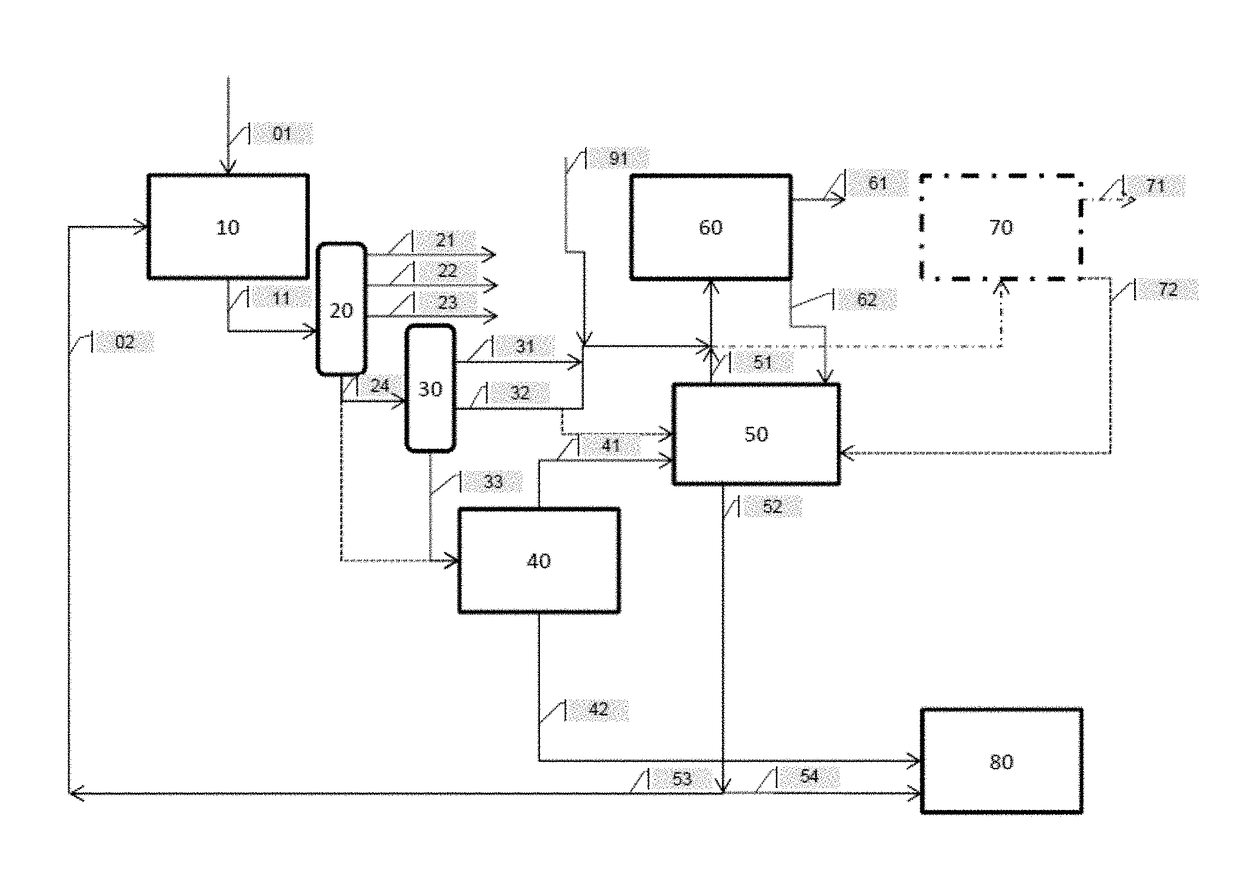
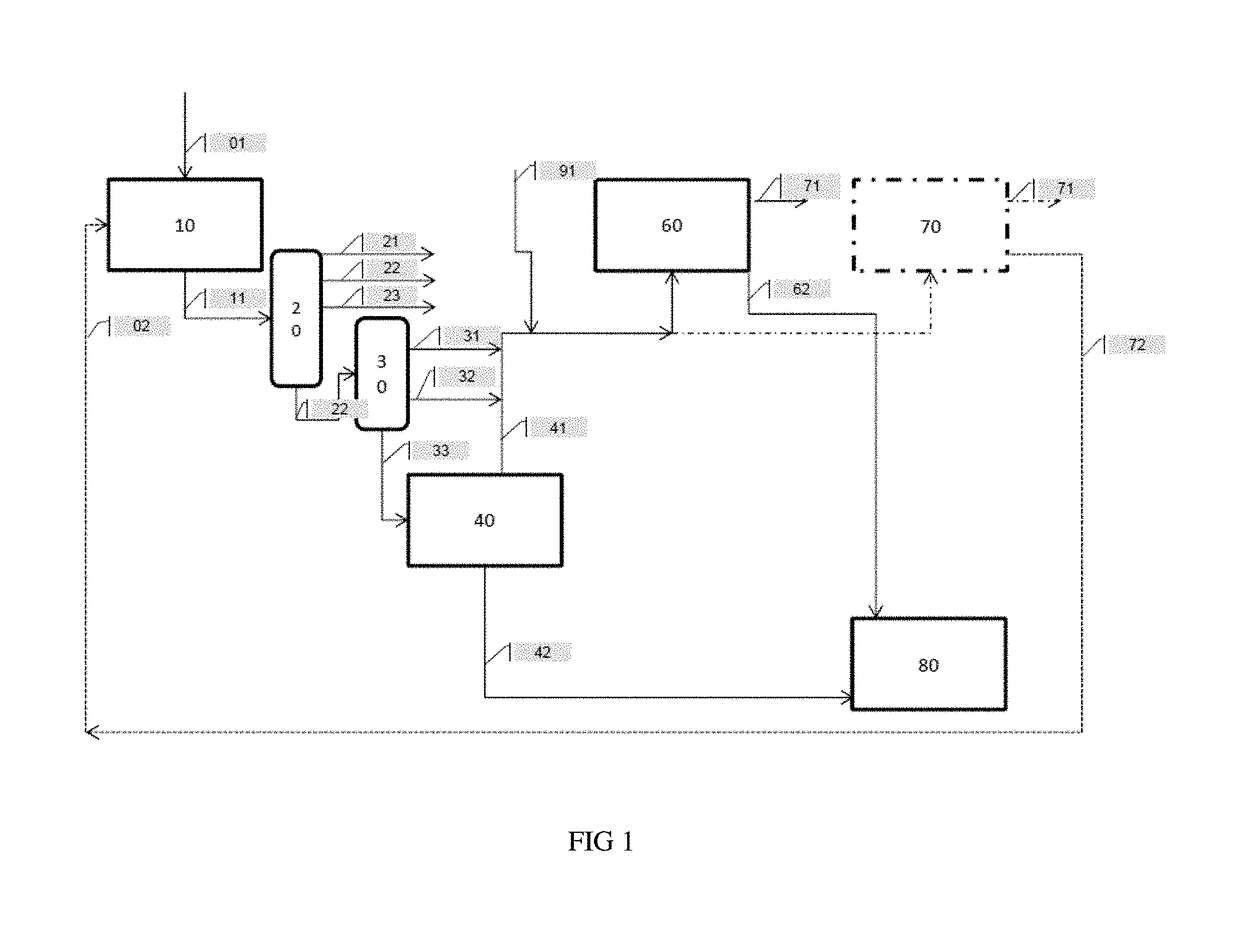
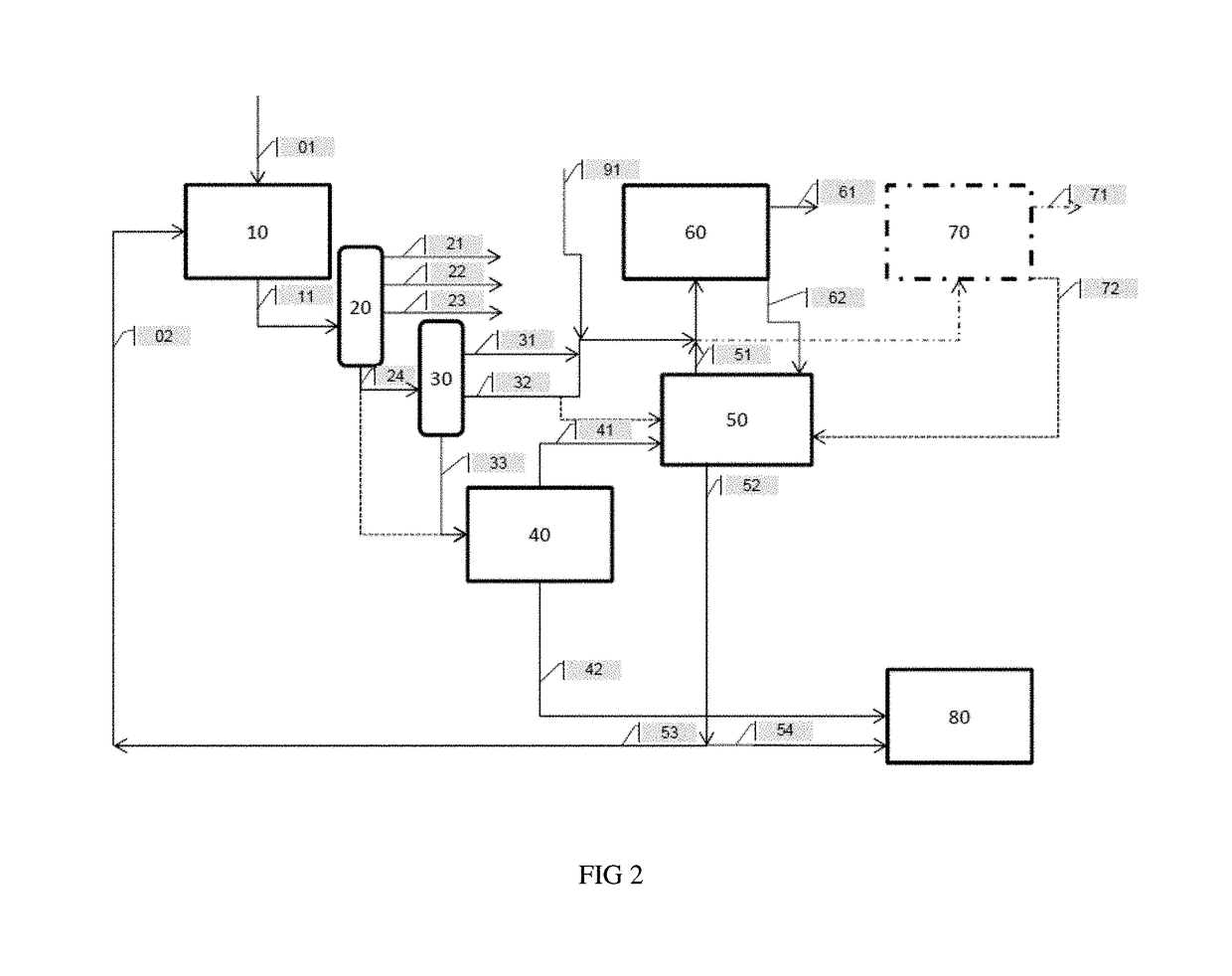
Deep hydroconversion process using an extraction of aromatics and resins, with upgrading of the hydroconversion extract and raffinate in downstream units
a hydroconversion and extracting technology, applied in the field of deep hydroconversion of heavy hydrocarbon feeds, can solve the problems of reducing the availability time, limiting the maximum conversion which can be obtained in deep hydroconversion units, and unstable asphaltenes with a tendency to precipita
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0173]The feed used in this example had the composition detailed in Table 1. It was a vacuum residue of the “Urals” type, and thus a vacuum residue obtained from crude oil originating from Russia.
TABLE 1Composition of the feed used (“Urals” type vacuum residue)PropertyUnitValueDensity—1.003Viscosity at 100° C.cSt540Conradson carbon% by wt15.0C7 asphaltenes% by wt4.0Nickelppm by wt70Vanadiumppm by wt200Nitrogenppm by wt5800Sulphur% by wt2.7540° C.− cut*% by wt10.0*Cut containing products with a boiling point below 540° C.
[0174]In this example, the feed was used in the process in accordance with the invention (FIG. 2) with neither hydrocracking in 60 nor catalytic cracking in 70, and thus also without adding vacuum distillate obtained by straight run crude oil distillation (SR VGO) 91 at the inlet to the hydrocracking and / or catalytic cracking steps.
[0175]However, in accordance with another variation, certain products obtained may subsequently be sent to a hydrocracking step, in parti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| catalytic bed temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com