Process for removing residual spin solvent from a gel spun filament, the filament, multi-filament yarn and products comprising the filament
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Preparation of Yarn
[0039]A commercial grade Dyneema™ SK 75, delivered by DSM Dyneema, the Netherlands, was washed several times with soaps and solvents, until no spin finish could be detected any more.
[0040]The amount of residual spin solvent was about 400 ppm. The yarn was treated at elevated temperature to remove spin solvent (step e)) as indicated below.
Measurement of Tensile Strength
[0041]Tensile properties: tensile strength (or strength), tensile modulus (or modulus) and elongation at break (or eab) are defined and determined on multifilament yarns with a procedure in accordance with ASTM D885M, using a nominal gauge length of the fibre of 500 mm, a crosshead speed of 50% / min and Instron 2714 clamps, of type Fibre Grip D5618C. On the basis of the measured stress-strain curve the modulus is determined as the gradient between 0.3 and 1% strain. For calculation of the modulus and strength, the tensile forces measured are divided by the titre, as determined by weighing 10 metres of...
experiment 1
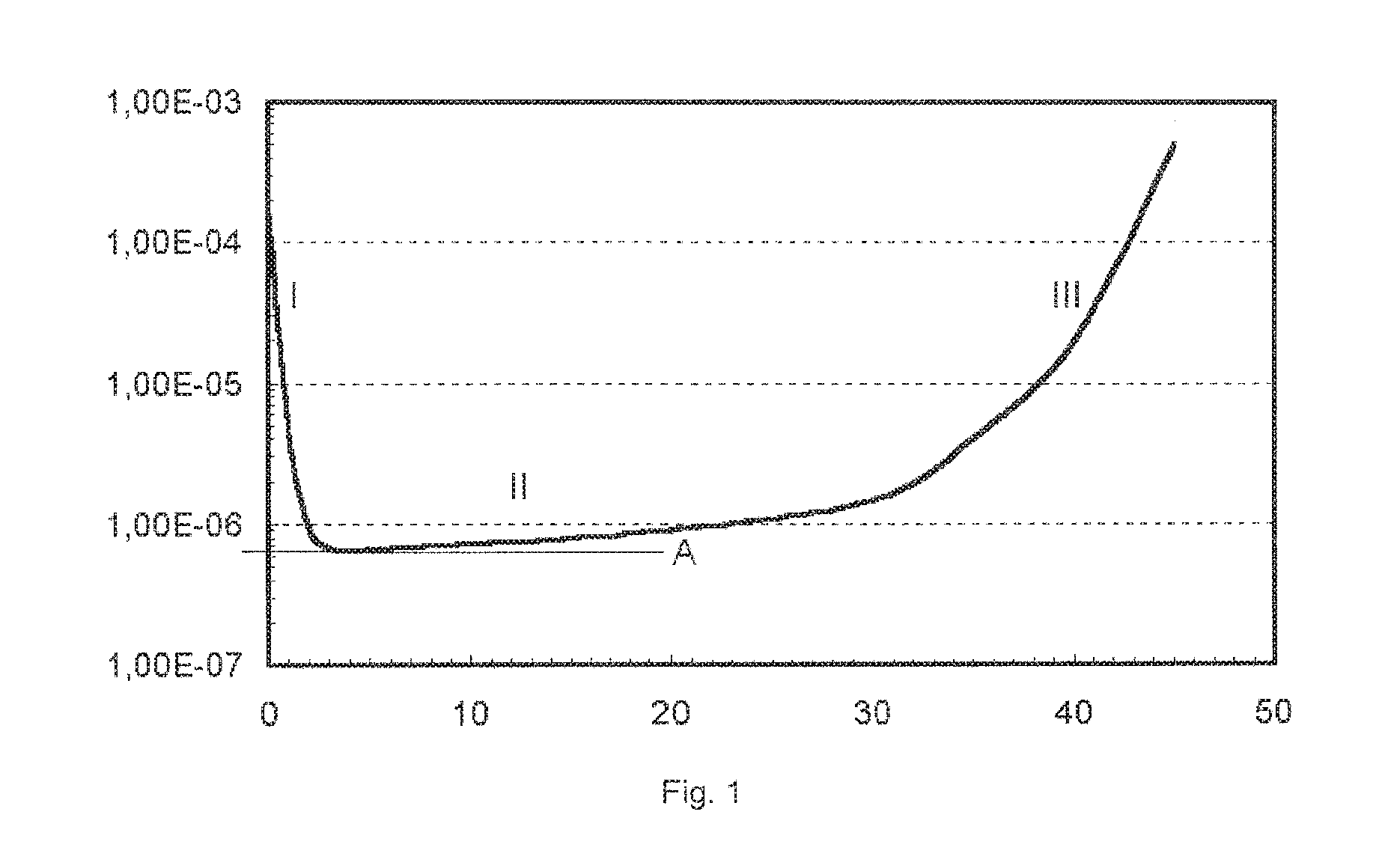
[0057]The Dyneema™ SK 75 yarn of comparative experiment A was kept for 64 hours at 120° C. The yarn was wound around a frame, so that the yarn was kept taut during the treatment. After the treatment creep, tensile strength and residual spin solvent of the yarn were measured according to the methods given above. The content of residual spin solvent was well below 100 ppm. Further results are given in Table 1. It shows that after the treatment (step e) the level of creep is even lower than the level of the untreated yarn.
experiment 2
[0058]The Dyneema™ SK 75 yarn of comparative experiment A was put in an autoclave, filled with supercritical CO2 at a temperature of 100° C. for one hour. The oxygen content of the super-critical CO2 environment in the autoclave was 1.2 mol / m3. The yarn was wound around a frame, so that the yarn was kept taut during the treatment. After the treatment creep, tensile strength and residual spin solvent of the yarn were measured according to the methods given above. The results are given in Table 1. The content of spin solvent is well below 100 ppm. It shows that after the treatment (step e) the level of creep is comparable to that before the treatment.
MinimumTensilecreepExample / comparativesttrengthrate experimentcN / dtex(1 / second)Comp. Exp. A359.0 · 10−7Comp. Exp. B3UndetectableComp. Exp. C107.0 · 10−6Ex. 1267.0 · 10−7Ex. 230.59.5 · 10−7
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com