Support Element for Supporting a Window Frame
a support element and window frame technology, applied in the direction of doors/windows, building components, base frames, etc., can solve the problems of chimney effect, combustibility of frequently used insulation materials, etc., to prevent upward spread of flames, weaken the pressure on the main wall or outer wall, and prevent burn-through or at least significantly delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
production examples
Example 1A: Support Element with Waterglass
[0099]Inert sodium or potassium silicate (10-20%) is mixed to form a homogeneous mass with the base material, e.g., a rigid PUR foam or a rigid PUR / PIR foam, and optionally with one or more additives such as a curing agent. The mixture is pressed in a mold and cured by heat. Panels can be cut and processed into strip-shaped support elements.
example 1b
ement with Expandable Graphite
[0100]Rigid PUR and / or PIR foam which originates from production residues and / or recycled material, e.g., old insulating panels, and which has been ground to a maximum particle size of approximately 5 mm, preferably of approximately 1 mm, is mixed with 5-10%, preferably 7.5%, of expandable graphite (average particle size, approximately 1 mm) and binder material, e.g., in liquid form, in a ratio of 1:5, calculated on the basis of the weight of the ground rigid foam. The mixture is introduced into a panel mold and treated by heat and pressure in a pressing direction P perpendicular to the surface of the panels, so that a rigid foam material with a bulk density of approximately 550 kg / m3 is obtained. The thickness of the panels is preferably 2-7 cm.
[0101]Alternatively, comminuted rigid foam pieces, expandable graphite flakes, and binder material can be introduced layer by layer in alternation (e.g., by interspersing) and then pressed.
[0102]Cured panels res...
example 1c
ement with an Expandable Graphite-Containing Layer
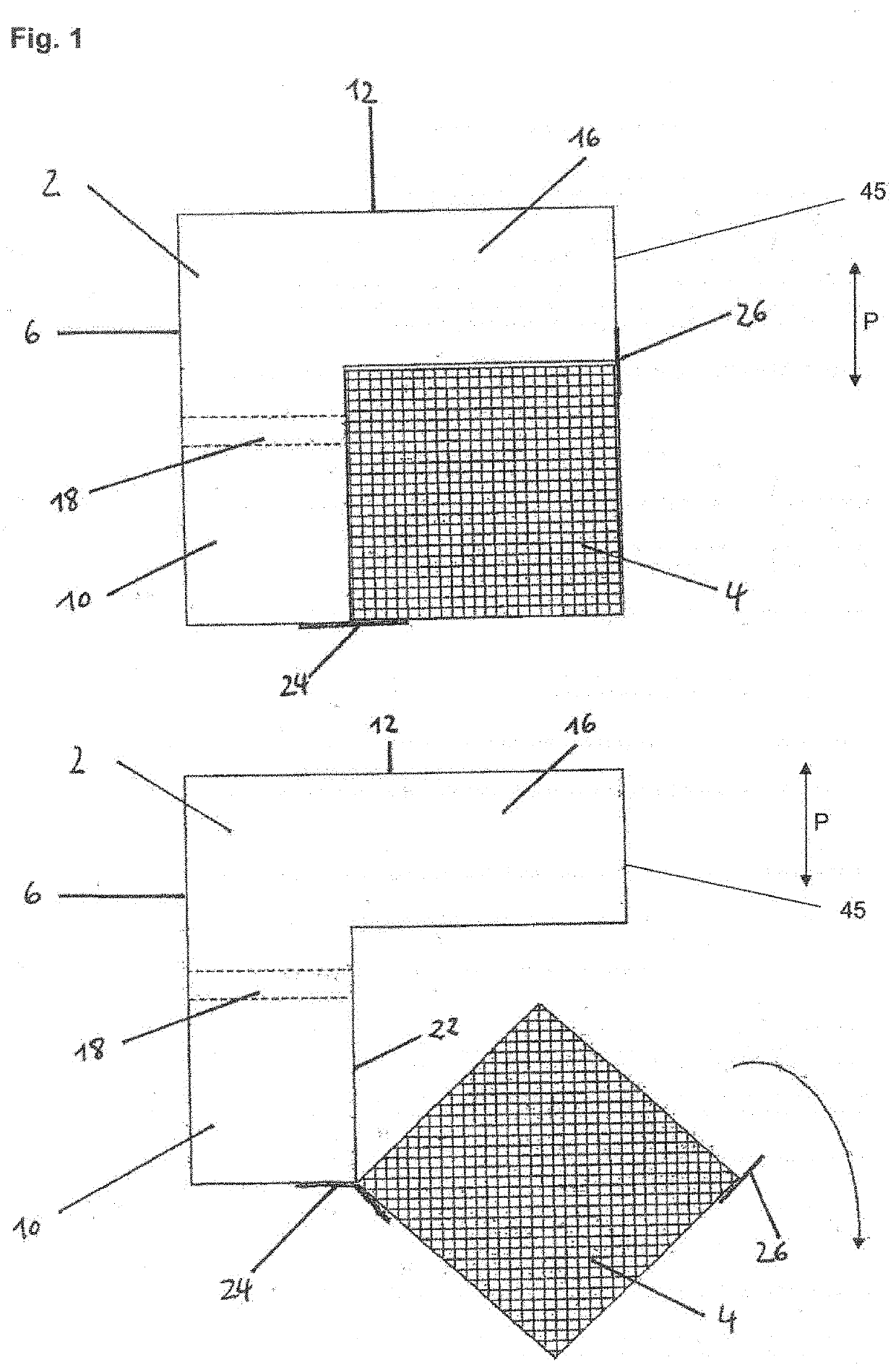
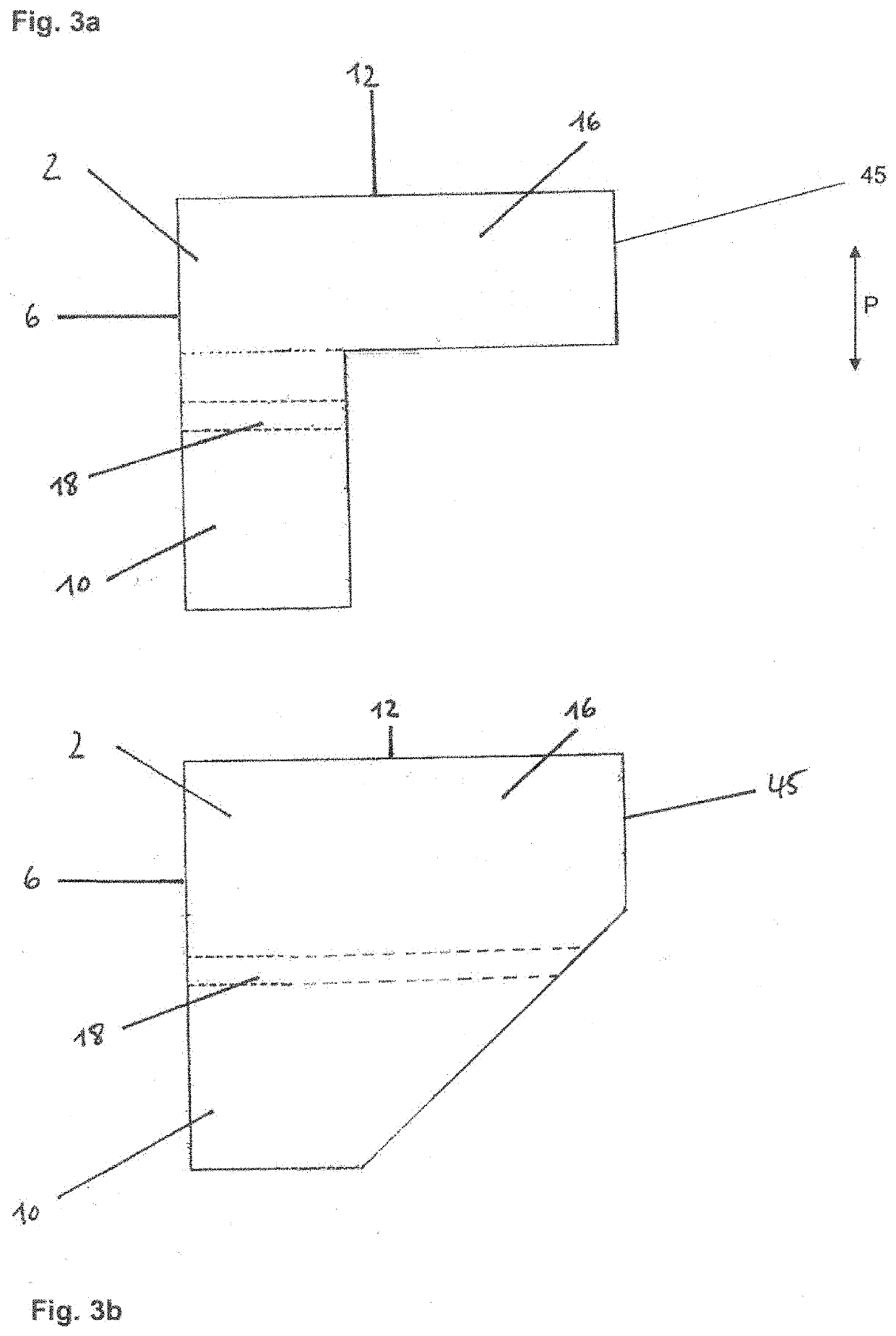
[0103]In the alternative embodiment shown in FIG. 3c, the upper layer 47 of the produced panel (i.e., a surface perpendicular to the pressing direction P) has a thickness of at least 10 mm, preferably of 15 mm, and has been combined with expandable graphite, wherein the remainder of the support element has not been combined with expandable graphite.
[0104]The strip-shaped support elements are produced as described in Example 1B.
Fire Tests
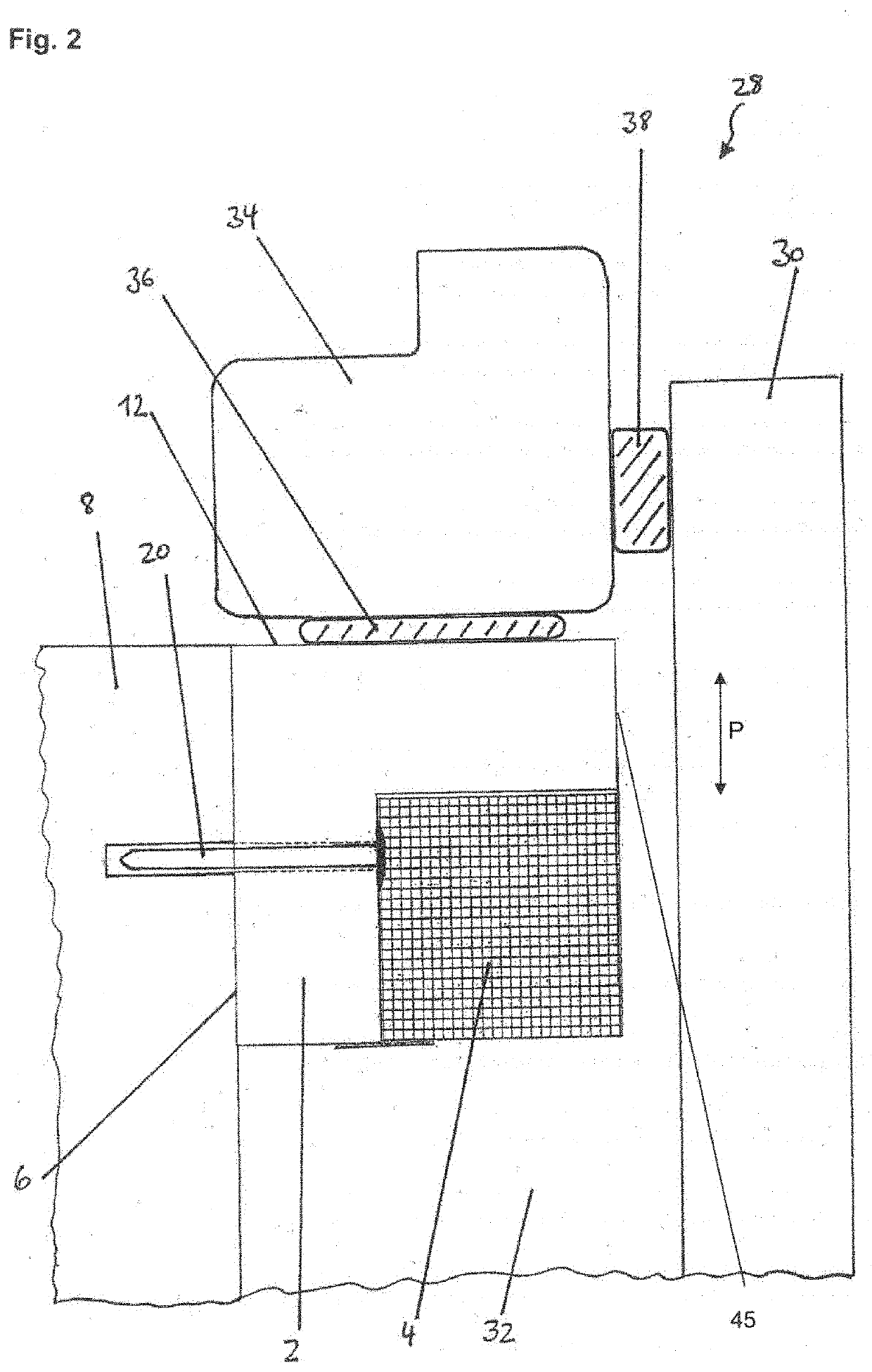
[0105]According to the test criteria of DIN 1366-5, support elements 2 of rigid PUR / PIR foam with expandable graphite, produced according to Example 1B with a thickness of 30 mm or 50 mm, were exposed to flames at 180° C. (see test layout in FIG. 5d), during which procedure the increase in temperature was measured on the opposite side after 5, 15, and 25 minutes in comparison to corresponding rigid foam without expandable graphite.
[0106]On the side facing away from the flames, the temperatures were me...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com