Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method
a magnetic resonance imaging and apparatus technology, applied in the direction of instruments, magnetic measurements, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of large changes in the position of the target section, the length of the required imaging time, and the inability to utilize all the collected data for reconstruction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031]An embodiment will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
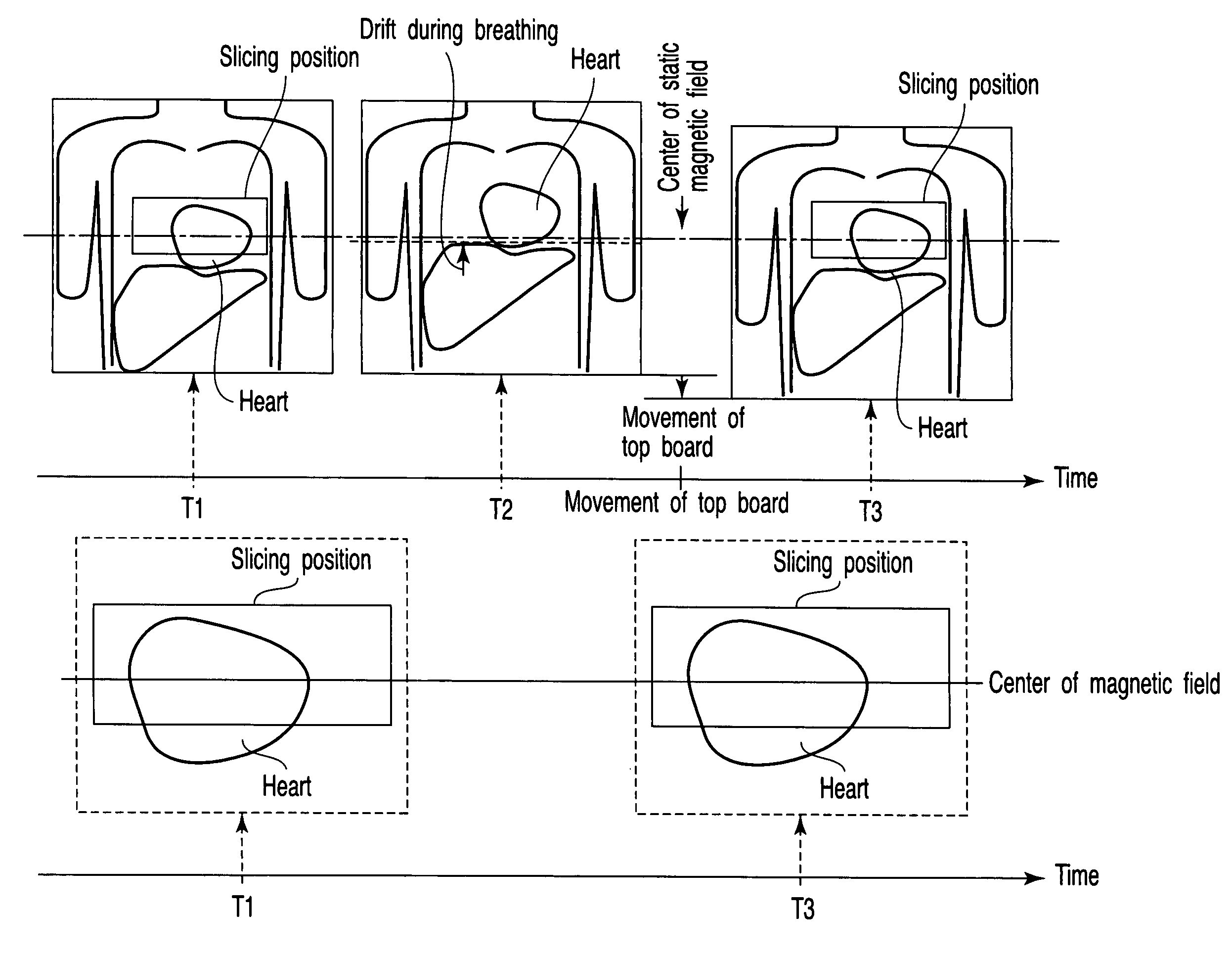
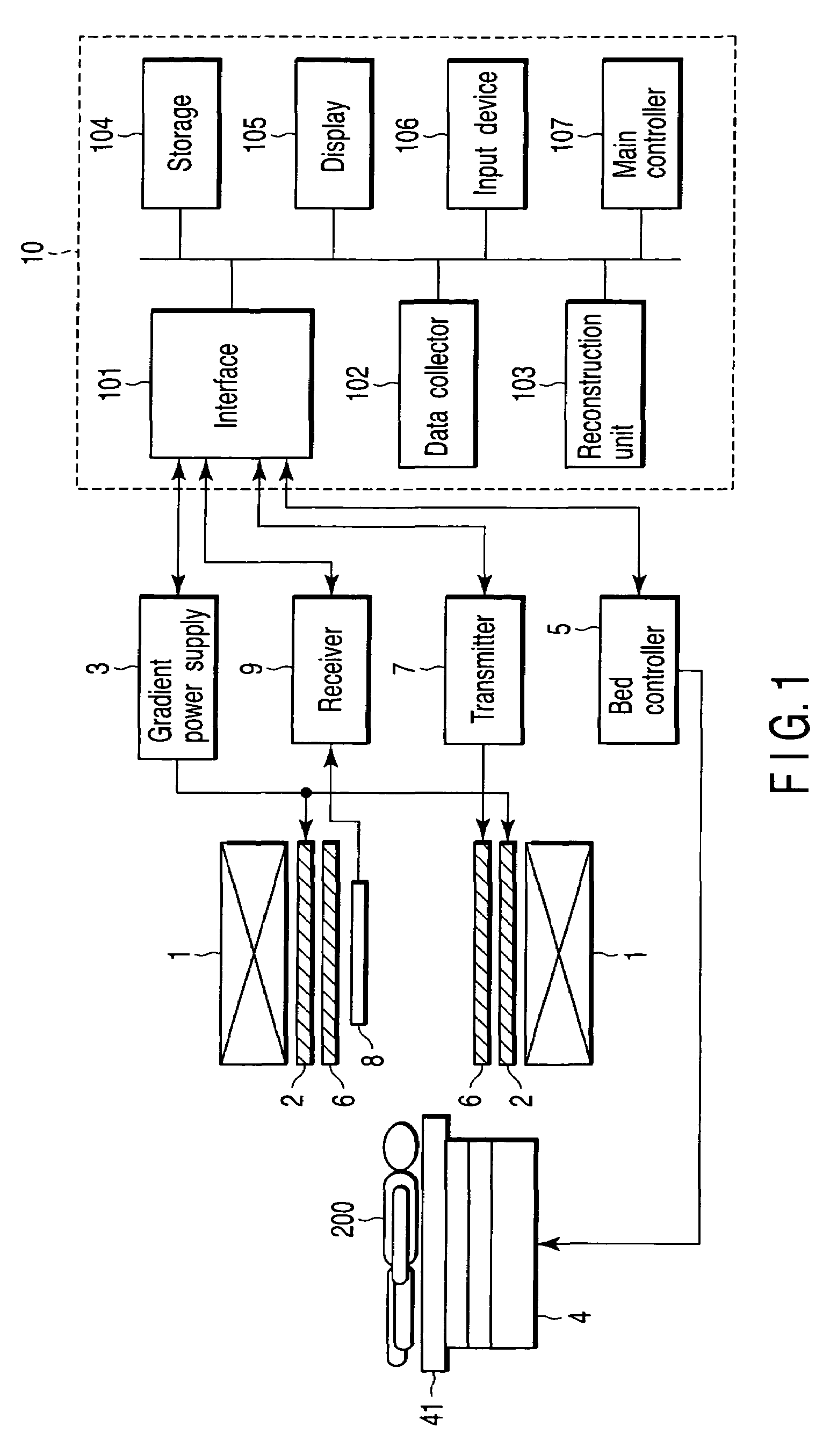
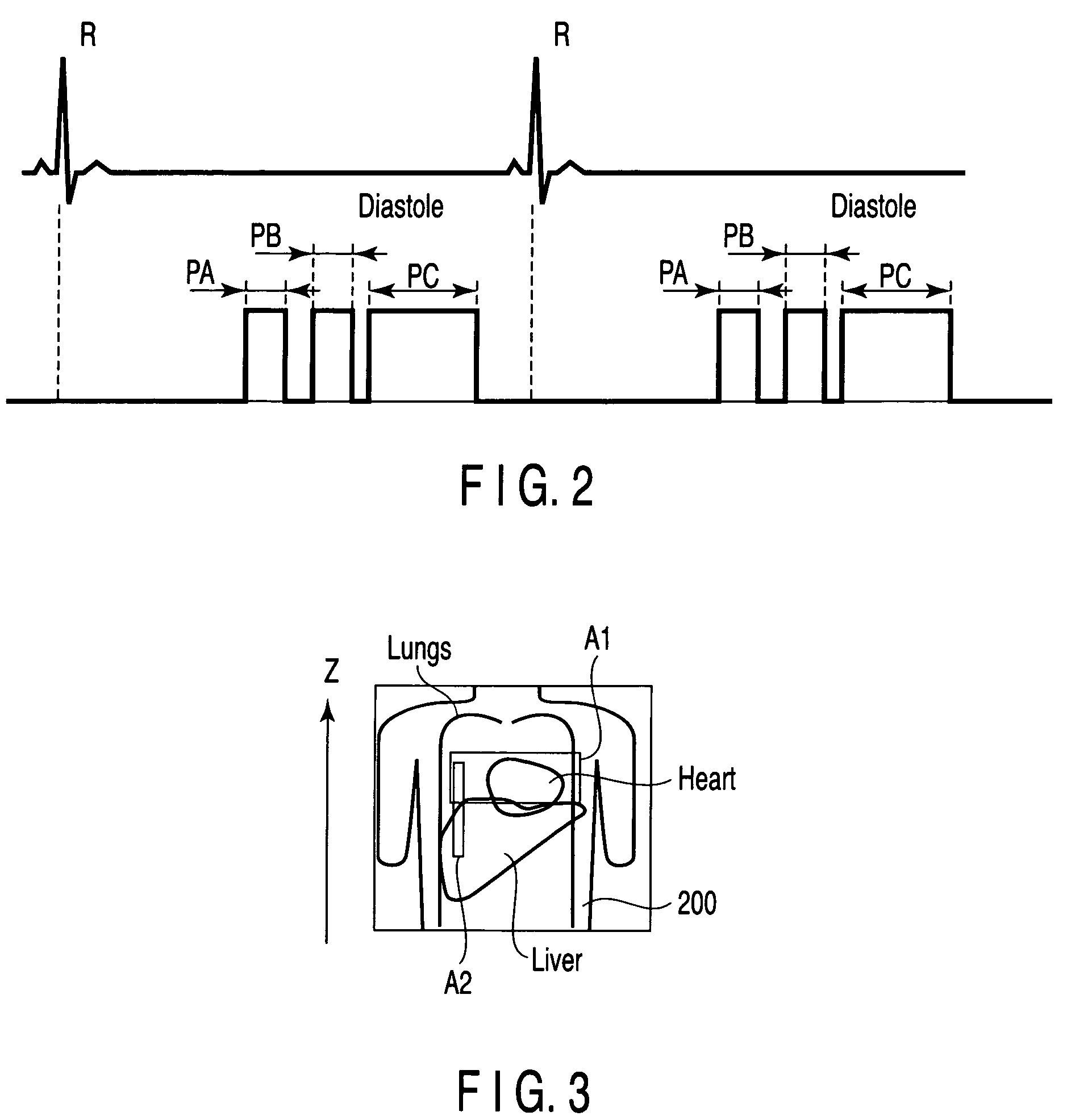
[0032]FIG. 1 shows an MRI apparatus according to the embodiment. As shown, the MRI apparatus comprises a static field magnet 1, gradient coil 2, gradient power supply 3, bed 4, bed controller 5, transmission RF coil 6, transmitter 7, receiving RF coil 8, receiver 9 and computer system 10.
[0033]The static field magnet 1 is a hollow cylinder and generates a uniform static magnetic field in its internal space. The static field magnet 1 is formed of, for example, a permanent magnet or superconductive magnet.
[0034]The gradient coil 2 is also a hollow cylinder and is provided inside the static field magnet 1. The gradient coil 2 is formed of three coils perpendicular to each other and corresponding to the X-, Y- and Z-axes. In the gradient coil 2, the three coils are supplied with a current from the gradient power supply 3 to generate gradient magnetic fields having their respective magnetic field intensitie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com