Antiviral compounds and method for treating hepatotropic viral infection, particularly hepatitis b and hepatitis d
a technology for which is applied in the field of antiviral compounds and methods for treating hepatitis b and d, can solve the problems of increasing the likelihood of liver failure, the inability of patients with hbv infection to use the currently approved anti-hbv drugs, and the inability to cure hepatitis b or d. to achieve the effect of controlling cytokines within homeostasis and inhibiting viral replication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment 1
ty Test with the Compounds
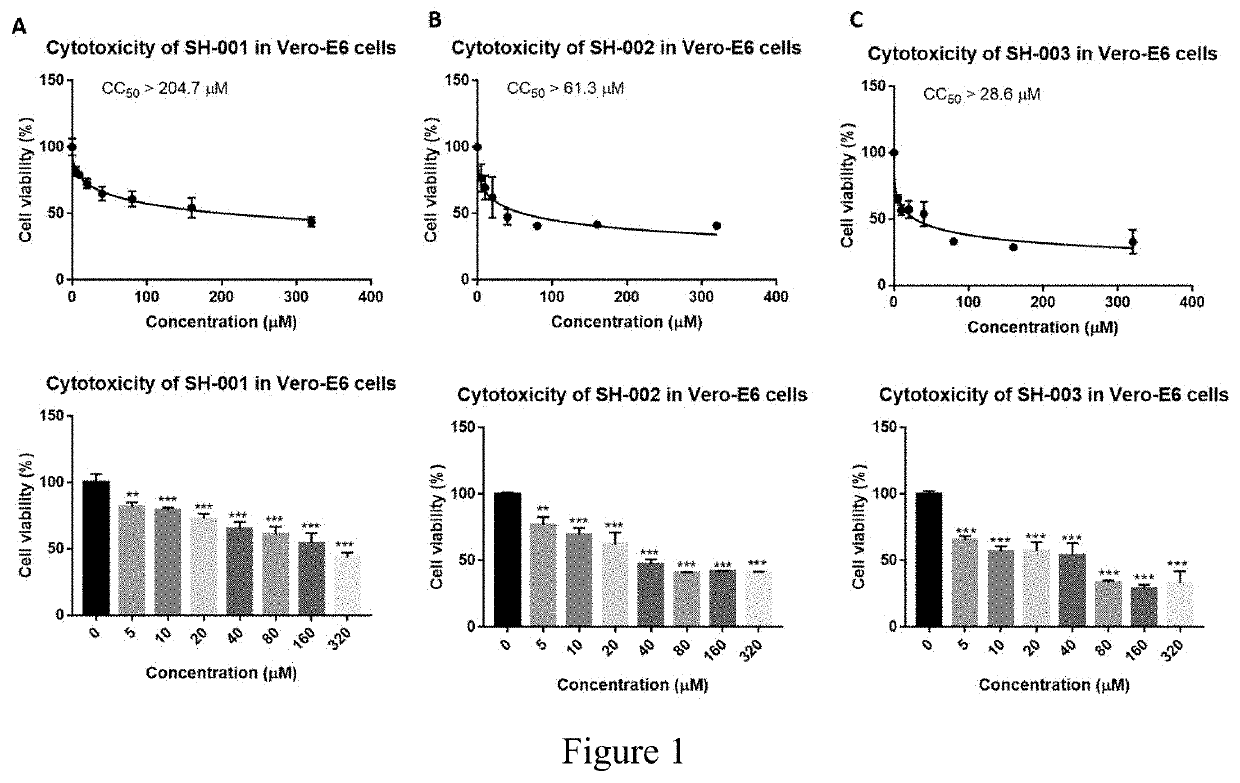
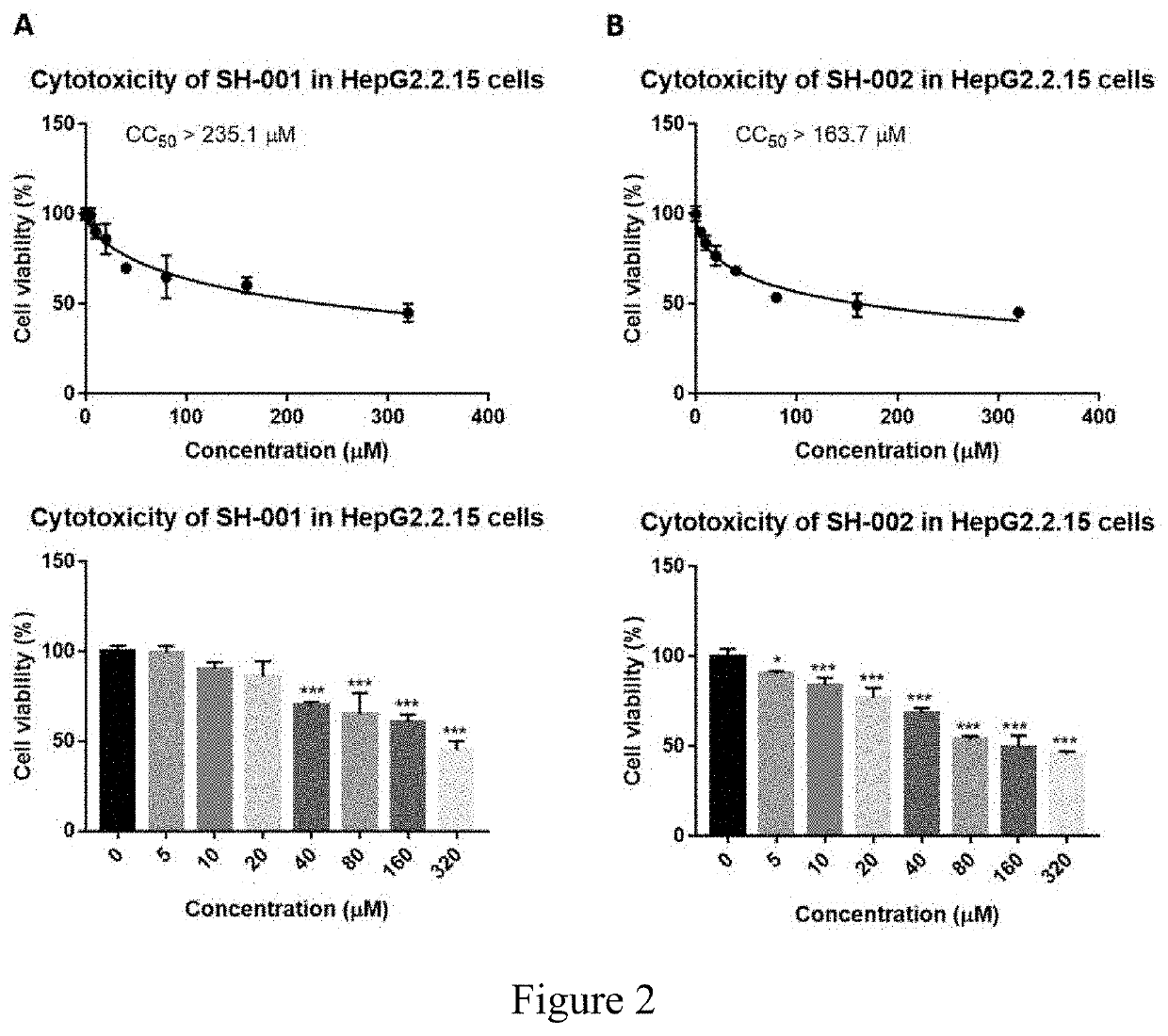
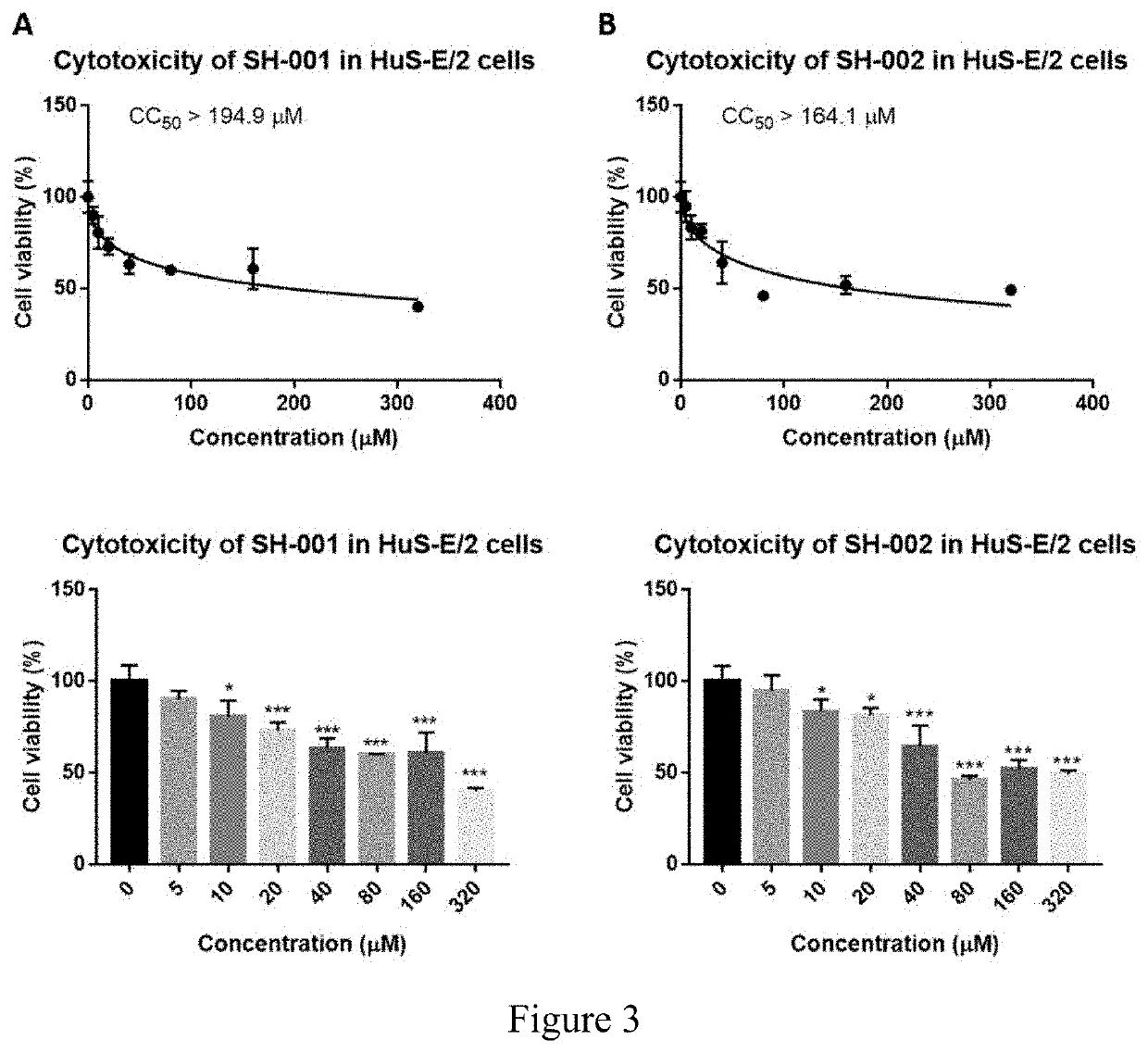
[0196]The compounds used were SH-001, SH-002, and SH-003. Before testing their potential antiviral effect on HBV and HDV infection, we first examined their toxicity on VeroE6 cells, HepG2.2.15 cells and HuS-E / 2 immortalized human primary hepatocytes cells at concentration from 0 to 320 μM as indicated. Our results showed the CC50>204.7 μM for SH-001, CC50>61.3 μM for SH-002, and CC50>204.7 μM for SH-003 in VeroE6 cells (FIG. 1). In HepG2.2.15 cells, the CC50>194.9 μM for SH-001 and the CC50>164.1 μM for SH-002 (FIG. 2). In HuS-E / 2 cells, The CC50>194.9 μM for SH-001 and the CC50>164.1 μM for SH-002 (FIG. 3).
experiment 2
ry Effect of SH-001 and SH-002 on HBV Replication in HepG2.2.15 Cells
[0197]To test the effect of the compounds on HBV replication, SH-001 and SH-002 were added to the cell culture medium at indicated concentrations and cultured for 48 h, and then the viruses are collected from supernatant. Q-PCR was performed to detect HBV DNA as an efficiency index of HBV replication. Moreover, the HBV HBsAg and HBeAg were examined by ELISA assay. The results from ELISA assays showed that levels of HBsAg (FIGS. 4A and 5A) and HBeAg (FIGS. 4B and 5B) in the culture supernatant, which reflects the quantity of secreted HBV particles, was significantly decreased in the presence of SH-001 and SH-002. In addition, as shown in FIGS. 4C and 5C, HBV DNA was also repressed in the treatment of SH-001 and SH-002 in a dose-dependent manner. Taken together, the results showed that both SH-001 and SH-002 suppress HBV replication in HepG2.2.15 cells.
[0198]After treated HepG2.2.15 cells with 10 μM SH-001 and 10 μM ...
experiment 3
ry Effect of SH-001 and SH-002 on HDV Replication in HuS-E / 2 Cells
[0199]To investigate the effect of the compounds on HDV infection, SH-001 and SH-002 were added to the medium at indicated concentrations during HDV infection in HuS-E / 2 cells for 18 h, respectively. The infected cells were then washed and incubated in medium containing the tested compounds for further 48 h, and real-time PCR was used to detect HDV mRNA as an efficiency index of HDV infection. The results showed that SH-001 and SH-002 significantly inhibited HDV replication in HuS-E / 2 human hepatocytes.
[0200]Using 2.5 and 5 μM SH-001, HDV RNA levels were reduced to 28.8±22.8% and 8.7±1.3%, respectively, compared to in its absence (FIG. 6A) and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was estimated to be approximately 0.1457 μM. Using 0.1 and 0.2 μM SH-002, HDV RNA levels were reduced to 53.1±16.8% and 40.8±18.6%, respectively, compared to in its absence, and the IC50 was estimated to be approximately 0.069 μM,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com