Methods of generating human inner ear sensory epithelia and sensory neurons
a technology of sensory epithelia and inner ear, which is applied in the field of generating human inner ear sensory epithelia and sensory neurons, can solve the problems of no pharmacological, genetic, or cell therapy that can treat hearing loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation of Inner Ear Organoids with Functional Hair Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
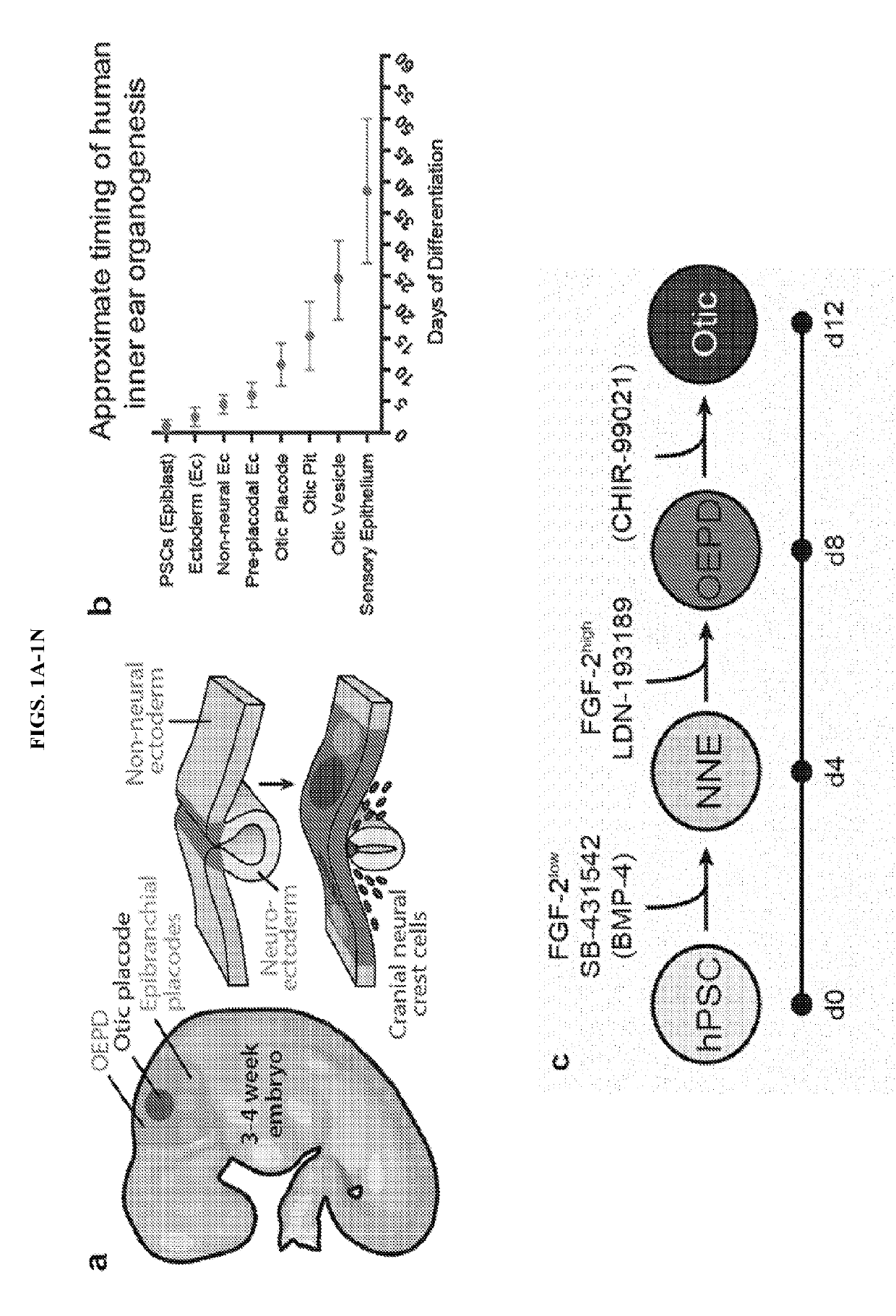
[0054]The human inner ear contains approximately 20,000 sensory hair cells that detect sound and movement via mechanosensitive stereocilia bundles1. Genetic mutations or environmental insults, such as loud noises, can cause irreparable damage to these hair cells, leading to dizziness or hearing loss2,3. We previously demonstrated how to generate inner ear organoids from mouse pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) using timed manipulation of the FGF, TGFβ, BMP, and Wnt signaling pathways in a 3D culture system4-6. We have shown that mouse inner ear organoids contain sensory hair cells with similar structure and function to native vestibular hair cells in the mouse inner ear7. Moreover, our past findings bolstered a working model of otic induction signaling dynamics, wherein BMP signaling activation and TGFβ inhibition initially specifies non-neural ectoderm and subsequent BMP inhibition and FGF acti...
example 2
Modeling Otic Neurogenesis
[0112]In day-12 aggregates, we observed patches of PAX8+ PAX2+ epithelia reminiscent of otic placodes; therefore, we assayed for culture conditions promoting otic vesicle formation. Under control conditions (DMSO), we did not observe vesicle formation (data not shown). Since otic induction is dependent on Wnt signaling, we treated 12-day aggregates with a potent GSK3β inhibitor and known Wnt signaling agonist27, CHIR99021 (CHIR), between days 12-18. Under these conditions, PAX8+ PAX2+ SOX10+ vesicles evaginate from the outer epithelium (˜10-30 vesicles per aggregate; see FIGS. 4A-4R). Remarkably, Islet1+ (ISL1+) neuroblasts appear to delaminate from the otic vesicles (FIGS. 16A-16B). We also see neuroblasts in DMSO-treated aggregates and in the non-otic interior of CHIR-treated aggregates (FIG. 16A, arrowheads). Thus, we hypothesized that CHIR-treated aggregates yield a mixture of otic (i.e. vesicle-derived) and epibranchial (i.e. epithelium-derived) neuron...
example 3
Exemplary Protocol for In Vitro Production of Inner Ear Organoids
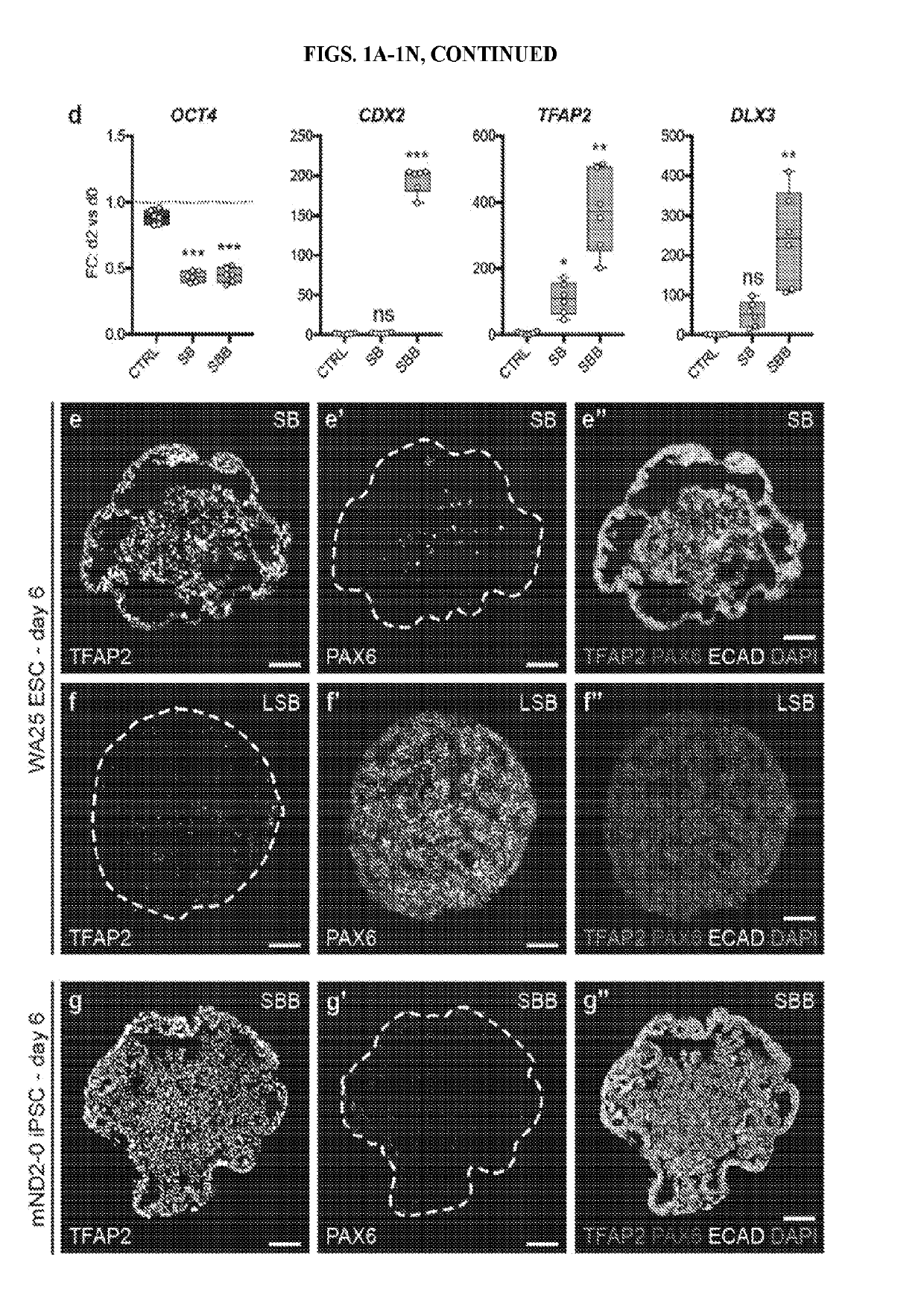
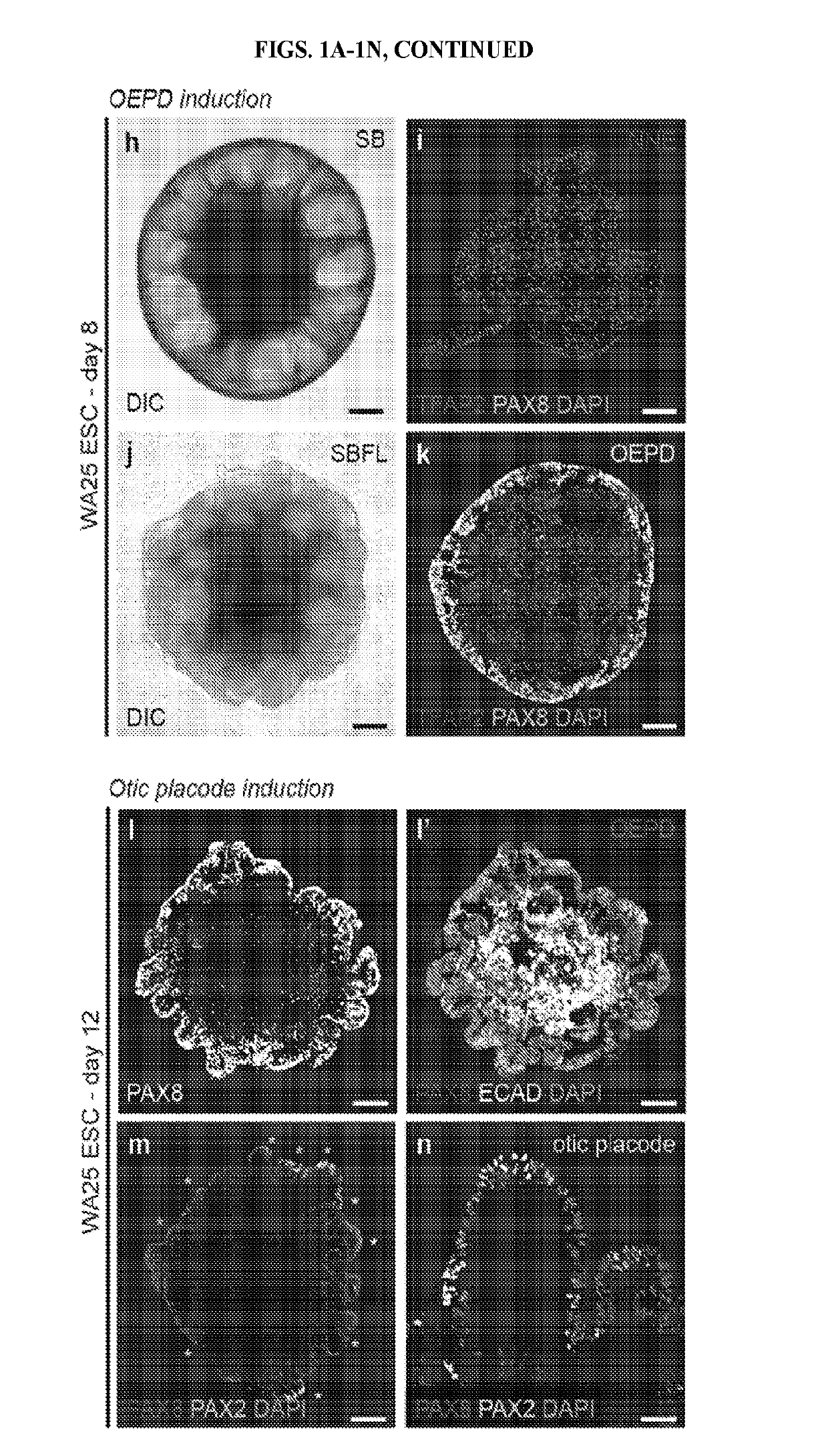
[0115]This example describes a protocol for inducing formation of non-neural ectoderm and inner ear sensory tissue from human pluripotent stem cells. As described in greater detail in the following paragraphs, pluripotent stem cells aggregates were cultured in a medium containing Matrigel, which is rich in basement membrane proteins, to induce ectoderm development and production of ectoderm epithelium on the aggregate surface. We then used a combined treatment of bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP4) and a transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) inhibitor such as the small molecule SB-431542 (“SB”) to promote non-neural differentiation in the epithelium. To further initiate inner ear induction, BMP signaling was inhibited and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling was activated using recombinant FGF-2 approximately 24 hours after the initial BMP4 and SB treatment. Remarkably, the combined treatment protocol initiated se...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| apparent thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com