Laminar-flow airfoil
a laminar-flow airfoil and trailing edge technology, applied in the direction of all-wing aircraft, wing shapes, drag reduction, etc., can solve the problems of large head-lowering pitching moment, drag-divergence phenomenon, difficulty in ensuring mileage, etc., to reduce undesirable head-lowering pitching moment and reduce drag on laminar-flow airfoils.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025]The present invention will now be described by way of a preferred embodiment with reference to the accompanying drawings.
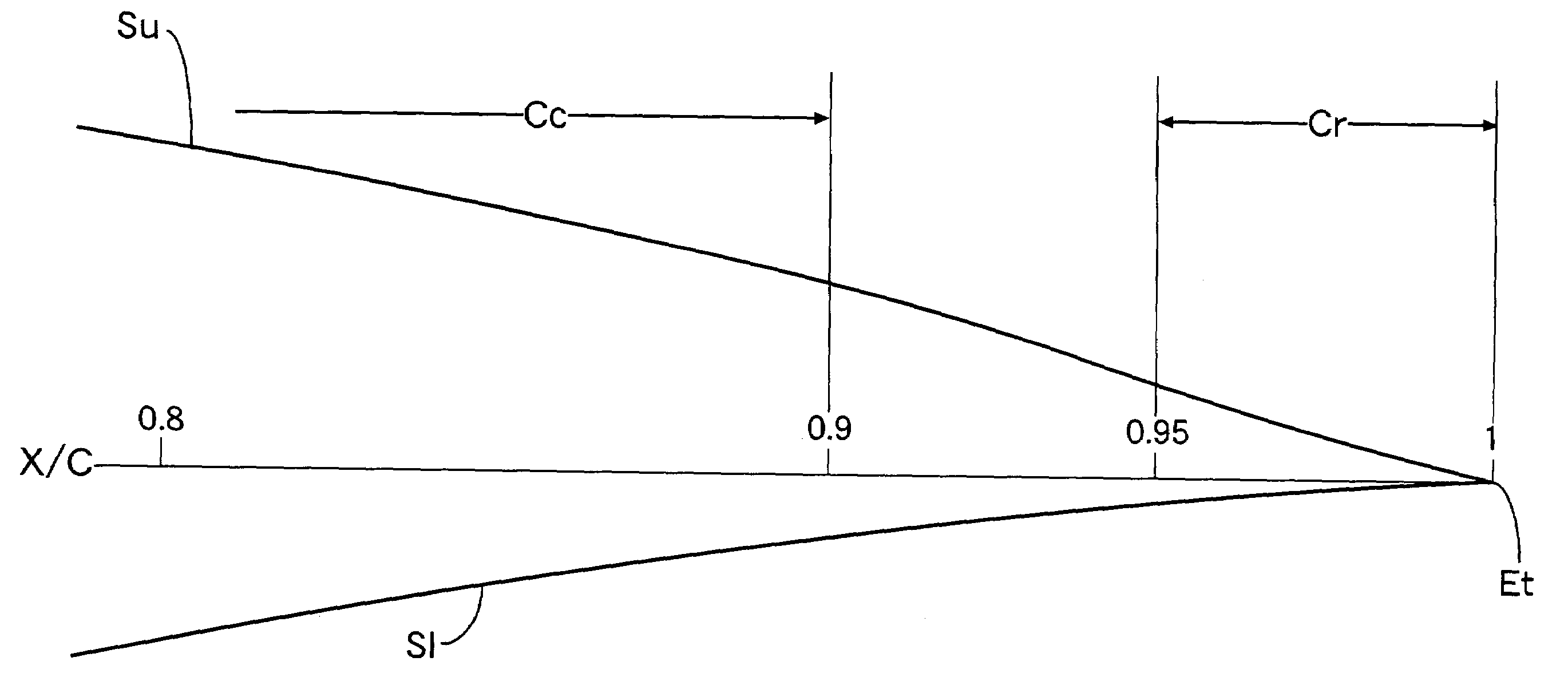
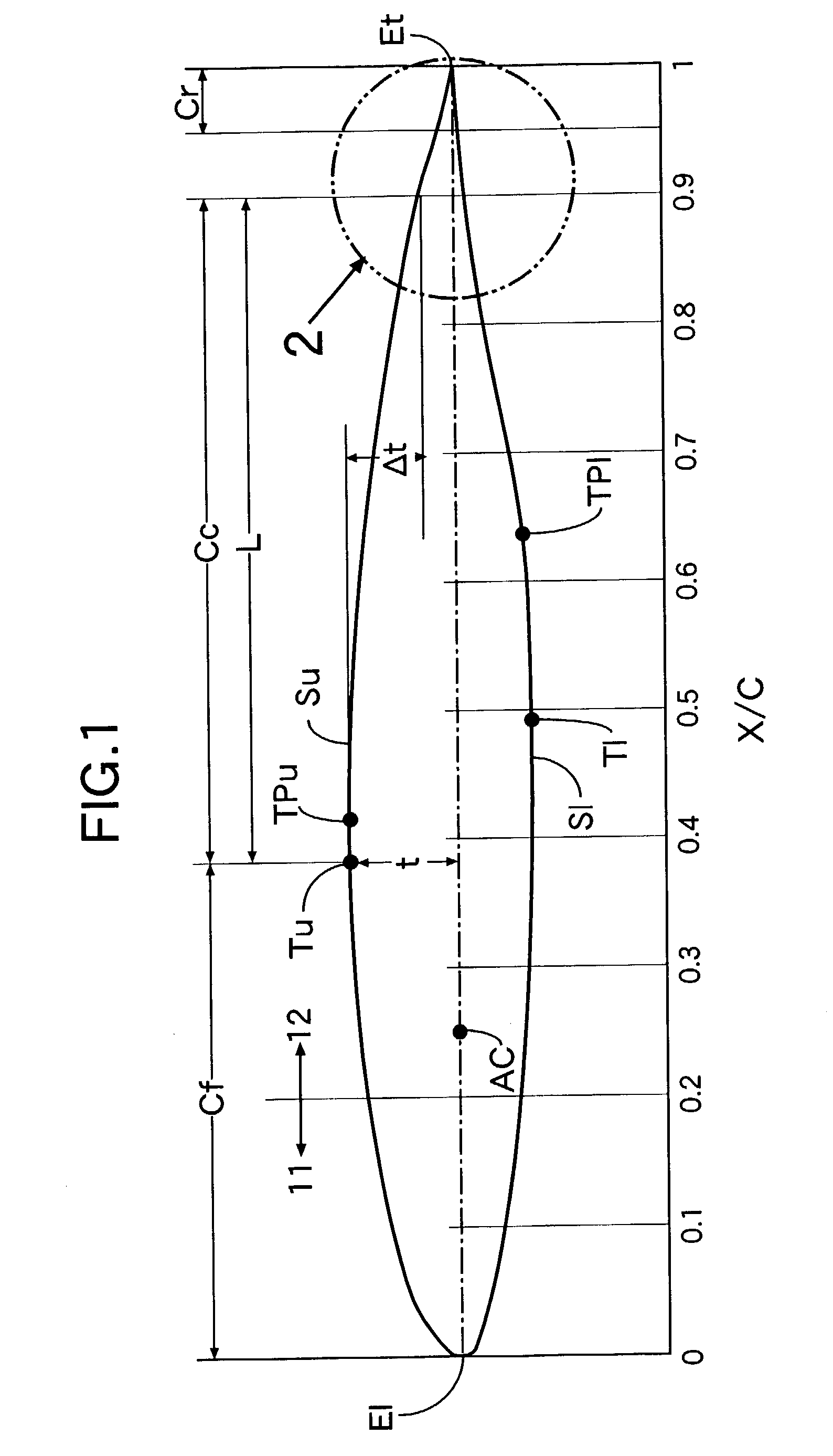
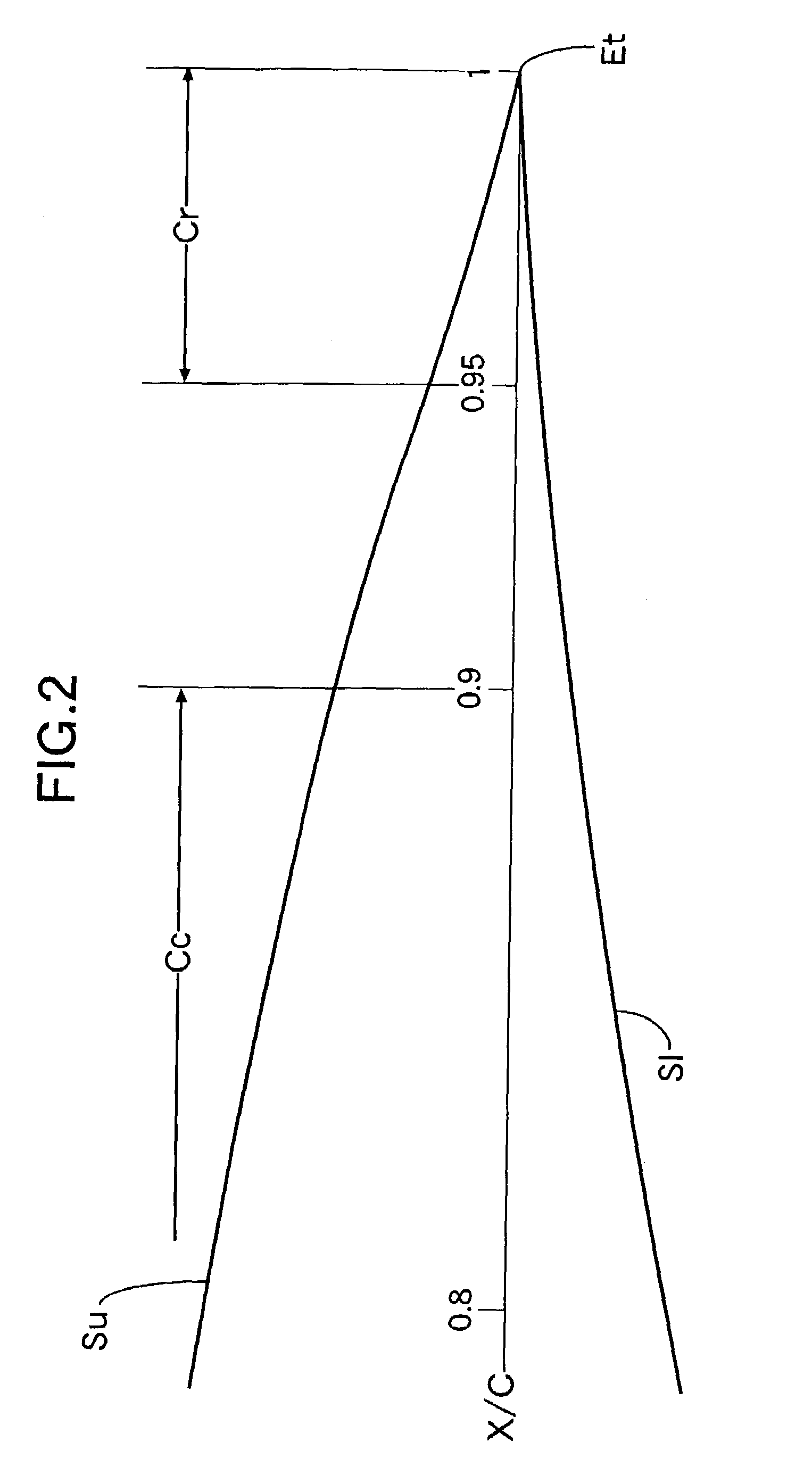
[0026]Referring first to FIG. 1, the profile of a laminar-flow airfoil according to the present embodiment is comprised of an upper wing surface Su, a lower wing surface S1, a leading edge E1 and a trailing edge Et. A largest-thickness position Tu on the upper wing surface SU measured from a cord line lies at a point corresponding to 38% of a wing chord length C in the present embodiment, to form a laminar-flow boundary layer region. A transition point TPu, at which the laminar-flow boundary layer region changes to a turbulent-flow boundary layer region, exists in the vicinity of the largest thickness position Tu. The transition point TPu lies near a position corresponding to 42% of the wing chord length C. A largest-thickness position T1 on the lower wing surface S1 measured from the cord line lies at a point corresponding to 49% of the wing chord length C ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com