Compact Low-power Cryo-Cooling Systems for Superconducting Elements
a superconducting element, low-power technology, applied in the direction of gas cycle refrigeration machines, refrigeration machines, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problem of lower thermodynamic efficiency than those coolers, and achieve the effect of minimizing the effect of secondary flows
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
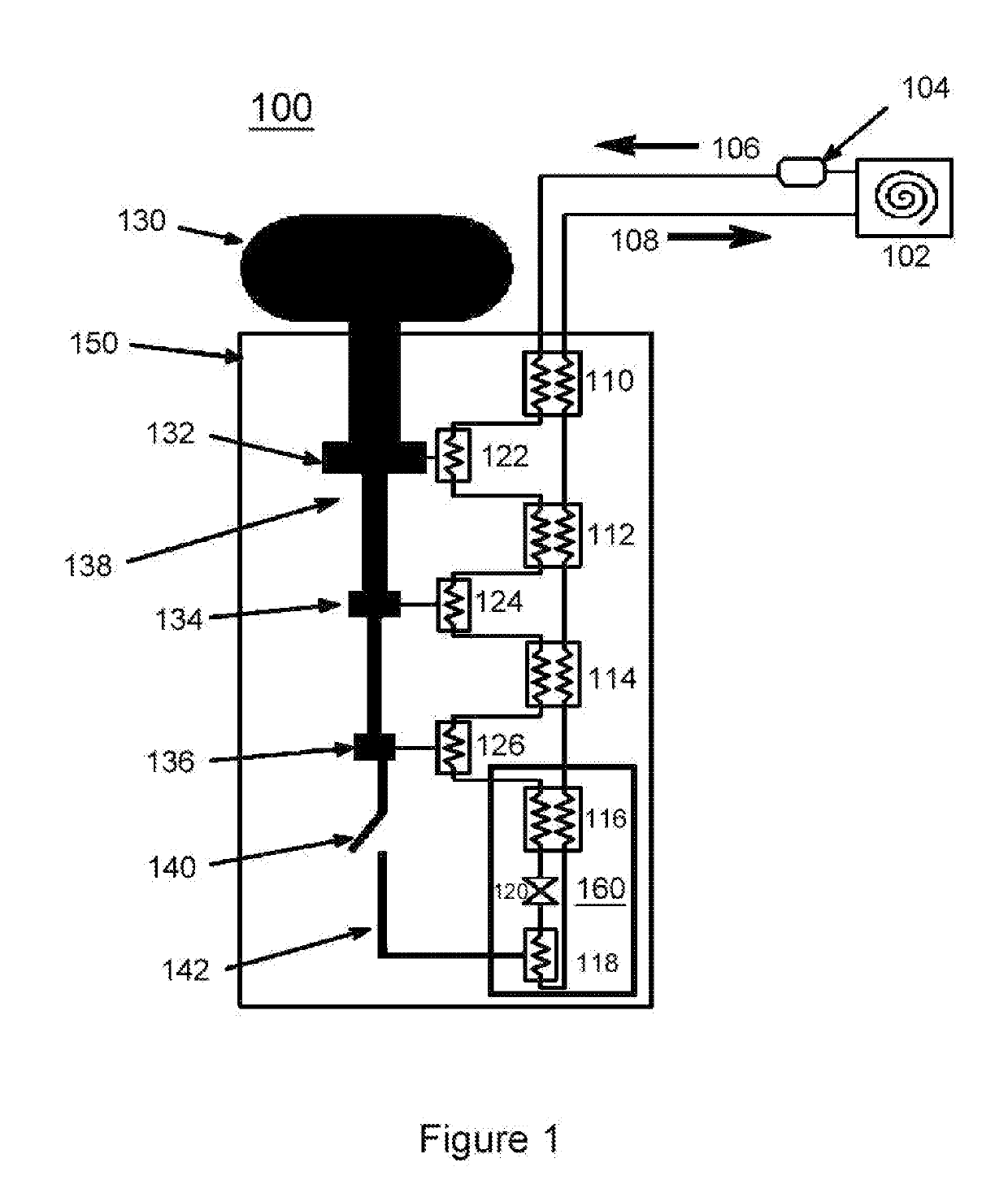
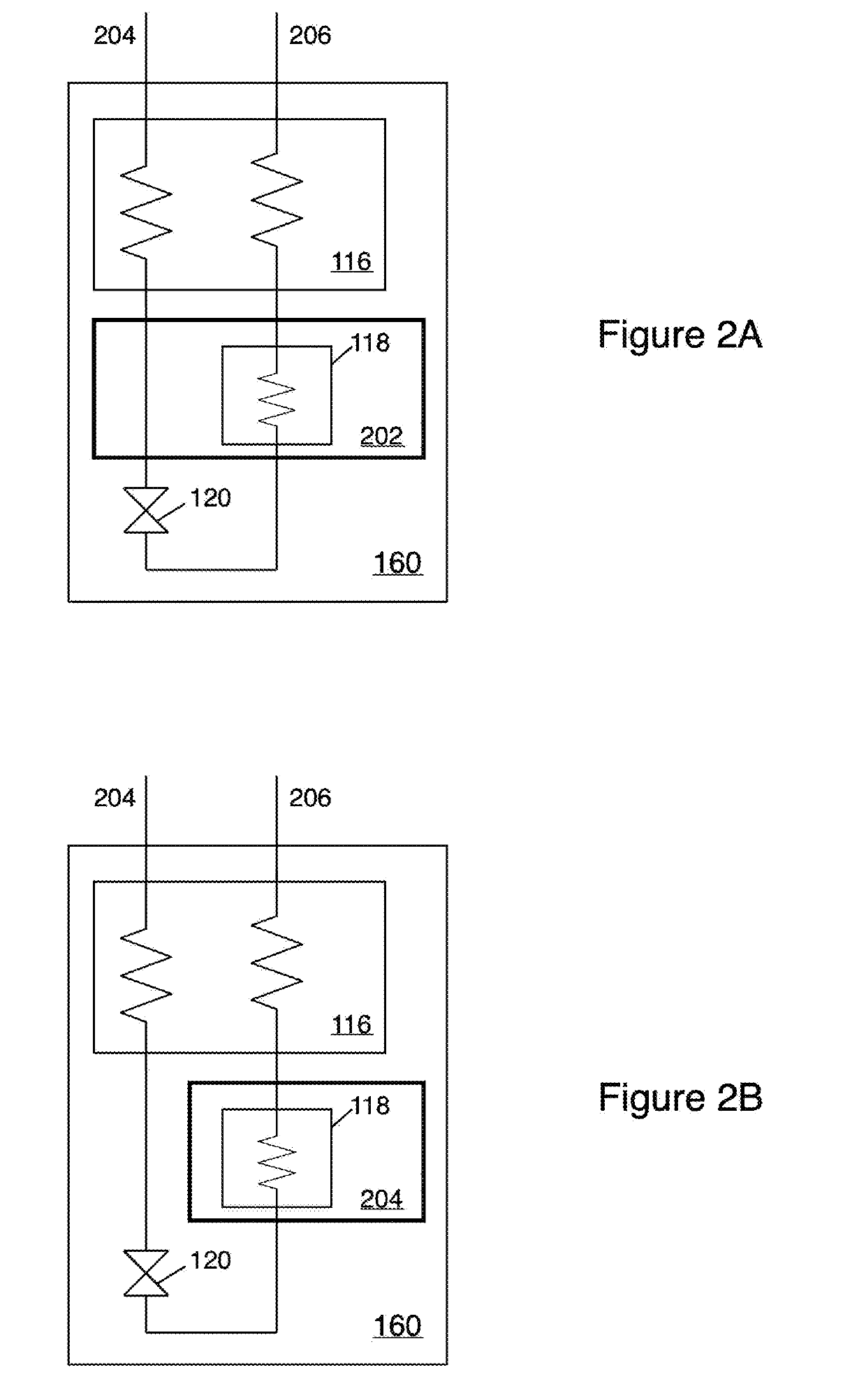
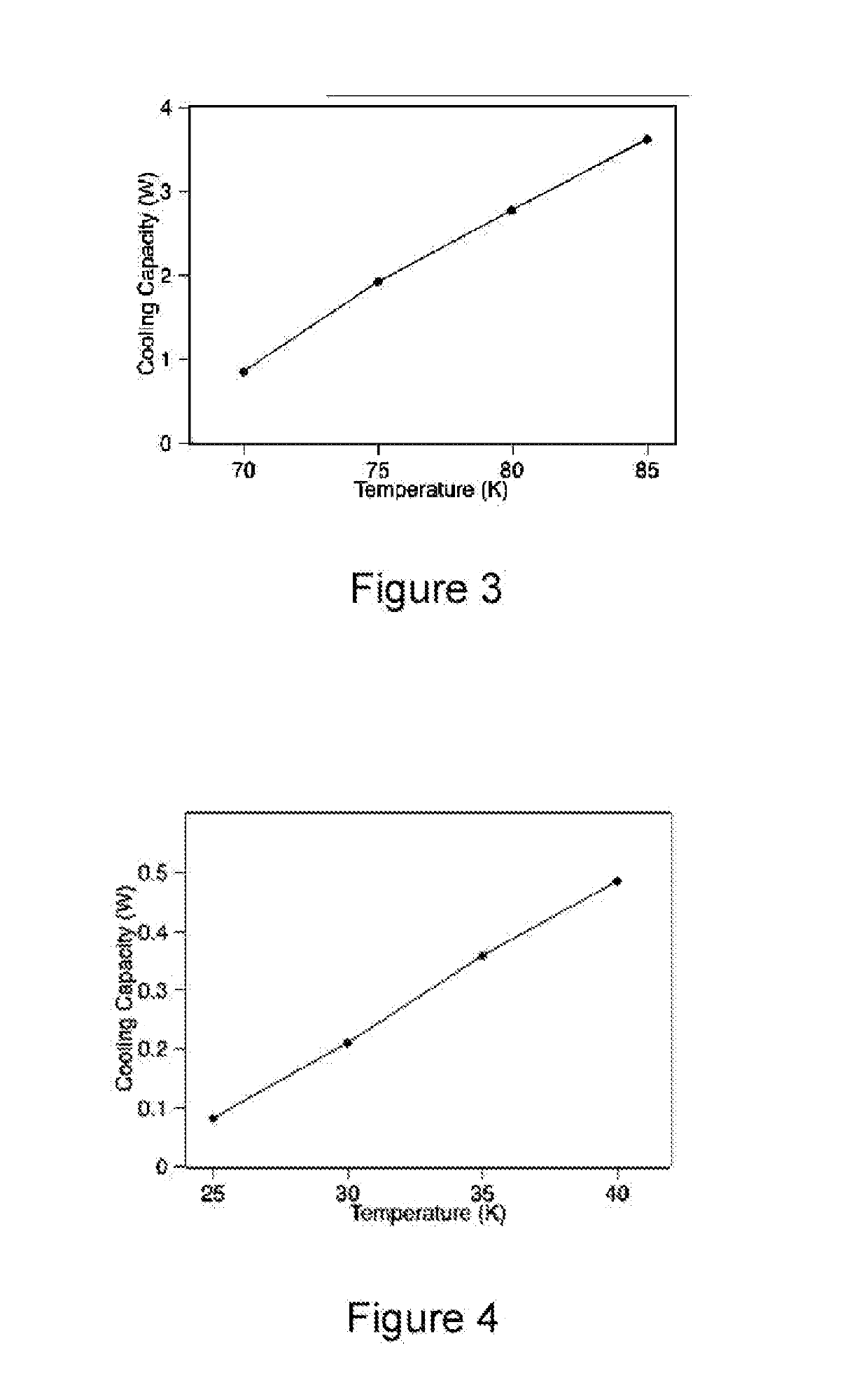
[0017]FIG. 1 is a schematic block diagram of the present cooler system 100. System 100 is a compact cooler having a form factor and low power draw of a standard rack-mountable electronics instrument. The cooler is a pulse tube / Joule-Thomson (PT / JT) hybrid, with the JT stage 160 achieving 1.4 mW of cooling at 1.7 K or 2.2K (depending on the configuration, see FIGS. 2A and 2B), and the three-stage 132, 134, 136 pulse tube 138 providing cooling at 80 K (132), 25 K (134), and 10 K (136).
[0018]Since one important application of the present invention is the cooling of quantum encrypted communication links that utilize superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors (SNSPD), and superconducting transition-edge sensor microcalorimeters for electron microscope microanalysis, the stages of this embodiment were developed with estimated cooling loads as shown in Table 1. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that specific applications will result in different cooling load requirements and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com