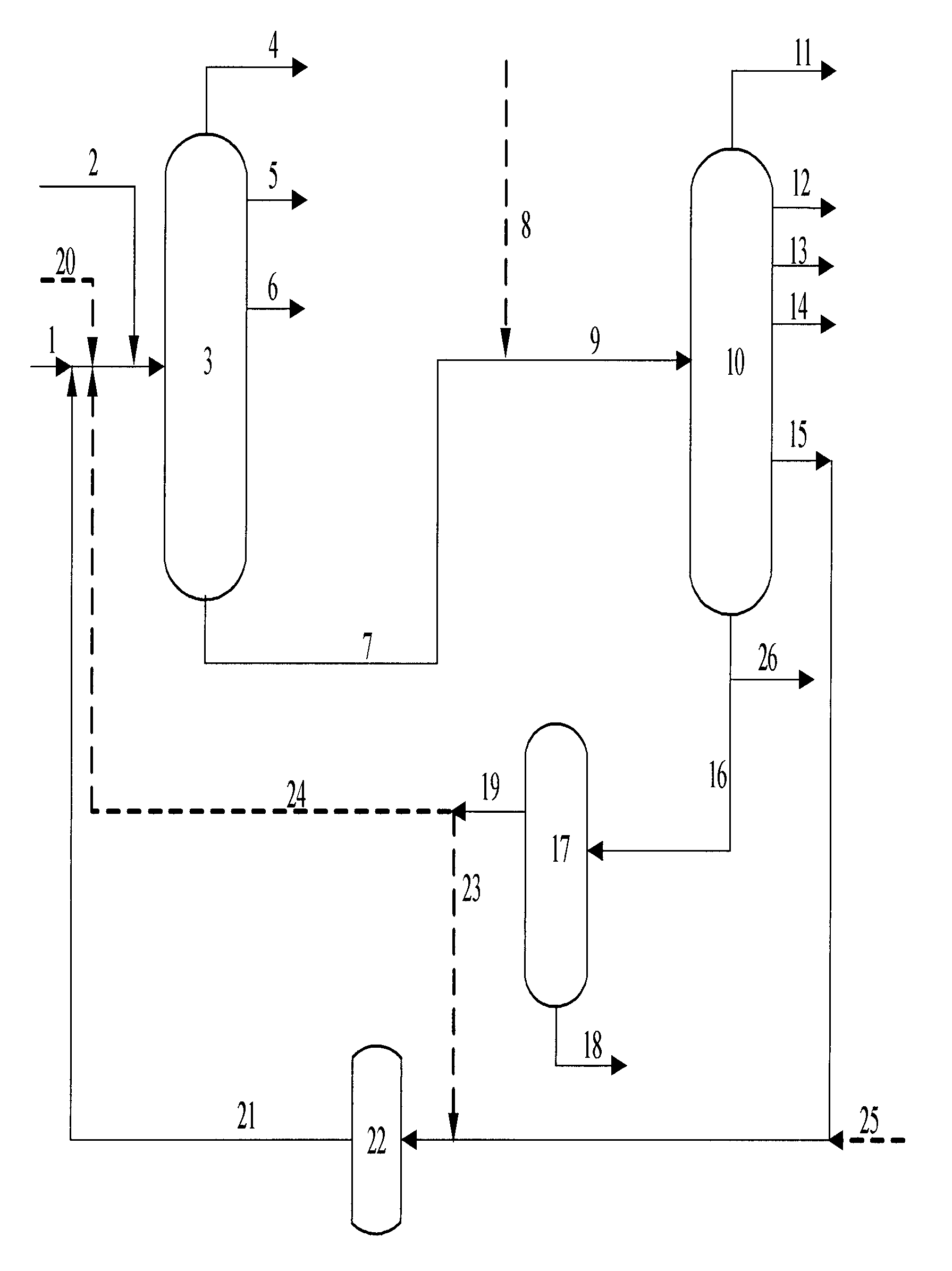
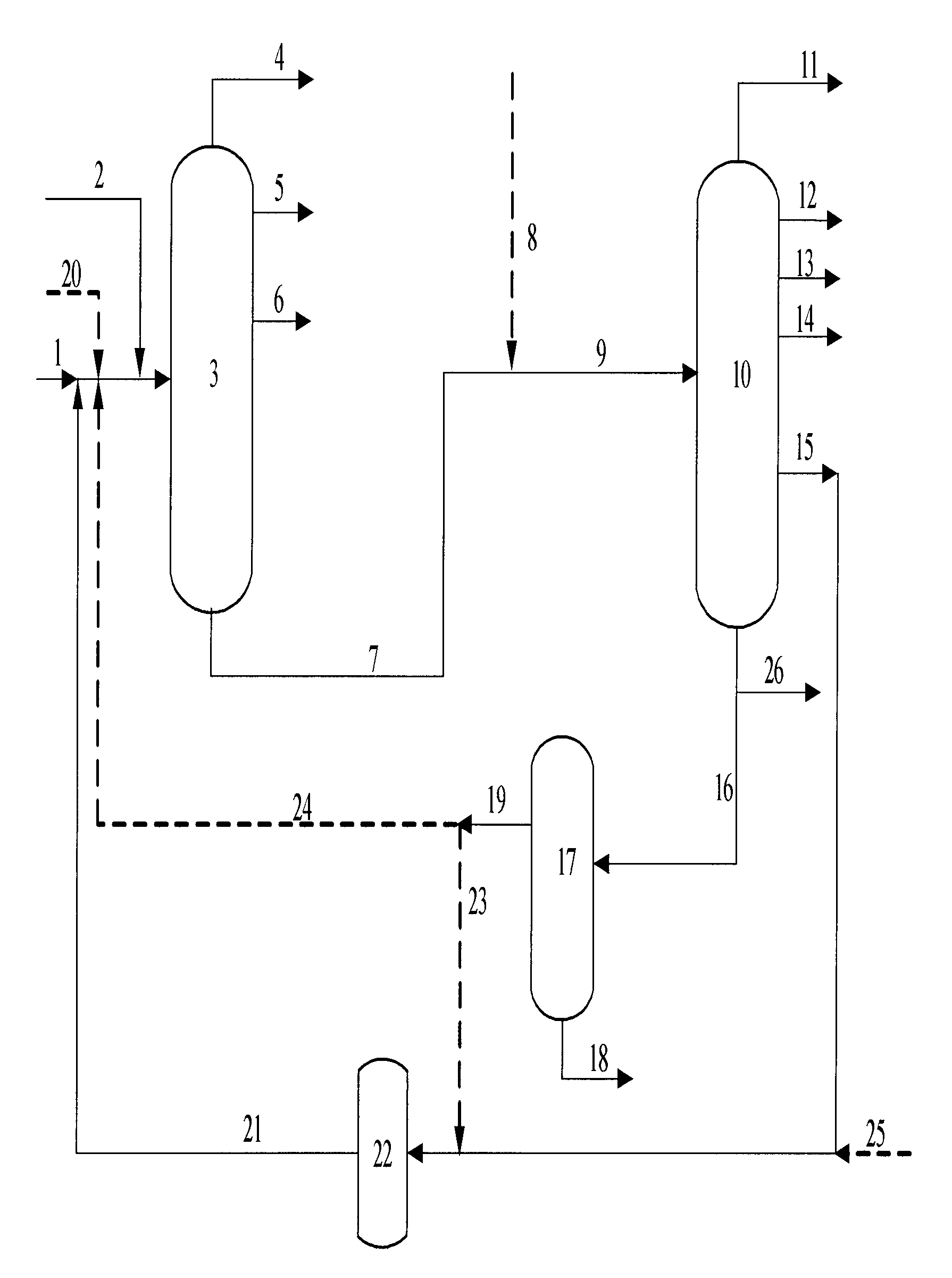
Combined process for hydrotreating and catalytic cracking of residue
a residue hydrotreating and catalytic cracking technology, applied in the direction of hydrocarbon oil cracking process, thermal non-catalytic cracking, effluent separation, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the requirement for light oils, decreasing down, and increasing the weight of crude oils, so as to reduce the reaction efficiency of residue hydrotreating and avoid disadvantages. factors, the effect of shortening the operation cycle of residue hydrotreating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0064]Feedstock oil B was finely filtered (at a filtration temperature of 230° C.) to decrease the content of acidic solid impurity from 83 ppm before the filtration to 7 ppm and the particle size from 14 micrometer to 1.5 micrometer. A mixture of feedstock oil A and feedstock oil B from which acidic solid impurity has been removed was used as feedstock oil C with the main properties being shown in Table 1, wherein feedstock oil B from which acidic solid impurity has been removed accounted for 9.1% by weight of the feedstock oil of the residue hydrotreating unit. The feedstock oil C was used as a feedstock of residue hydrotreating unit, and contacted with hydrogenation catalysts to carry out hydrotreating reaction after being mixed with hydrogen. The reaction products were separated to obtain gas, hydrogenated naphtha, hydrogenated diesel oil and hydrogenated tail oil. The hydrogenated tail oil obtained as a catalytic cracking feedstock was fed into the catalytic cracking unit to ca...
example 2
[0071]A catalytic cracking slurry oil was vacuum flashed, and <470° C. distillate obtained from the top of flash tower was used as feedstock oil S. Feedstock oil S and feedstock oil B were combined together, then fine filtered at a filtering temperature of 230° C., wherein the content of the acidic solid impurity was decreased from 123 ppm before filtering to 10 ppm, and the particle size was decreased from 16 micrometer to 2 micrometer. Feedstock oil D, feedstock oil B from which the acidic solid impurity has been removed and distillate S of the slurry oil from which the acidic solid impurity has been removed were mixed together as feedstock oil F with main properties being shown in Table 4, wherein feedstock oil B from which the acidic solid impurity has been removed accounted for 15.0% by weight of feedstock oil F of the residue hydrotreating unit, the distillate S of the slurry oil from which the acidic solid impurity has been removed accounted for 1.7% by weight of feedstock oi...
example 3
[0077]Catalyst used for the hydrogenating test in the present Example was the same as that used in hydrogenation test of Comparative Example 3. Feedstock oil B was processed by fine filtration at a filtering temperature of 230° C. and then contained 7 ppm of the catalytic cracking catalyst with a particle size of less than 1.5 micrometer. Hydrogenating feedstock oil was a mixed oil of finely filtered feedstock oil B and atmospheric residuum in a mass ratio of 25:75. Hydrogenating reaction was carried out under the same reaction conditions as that in Comparative Example 3: a hydrogen pressure of 13.0 MPa, a volume space velocity of 0.30 h−1, a hydrogen-to-oil ratio of 800 Nm3 / m3, a reaction temperature of 370° C. in the first 1000 hrs, 380° C. in the subsequent 2000 hrs, and 390° C. in the last 2000 hrs. After the test was carried out for 5000 hrs, the formation oil obtained in hydrogenating has properties shown in Table 7. Catalytic cracking test of the hydrogenated formation oil wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com