Methods and systems for operating a secure mobile device
a mobile device and mobile technology, applied in the field of methods and systems for operating a machine to machine (m2 m) device, can solve the problems of difficult to reach, difficult management, complex approach, and inability to secure broadcasts such as firmware updates or public warning messages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
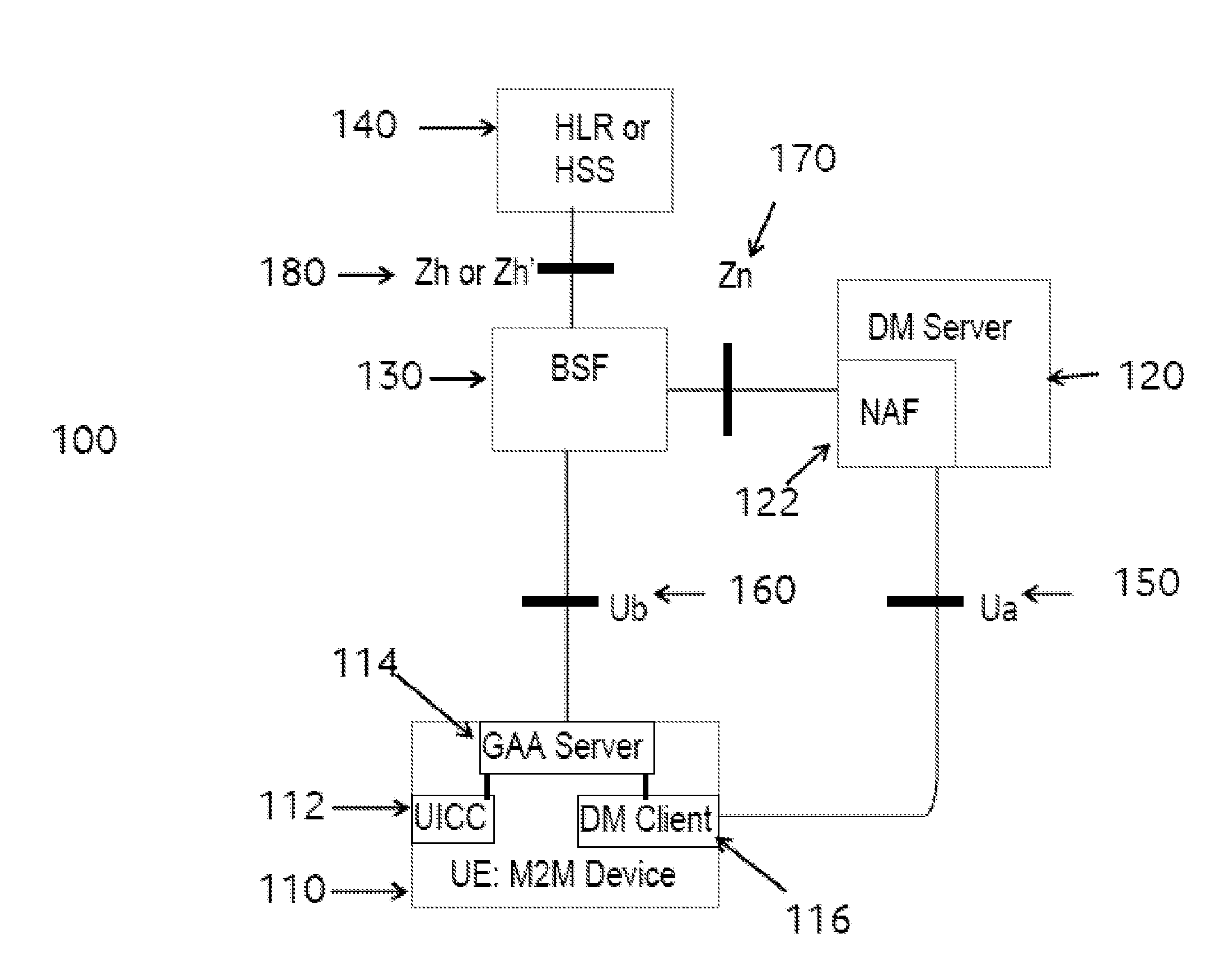
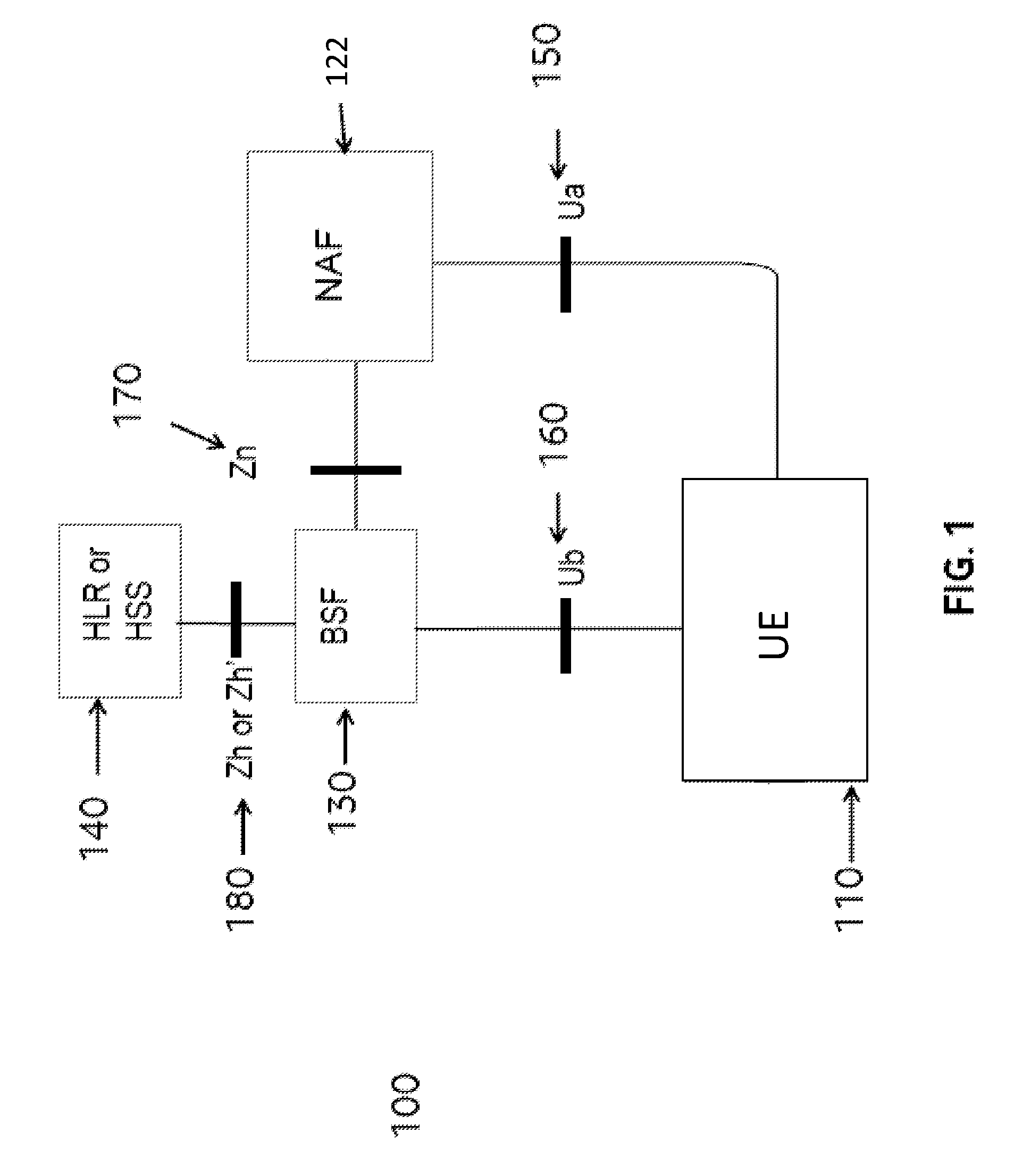
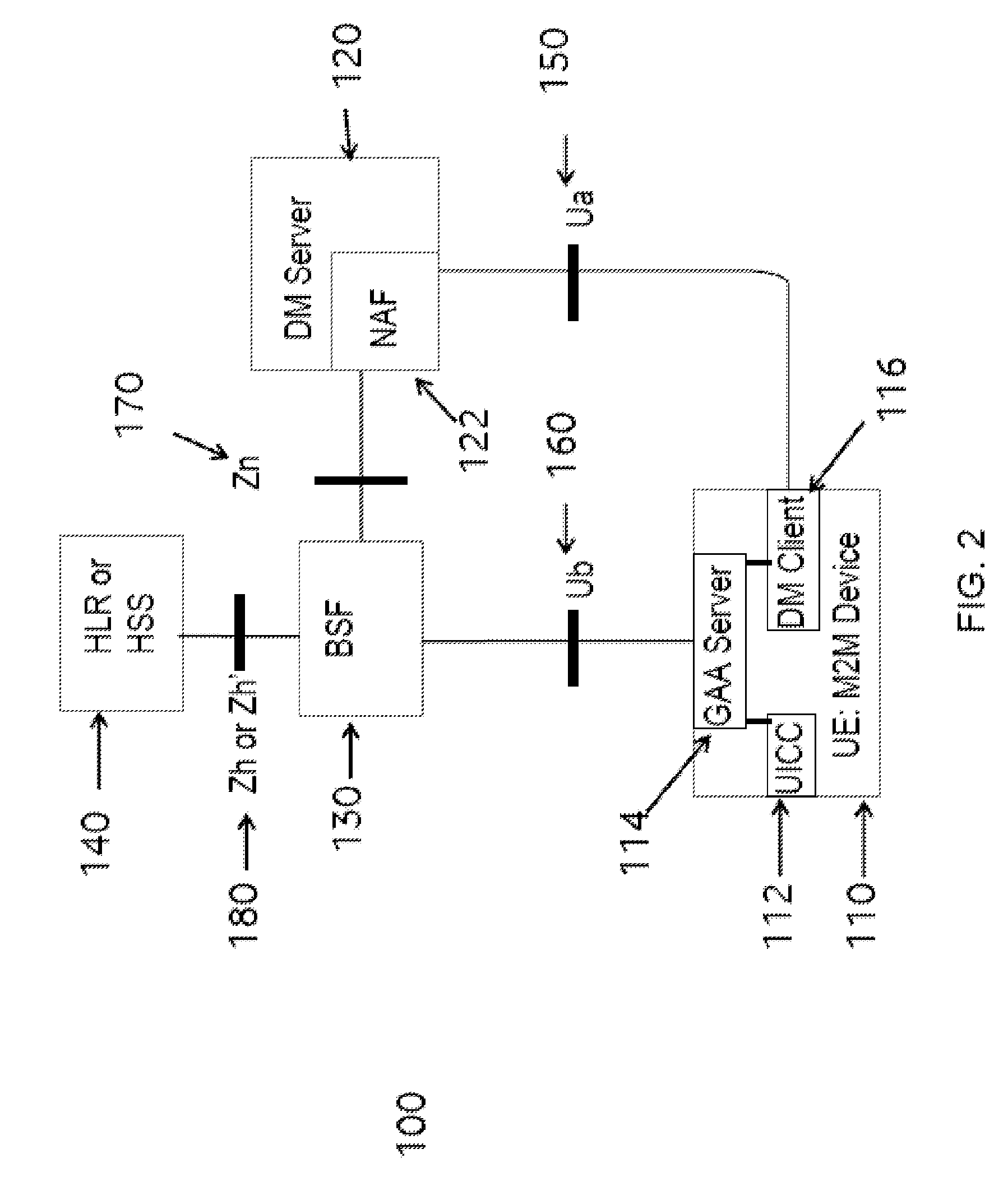
[0106]A device may communicate securely with a server. The device may be a Machine to Machine (M2M) device, or an equivalent device (e.g. a device, a generic or specific communication device, including one or more modules capable of providing M2M capabilities).
[0107]Aspects of the Generic Authentication Architecture (GAA) and Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA) are identified in “Details of 3GPP standards and technologies used to implement aspects of the method and system” above. In particular, the specific architecture on which the method and system may be based is GBA.
[0108]Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA) uses existing security associations between a network (e.g. a mobile network) and a card (e.g. a SIM card or UICC) to derive a key that can be used for the secure communication between the client and the server. Accordingly, if the device is associated with such a card, as well as with the client, the method can advantageously use the GBA to derive the security elem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com