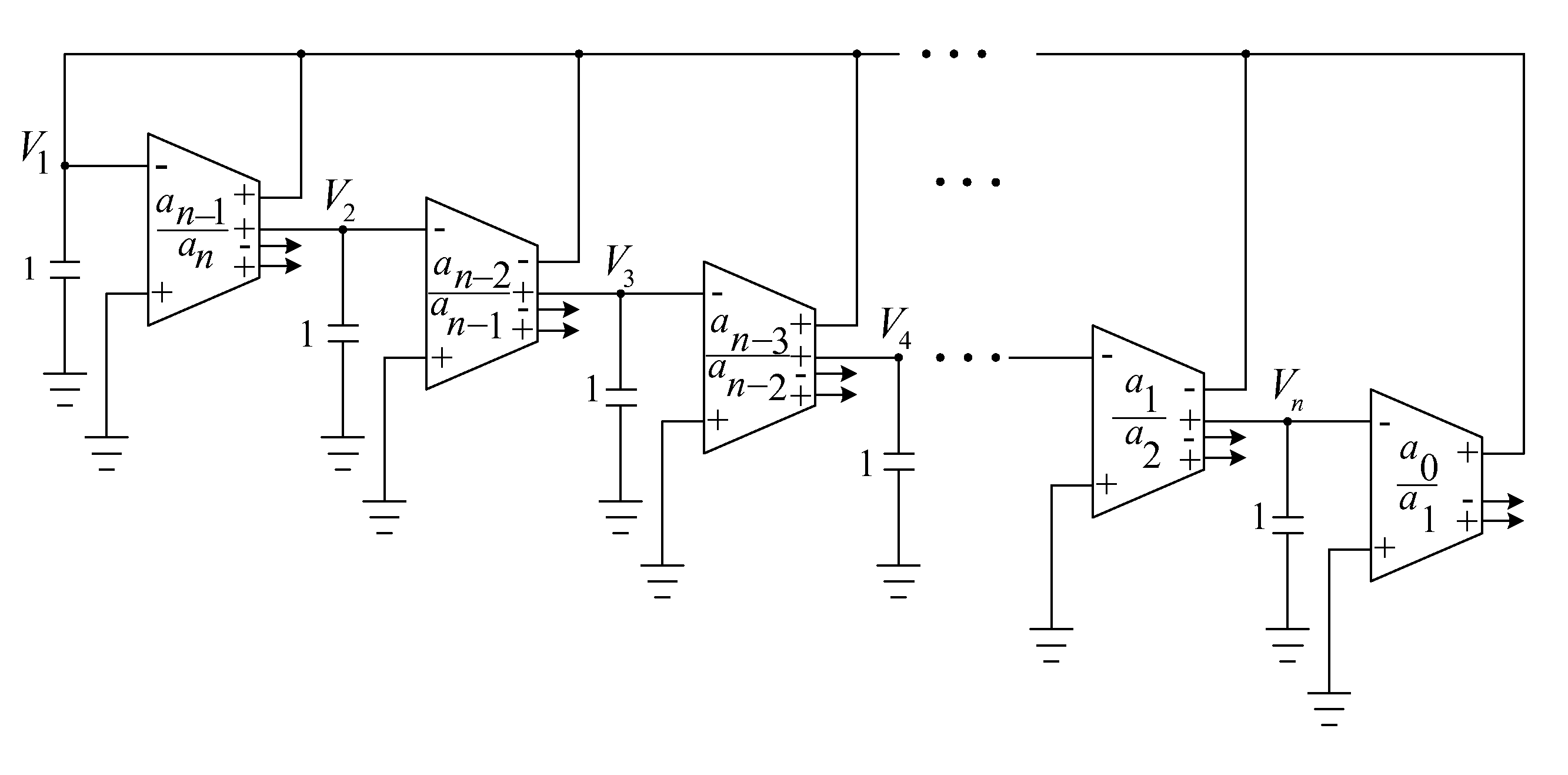
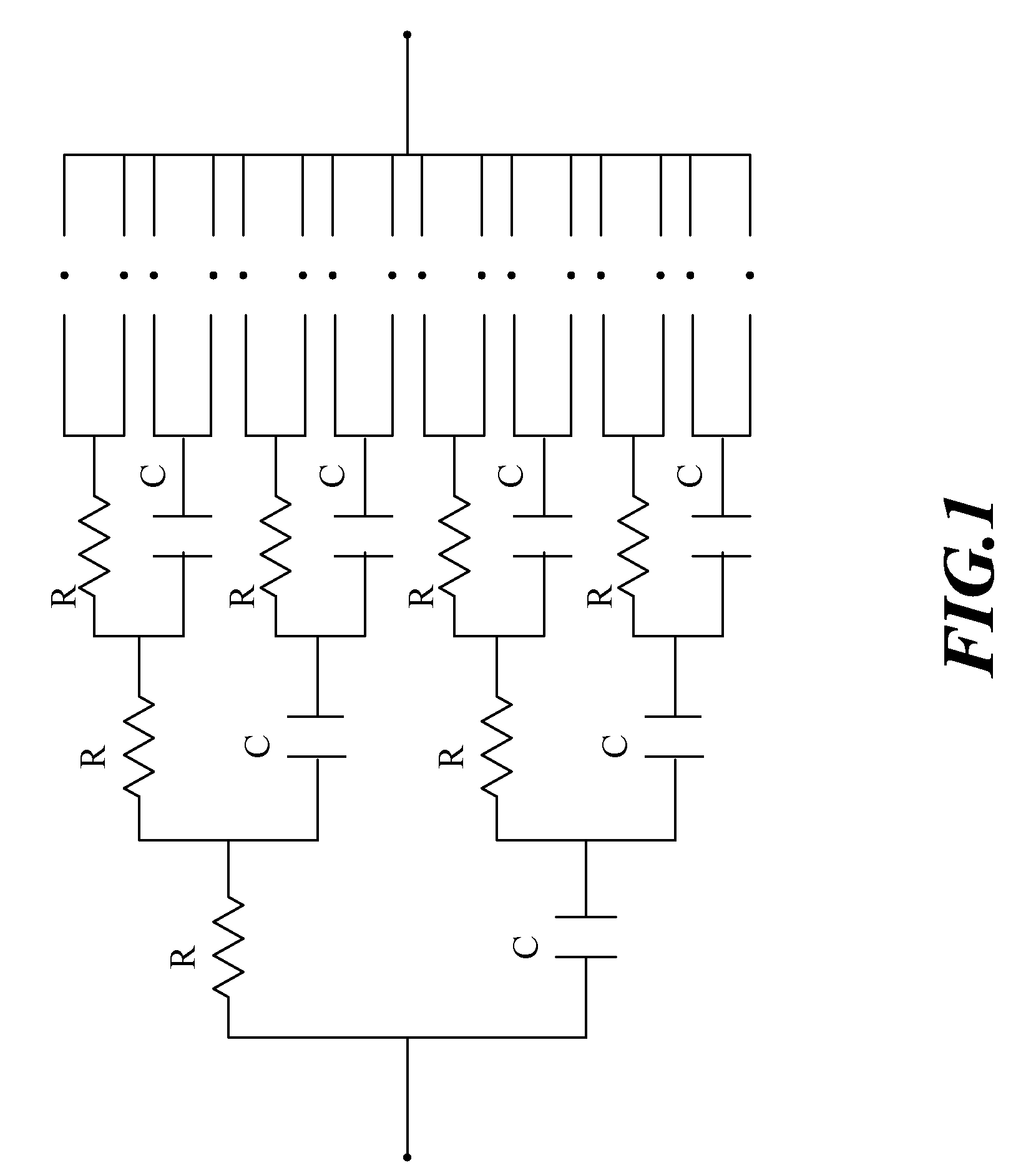
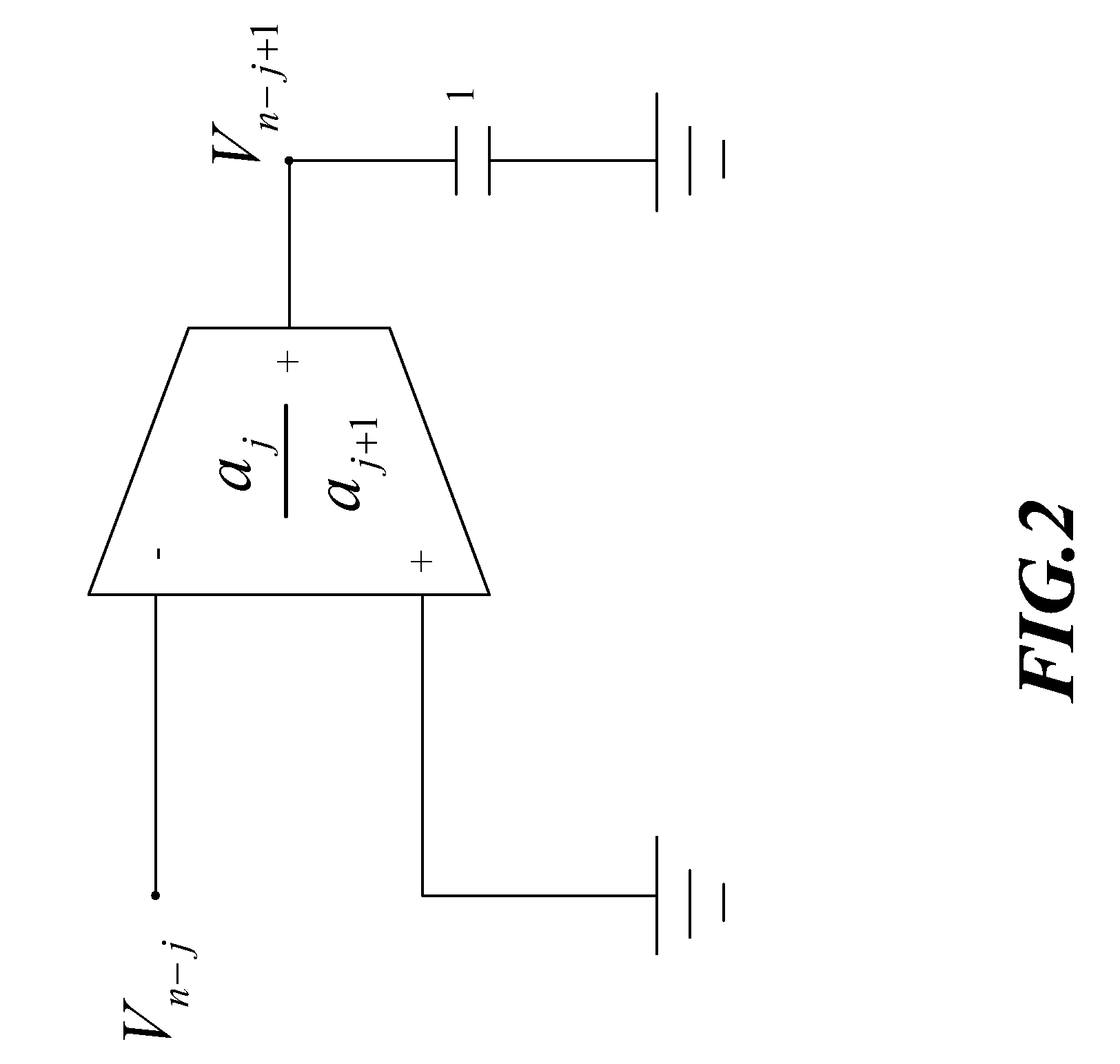
Nth-order arbitrary-phase-shift sinusoidal oscillator structure and analytical synthesis method of making the same
a sinusoidal oscillator and phase shift technology, applied in the direction of oscillator generators, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems that none of the analytical synthesis methods have been applied to the design of oscillator structures, and achieve the effects of reducing total parasitics, power consumption, chip areas, and nois
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
case ii (
Third-Order One with Two 120° Phase Shifts):
[0220]Let the W / L be (i) 5μ / 0.5μ and 5μ / 0.5μ, (ii) 20μ / 0.5μ and 20μ / 0.5μ, (iii) 20μ / 0.5μ and 20μ / 0.5μ, (iv) 5μ / 2.5μ and 10μ / 2.5μ, and (v) 5μ / 2.5μ and 10μ / 2.5μ, for NMOS and PMOS transistors, respectively, in the (i) OTA1, (ii) OTA2, (iii) OTA3, (iv) OTA4, and (v) OTA5. The component values are given by C1=20 pF, C2=10 pF, C3=10 pF, and g1=24.184 μS (Ib=2.042 μA), g2=g3=145.039 μS (Ib=12.638 μA), g4=g5=36.276 μS (Ib=5.465 μA). The oscillation waveforms of the node voltages, V1, V2, and V3, are shown in FIG. 34, whose frequency spectrums are shown in FIG. 35. The THDs of V1, V2, and V3, are 0.6119%, 1.8691%, and 0.7293%, respectively. The phase of V1 lags behind V2 by 121.141° with error 0.951% and the phase of V2 lags behind V3 by 121.378° with error 1.148%. The simulation frequency is 938.262 kHz with error 6.174% compared to the theoretical 1 MHz.
Case III (Third-Order One with Two 60° Phase Shifts):
[0221]We give the W / L=(i) 5μ / 1μ and 10μ / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com