Method for heating a blast furnace stove
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
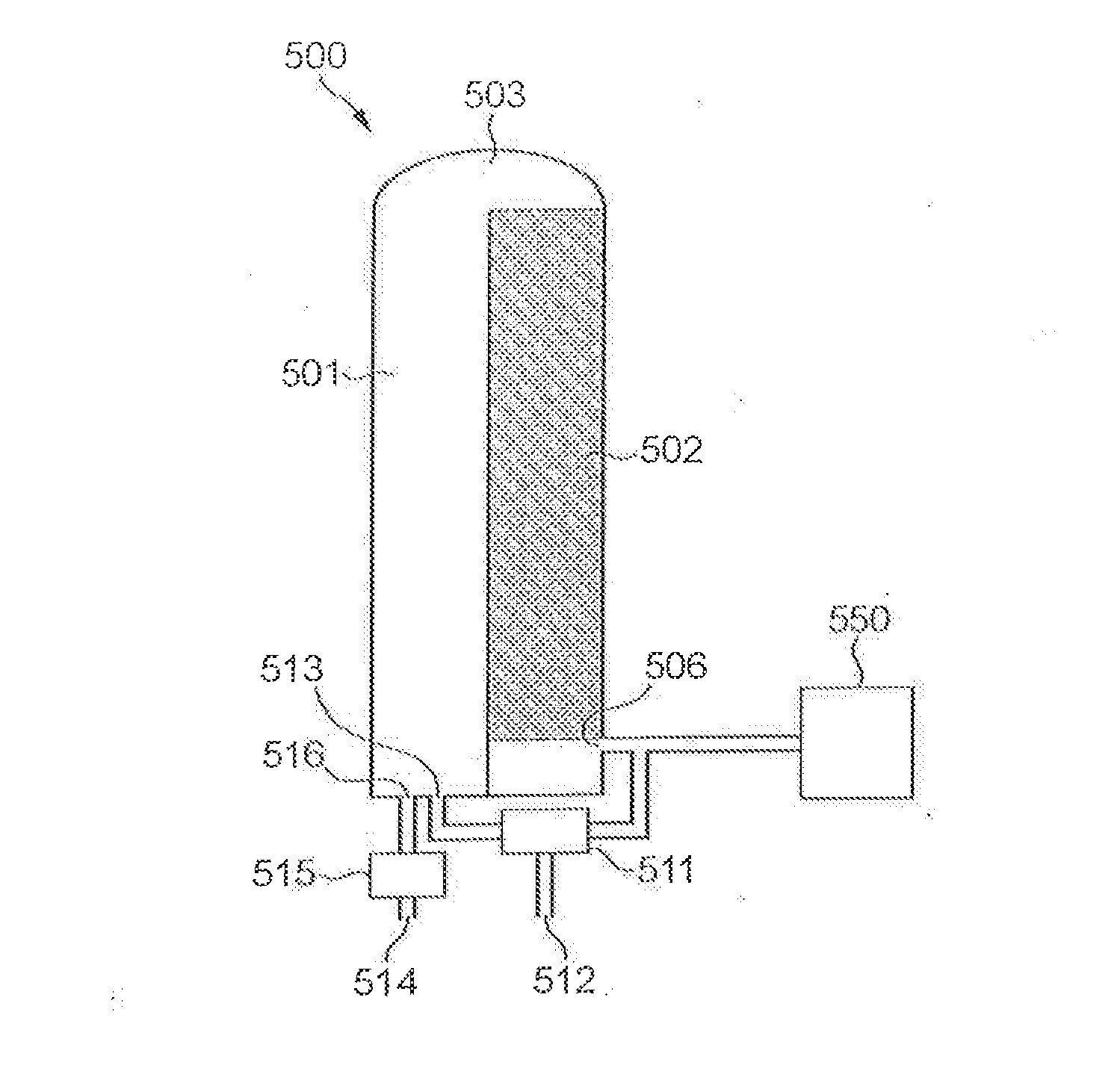
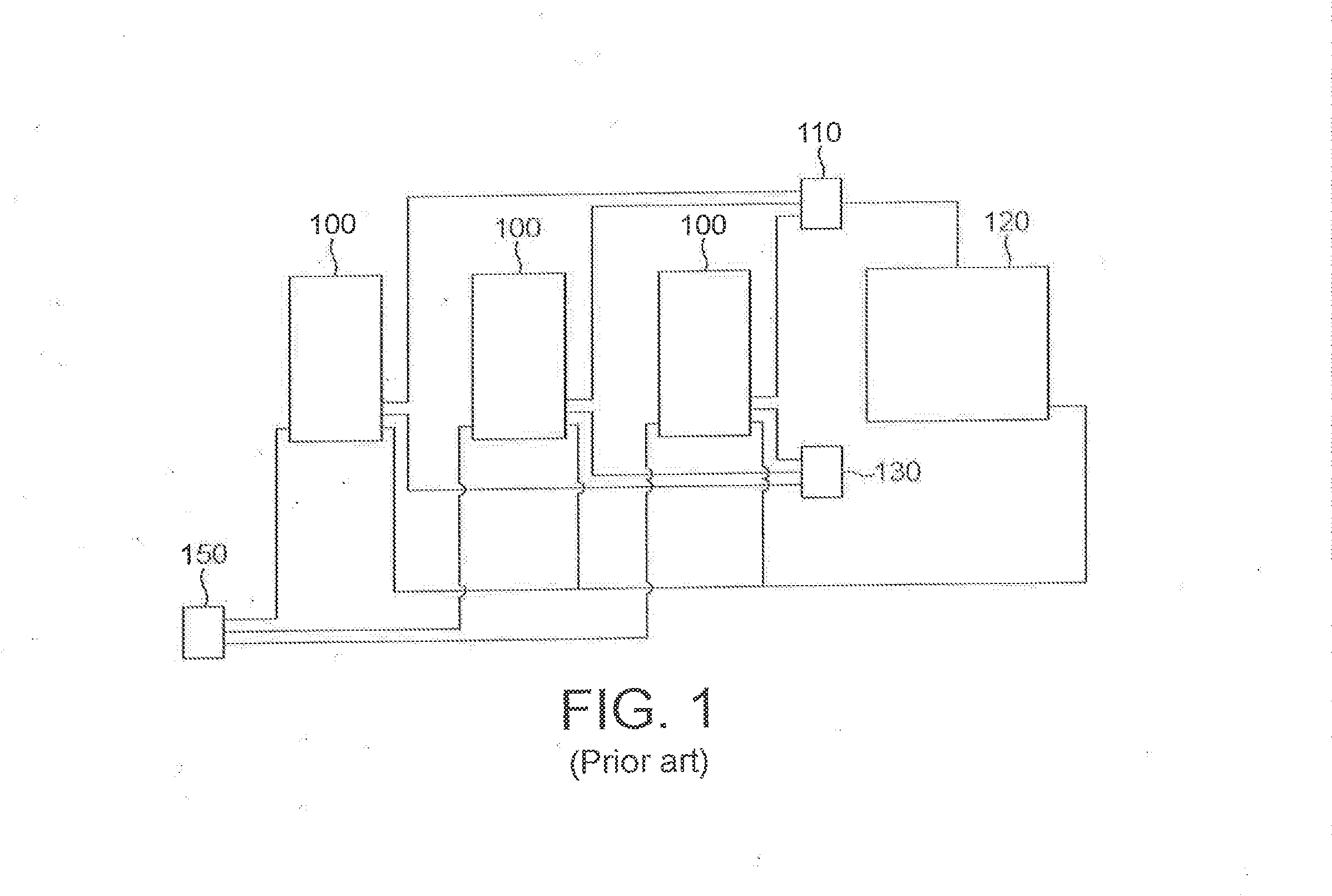
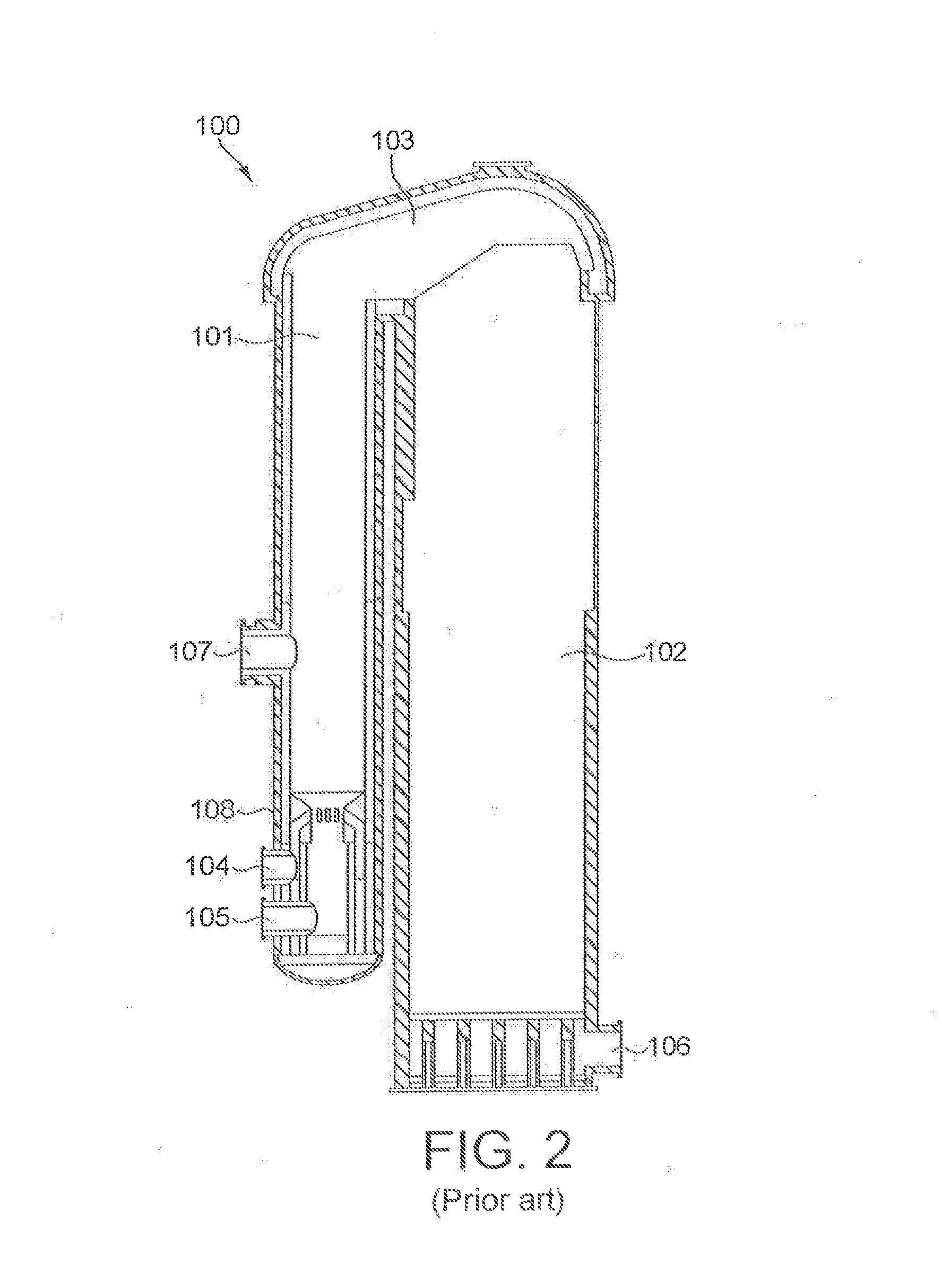
[0030]It is preferred, in the context of the present invention, to heat the stove with blast furnace top gas, as described above. It is furthermore preferred to use top gas from a blast furnace to which blast air is provided from the stove. This allows for the arrangement of the stove near the blast furnace, is energy efficient and leads to low total emissions from the plant.
[0031]However, it is to be understood that the present invention can be equally advantageously applied to stoves heated with other low-grade fuels. By way of example, typical chemical compositions (percentage values) and lower heating values (LHV) are provided in Tables I and II, respectively, for blast furnace top gas and converter off-gas.
TABLE 1N2H2OO2H2COCO2CH4CmHnTop gas52.50.552.323.520——1.15Off-gas17.20.12.564.515.6——0.1
TABLE 2LHV (MJ / Nm3)LHV (MJ / kg)Top gas3.22.4Off-gas6.38.4
[0032]According to the present invention, the stove is heated with a gaseous fuel the LHV value of which is not higher than 9 MJ / Nm3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com