtain N-terminal amides. Rink amide MBHA resin LL (100-200 mesh) was used. The synthesis was performed as described in the Example 1.
[0378]b) Coupling with the alkyl group propargyl-dPEG1-NHS-ester
[0379]Prior to coupling with the alkyl group, the N-terminal Fmoc-protection was removed from the resin bound peptides. The resin was swelled for 15 min in DMF, treated twice with a solution of 20% piperidine in DMF (15 min) and washed three times with DMF. The solution from the piperidine treatment and the following DMF washings were collected for Fmoc determinat...
example 3 (
A-B-C2)
[0396]DOTA-Spacer-Xaa16-Gln7-Trp8-Ala9-Val10-Xaa211-His12-Leuψ(CH2)2—CH3
[0397]All the pseudopeptides were synthesized in solution phase by condensation of the heptapeptide Fmoc-D-Phe-Gln-Trp-Ala-Val-Xaa2-His-OH with the modified aminoacid H-Leuψ(CHOH)—(CH2)3—CH3.
[0398]a) Synthesis of the heptapeptide Fmoc-D-Phe-Gln-Trp-Ala-Val-Xaa2-His-OH
[0399]Peptides were synthesized manually on 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin using Fmoc strategy. In general, 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin with a theoretical loading of 1.4 mmole / g resin was given to the reactor. The resin was swelled in DCM for 30 min and the first amino acid was coupled by adding 1 equivalent of amino acid, mixed with 4-fold molar excess of DIPEA in DCM. The coupling reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h and then the resin was washed twice with a mixture of DCM / MeOH / DIPEA (17 / 2 / 1), twice with DCM and finally swelled in DMF. The Fmoc was deprotected using 20% of piperidine in DMF and the amount of removed F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com