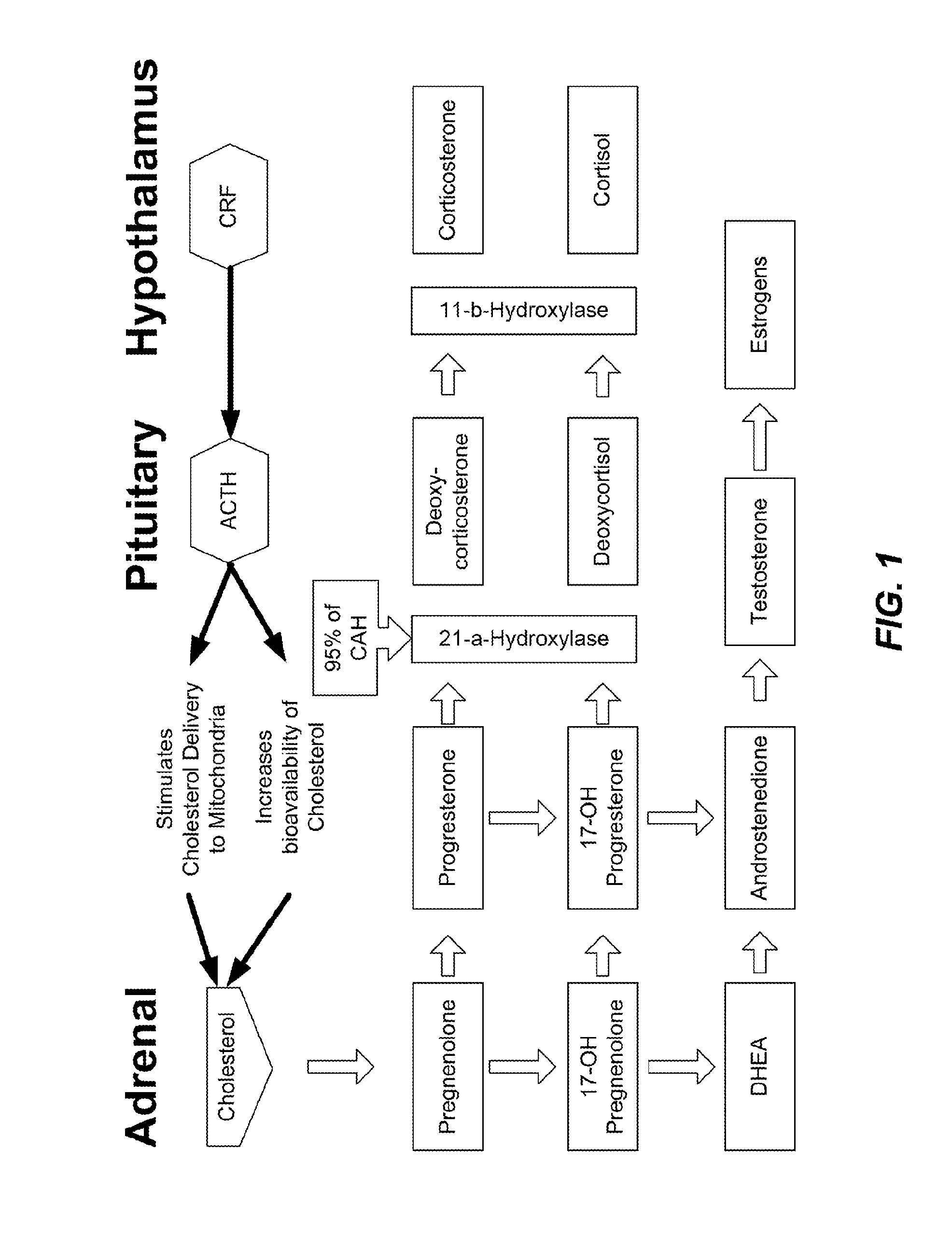
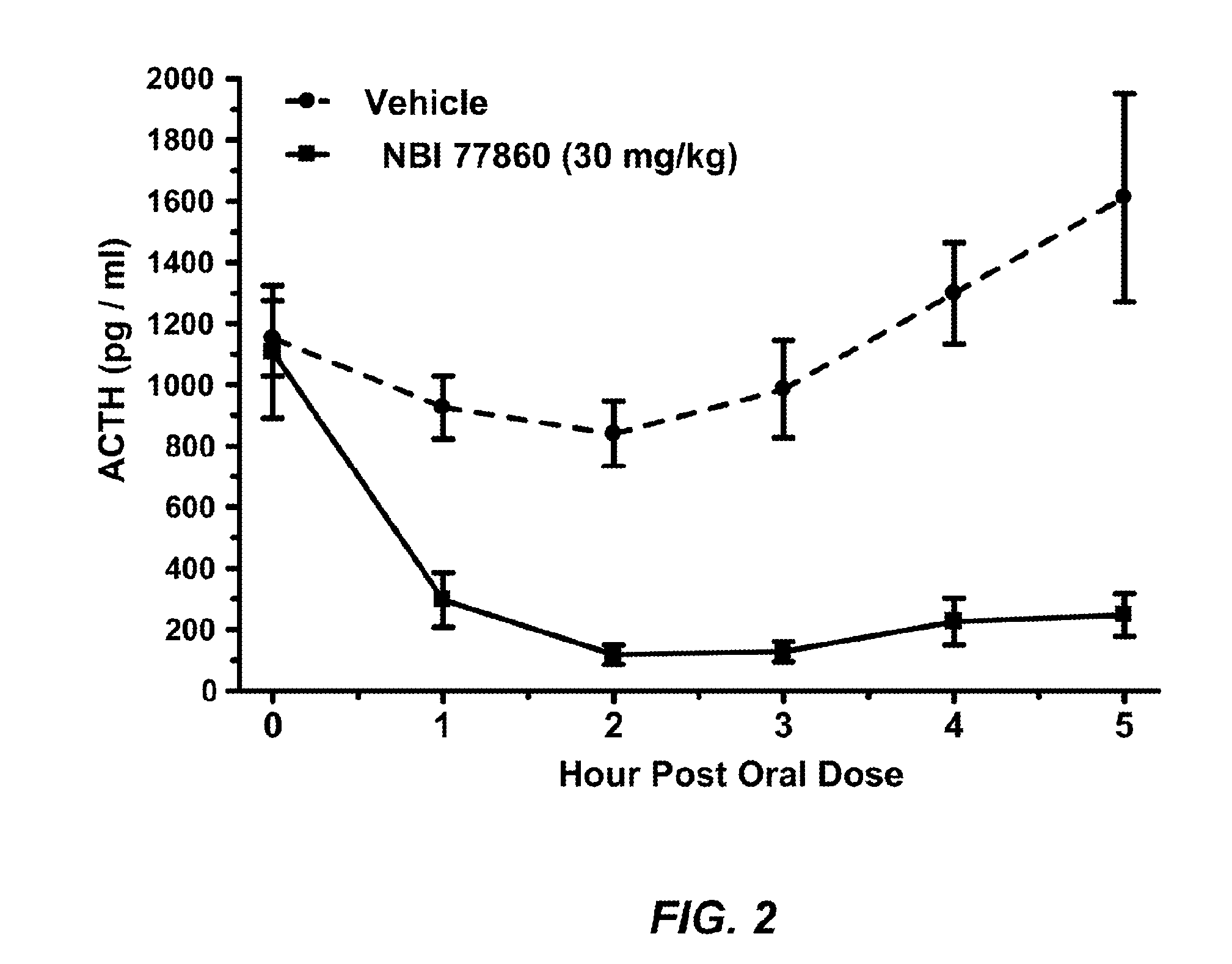
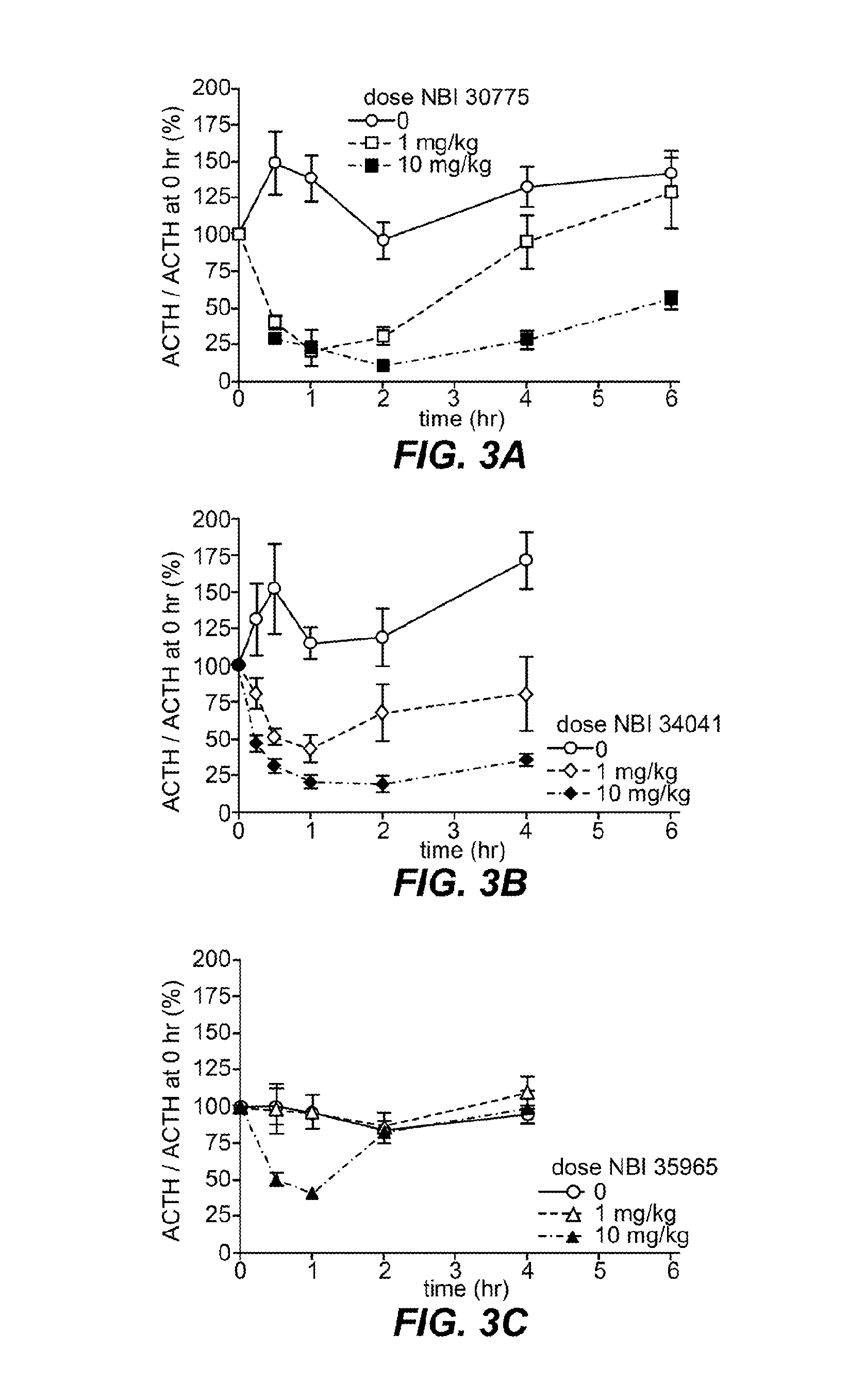
Crf1 receptor antagonists for the treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia
a technology of congenital adrenal hyperplasia and receptor antagonists, which is applied in the direction of endocrine system disorders, drug compositions, medical preparations, etc., can solve problems such as disease severity, and achieve the effects of reducing high plasma acth levels, potent ability to lower acth, and inhibiting specific binding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
CRF Receptor Binding Activity
[0075]CRF antagonists as used in the methods described herein may be evaluated for binding activity to the CRF receptor by a standard radioligand binding assay as generally described by Grigoriadis et al. (see, e.g., Mol. Pharmacol vol 50, pp 679-686, 1996) and Hoare et al. (see, e.g., Mol. Pharmacol 63: 751-765, 2003.) By utilizing radiolabeled CRF ligands, the assay may be used to evaluate the binding activity of the compounds described herein with any CRF receptor subtype.
[0076]Briefly, the binding assay involves the displacement of a radiolabeled CRF ligand from the CRF receptor. More specifically, the binding assay is performed in 96-well assay plates using 1-10 μg cell membranes from cells stably transfected with human CRF receptors. Each well receives about 0.05 mL assay buffer (e.g., Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline, 10 mM magnesium chloride, 2 mM EGTA) containing compound of interest or a reference ligand (for example, sauvagine, urocortin I...
example 2
CRF1 Receptor Agonist Activity
[0077]As reported in Fleck et al. (J. Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 341(2):518-531, 2012) (hereinafter “Fleck et al.” and incorporated by reference in it's entirely) the activity of previously identified CRF1 receptor antagonists are presented. Such activity is reported as the kinetically derived affinity (Ki) calculated from the association (k1) and dissociation (k−1) rate constants by the following equation:
Ki=k−1 / ki
[0078]Also as reported in Fleck et al., the kinetic Ki of the CRF1 receptor antagonists listed in Table 1 below have been reported:
TABLE 1Representative CRF1 Receptor Antagonistsk1Kinetic KiLigand(106 M−1min−1)(nM)NBI-279149.4 ± 3 25CP-316,31113 ± 2 12NBI-462006.2 ± 2 22DMP6967.7 ± 2 9.5pexacerfont2.6 ± 0.119NBI-3596520 ± 2 2.3ONO-2333Ms4.4 ± 2.215antalarmin3.4 ± 0.63.9NBI-340418.3 ± 2.01.7DMP90418 ± 1 0.38NBI-30775 14 ± 2.00.36SSR125543A33 ± 5 0.049NBI-778600.24 ± 0.0548 ± 9
[0079]By this same technique, the kinetic Ki of...
example 3
Dissociation Half-Life (T1 / 2) of CRF1 Receptor Antagonists
[0080]The dissociation half-life (t1 / 2) of a CRF1 receptor antagonist as used in the methods described herein is evaluated by the technique described in Fleck et al. As described therein, the dissociation rate constant for labeled and unlabeled ligands is denoted as k−1, while the half-life of drug dissociation from the receptor (t1 / 2), which is equal to the median residence time, is calculated from the dissociation rate constant (k−1) by the following equation:
t1 / 2=0.693 / k−1
[0081]As reported in Fleck et al., the dissociation half-life (t1 / 2) of the CRF1 receptor antagonists listed in Table 2 below have been reported.
TABLE 2Dissociation Half-Life of Representative Compoundsk−1,Dissociation t1 / 2,Ligand(min−1)(min)NBI 279140.27 ± 0.072.6CP-316,3110.17 ± 0.044.1NBI-46200 0.13 ± 0.0025.3DMP6960.095 ± 0.02 7.3pexacerfont0.049 ± 0.00114NBI-359650.048 ± 0.00516ONO-2333Ms0.063 ± 0.02917antalarmin0.013 ± 0.00253NBI-340410.013 ± 0.002...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dissociation half-life | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compositions | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com