Treatment of cancer by manipulation of commensal microflora
a commensal microflora and cancer technology, applied in the direction of antibacterial agents, drug compositions, antibody medical ingredients, etc., can solve the problems that the mechanisms that govern the presence or absence of this phenotype have not been well understood, and achieve the effects of inhibiting the growth or spread of cancer, enhancing immune response, and inhibiting immune evasion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
[0132]Animals and Tumor Model:
[0133]C57BL / 6 mice were obtained from Jackson laboratory or Taconic farms. 6-8-week-old female mice were used. The C57BL / 6-derived melanoma cell line B16.F10.SIY (referred to herein as B16.SIY) was generated (Blank et al. Cancer research 64, 1140-1145 (2004); herein incorporated by reference in its entirety). For tumor growth experiments, mice were injected subcutaneously with 1×106 B16.SIY tumor cells. Tumor size was measured twice a week until endpoint and tumor volume was determined as length×width2×0.5. For B16 parental tumor model experiments, mice were injected subcutaneously with 1×106 B16.F10 tumor cells. For bladder cancer model experiments, mice were injected subcutaneously with 2×106 MB49 cells. All experimental animal procedures were approved by the University of Chicago Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC).
[0134]IFN-γ ELISPOT and SIY Pentamer Analyses:
[0135]Elispot plates (Millipore, MAIP S4510) were coated with purifi...
example 2
Results
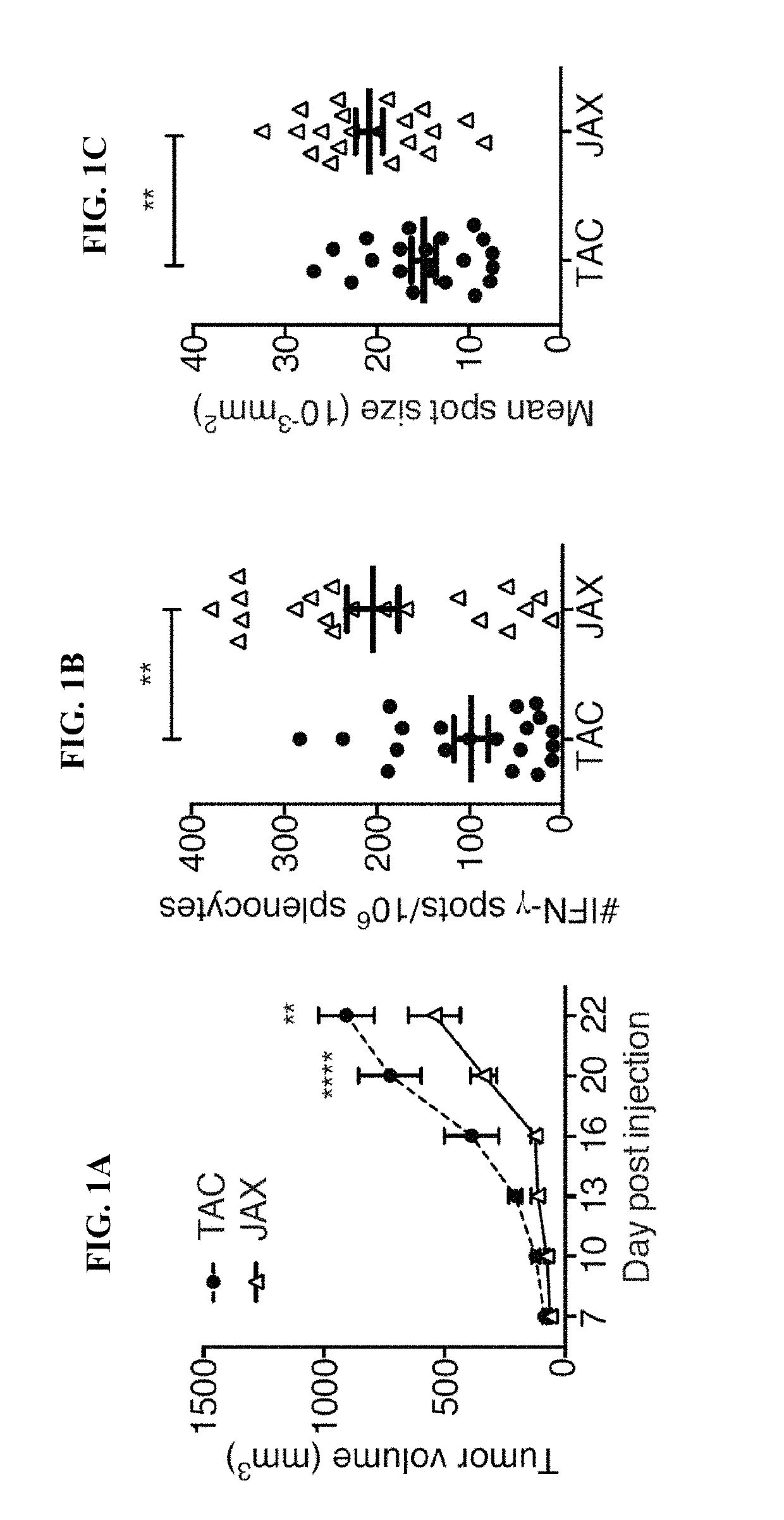
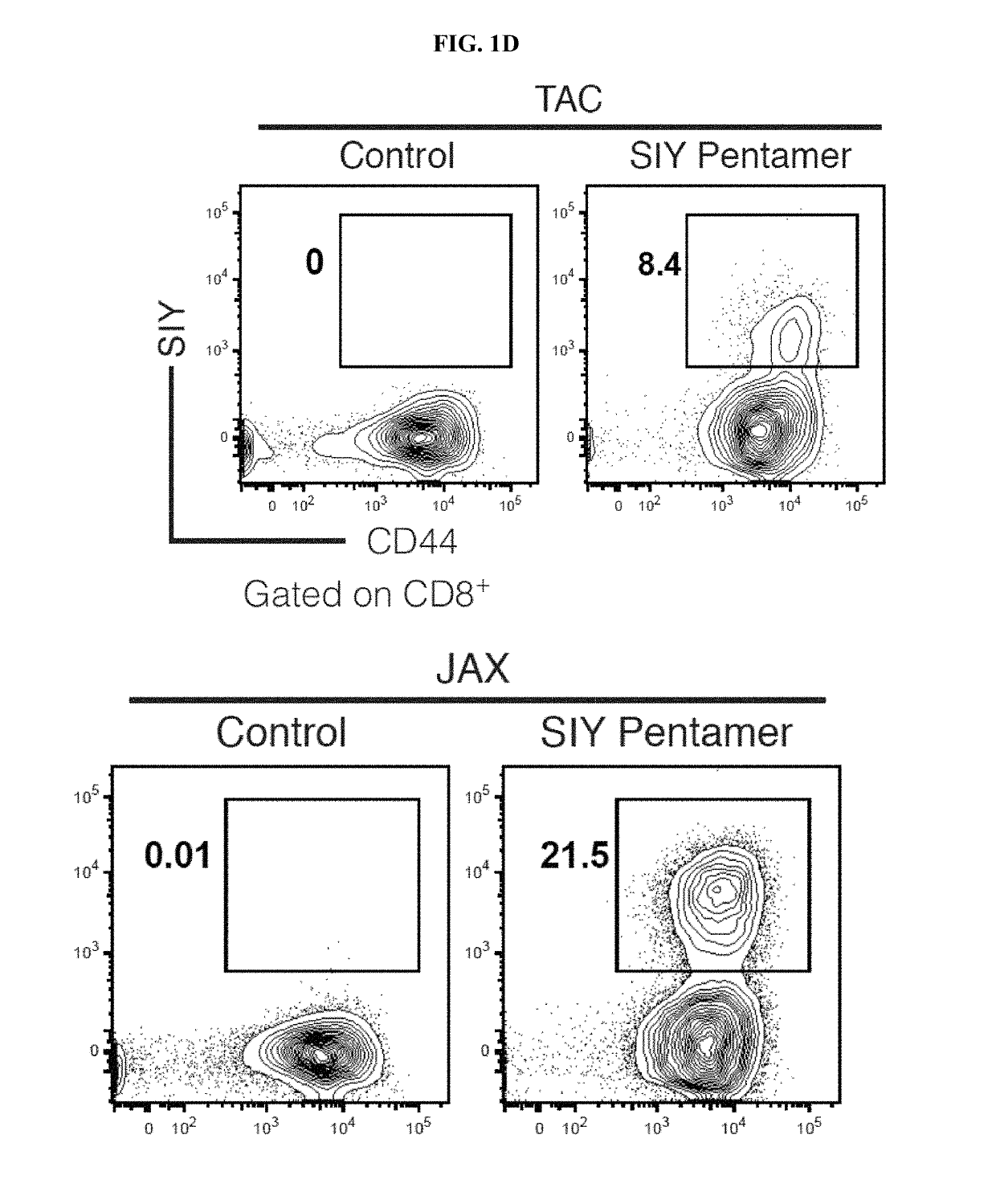
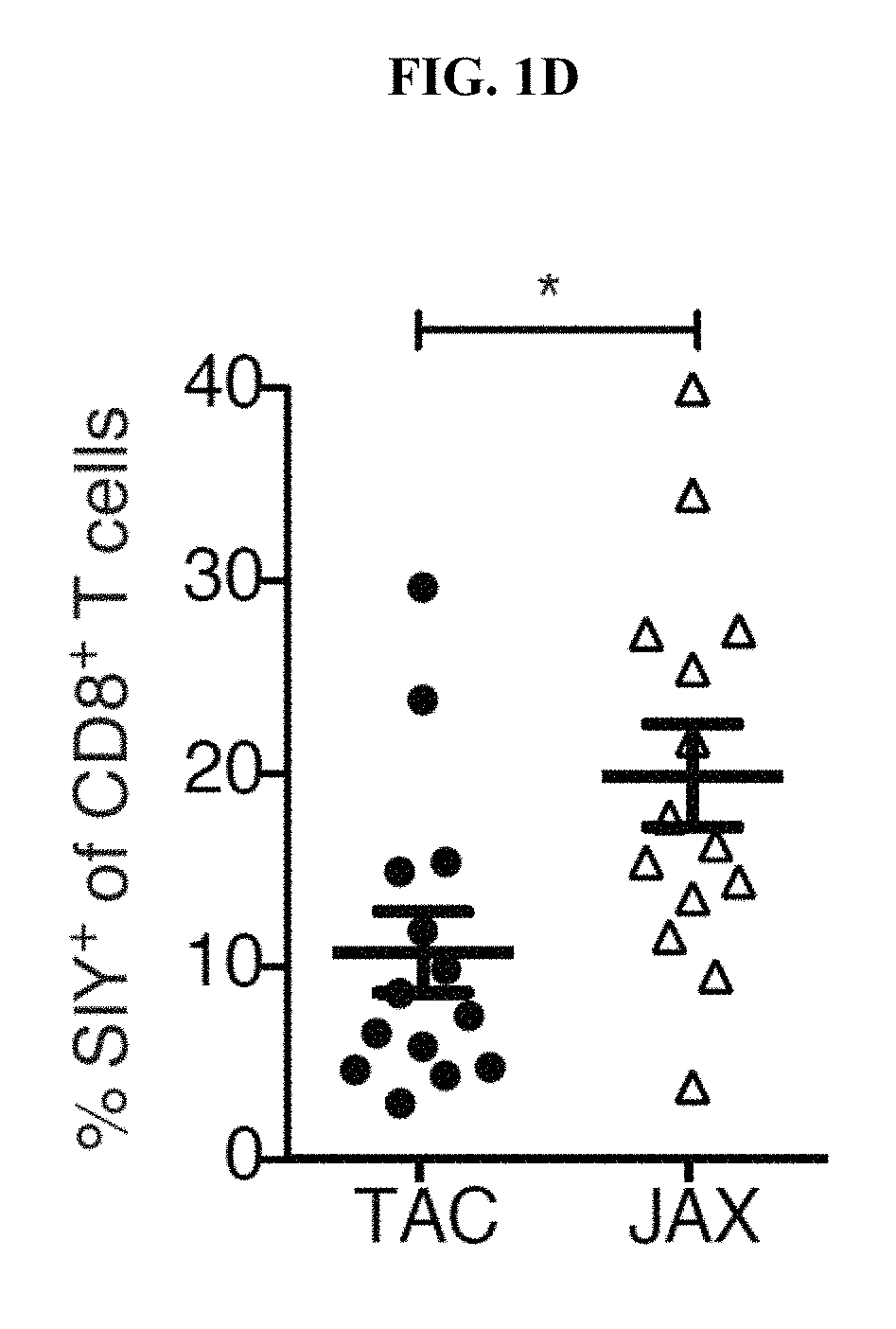
[0148]Experiments were conducted during development of embodiments of the present invention to test whether differences in the specific composition of the normal microbiota influence the immune response to a growing tumor in vivo. Subcutaneous B16.SIY melanoma growth was observed in genetically similar C57BL / 6 mice derived from two different mouse facilities, Jackson Laboratory (JAX) and Taconic Farms (TAC), which have been shown to differ in their commensal microbes (Ivanov et al. Cell 139, 485-498 (2009); herein incorporated by reference in its entirety). It was found that JAX and TAC mice exhibited significant differences in B16.SIY melanoma growth rate, with tumors growing more aggressively in TAC mice (FIG. 1A). To evaluate whether this difference was immune-mediated, tumor antigen-specific T cell responses, as well as T cell accumulation in the tumor microenvironment, were assessed. In fact, tumor-specific T cell responses were significantly higher in JAX mice (FIGS. 1B...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com