Plaque detection using a stream probe
a detection apparatus and stream probe technology, applied in the field of stream probes, can solve the problems of inconvenient detection of plaque detection apparatus, damage to the eye, and difficulty in identifying dental plaques by the naked eye, and achieve the effect of improving the detection of substances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
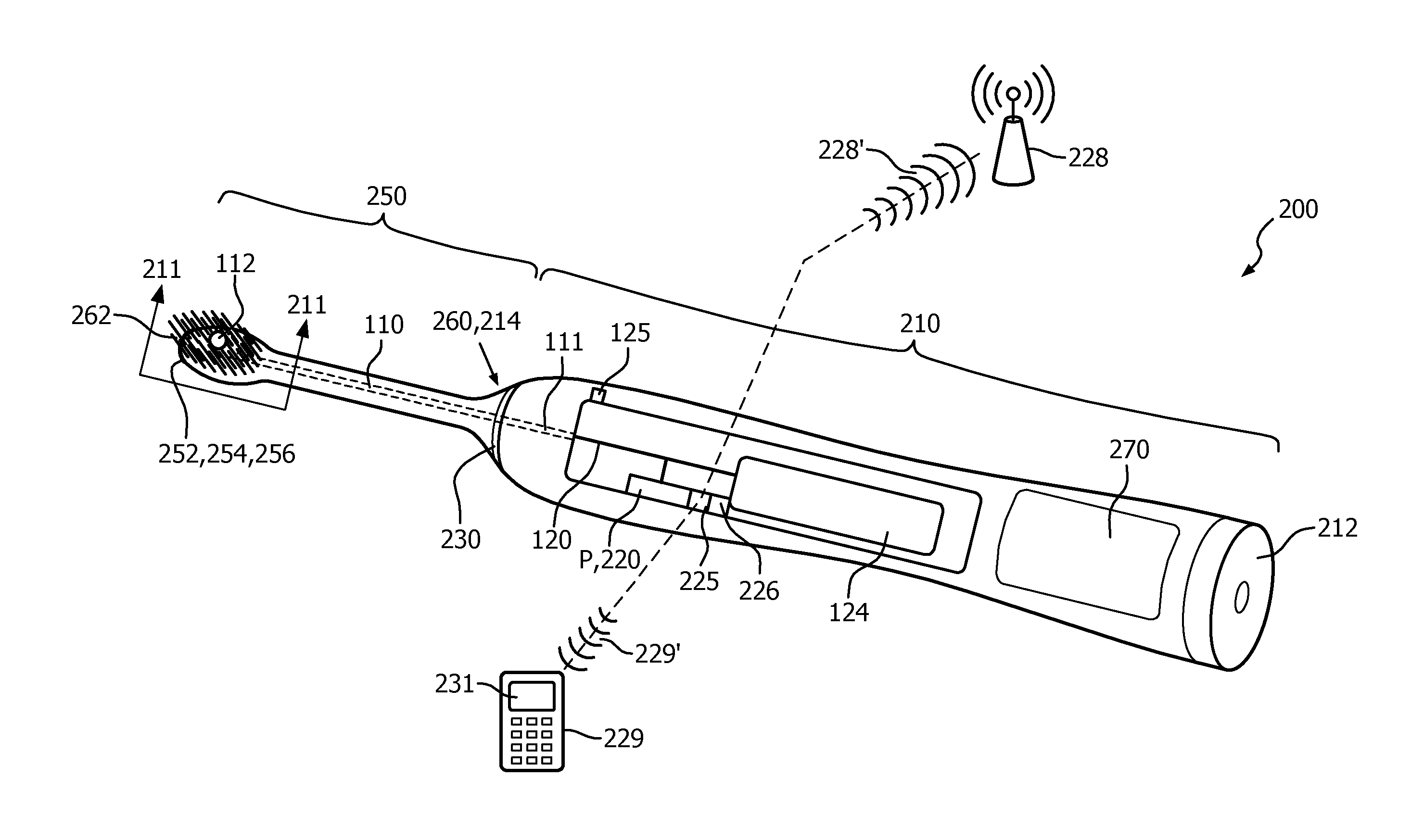
[0210]With reference to FIGS. 24A and 24B there are shown examples of probes 2400, 2402 having a castle-shape 2404 and a round shape 2406 distal tip (i.e., these shapes for the distal tips are structural configurations) to prevent false positive signals according to the present disclosure. Though these tip shapes are suitable to prevent false positives, a risk is that the signal level from the plaque layers reduces as well. Therefore, it is favorable to limit the dimension(s) of the open area. In one preferred embodiment, the height of the opening should be below 100 microns in order to achieve sufficiently large signals from plaque layers on the PMMA surface. Using the tip shape shown by FIG. 24B, and measuring the pressure versus distance to the PMMA surface, there is shown in FIG. 25 a clear improvement in pressure versus distance of the shaped tip probe 2400 with respect to the unshaped tip (negative values means no contact with the PMMA surface, zero means just in contact with ...
second embodiment
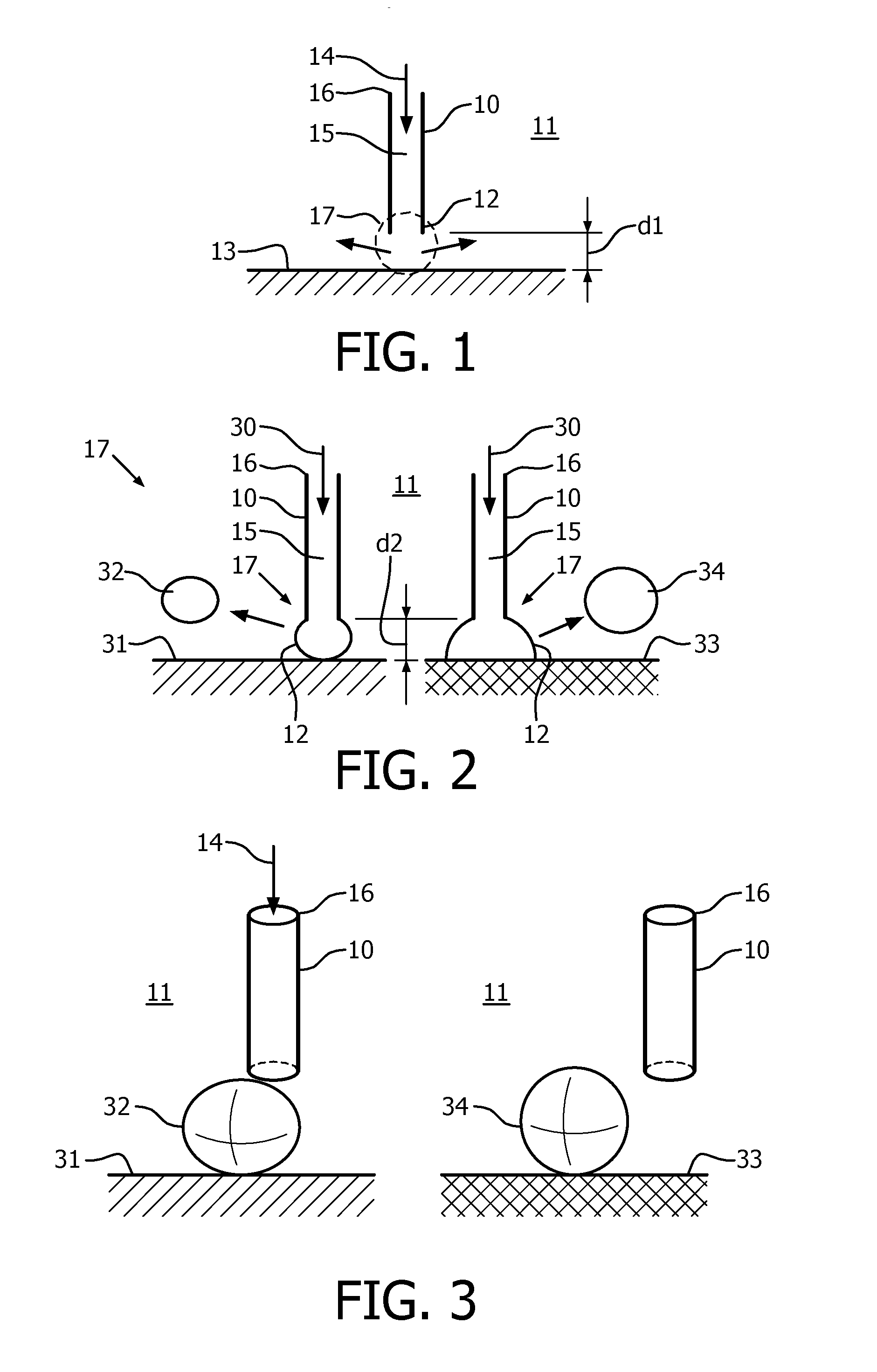
[0211]With reference to FIG. 26, according to the present disclosure, false positive signals are prevented by providing a structural configuration to a stream probe 2600 which includes small holes 2602 near the distal tip of the probe 2600 or at a proximal location from an open port 2604. The holes 2602 are preferably within 100 microns of the distal tip of the probe 2600. An advantage of this embodiment is that it results in a stronger probe tip, which can be beneficial in case of wear issues.
third embodiment
[0212]With reference to a cross-sectional view as shown by FIG. 27A, according to the present disclosure, the distal tip of a probe 2700 has a trumpet shape 2702 (i.e., structural configuration). That is, the inner diameter of the probe 2700 is larger at the end of the tube (at the distal tip) as compared to a position further away from the end. The tube appears to diverge at the distal tip. This shape prevents blocking of the distal tip of the probe 2700 by dental plaque or toothpaste.
[0213]In order to obtain large signals in case of a non-perpendicular tube orientation with respect to the tooth surface, it is beneficial to have a small tube diameter. Therefore, with respect to the embodiment shown by FIG. 27A, it is advantageous to apply a trumpet-like shape at the inside of the tube only, while the outside of the tube has a constant diameter throughout the length of the probe.
[0214]Another embodiment can be a tube having an inverse trumpet shape 2710 (i.e., structural configurati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com