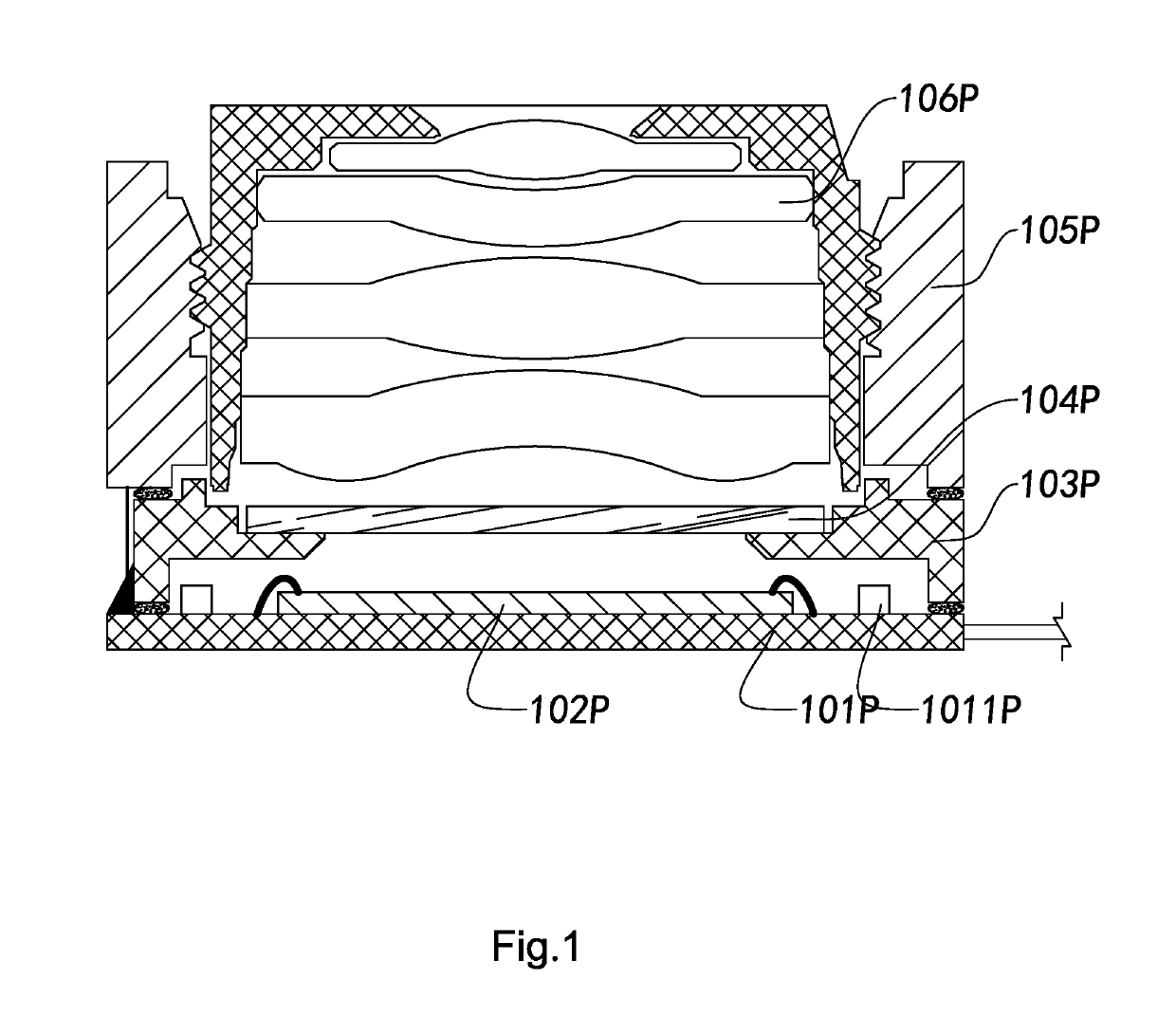
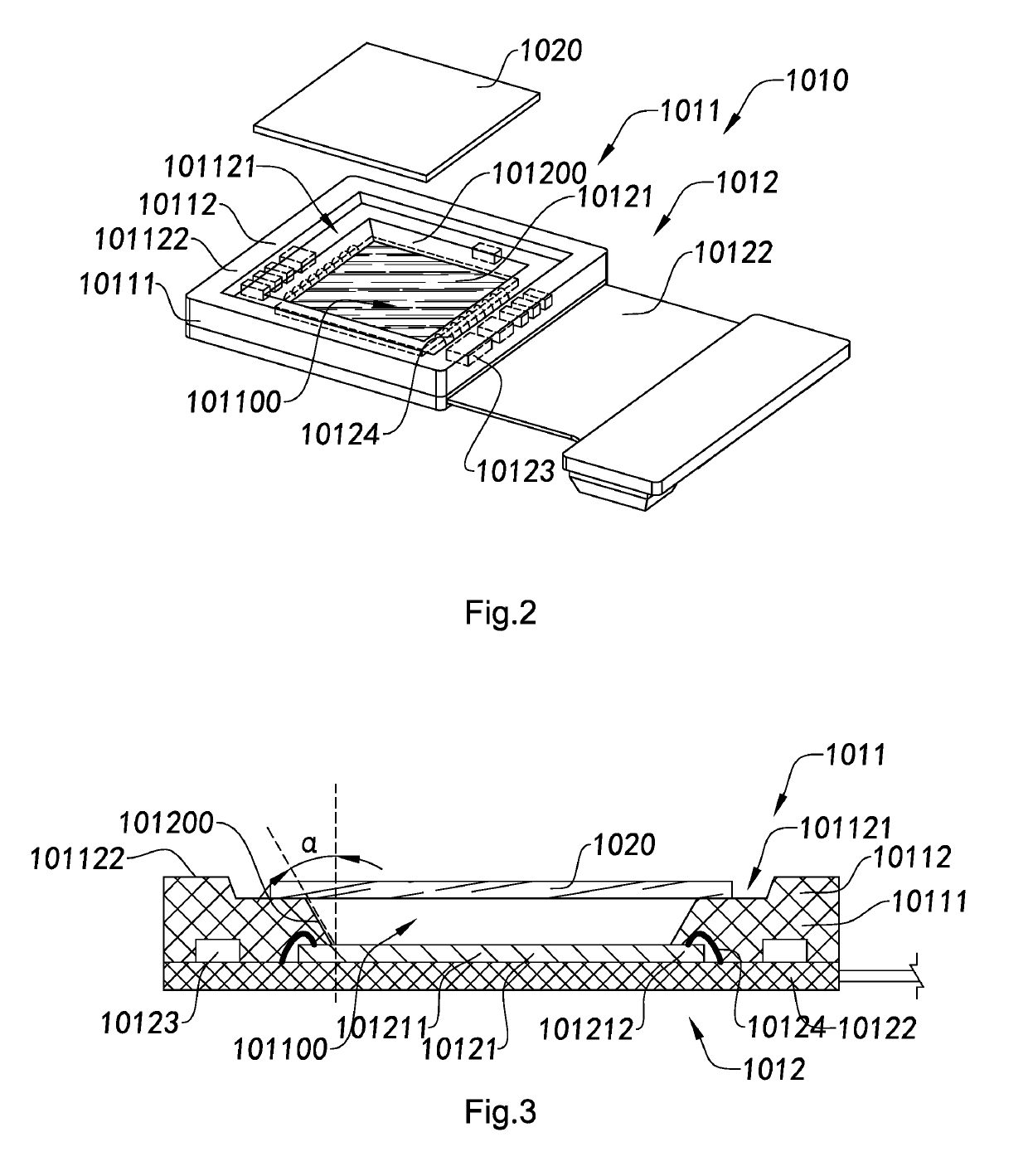
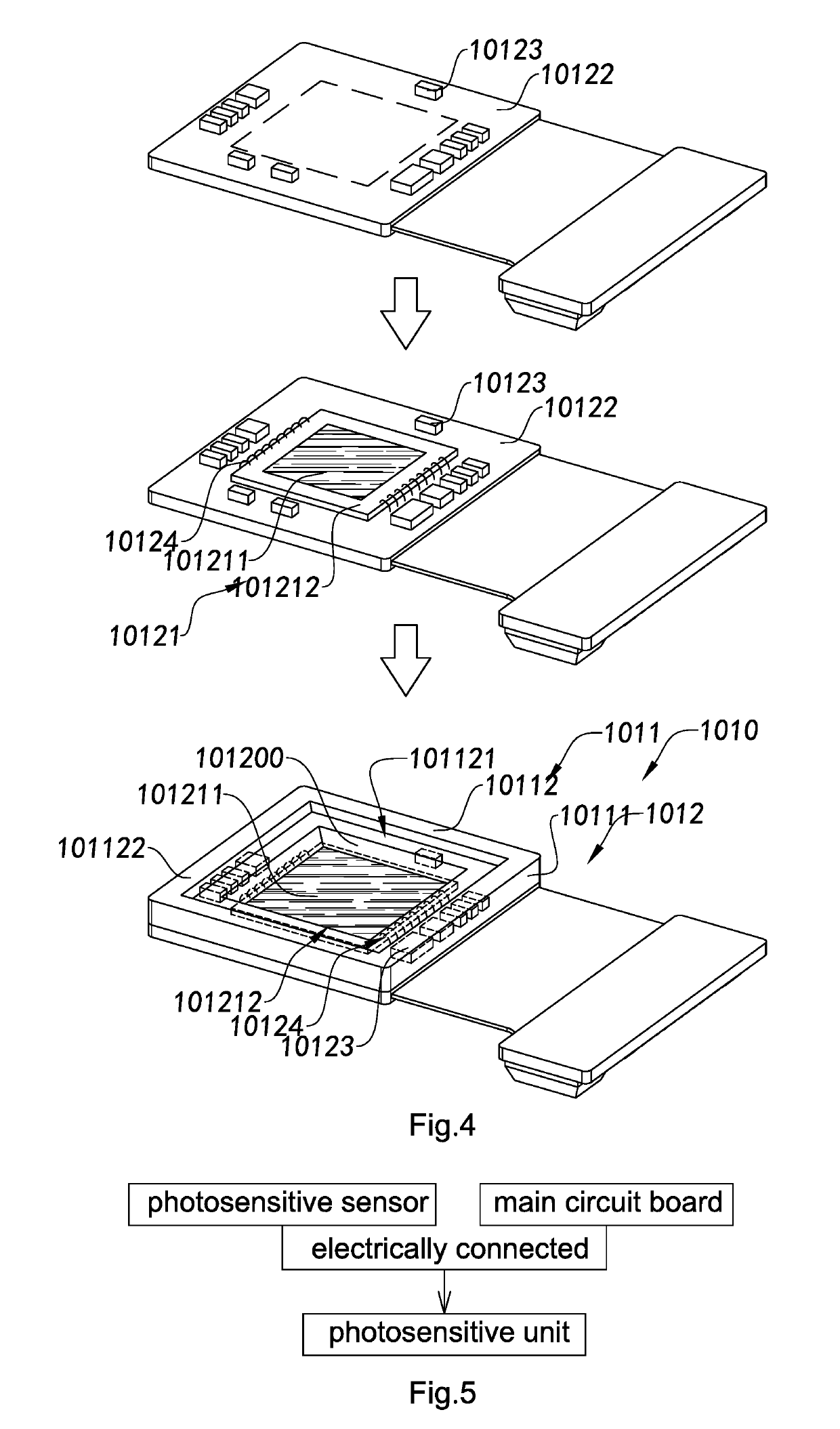
Camera module, and photosensitive component thereof and manufacturing method therefor
a technology of camera modules and photosensitive components, applied in the field of camera modules, can solve the problems of increasing the defective rate restricting the development increasing the thickness of the camera module, so as to reinforce the electromagnetic immunity of the photosensitive unit and the structural strength of the main circuit board
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0244]The following is disclosed in order that those skilled in the art can implement the present invention. Preferred embodiments in the following descriptions are to give examples only. Those skilled in the art can think of other obvious modifications. The basic notions of the present invention defined in the following descriptions can apply to other implementations, modifications, improvements, equivalences, and other technical solutions that do not deviate from the scope or spirit of the present invention.
[0245]Those skilled in the art should understand that in the disclosure of the present invention, terms such as “longitudinal,”“lateral,”“upper,”“lower,”“front,”“back,”“left,”“right,”“perpendicular,”“horizontal,”“top,”“bottom,”“inner,”“outer,” etc., which indicate directions or positional relations are based on the directions or positional relations demonstrated in the figures and only to better describe the present invention and simplify the description, rather than to indicat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com