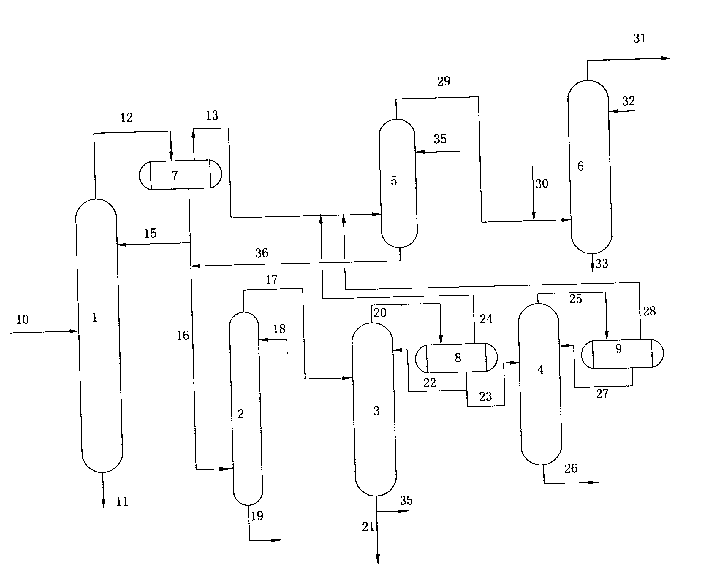Patents
Literature
213results about "Effluent separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
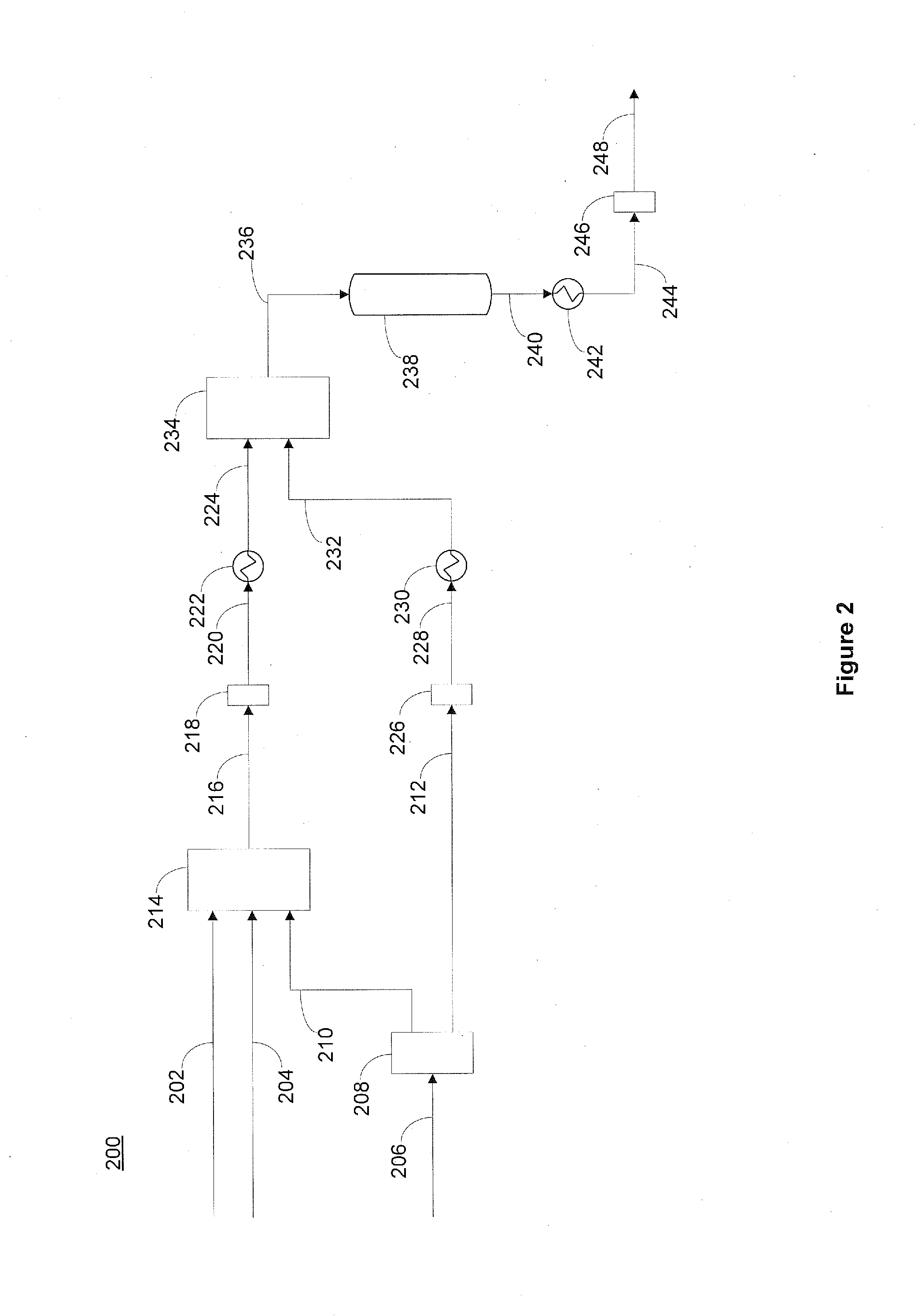
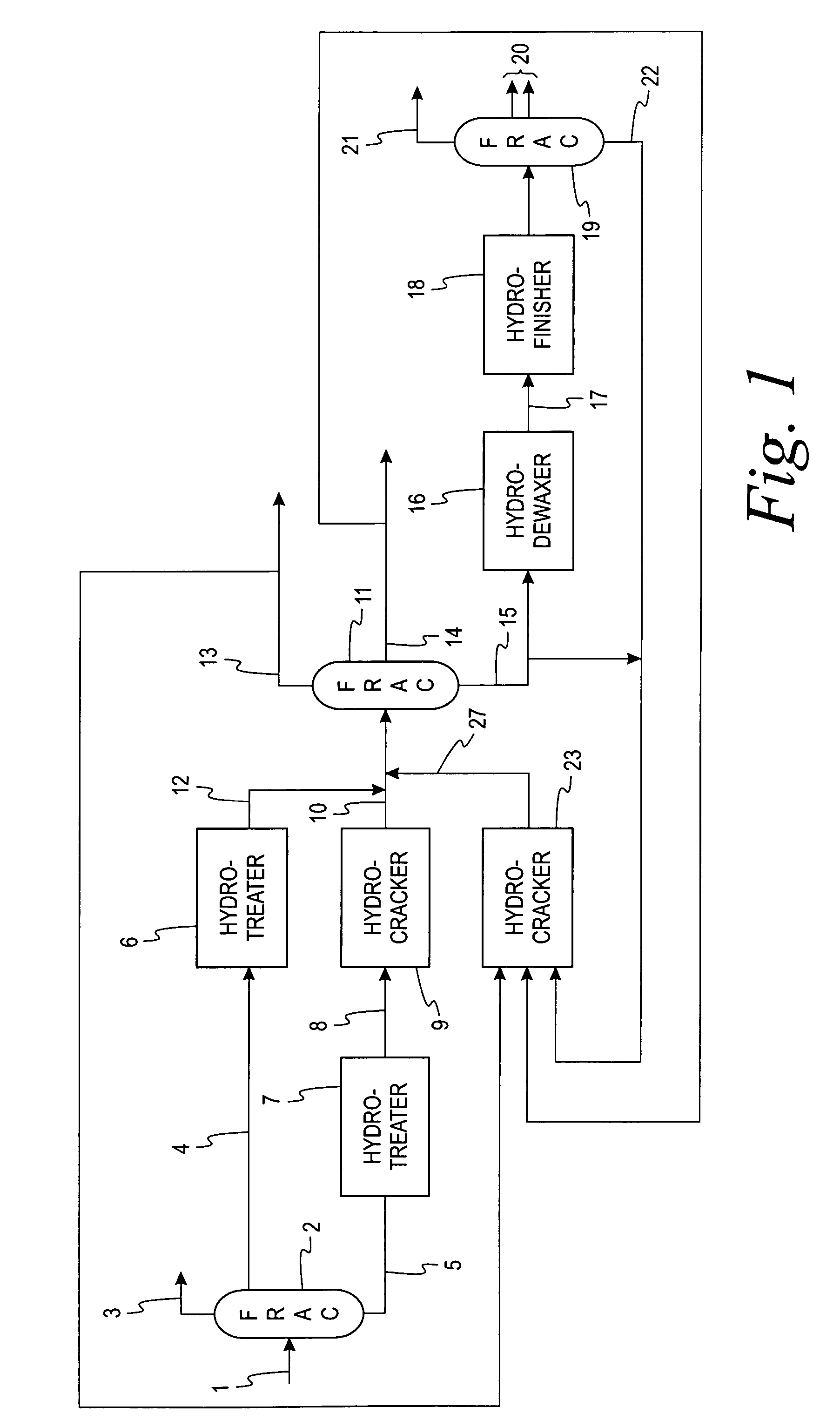
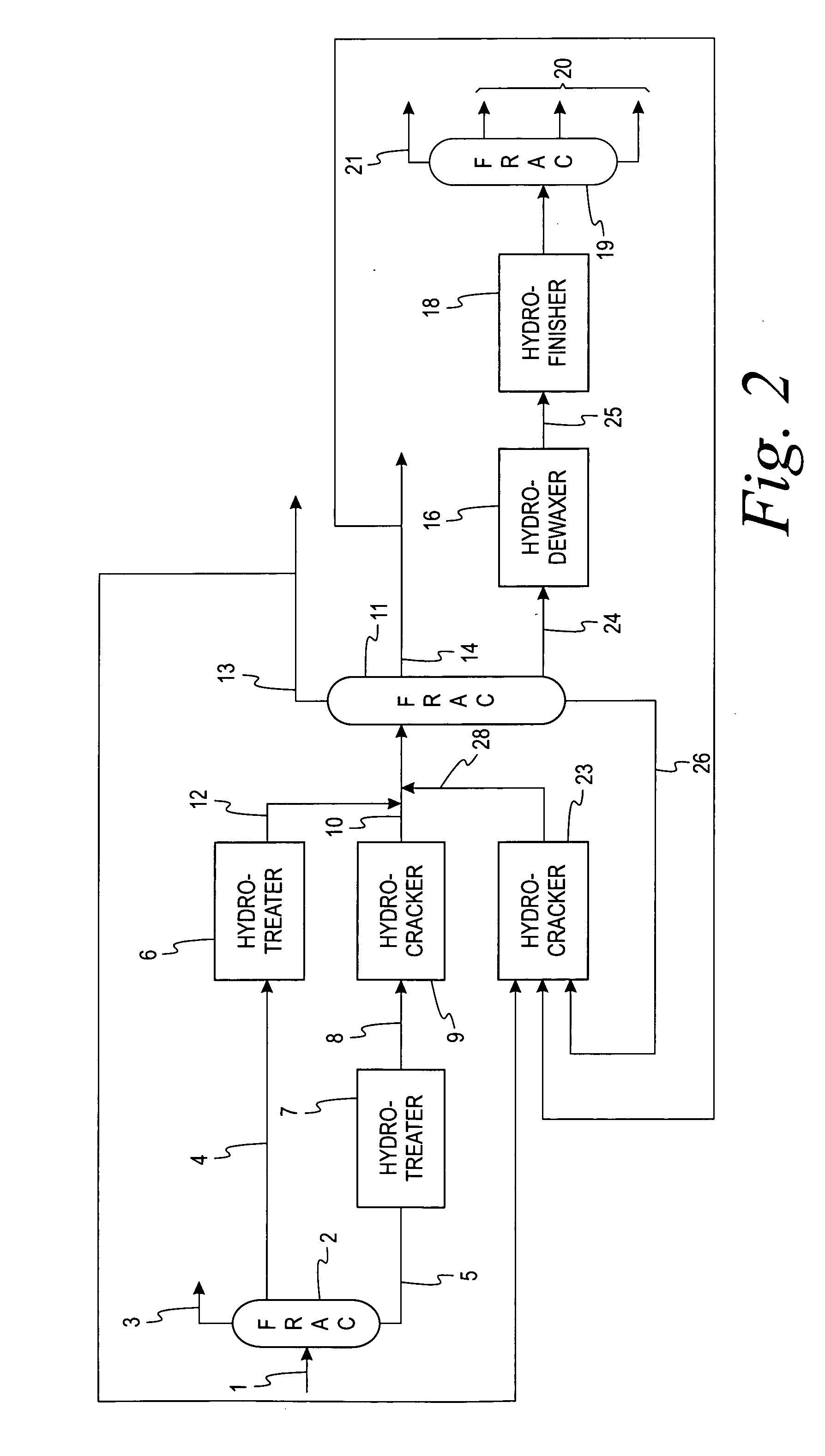
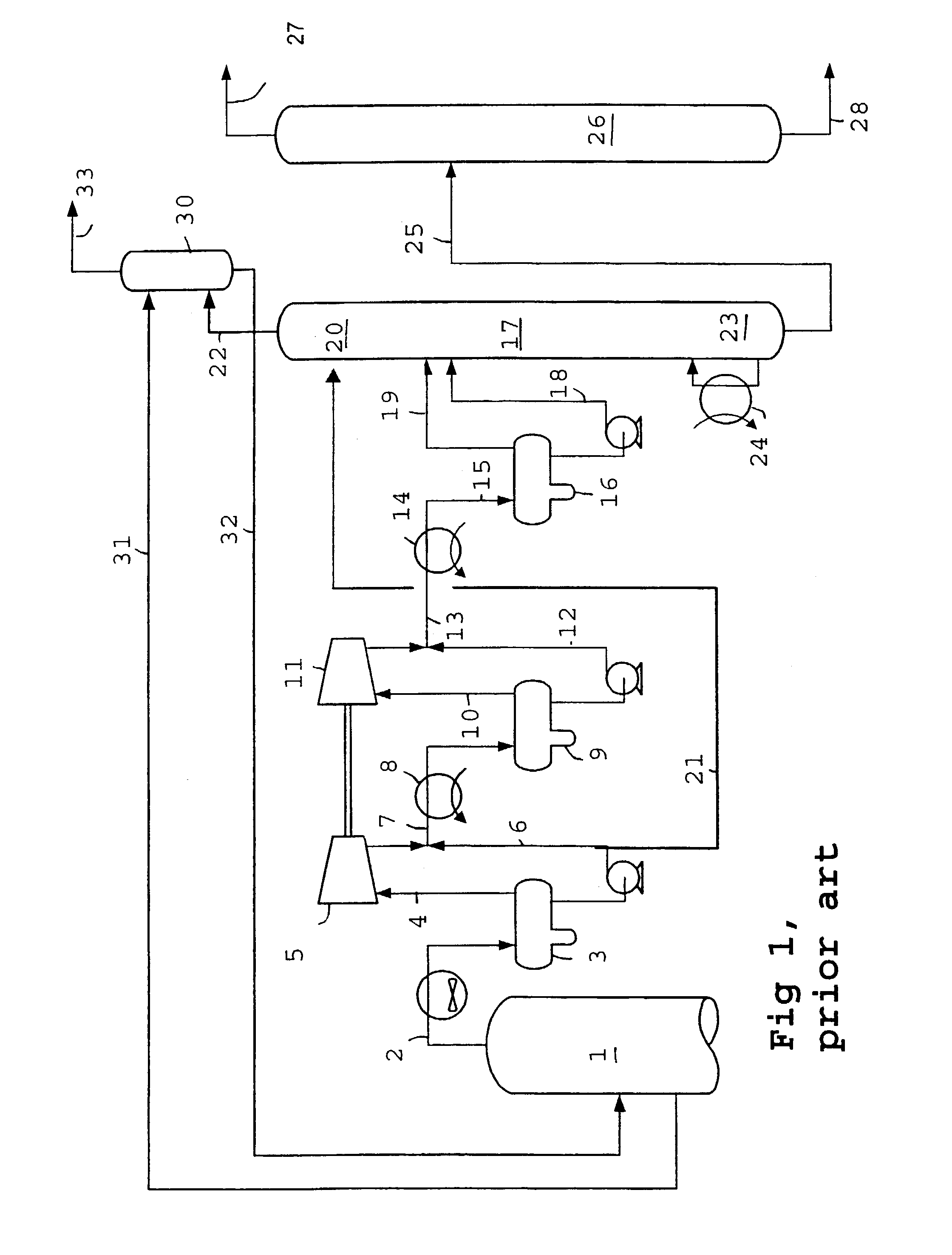
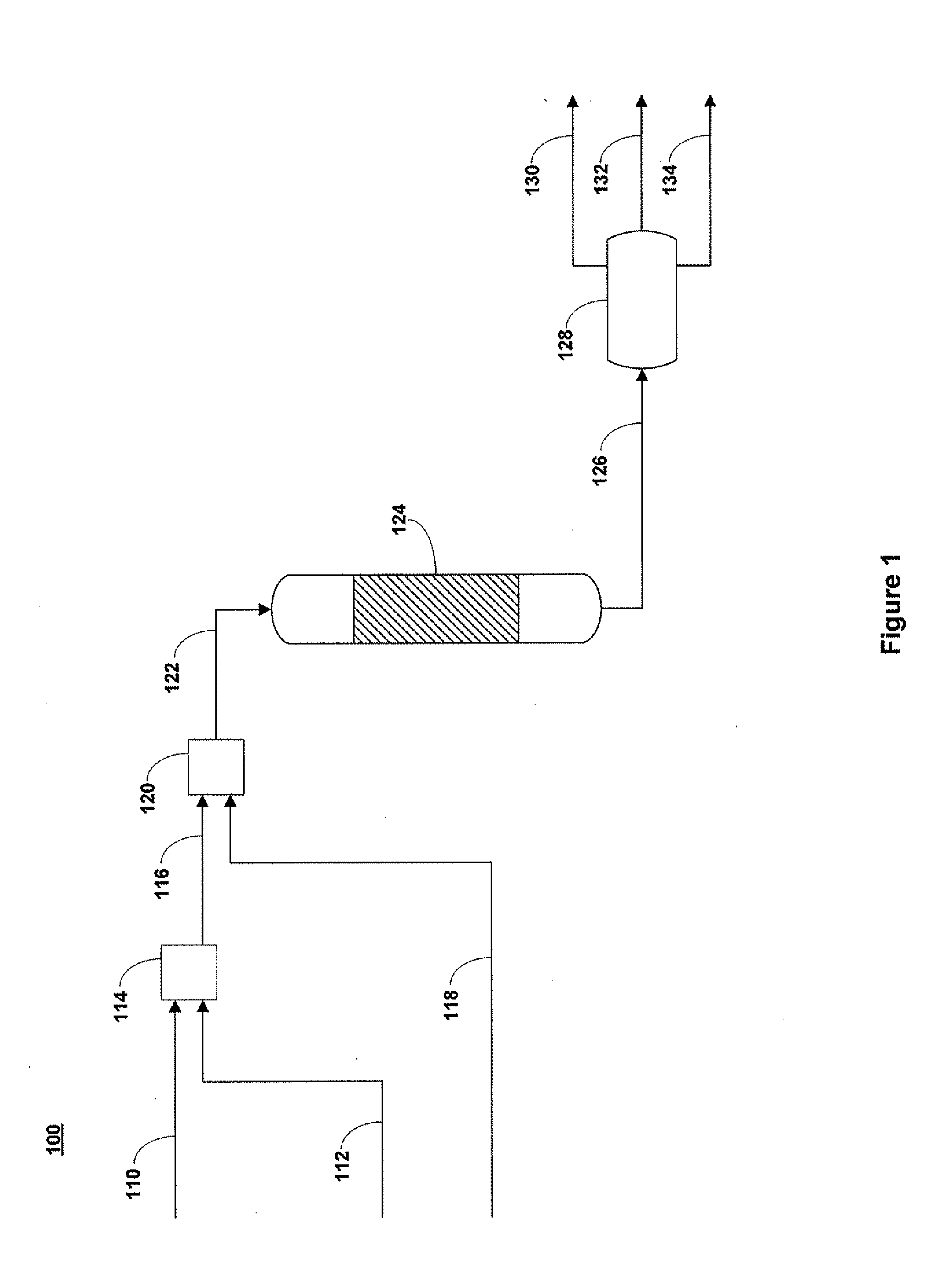
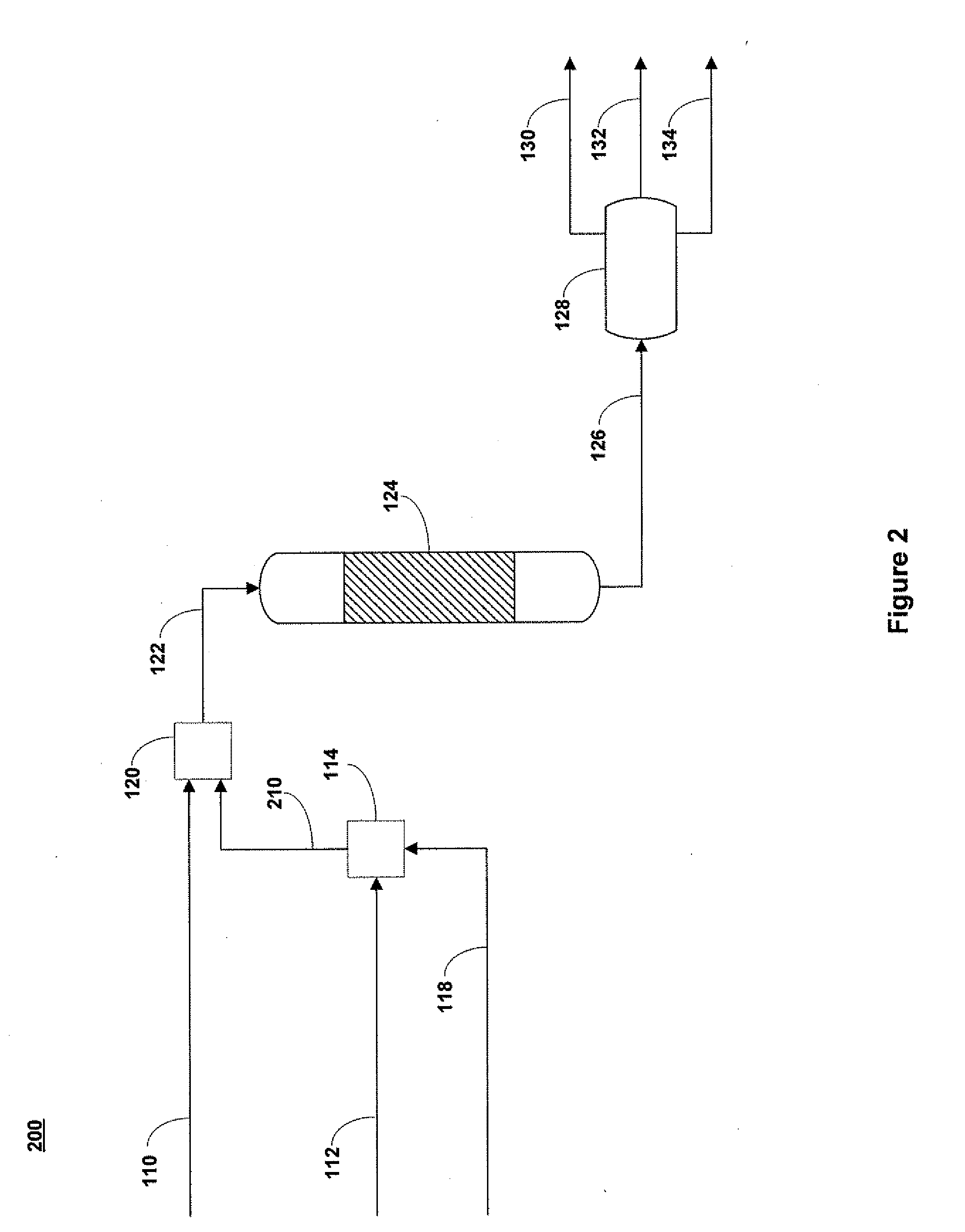
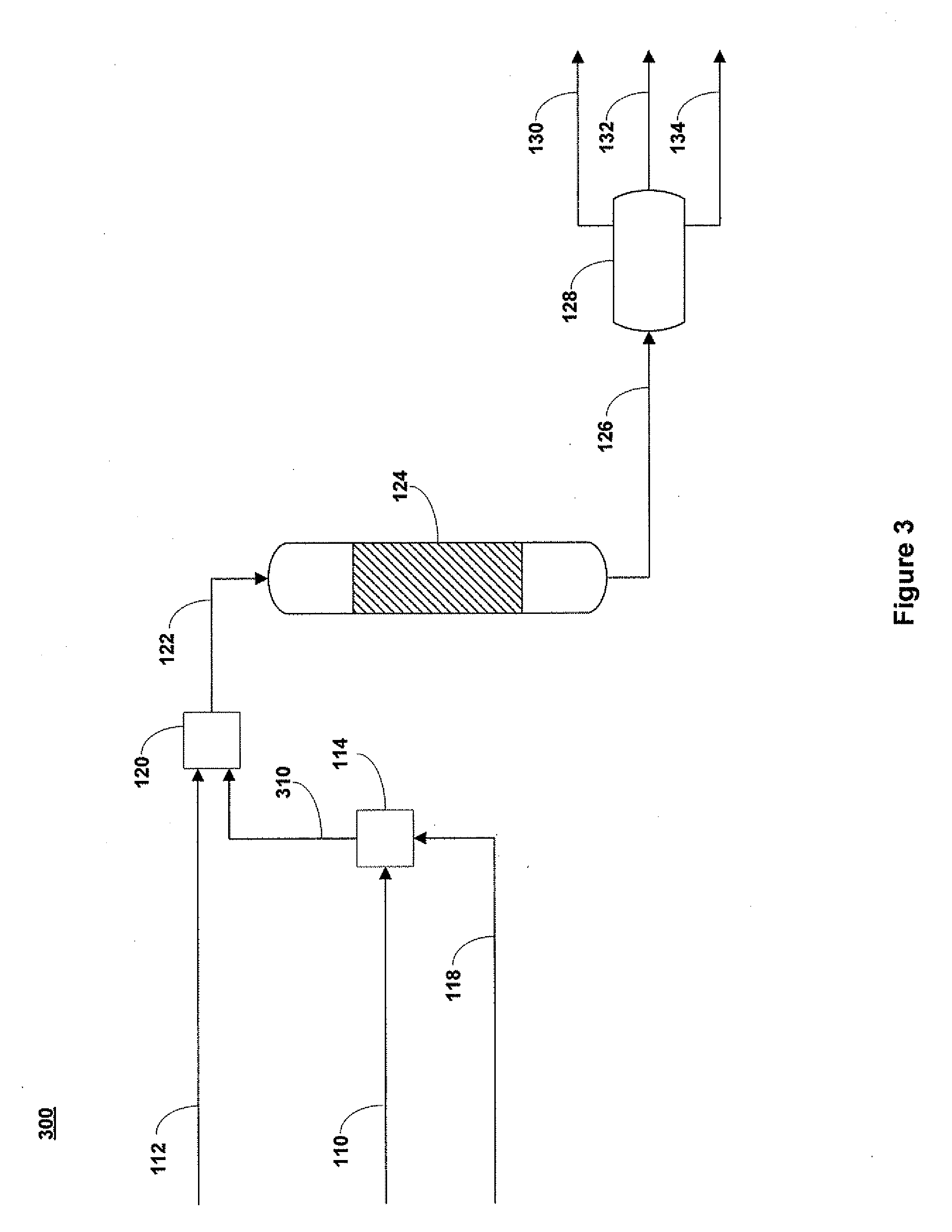
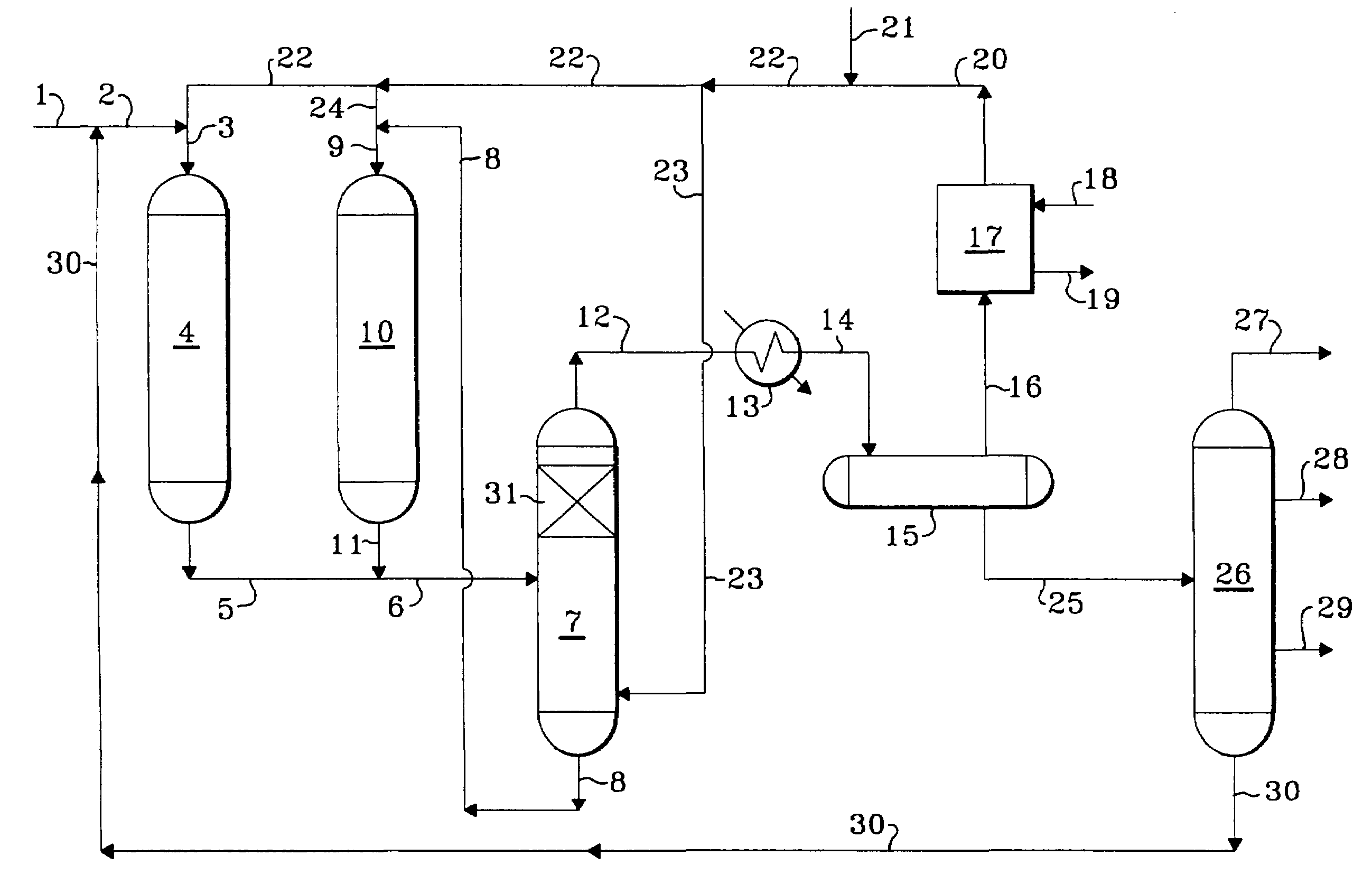
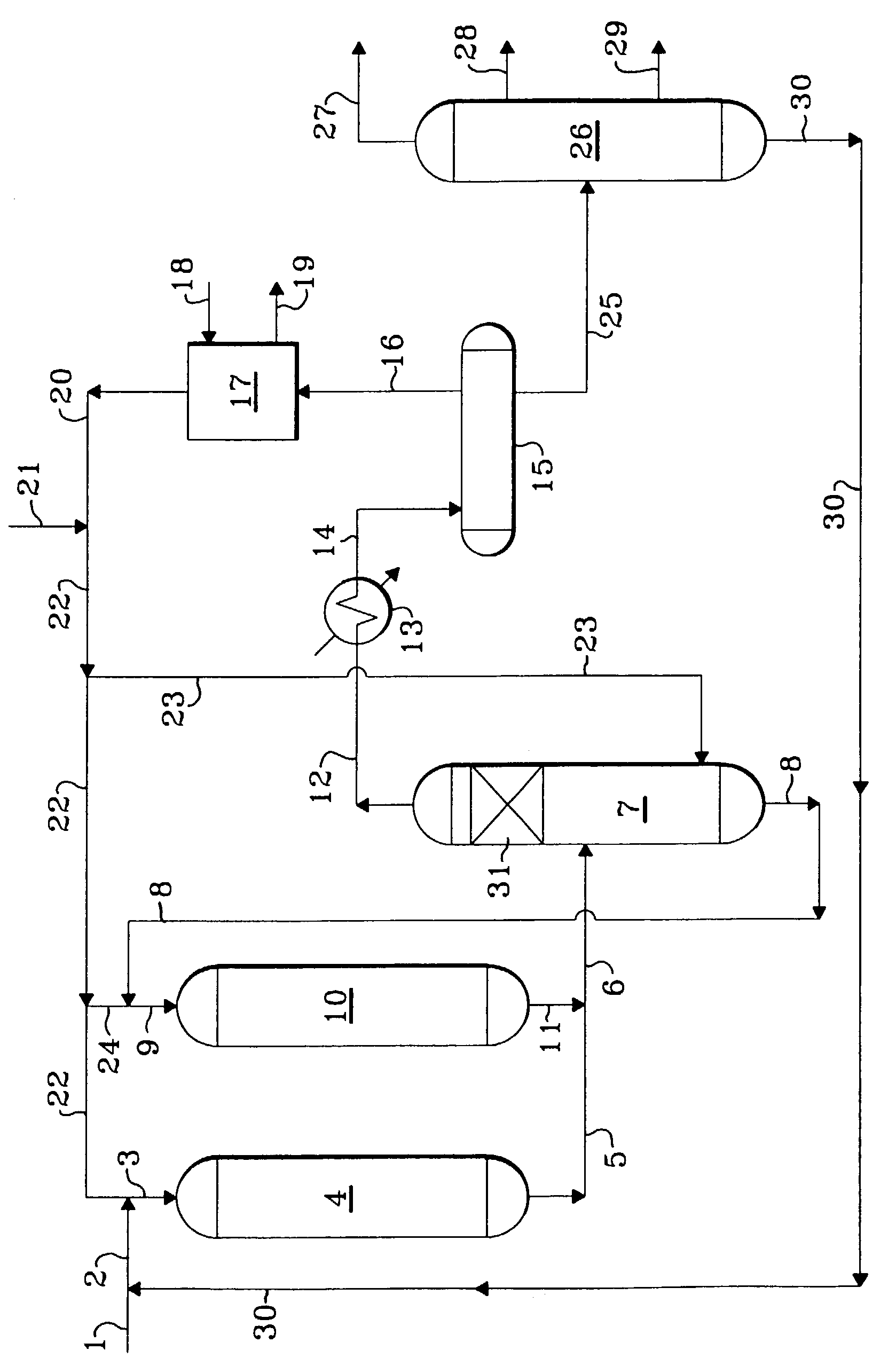
Methods of hydrotreating a mixture made up of oils of animal or vegetable origin and of petroleum cuts with intermediate stripping
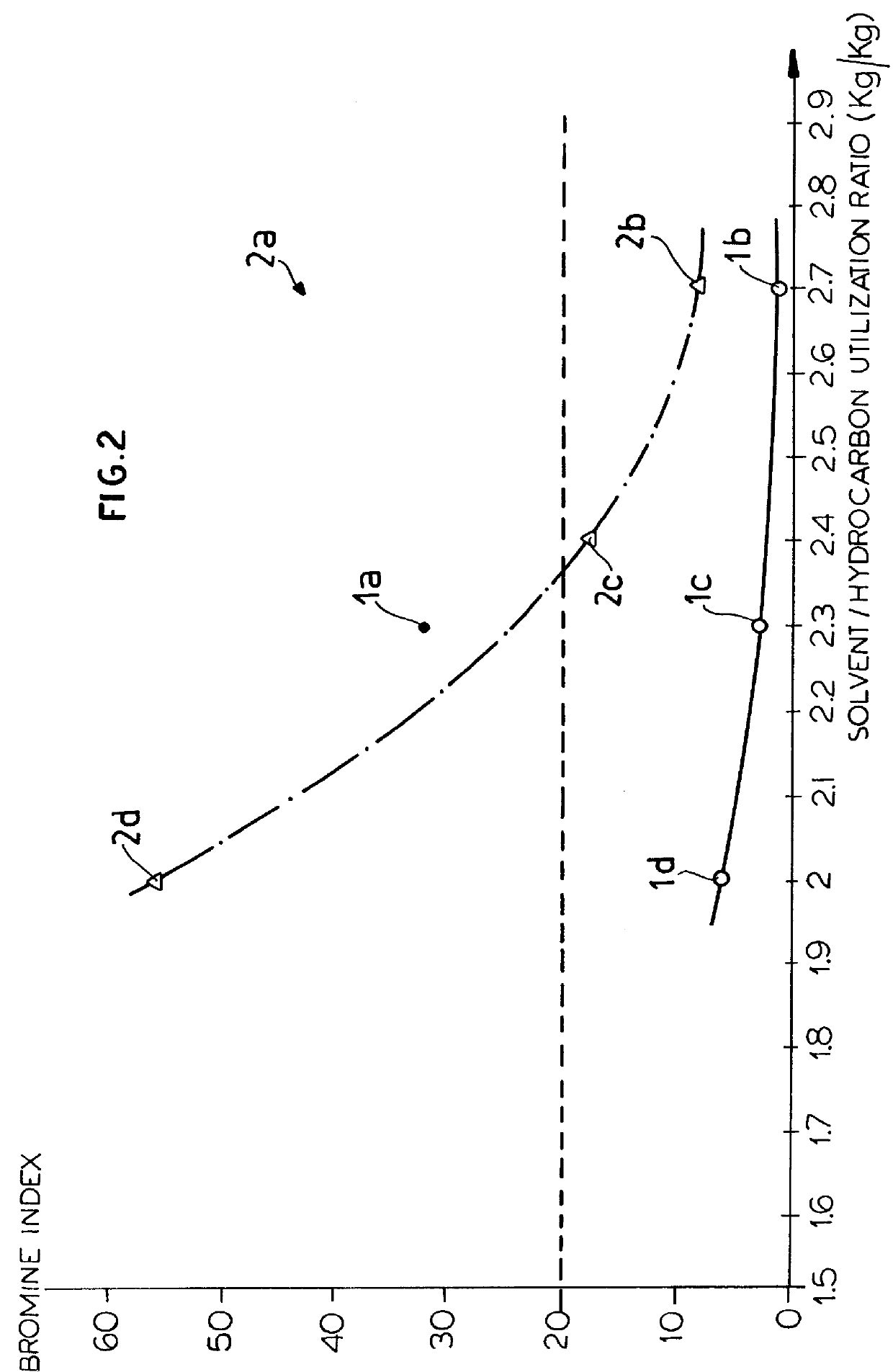
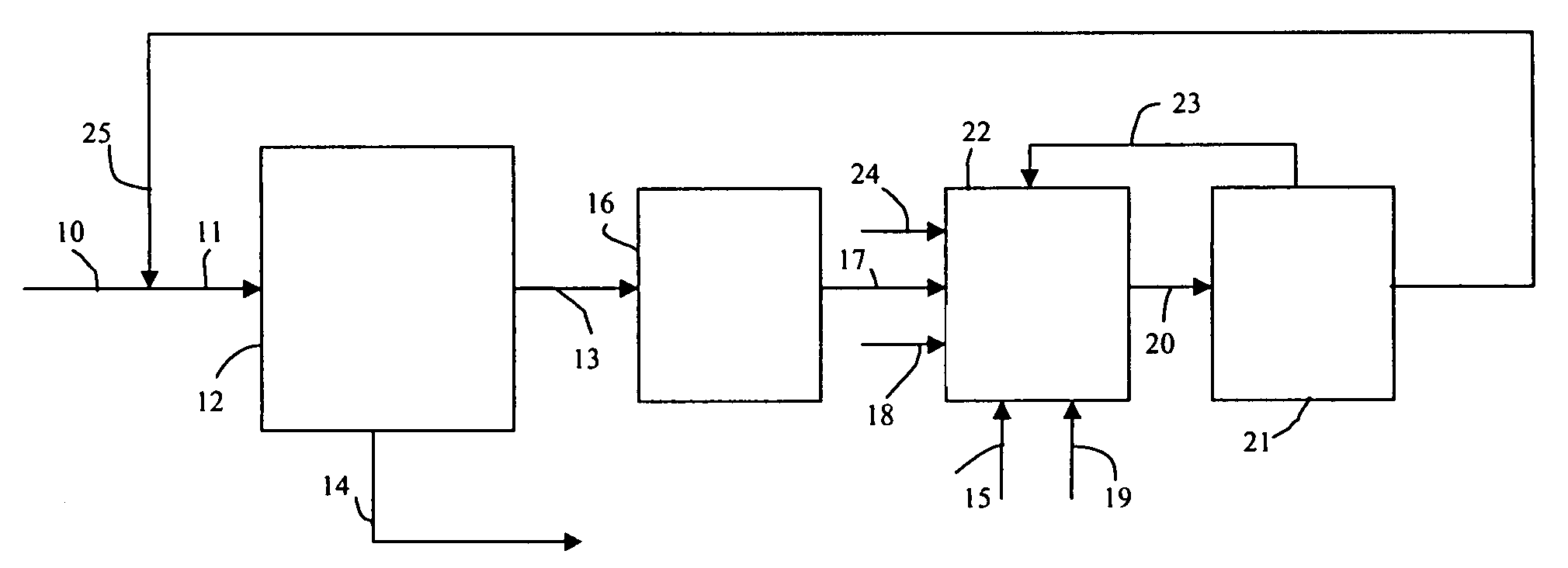
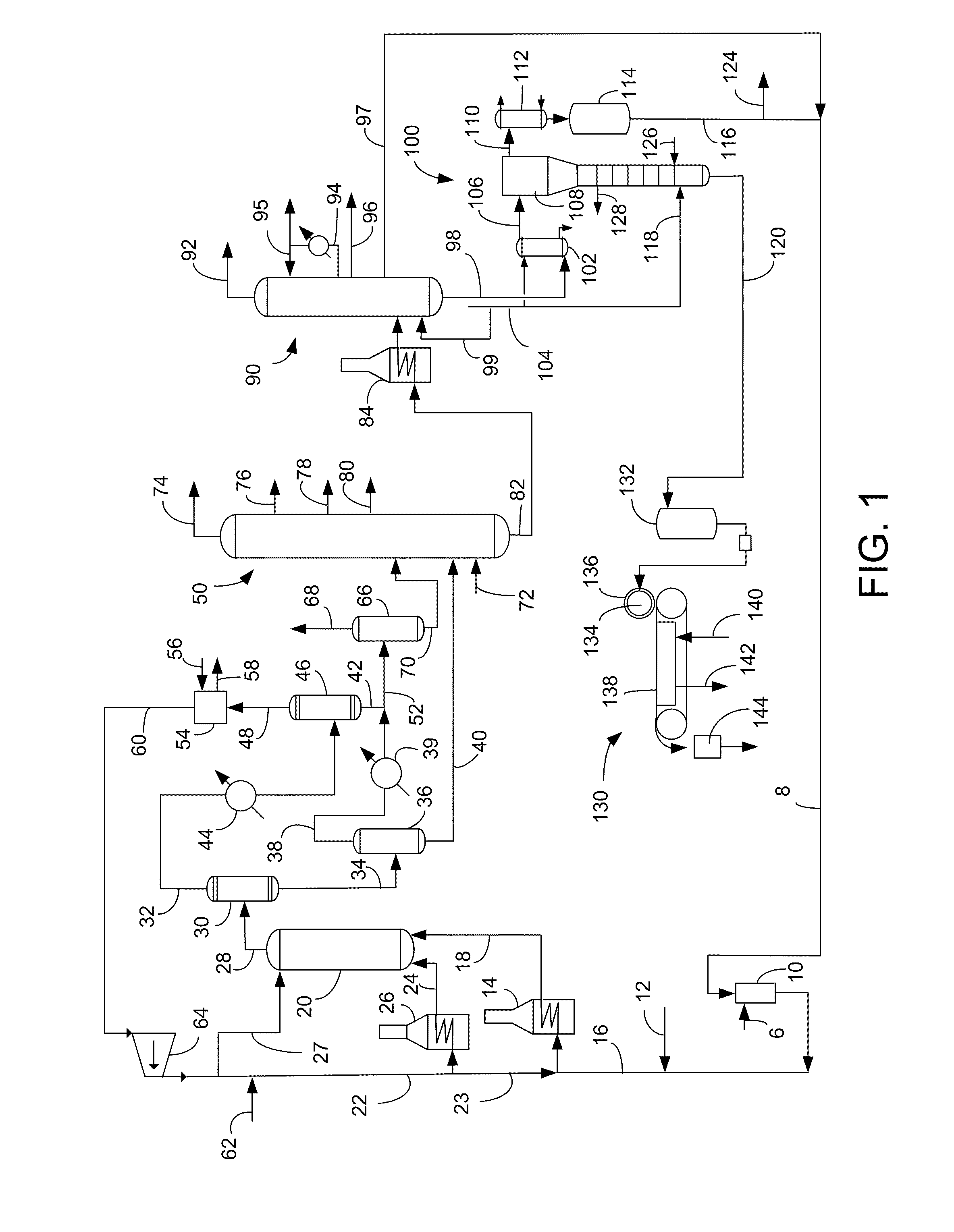
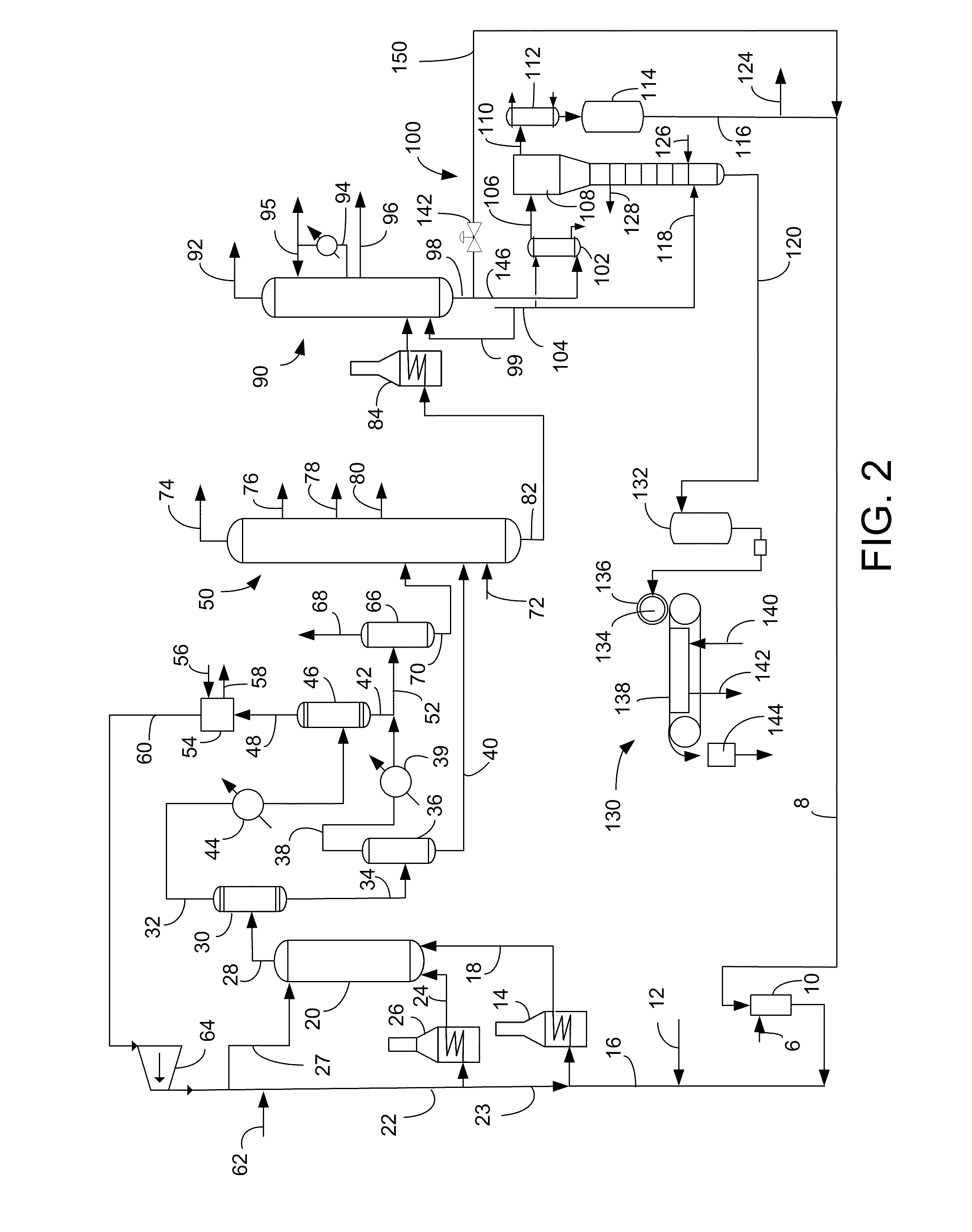
ActiveUS20080161614A1Low costLimit consumption of hydrogenThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingVegetable oilVolumetric Mass Density
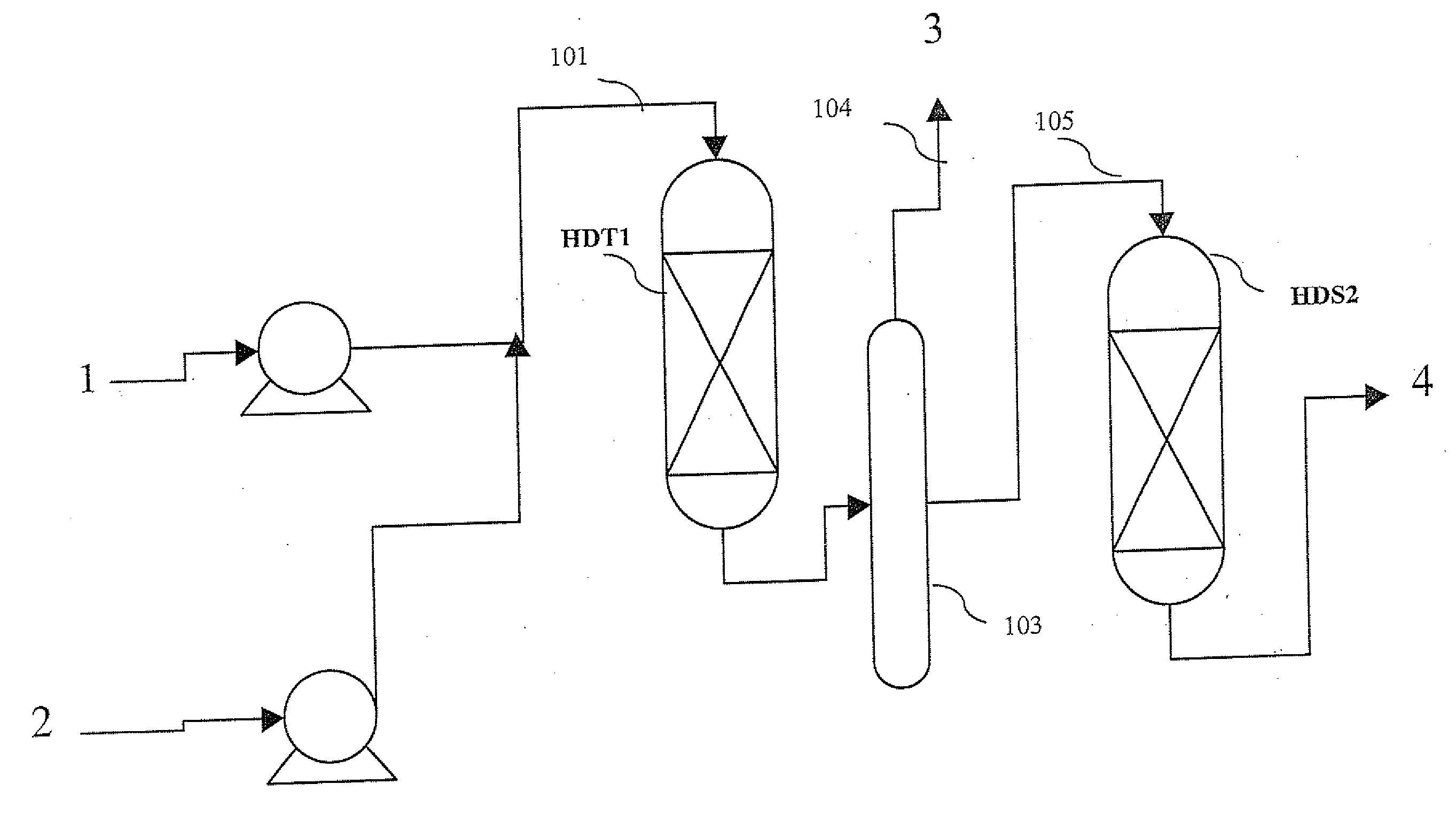
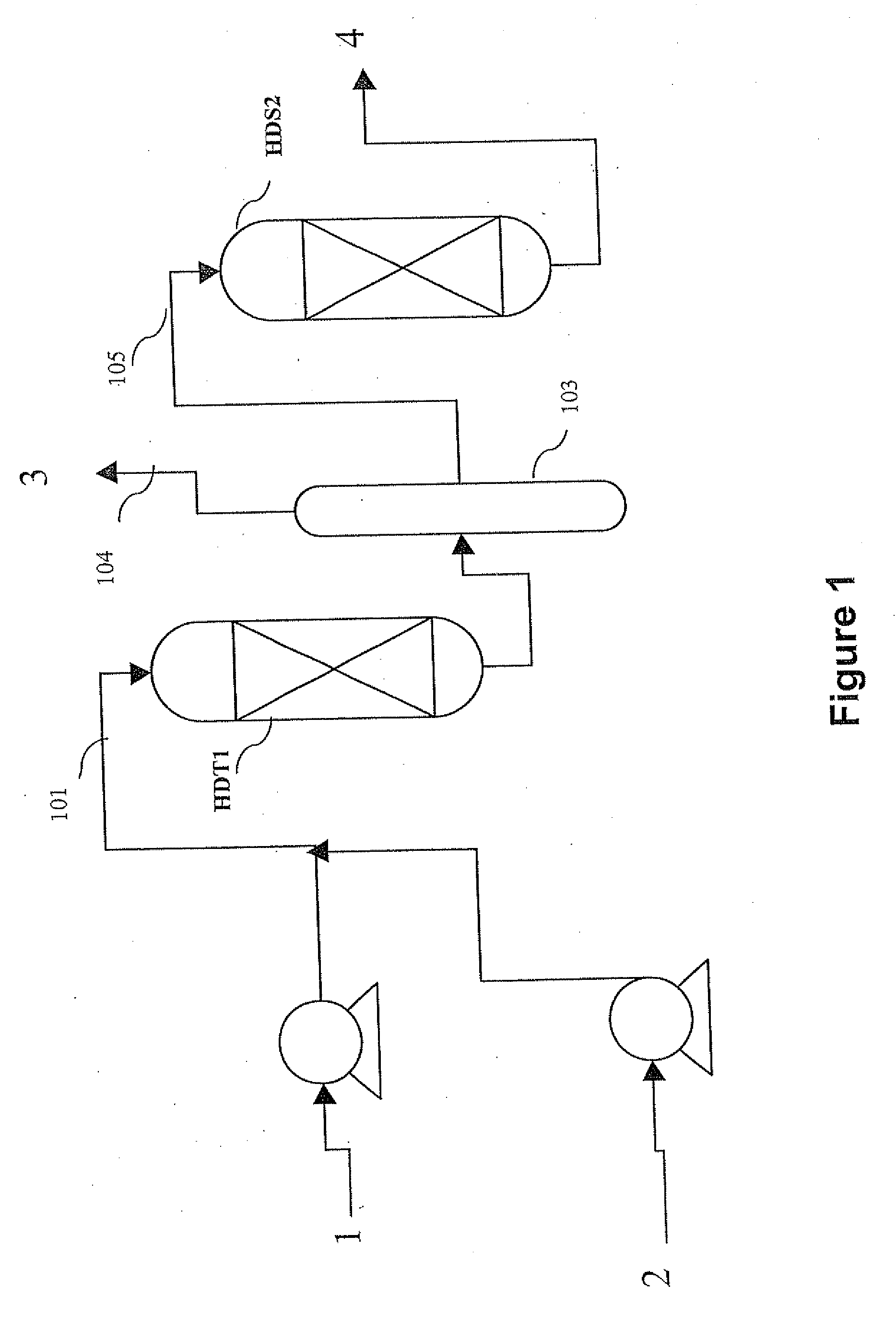
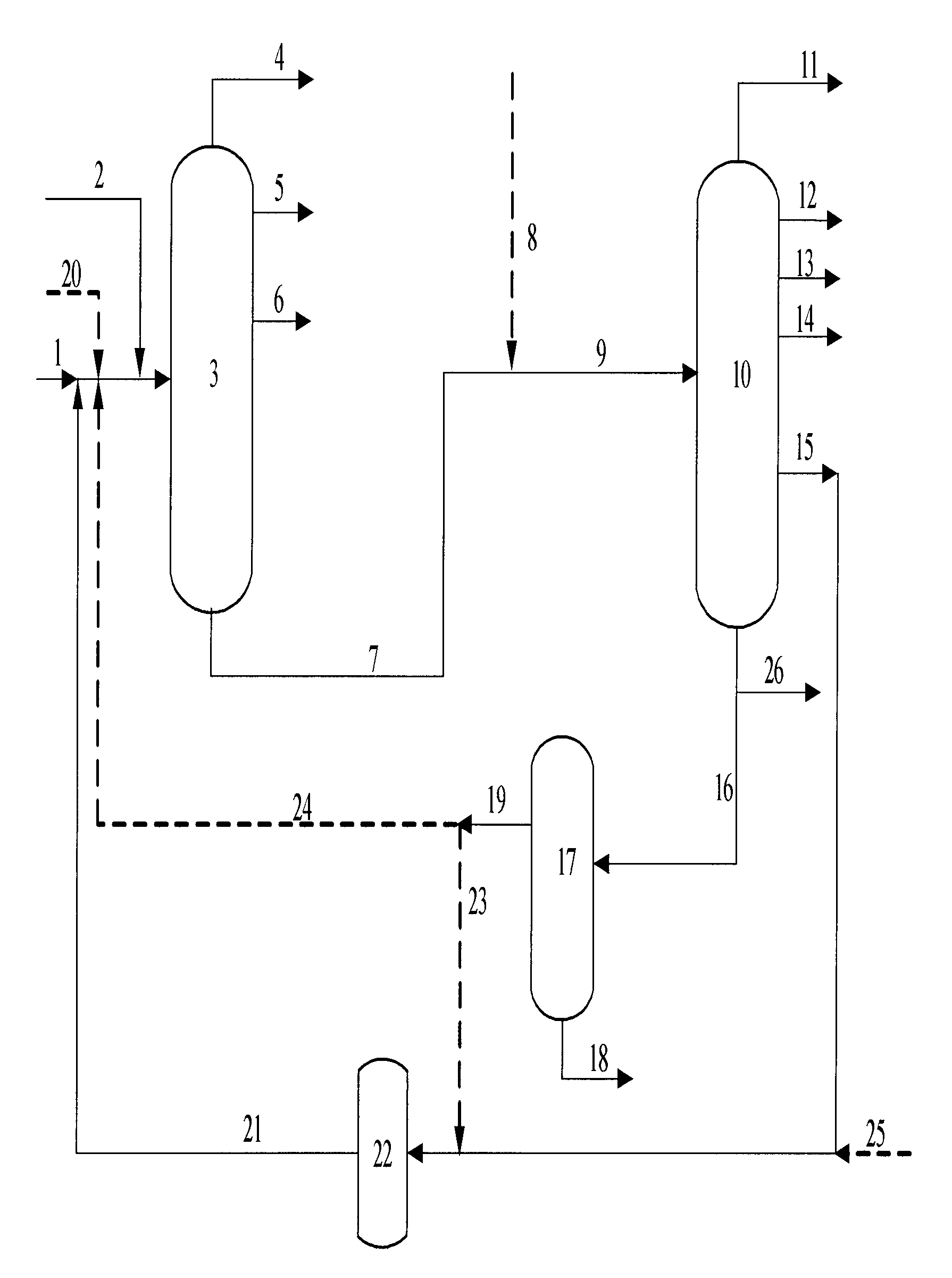
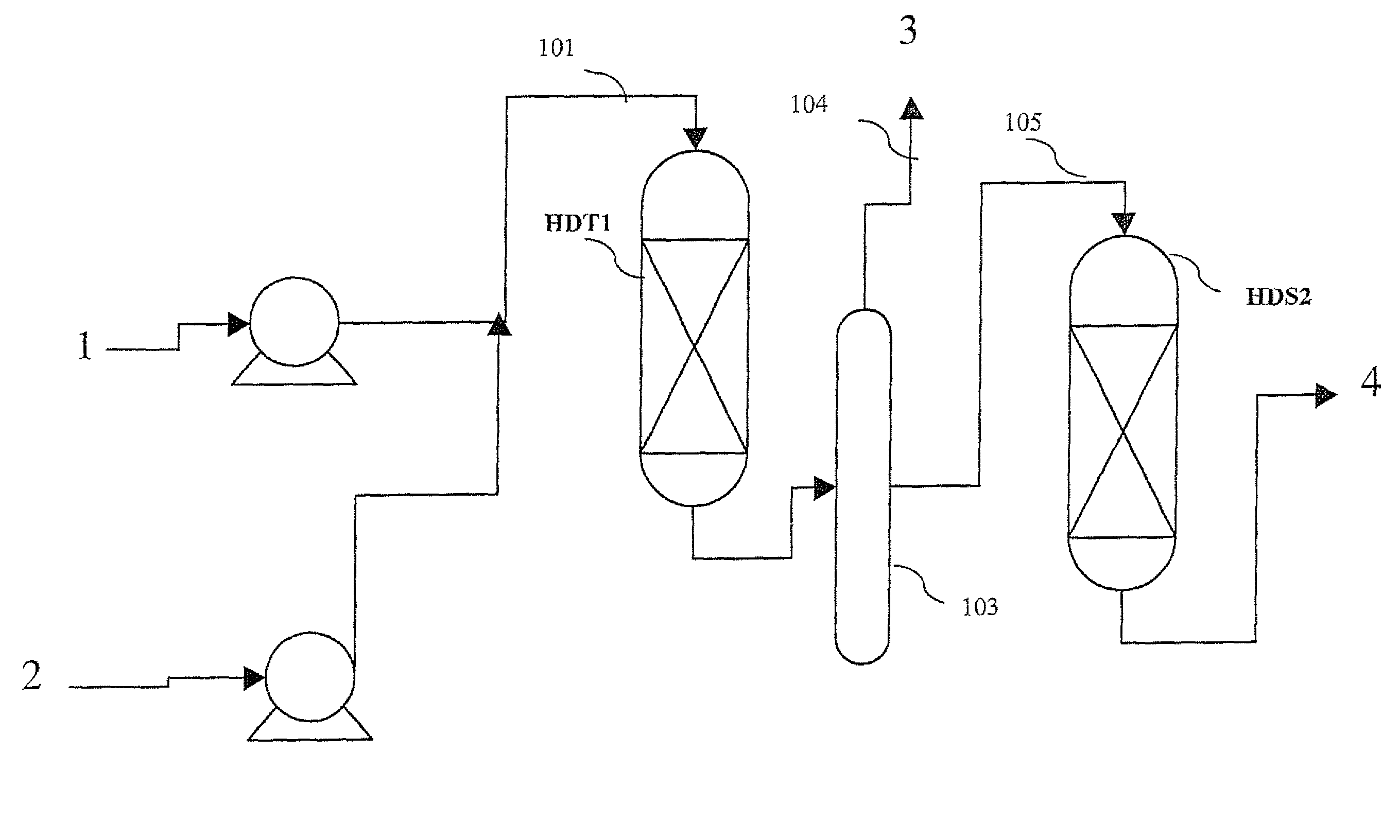
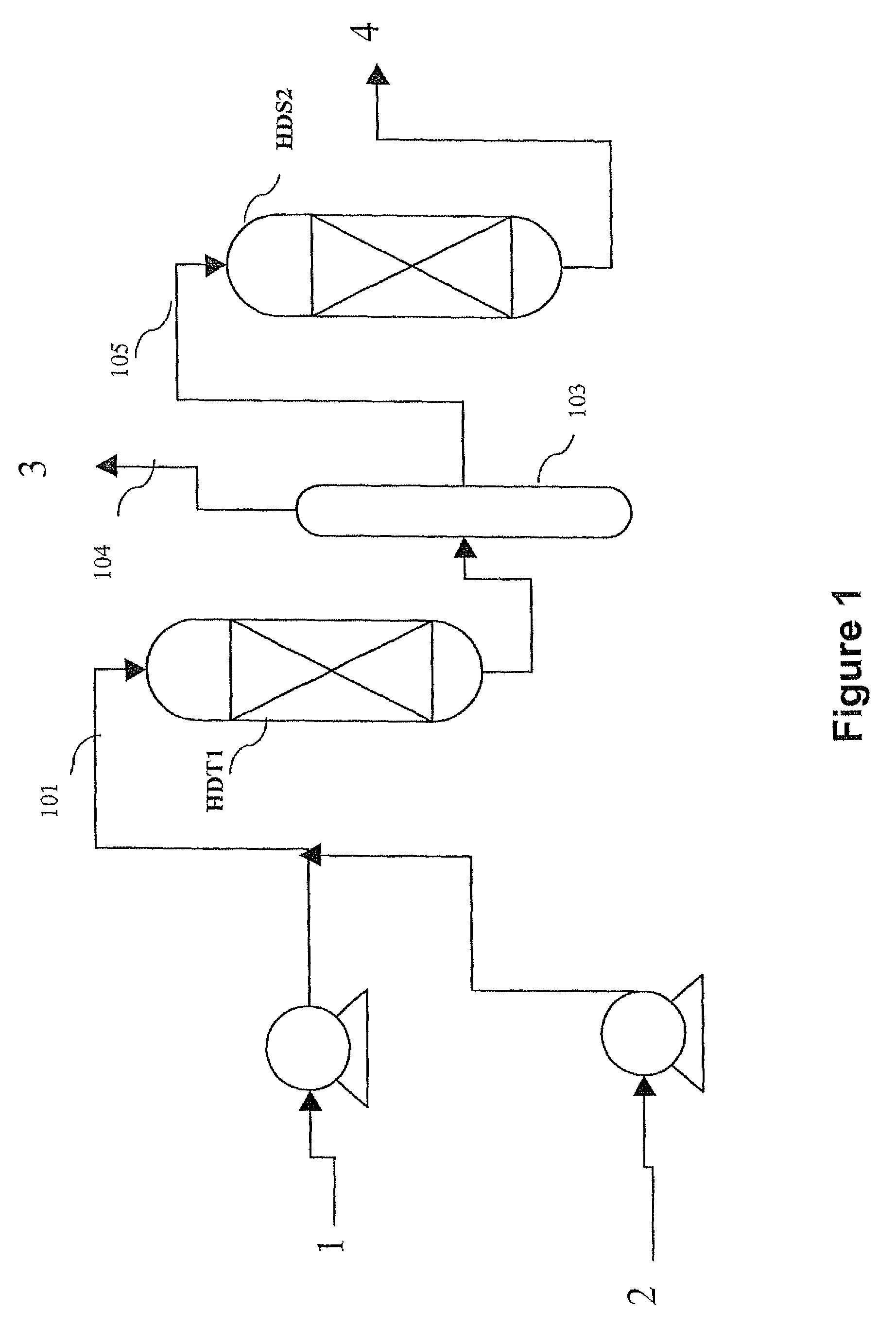
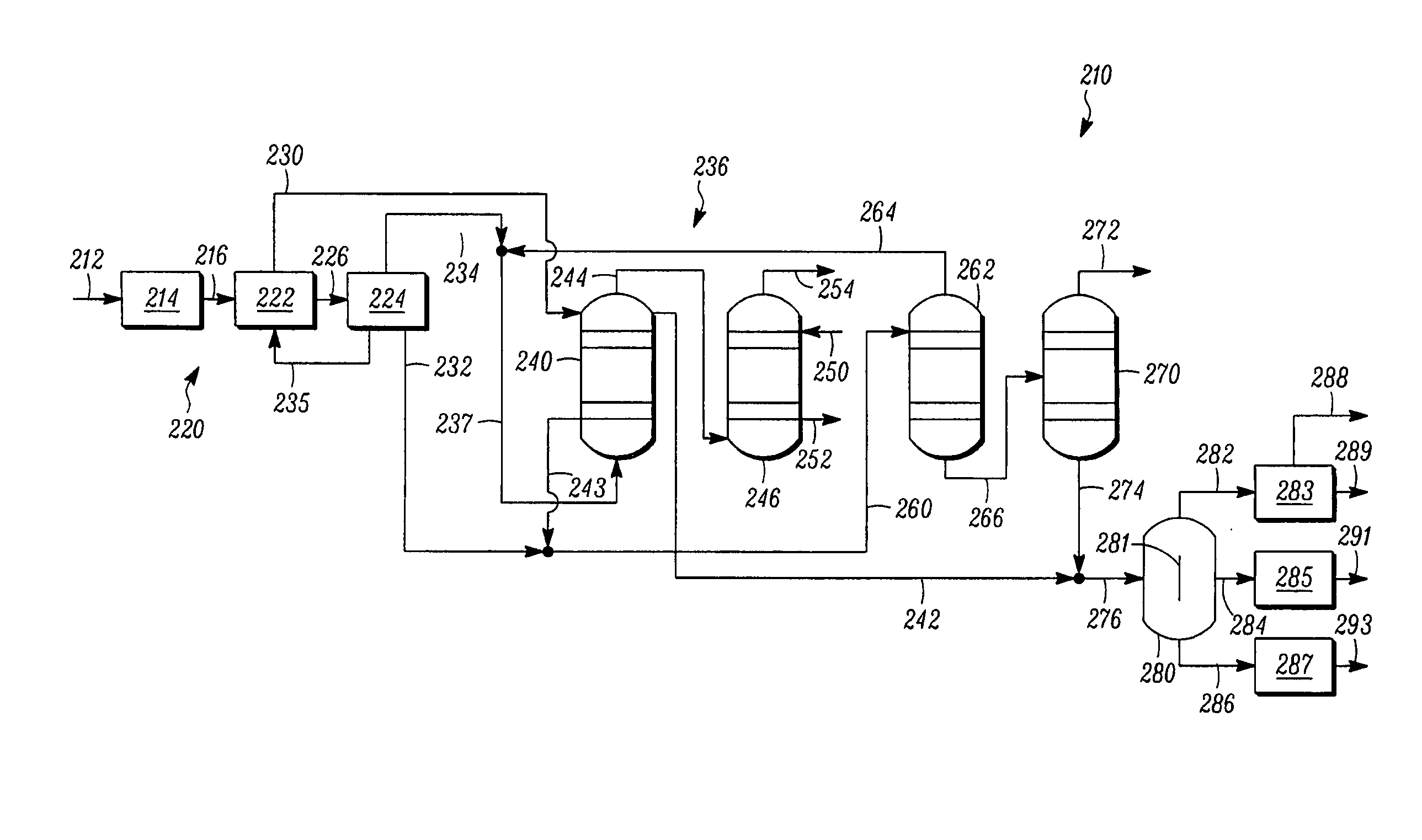
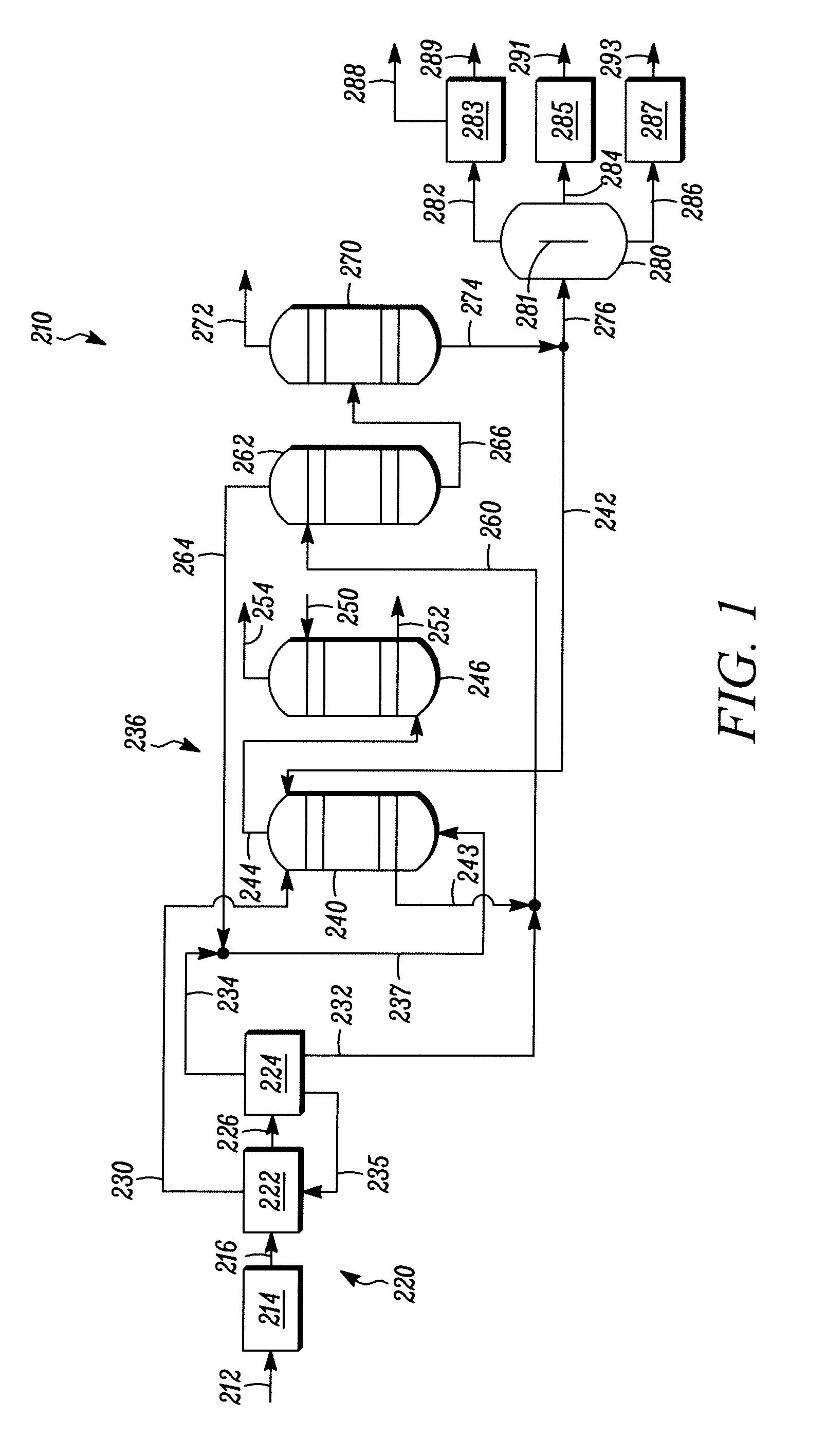
The invention relates to a hydrotreating method (HDT) using two plants working under different operating conditions with an intermediate stripping for co-treating a mixture made up of oils of vegetable or animal origin and petroleum cuts (gas oil cuts (GO) and middle distillates) in order to produce gas oil fuel bases meeting specifications. The first plant (HDT1) is more particularly dedicated to the reactions concerning oils of vegetable or animal origin in comixture while pretreating the hydrocarbon feed, whereas the second plant (HDS2) works under more severe conditions to obtain diesel fuel according to standards, in particular in terms of effluent sulfur content, density and cold properties. The process economy, the activity and the stability of the catalyst of the second plant are greatly improved by the intermediate stripping.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for generating pure benzene from reformed gasoline
InactiveUS6124514AReduce benzene contentAchieve separationThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingBenzeneExtractive distillation
A process is disclosed for generating pure aromatic compounds from a reformed gasoline which contains aromatic compounds, olefins, diolefin, and triolefins, which comprises the steps of: (a) selectively hydrogenating the olefins, diolefins and triolefins in the reformed gasoline to obtain a mixture of hydrogenated, non-aromatic compounds and aromatic compounds; and (b) separating the aromatic compounds from the hydrogenated, non-aromatic compounds in the mixture formed during step (a) by either extractive distillation, liquid-liquid extraction or both to obtain the pure aromatic compounds.
Owner:BASF AG
Production of liquid fuels by a concatenation of processes for treatment of a hydrocarbon feedstock
ActiveUS7214720B2Maximize conversion of carbonReduce and to upgrade naphthaThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNaphthaKerosene
The invention relates to an installation and a process for the production of liquid fuels starting from a solid feedstock that contains the organic material in which:a) the solid feedstock is subjected to a gasification stage so as to convert said feedstock into synthesis gas,b) the synthesis gas is subjected to a purification treatment,c) the purified synthesis gas is subjected to a conversion stage that comprises the implementation of a Fischer-Tropsch-type synthesis so as to convert said synthesis gas into a liquid effluent and a gaseous effluent,d) the liquid effluent is fractionated so as to obtain a gaseous fraction, a naphtha fraction, a kerosene fraction and a gas oil fraction, ande) at least a portion of the naphtha fraction is recycled in gasification stage a).
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +1
Supercritical water process to upgrade petroleum
ActiveUS20130140214A1Proceed efficientlyThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingSludgePetroleum
Provided is a process for the supercritical upgrading of petroleum feedstock, wherein the process includes the use of a start-up agent, wherein the use of the start-up agent facilitates mixing of the petroleum feedstock and water, thereby reducing or eliminating the production of coke, coke precursor, and sludge.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Process to produce synthetic fuels and lubricants
InactiveUS20050183988A1Yield maximizationEquipment cost can be minimizedThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingBase oilPetroleum
A process utilizing a low severity hydrocracker prior to a high severity hydrocracker for the processing of petroleum based and synthetic hydrocarbon feedstocks into distillate fuels and high quality lubricant base oils. The process minimizes the size and conditions required by the high severity hydrocracker by closely matching such configuration with the desired product slate.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
Use of low pressure distillate as absorber oil in a FCC recovery section
InactiveUS7074323B2Less equipmentImprove throughputThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNaphthaDistillation
A process for the recovery of gaseous products from the product mixture obtained by contacting a hydrocarbon feed with a catalyst in a fluid catalytic cracking process, wherein the liquid, obtained by separating the top product of main fractionators into gaseous and liquid fraction, when supplied to the absorber has a temperature of between about 8–25 DEG C. This liquid may be pre-saturated with gaseous top product from absorber; or also a high boiling fraction (cat cracker naphtha / light cycle oil) may be first separated from this liquid by distillation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Slurry hydrocracking apparatus or process
InactiveUS20110303580A1Easy to separateAvoid disintegrationWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumenHydrocarbon oil crackingSlurryProcess engineering
One exemplary embodiment can include a slurry hydrocracking process. The process can include combining one or more hydrocarbons and a slurry hydrocracking catalyst as a feed to a slurry hydrocracking reaction zone, fractionating an effluent from the slurry hydrocracking reaction zone, separating the pitch from at least a portion of the slurry hydrocracking catalyst, and recycling the suspension to the slurry hydrocracking reaction zone. The slurry hydrocracking catalyst may include a support. Fractionating the effluent may provide a light vacuum gas oil, a heavy vacuum gas oil, and a mixture comprising a pitch and the slurry hydrocracking catalyst. Generally, the separated slurry hydrocracking catalyst is comprised in a suspension.
Owner:UOP LLC
Upgrading of Hydrocarbons by Hydrothermal Process
ActiveUS20120061291A1Good physical propertiesLow costThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyHydrogenWater flow
A hydrocarbon feedstock upgrading method is provided. The method includes supplying the hydrocarbon feedstock, water and a pre-heated hydrogen donating composition to a hydrothermal reactor where the mixed stream is maintained at a temperature and pressure greater than the critical temperatures and pressure of water in the absence of catalyst for a residence time sufficient to convert the mixed stream into a modified stream. The hydrogen donating composition is pre-heated and maintained at a temperature of greater than about 50° C. for a period of at least about 10 minutes. The modified stream includes upgraded hydrocarbons relative to the hydrocarbon feedstock. The modified stream is then separated into a gas stream and a liquid stream and the liquid stream is separated into a water stream and an upgraded hydrocarbon product stream.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
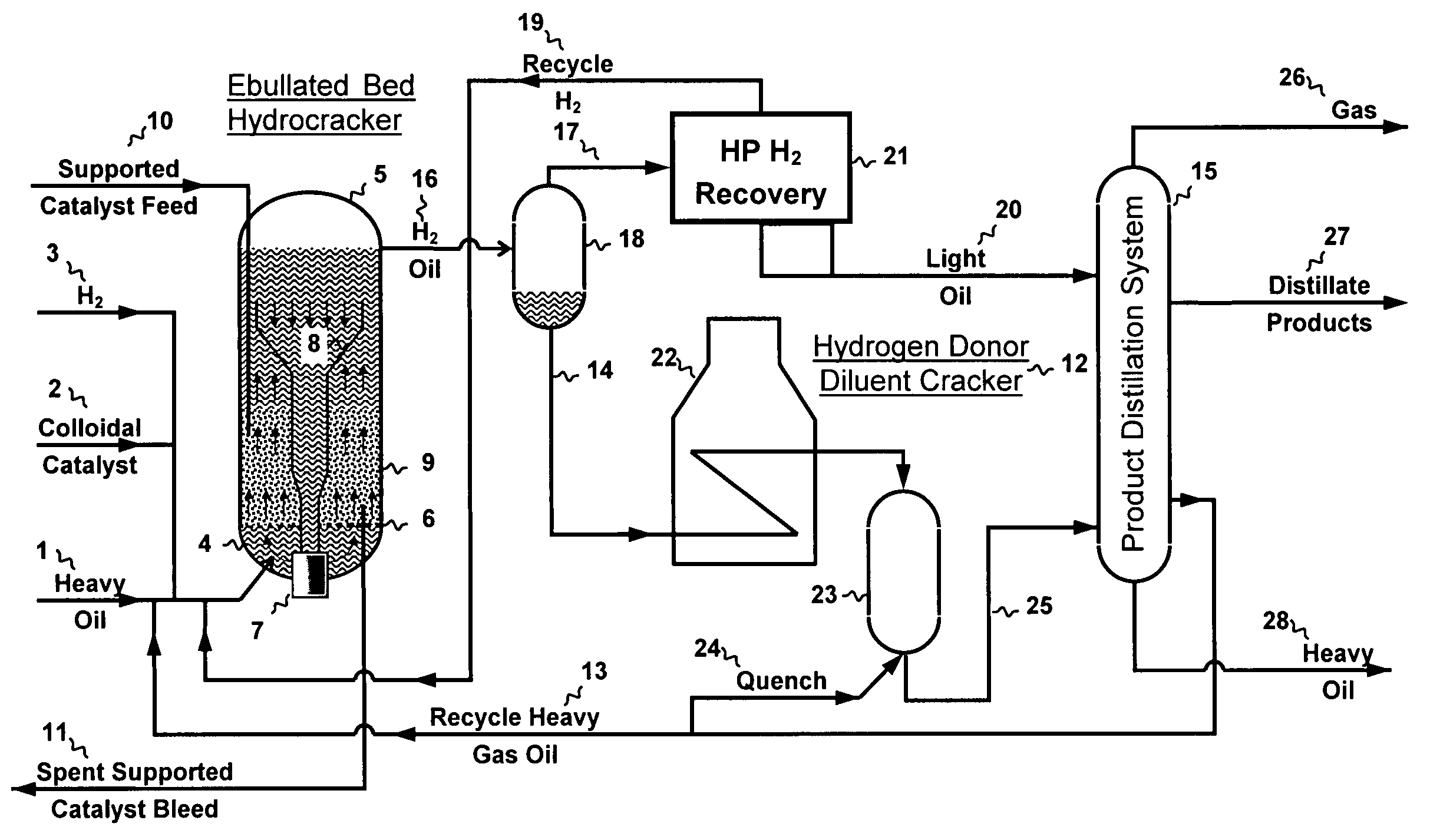
Heavy oil hydroconversion process
InactiveUS20070158239A1Easy transferReduce pressureThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingHydrogenDiluent
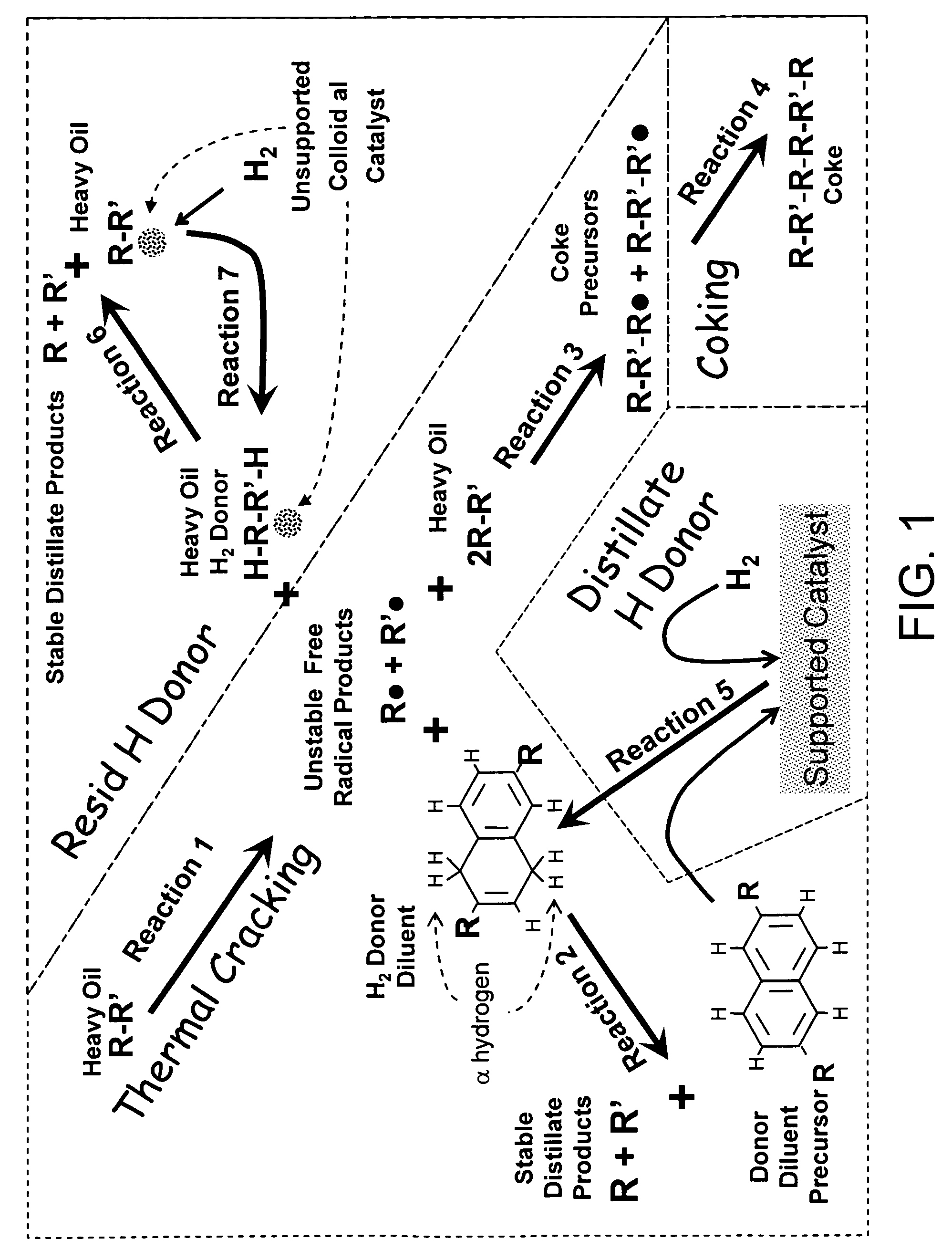
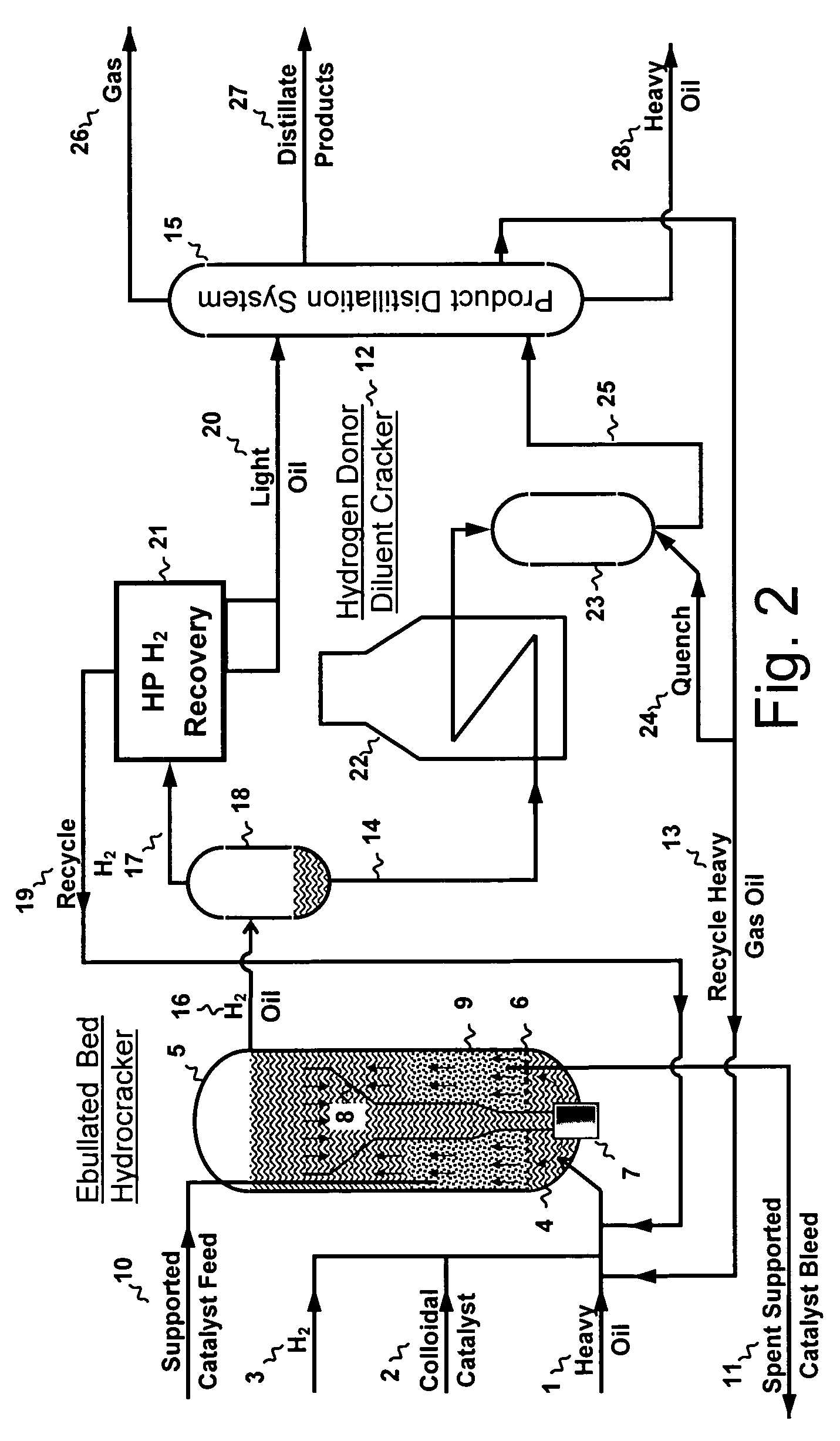
A method for the efficient conversion of heavy oil to distillates using sequential hydrocracking in the presence of both supported and colloidal catalyst immediately followed by a high temperature-short residence time thermal treatment. The hydrocracker reaction products or a heavy oil and hydrogen donor diluent may be advantageously heated by direct contact with high velocity combustion products.
Owner:BOC GRP INC
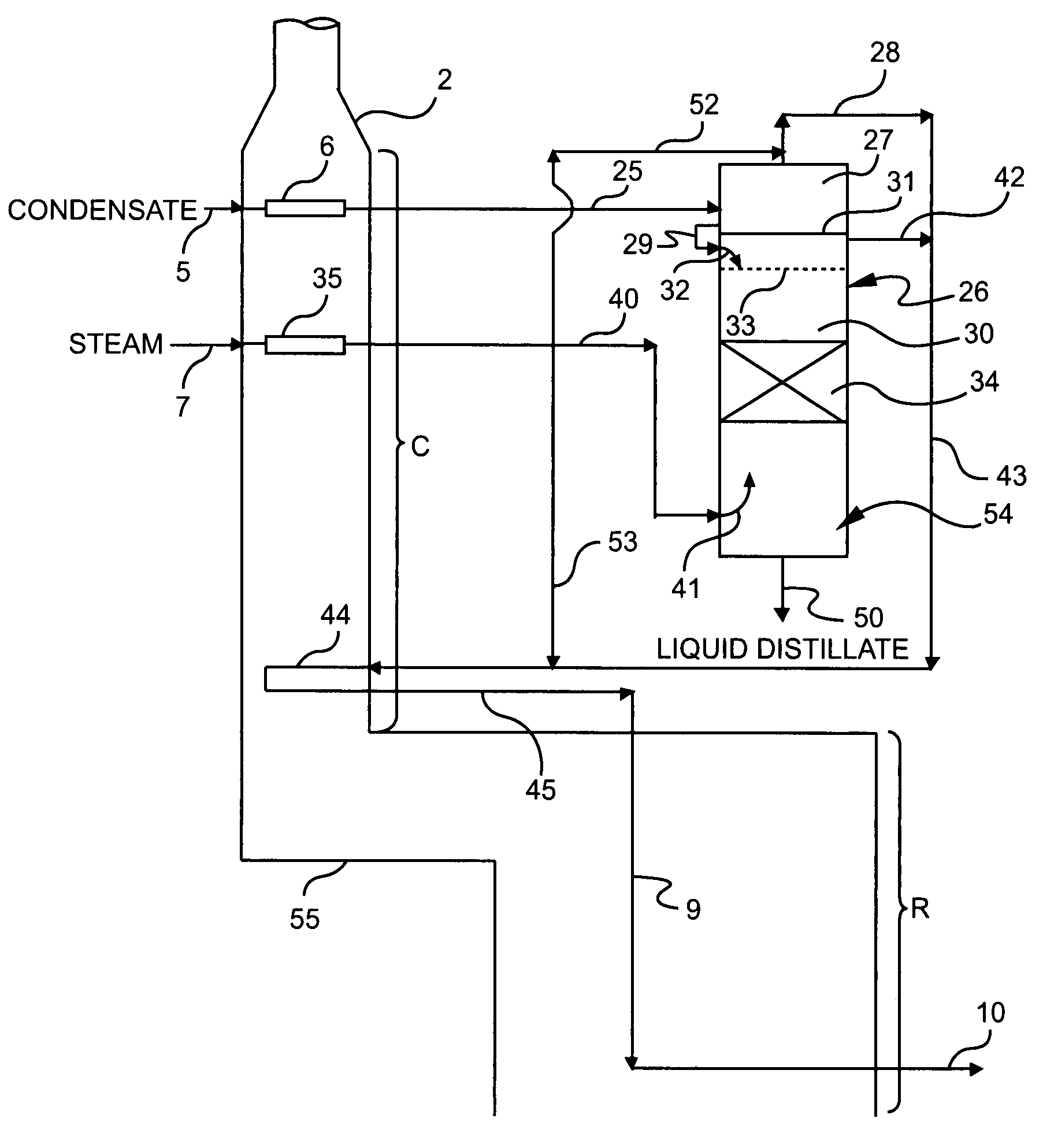
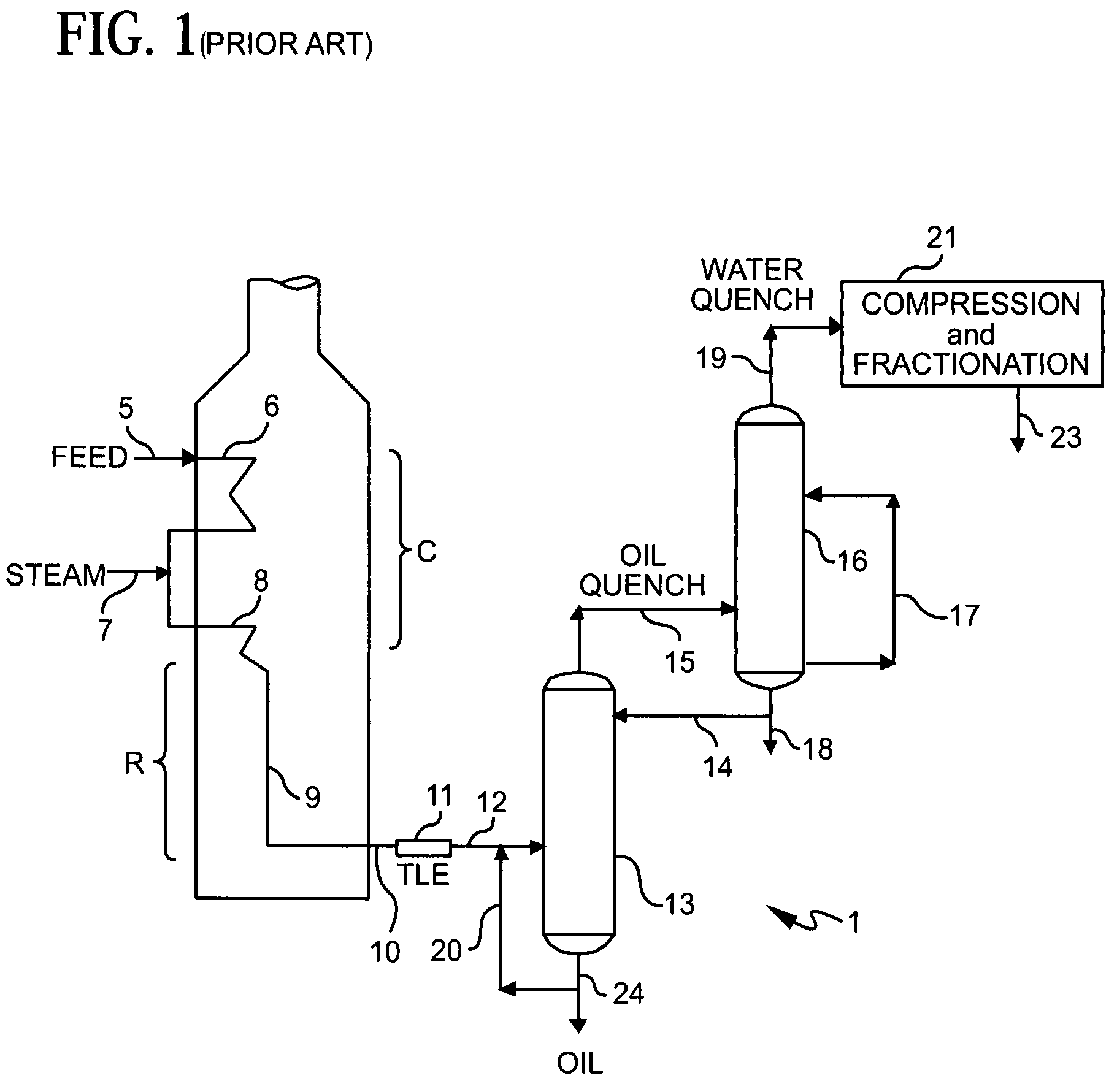
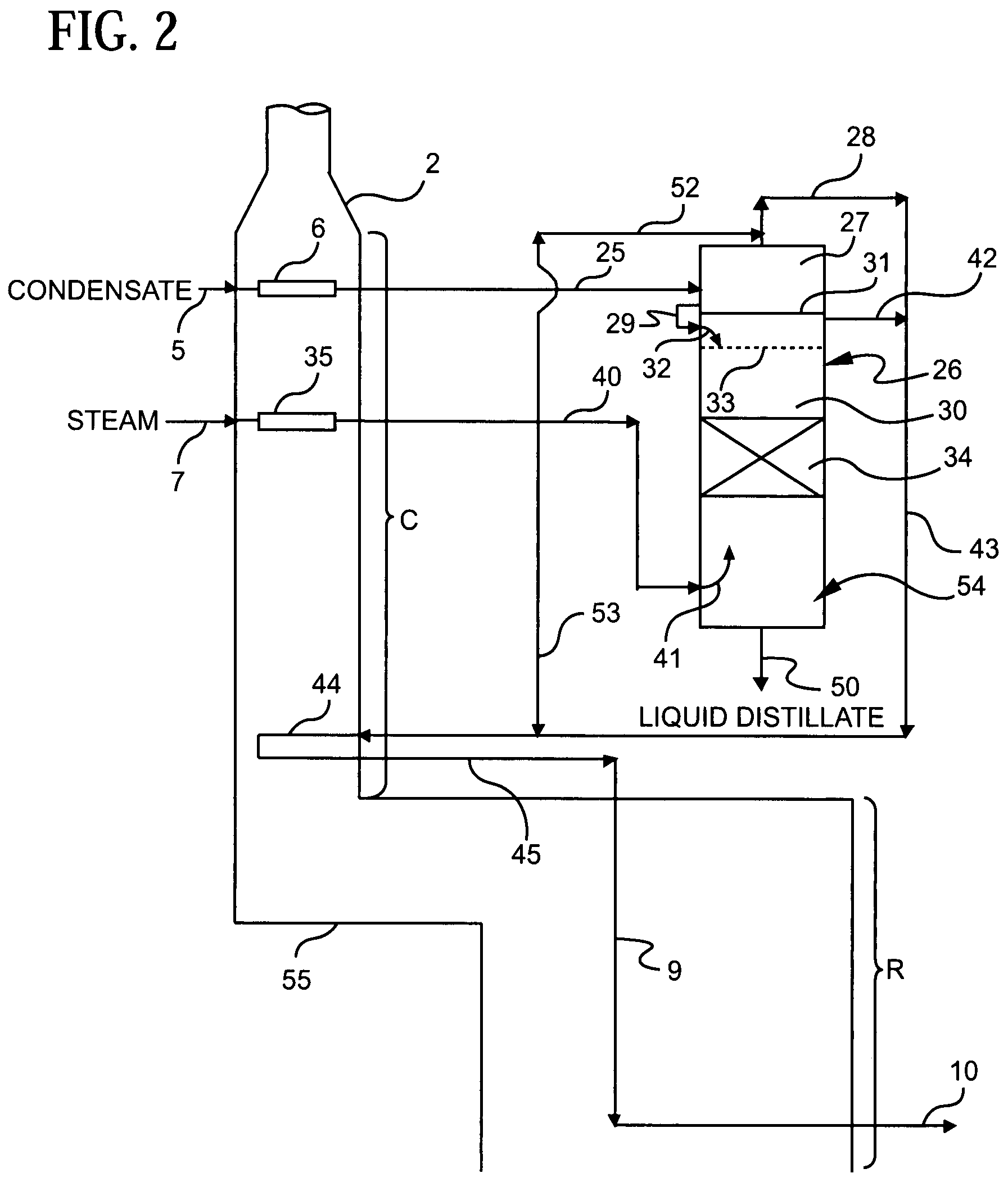
Olefin production utilizing condensate feedstock
InactiveUS7396449B2Maximize recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNatural-gas condensateThermodynamics
A method for utilizing natural gas condensate as a feedstock for an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock is subjected to vaporization and separation conditions that remove light hydrocarbons from the condensate for thermal cracking in the plant, and leave liquid distillate for separate recovery.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Method for adjusting the high heating value of gas in the LNG chain
The subject of the invention is a method for treating a natural gas containing ethane, comprising the following stages: (a) extraction of at least one part of the ethane from the natural gas; (b) reforming of at least one part of the extracted ethane into a synthesis gas; (c) methanation of the synthesis gas into a methane-rich gas; and (d) mixing of the methane-rich gas with the natural gas. Installation for implementing this method.
Owner:TOTAL PUTEAUX FR
Series of hydroconversion and steam reforming processes to optimize hydrogen production on production fields
The invention concerns a process for treating a hydrocarbon feed comprising a series of a first upstream process for hydrocarbon hydroconversion comprising at least one reaction chamber, the reaction or reactions occurring inside said chambers and employing at least one solid phase, at least one liquid phase and at least one gas phase, and a second downstream steam reforming process comprising at least one reaction chamber, characterized in that the said upstream process is carried out in a “slurry” and / or an ebullated bed mode and in that the downstream process comprises a first step for at least partial conversion of hydrocarbons heavier than methane into methane, termed the pre-reforming step, and in that the reaction or reactions occurring inside the chambers of the downstream stream reforming process enables the production of a reagent, namely hydrogen, which is necessary for the reactions in the first upstream process.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Integrated unsupported slurry catalyst preconditioning process
InactiveUS20080135450A1Reduce shockIncrease temperatureOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCentrifugal force sediment separationSlurryEngineering
A process for slurry hydroprocessing, which involves preconditioning a slurry catalyst for activity improvement in vacuum residuum hydroprocessing units Preconditioning the slurry catalyst raises its temperature, thereby reducing shock on the catalyst slurry as it enters the hydroprocessing reactor.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Olefin production utilizing a feed containing condensate and crude oil
A method for utilizing a feed comprising condensate and crude oil for an olefin production plant is disclosed. The feed is subjected to vaporization and separated into vaporous hydrocarbons and liquid hydrocarbons. The vaporous hydrocarbons stream is thermally cracked in the plant. The liquid hydrocarbons are recovered.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Pyrolysis tar upgrading using recycled product
ActiveUS9657239B2Pyrolysis tar hydroprocessing is improvedLesser rateHydrotreatment operations starting-upRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonProcess engineeringFuel oil
The invention relates to a process for upgrading pyrolysis tar in the presence of a utility fluid. The utility fluid contains 1-ring and / or 2-ring aromatics and has a final boiling point ≦430° C. The invention also relates to the upgraded pyrolysis tar, and to the use of the upgraded pyrolysis tar, e.g., for fuel oil blending.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
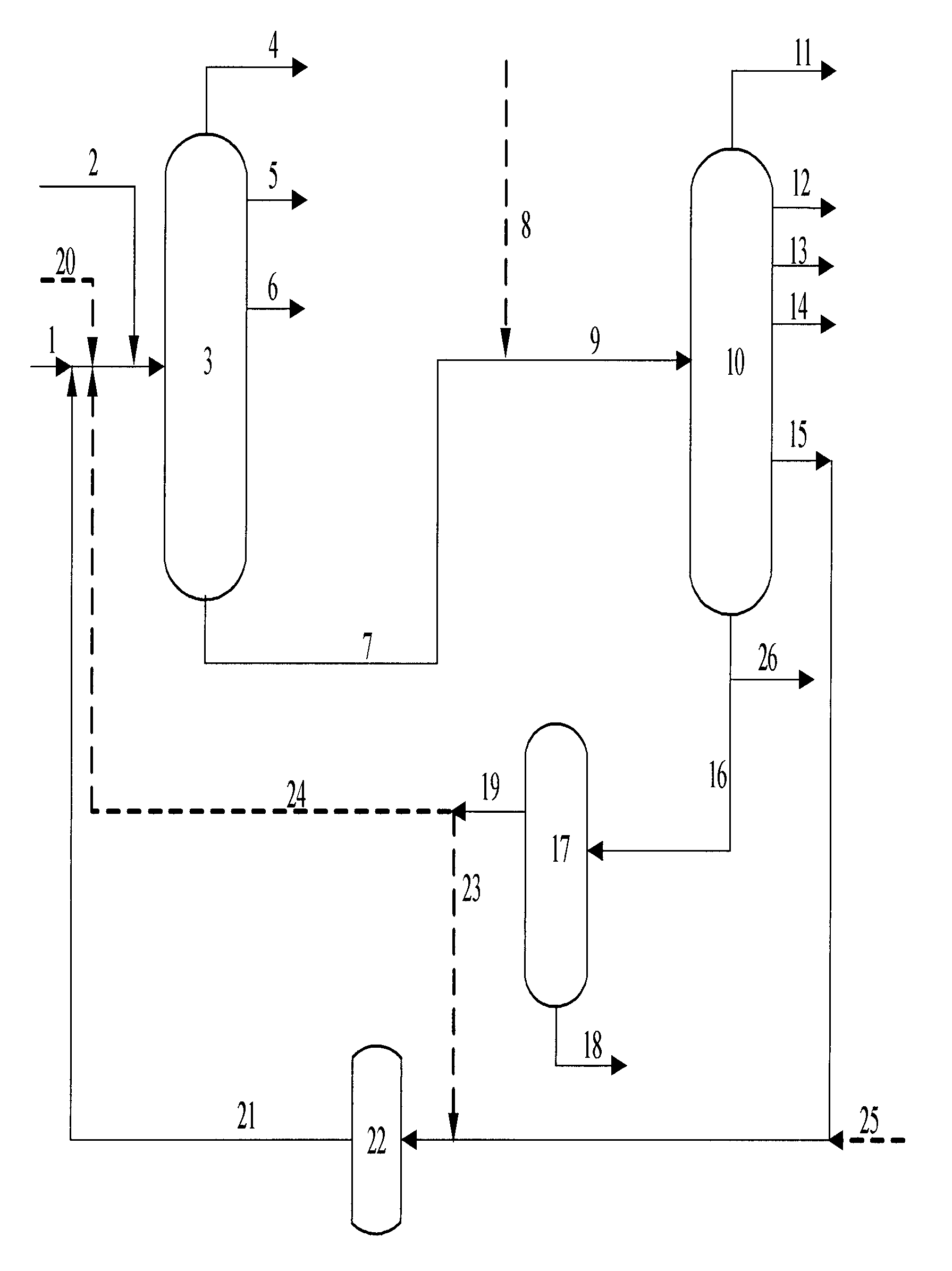
High severity, low conversion hydrocracking process
InactiveUS6294079B1Hydrocarbon oil crackingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesReaction zoneHigh pressure
A feed stream is first processed in a hydrotreating reaction zone and then the effluent is separated into three fractions in an augmented first high pressure separator. Controlled portions of the middle and heavy hydrocarbon fractions are passed into a high severity hydrocracking zone, while the remaining portions of these two fractions are passed into a second high pressure separator for recovery. The effluent of the hydrocracking zone is also fed to the second high pressure separator.
Owner:UOP LLC
Combined process for hydrotreating and catalytic cracking of residue
ActiveUS8529753B2Improve efficiencyLow costThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingSlurryImpurity
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
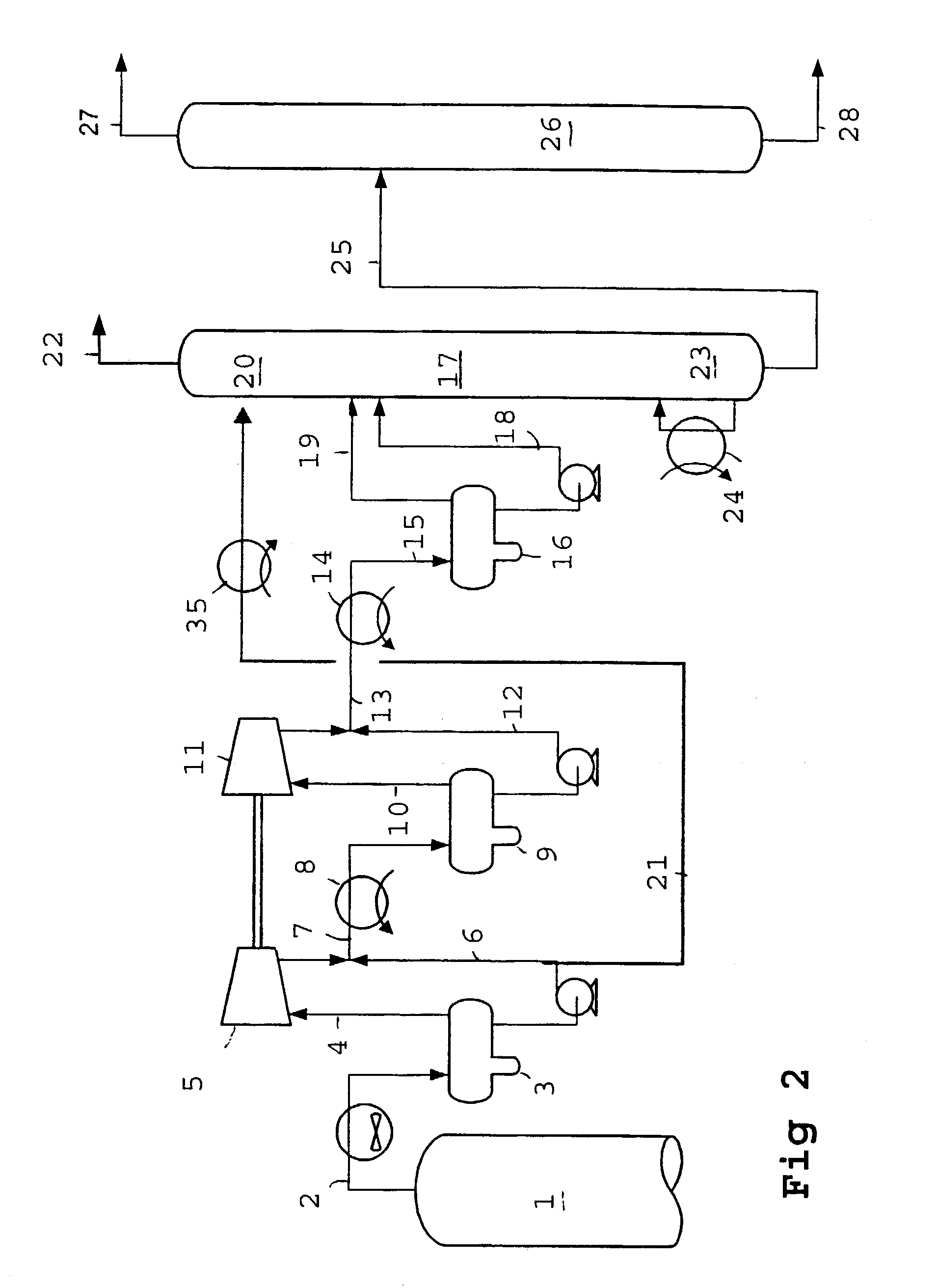
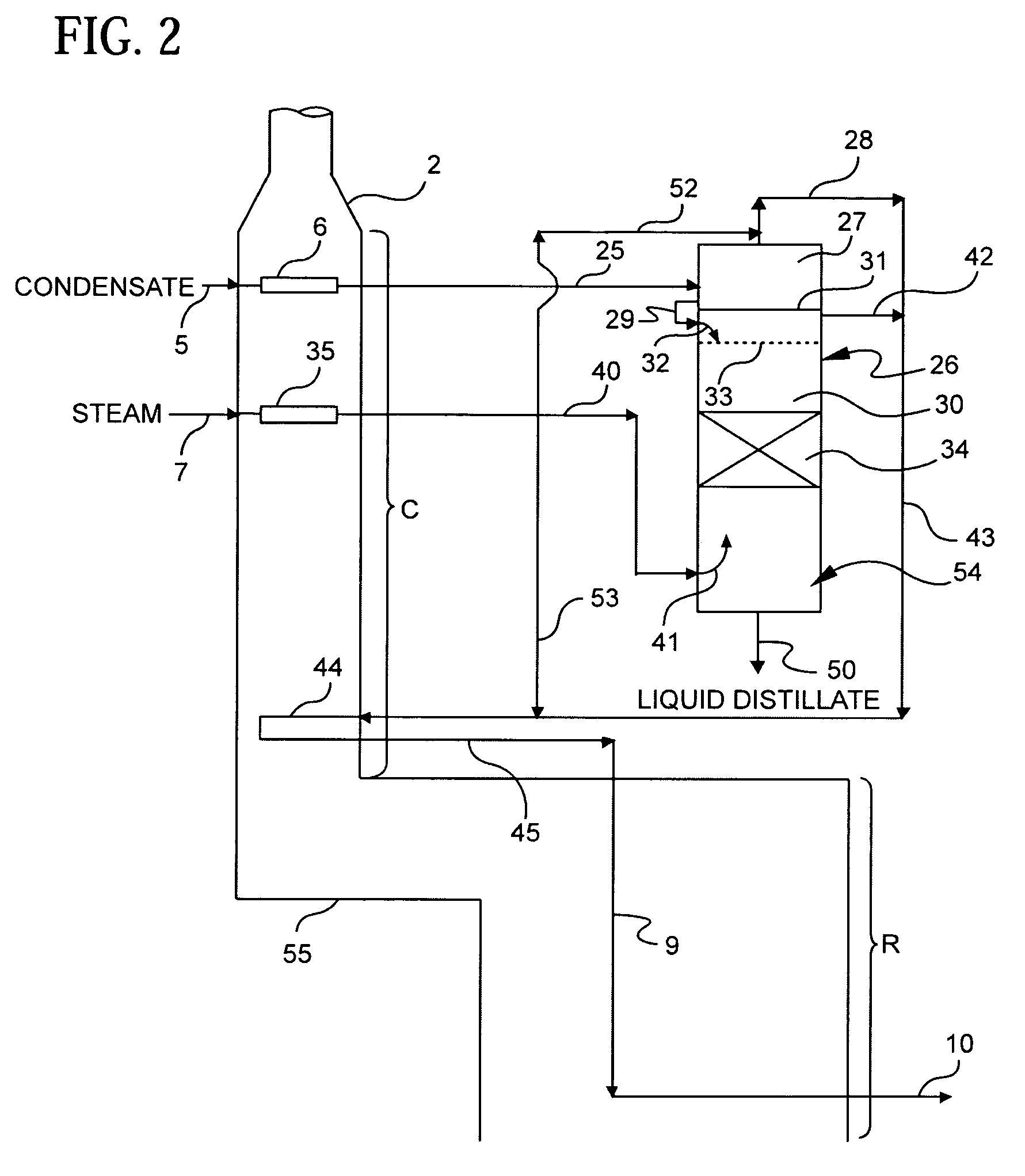
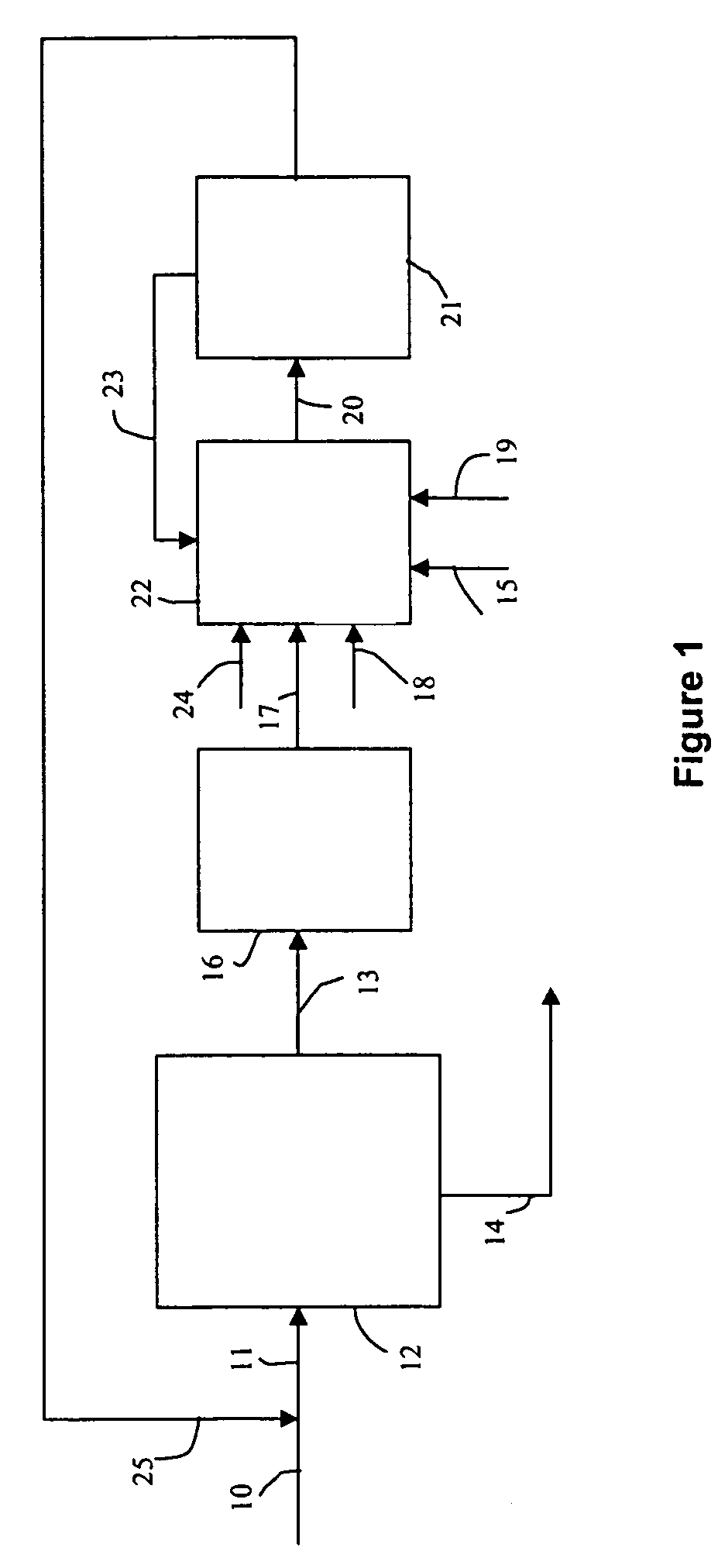
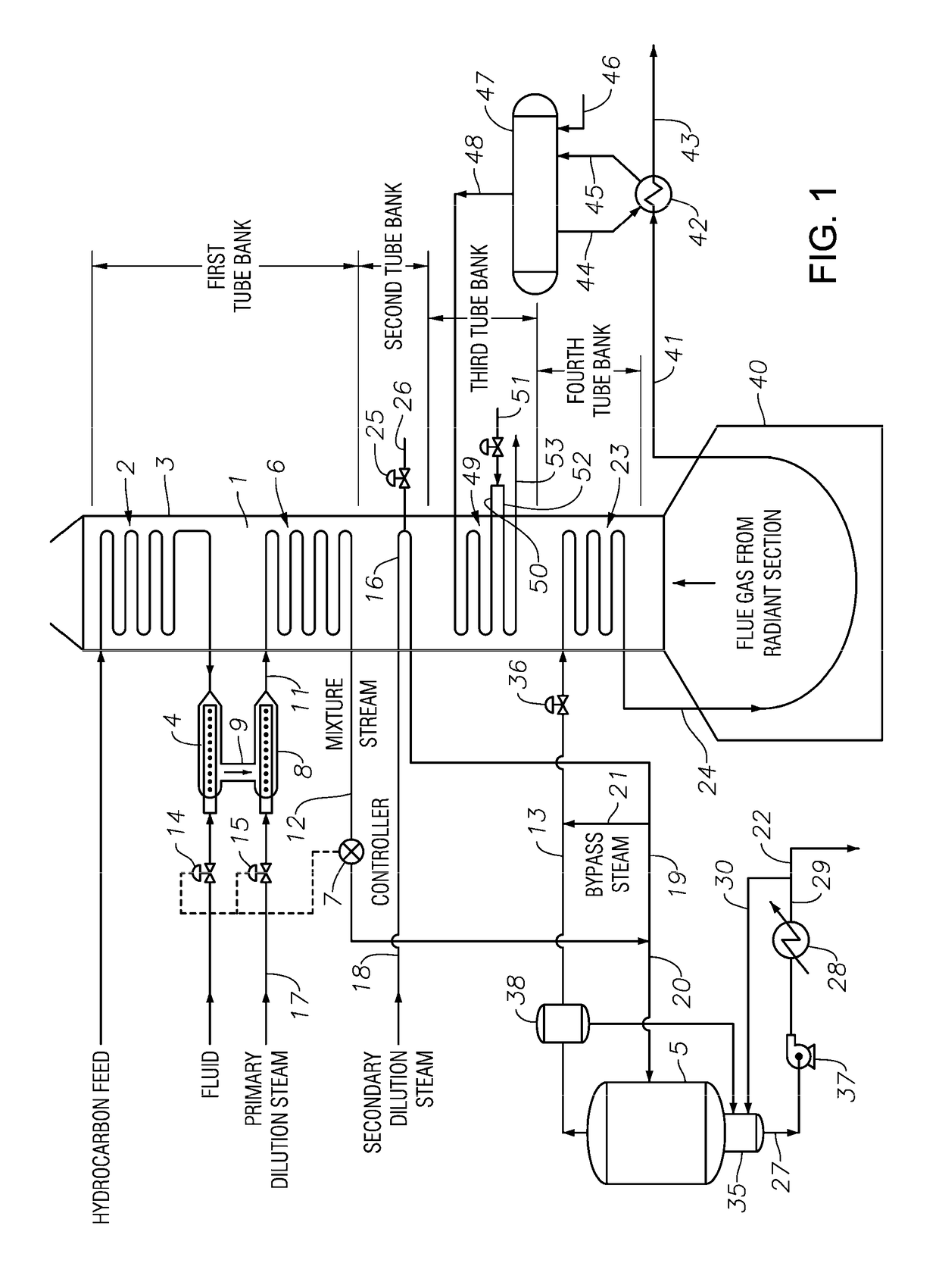
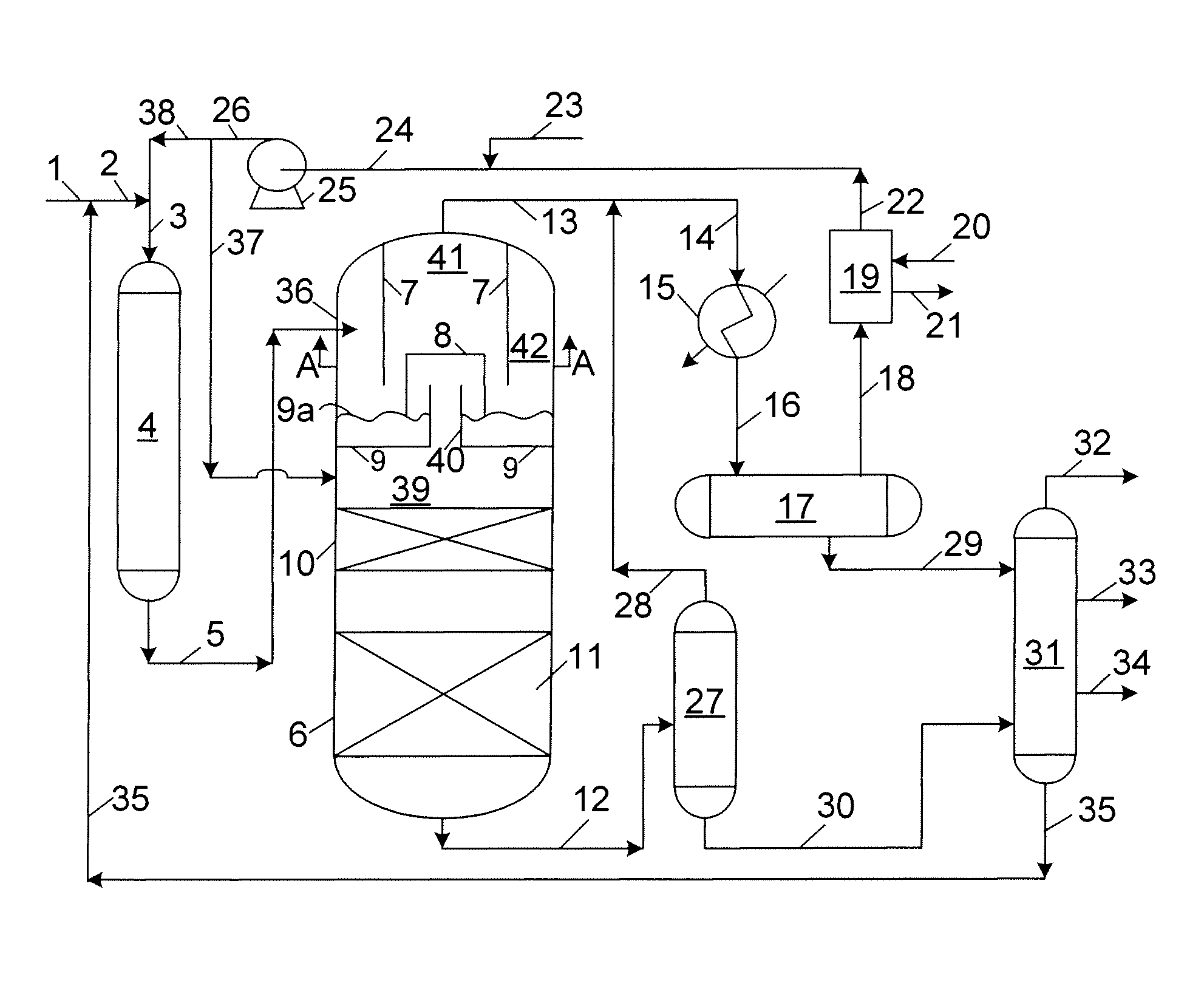
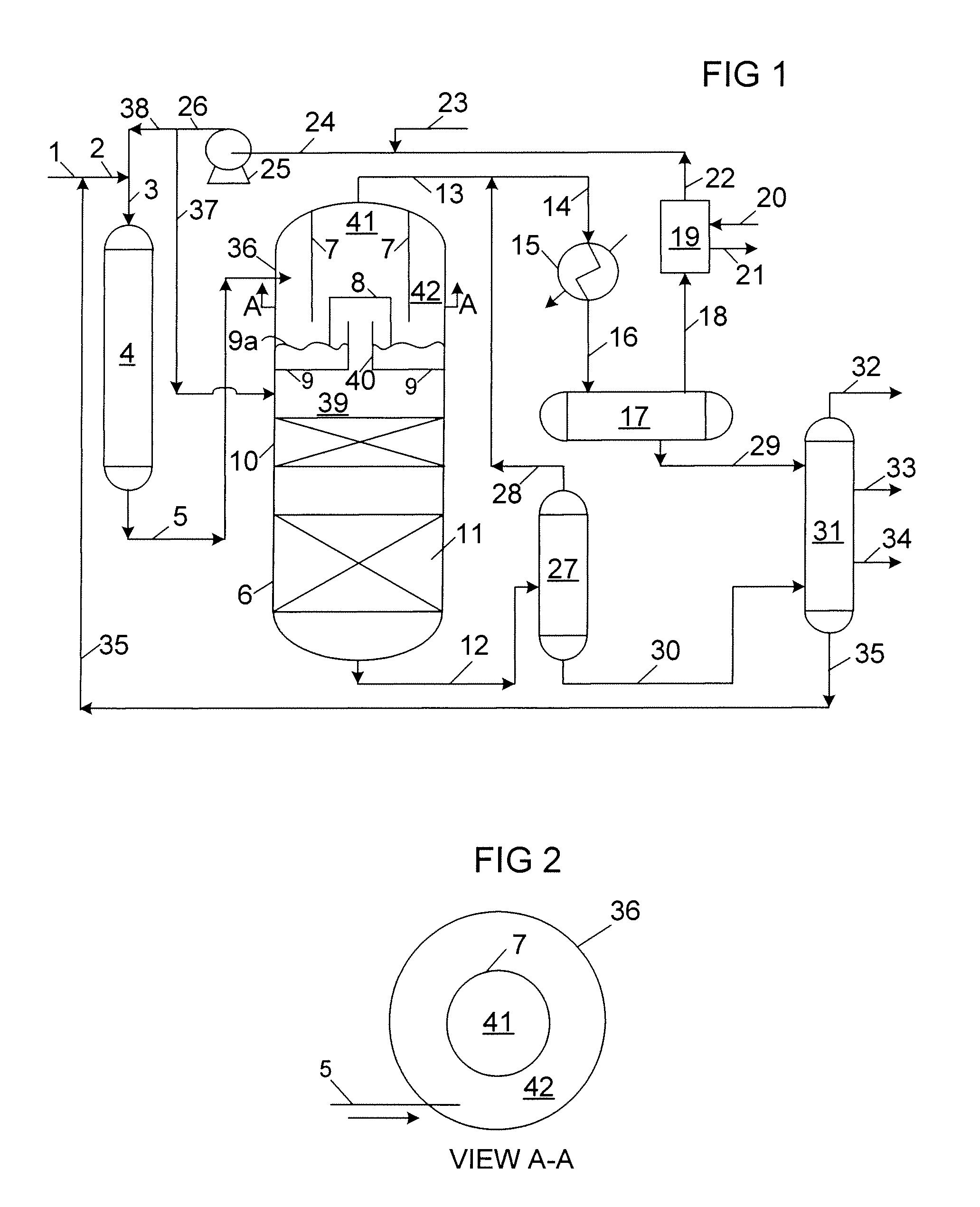
Methods of hydrotreating a mixture made up of oils of animal or vegetable origin and of petroleum cuts with intermediate stripping
ActiveUS7872165B2Low costControl consumptionThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingVegetable oilPlant Sources
A hydrotreating method (HDT) utilizes two plants working under different operating conditions with an intermediate stripping for co-treating a mixture made up of oils of vegetable or animal origin and petroleum cuts (gas oil cuts (GO) and middle distillates) in order to produce gas oil fuel bases meeting specifications. The first plant (HDT1) is more particularly dedicated to the reactions concerning oils of vegetable or animal origin in comixture while pretreating the hydrocarbon feed, whereas the second plant (HDS2) works under more severe conditions to obtain diesel fuel according to standards, in particular in terms of effluent sulfur content, density and cold properties.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Dividing wall separation in light olefin hydrocarbon processing
ActiveUS20080081937A1Speed up the processIncrease volumeThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNaphthaCell separation
Processing schemes and arrangements for application of a dividing wall separation column in the processing of an effluent resulting from FCC processing modified for increased light olefin production. The dividing wall separation column desirably splits a naphtha feedstock produced or resulting from such modified FCC processing to produce or form a light fraction containing C5-C6 compounds, an intermediate fraction containing C7-C8 compounds and a heavy fraction containing C9+ compounds.
Owner:UOP LLC
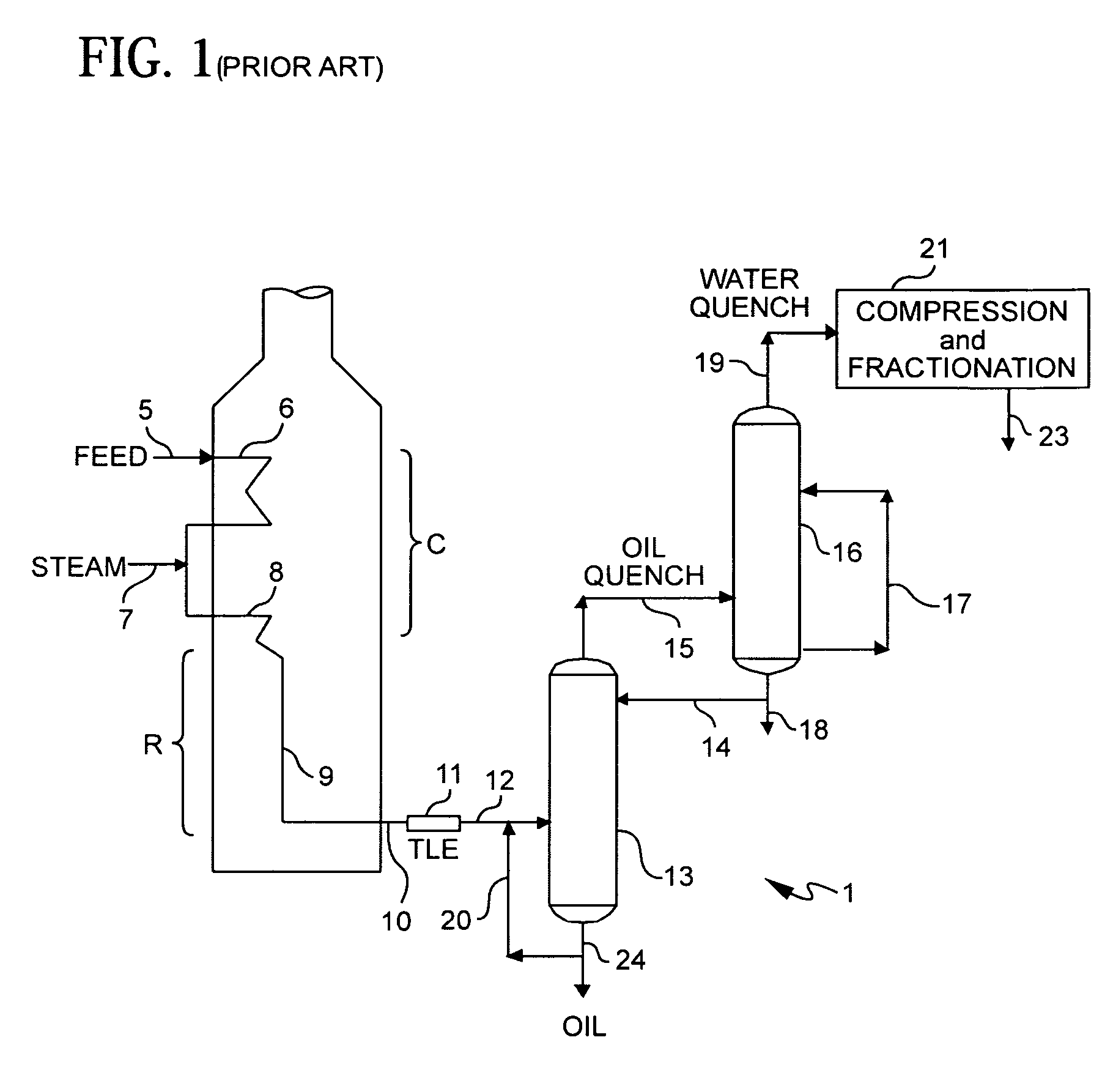
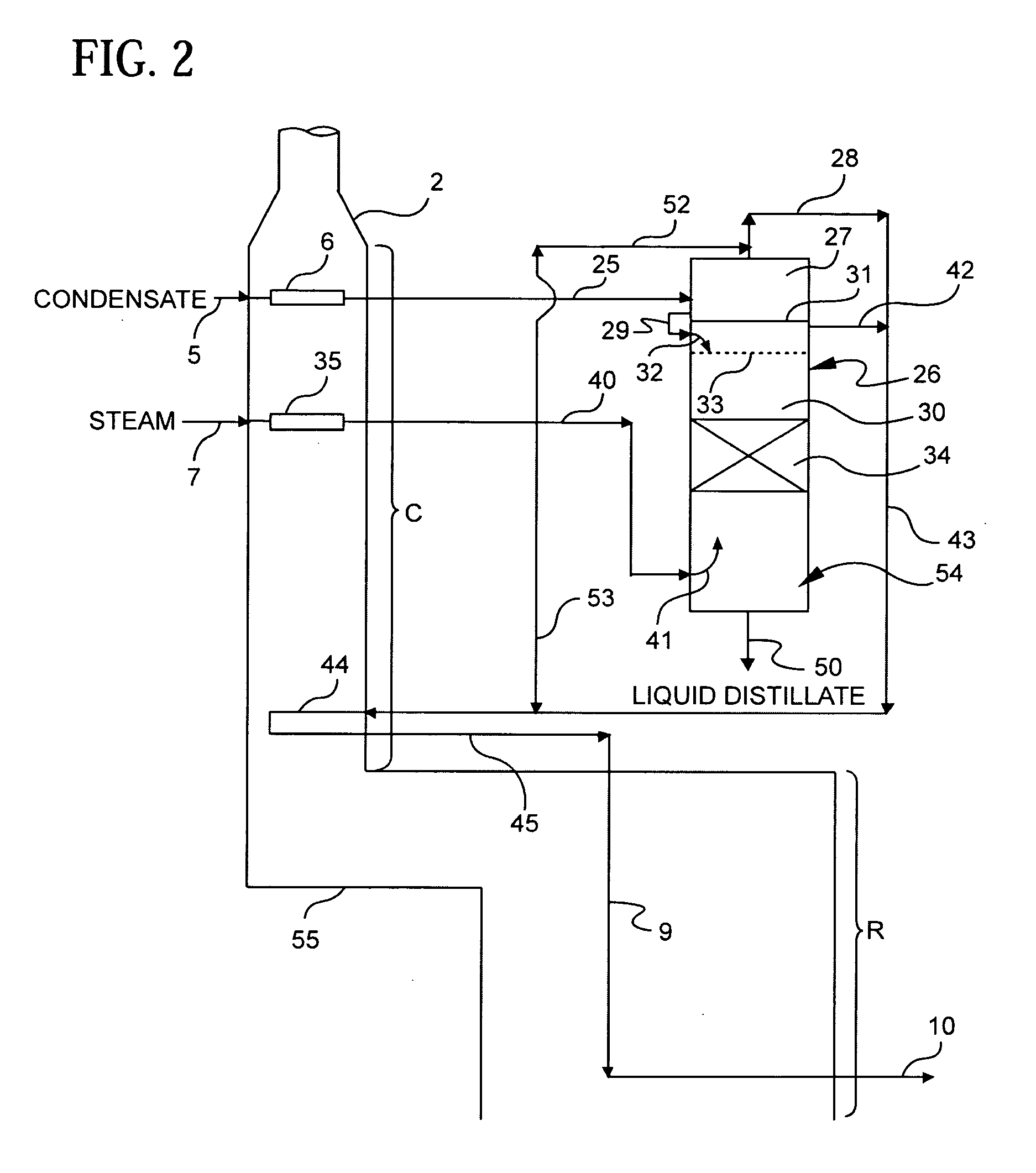
Method for processing hydrocarbon pyrolysis effluent
ActiveUS20070007170A1Tar temperatureLow viscosityThermal non-catalytic crackingCombination devicesTarToluene
A method is disclosed for treating gaseous effluent from a hydrocarbon pyrolysis unit to provide steam cracked tar of reduced asphaltene and toluene insolubles content. The method is suitable for preparing reduced viscosity tar useful as a fuel blending stock, or feedstock for producing carbon black, while reducing or eliminating the need for externally sourced lighter aromatics additives to meet viscosity specifications. The method comprises drawing steam cracked tar from a separation vessel, e.g., a primary fractionator or tar knock-out drum, cooling the tar, and returning it to the separation vessel to effect lower overall tar temperatures within the separation vessel, in order to reduce viscosity increasing condensation reactions. An apparatus for carrying out the method is also provided.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Method For Processing Hydrocarbon Pyrolysis Effluent
InactiveUS20120024749A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingVapor–liquid separatorProcess engineering
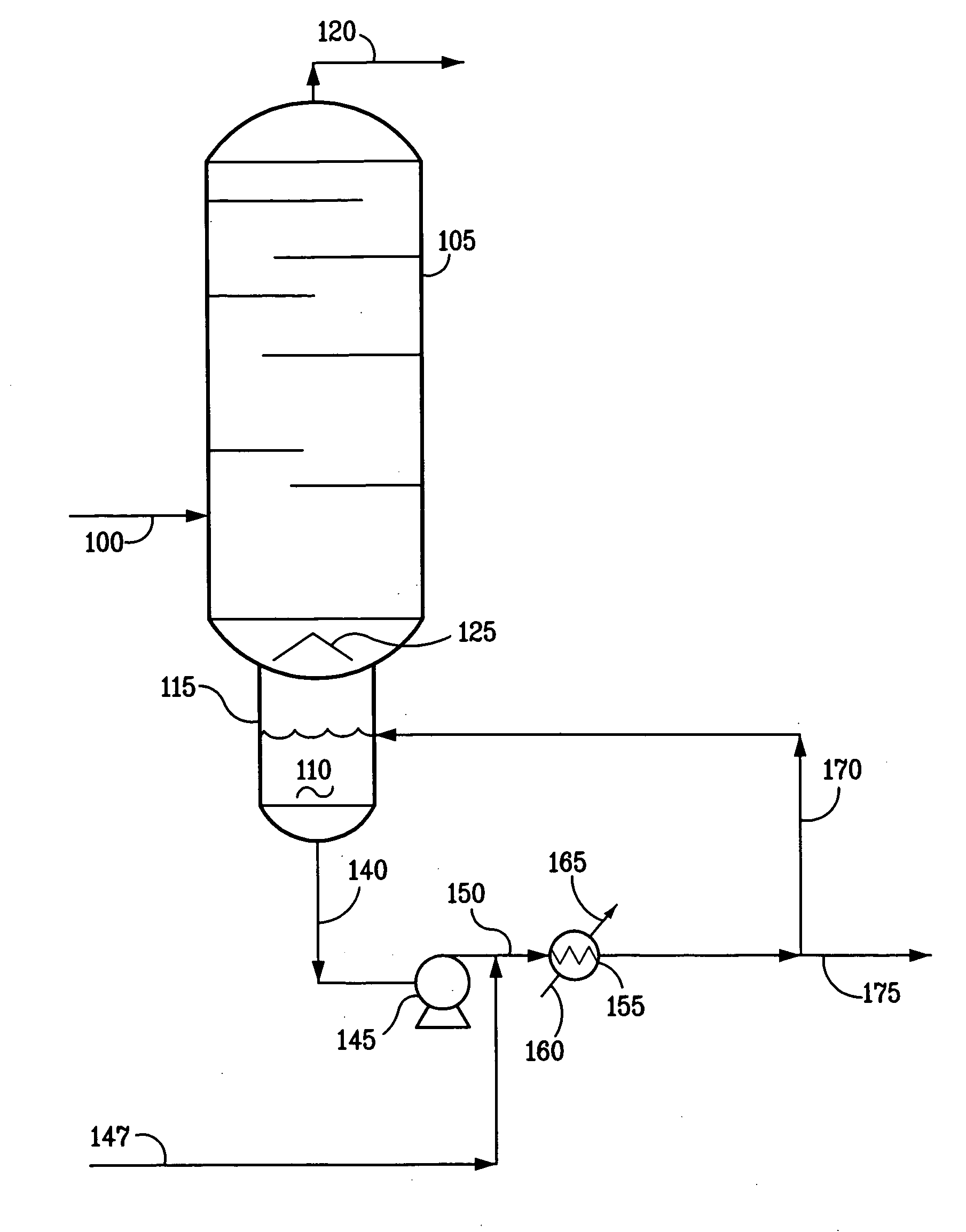
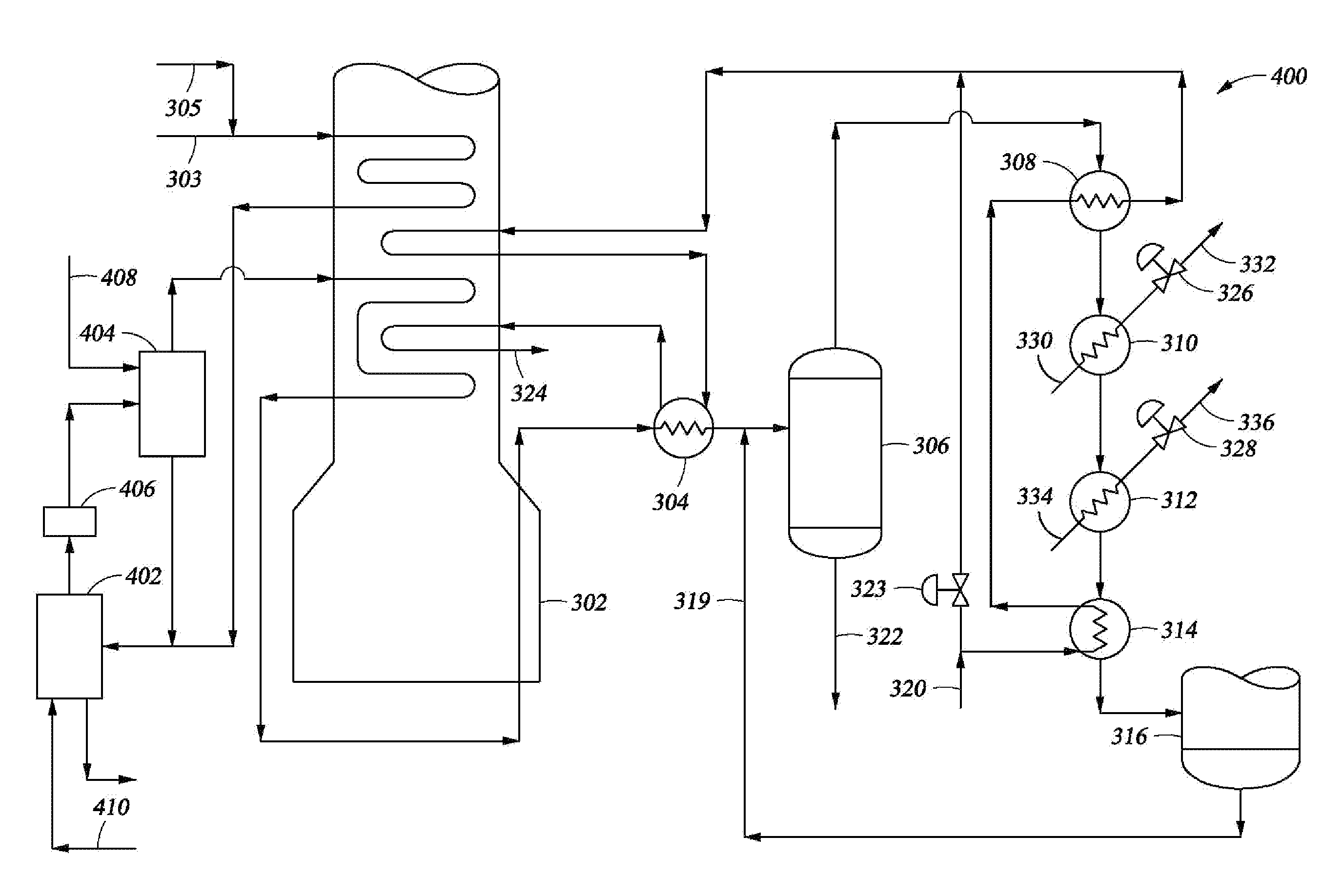
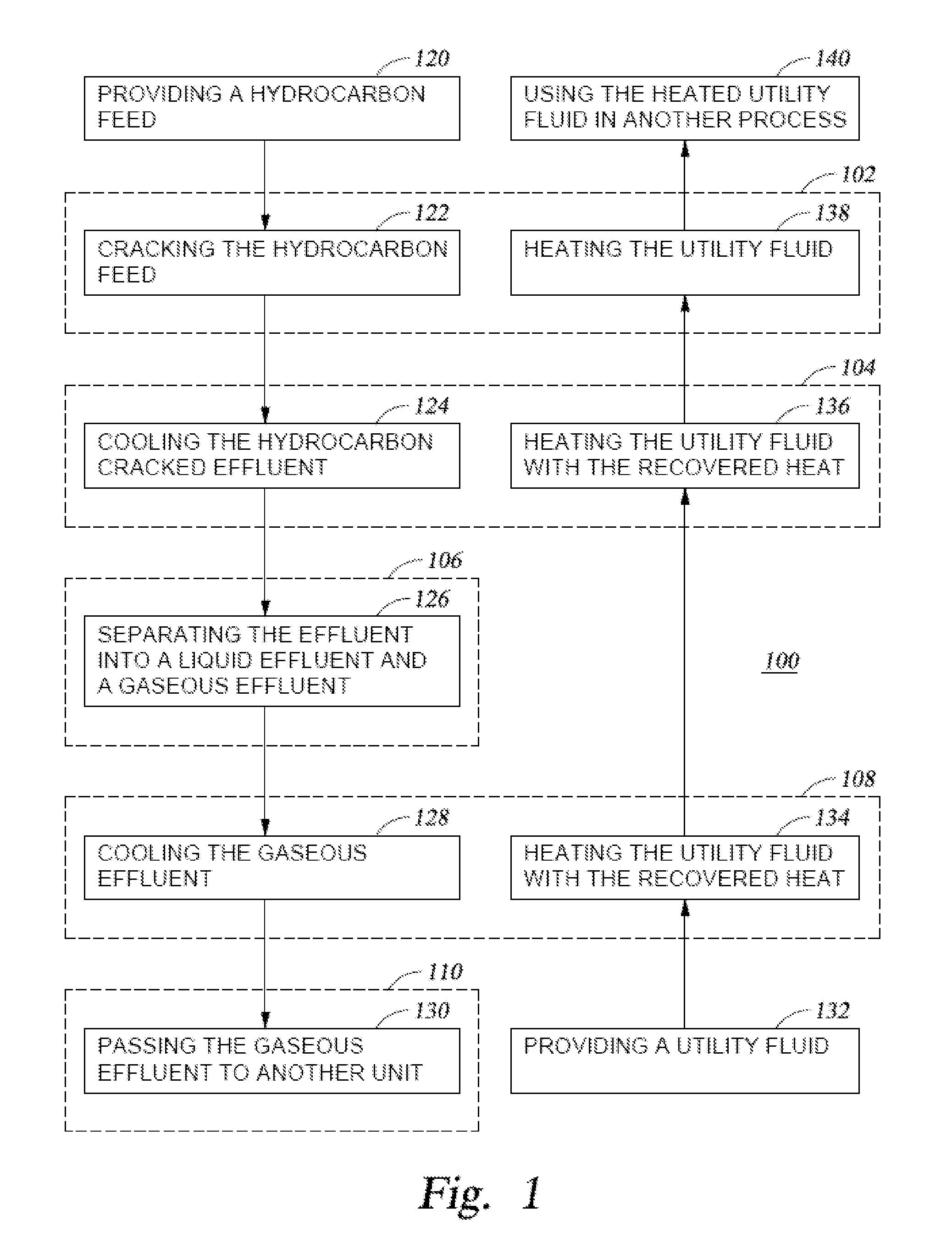
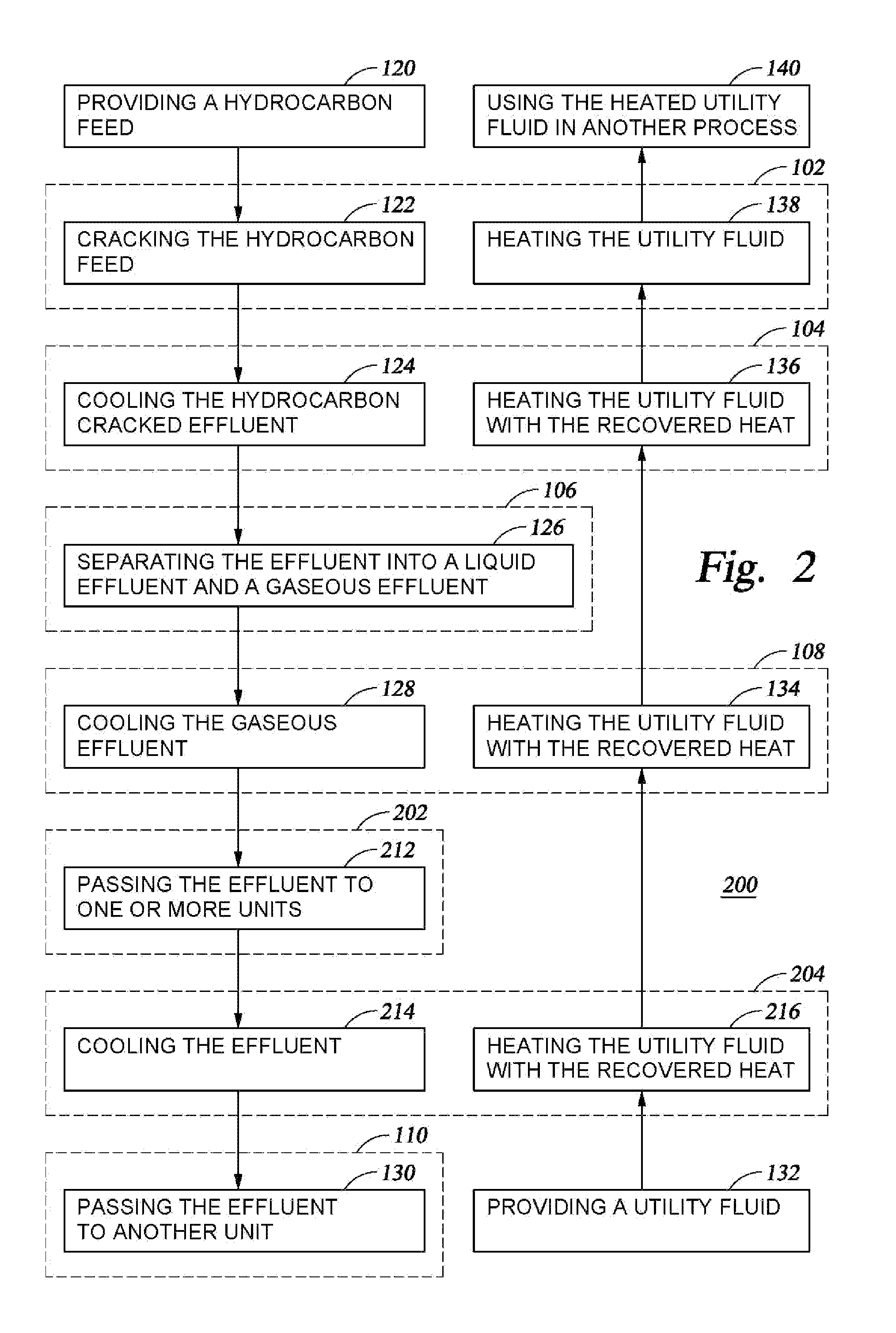
A method and system are disclosed for treating the effluent from a hydrocarbon pyrolysis unit employing a small primary fractionator. The method comprises cooling the effluent from a furnace through a first heat exchanger, a vapor-liquid separator, and a second heat exchanger before it is passed to a fractionator for further processing. These heat exchangers may also be utilized to heat a utility fluid as part of the cooling process. Further, one or more generators and a third heat exchanger may also be used to assist in heat recovery for the process.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
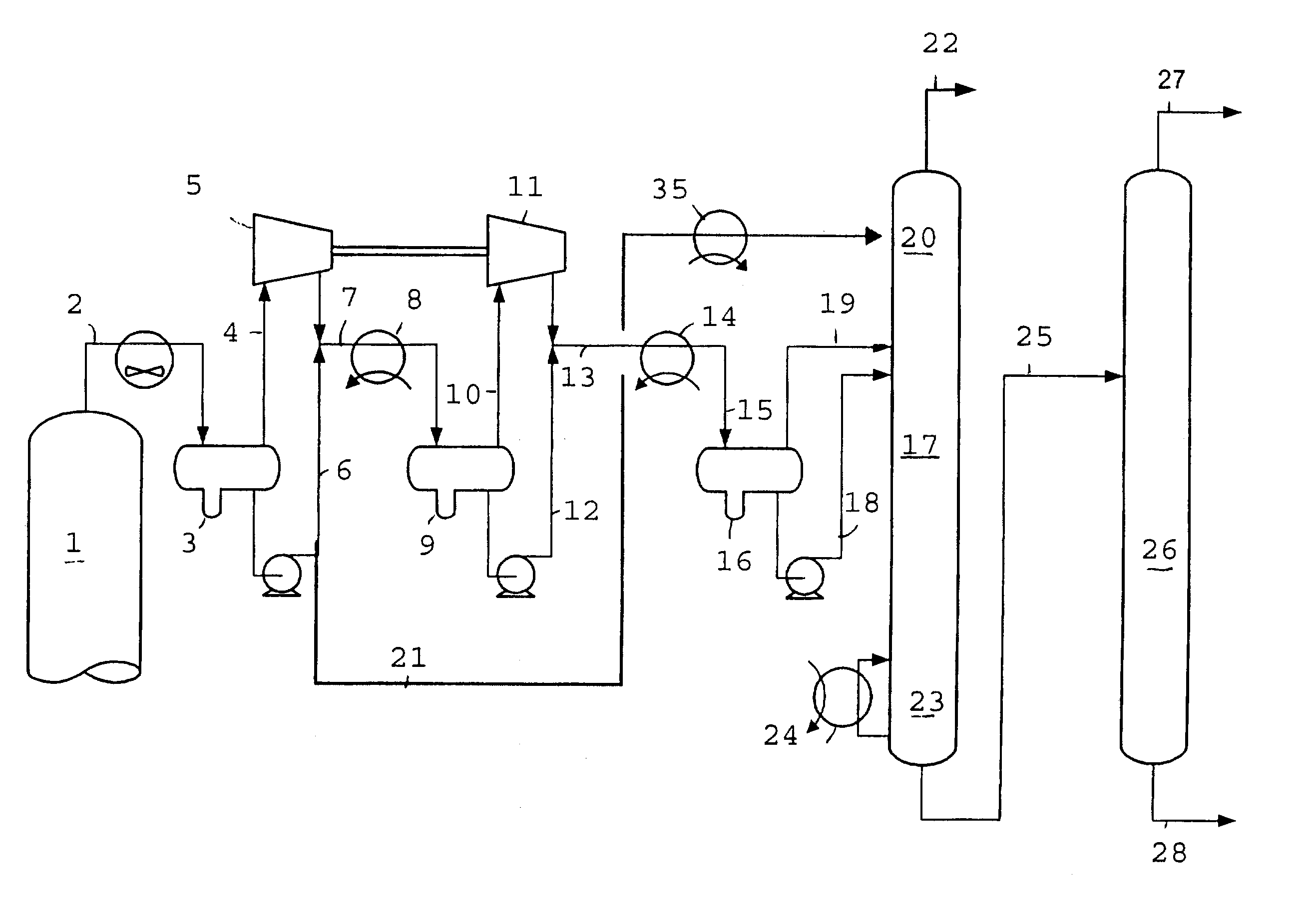
Hydrocracking process
InactiveUS7041211B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingHydrogenation reactionReaction zone
A hydrocracking process wherein a hydrocarbonaceous feedstock and hydrogen is passed to a denitrification and desulfurization reaction zone and then directly to a hot, high pressure stripper utilizing a hot, hydrogen-rich stripping gas to produce a liquid hydrocarbonaceous stream which is passed to a hydrocracking zone. The resulting effluent from the hydrocracking zone is then directly passed to the hot, high pressure stripper. A vapor stream from the hot, high pressure stripper is passed to a post-treat hydrogenation reaction zone to saturate at least a portion of the aromatic compounds contained therein.
Owner:UOP LLC
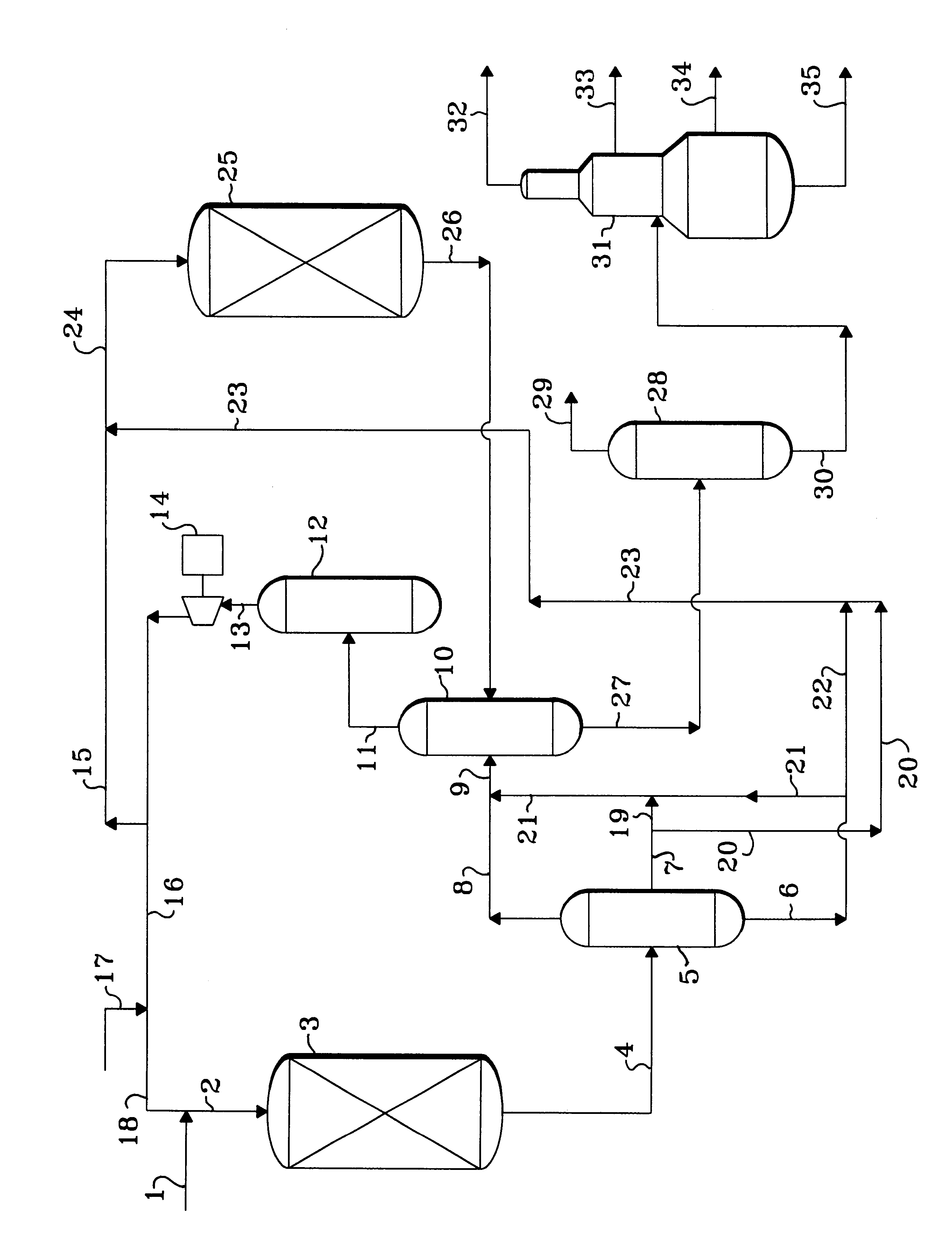
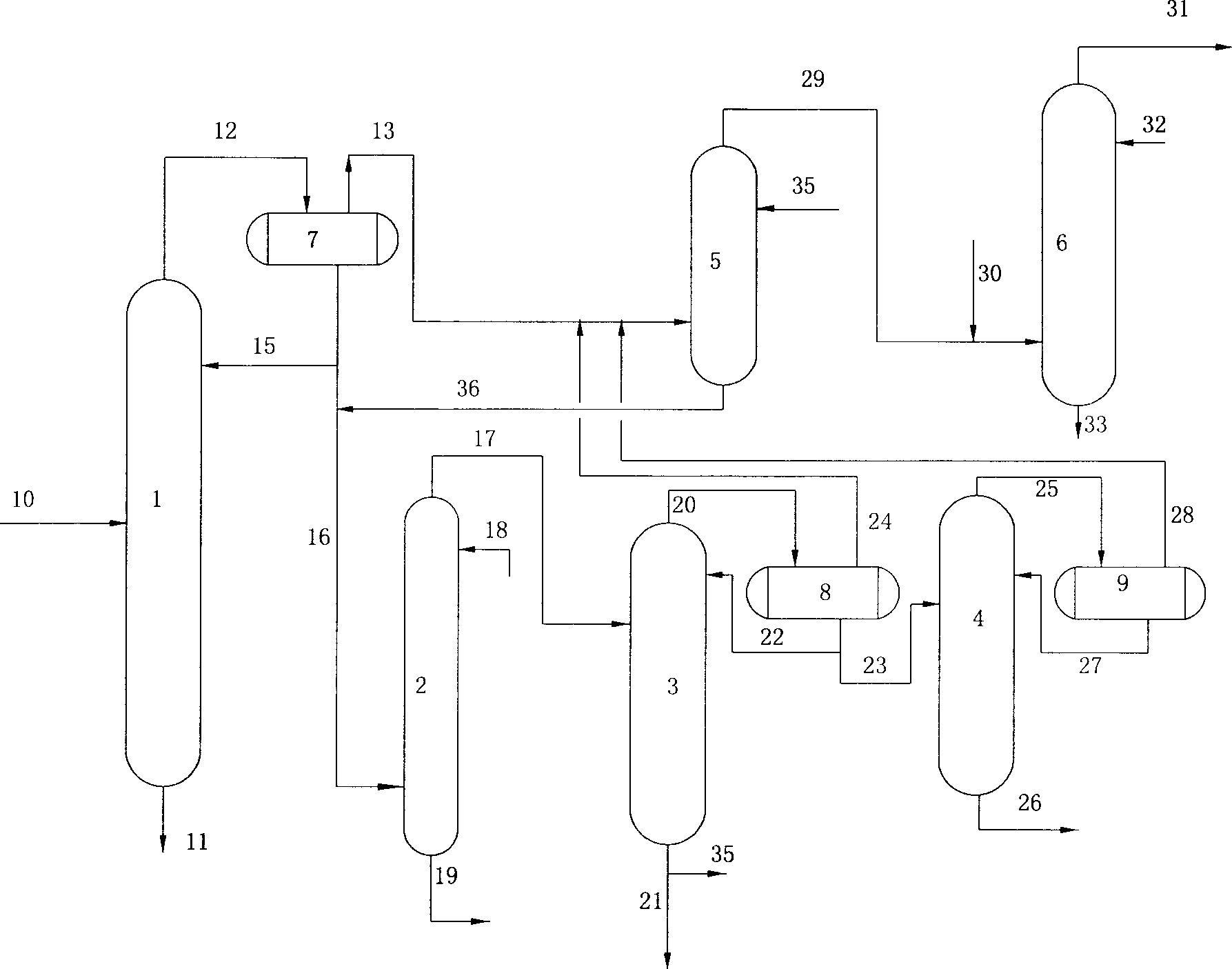
Method for separating hydrocarbon hydrocracking products
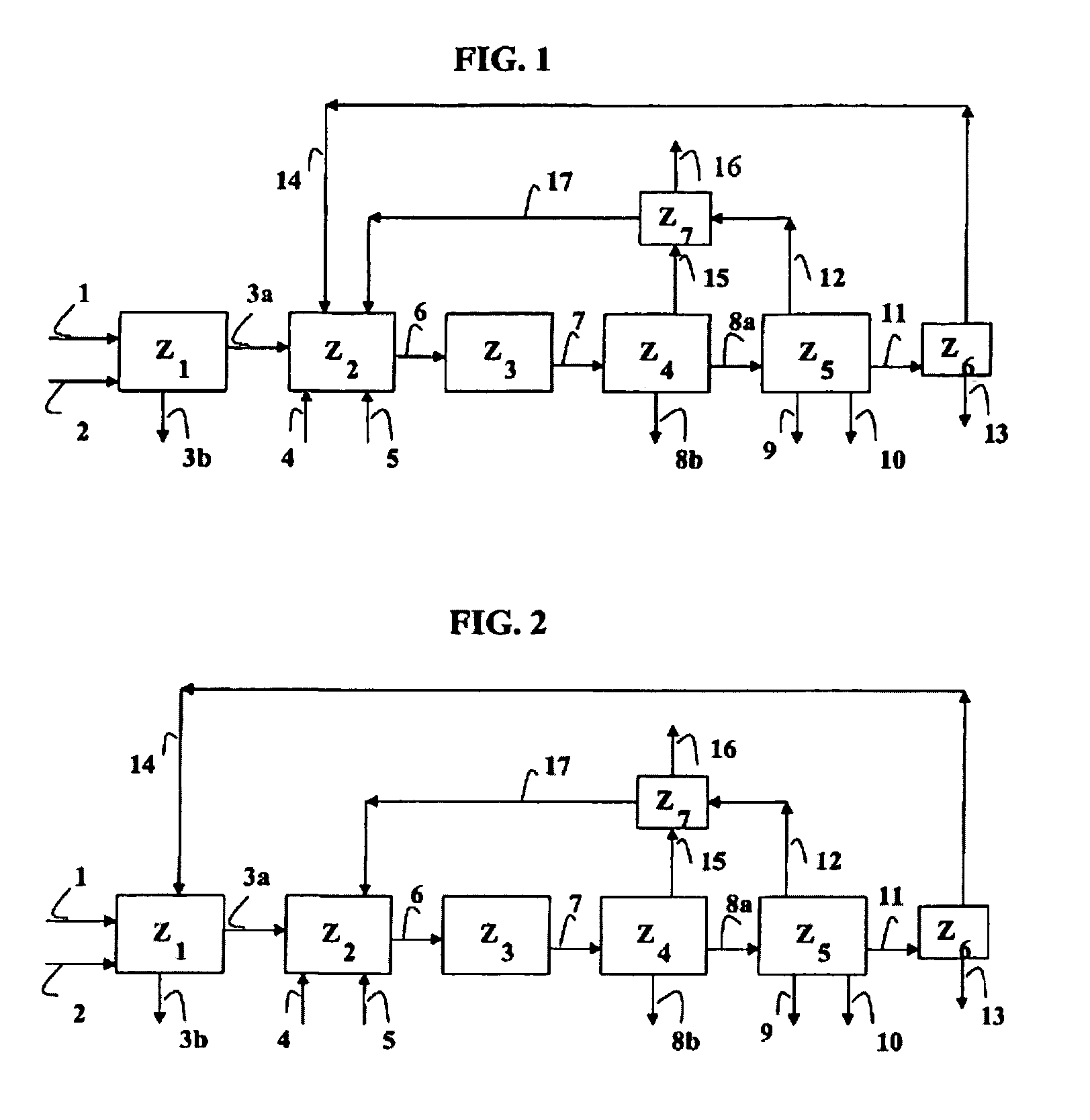
The separation method of hydrocracked product of hydrocarbons incldudes stabilization tower, hydrogen sulfide washing tower, debutanizing tower, deethanizing column and light hydrocarbon absorption tower. The stabilizatino tower is designed according to cutting portion or all C6 component, the absorption oil of light hydrocarbon absorption tower is from tower bottom product flow of debutanizing tower, the overhead gas of stabilizaltion tower, overhead gas of debutanizing tower and overhead gas of deethanizing column are mixed, and fed into light hydrocarbon absorption tower to recover light hydrocarbon, and the tower bottom rich absorption oi lof light-hydrocarbon absorption tower and hydrogen sulfide washing tower feeding material coming from stabilizatino tower and mixed, and fed into hydrogen sulfide washing tower. The C3 and C4 components can be completely recovered, and its liquified gas yield is high.
Owner:LUOYANG PETROCHEMICAL ENG CORP SINOPEC
Process for hydrocracking a hydrocarbon feedstock
ActiveUS7419582B1Reduce concentrationReduce business costsThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingThermodynamicsPtru catalyst
A hydrocracking process wherein the feedstock is hydrotreated and the liquid and gaseous effluent from the hydrotreater is directly introduced into the upper end of a hydrocracking vessel which provides a liquid seal to prevent the passage of the gaseous stream containing hydrogen sulfide and ammonia from the hydrotreater to enter the hydrocracking zone containing hydrocracking catalyst. Fresh hydrogen is then introduced into the hydrocracking zone. An apparatus for hydrocracking a hydrocarbon feedstock is also disclosed.
Owner:UOP LLC
Olefin production utilizing condensate feedstock
InactiveUS20070208207A1Maximizes recovery of distillateMaximize recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNatural-gas condensateVaporization
A method for utilizing natural gas condensate as a feedstock for an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock is subjected to vaporization and separation conditions that remove light hydrocarbons from the condensate for thermal cracking in the plant, and leave liquid distillate for separate recovery.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Process for the treatment of a hydrocarbon feedstock
ActiveUS20060021914A1Maximize recoveryReduce lossesThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingHydrogenHydrocarbon
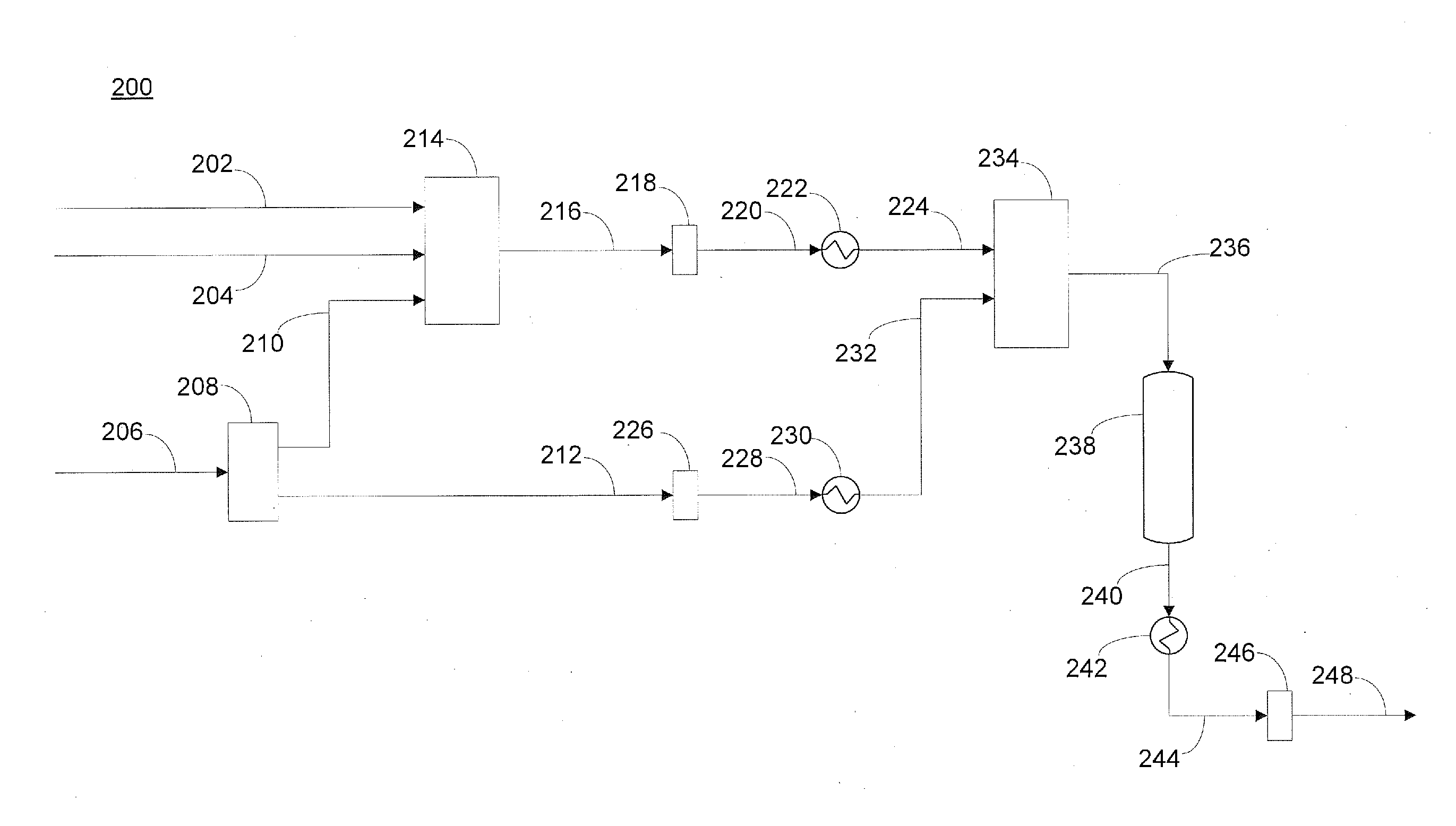
Process for treatment of a hydrocarbon feedstock that comprises a hydrocarbon-containing liquid phase and hydrogen, in which the feedstock is separated under a pressure P1 into a liquid L1 and a gas G1, that is compressed and brought into contact with a portion of L1 under a pressure P2>2×P1 to recover a liquid L2 and a hydrogen-rich gas G2; L2 is fractionated to obtain a stabilized liquid L4a that is free of LPG and lighter products, a liquid stream of LPG, and a gas stream G4 that is recycled, and in which one of gas streams: recompressed G1 and G4 is in counter-current contact with an unstabilized liquid AL that is obtained from or extracted from L1 or L2, whereby this unstabilized liquid is supercooled by at least 10° C. below its bubble point at pressure P2.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
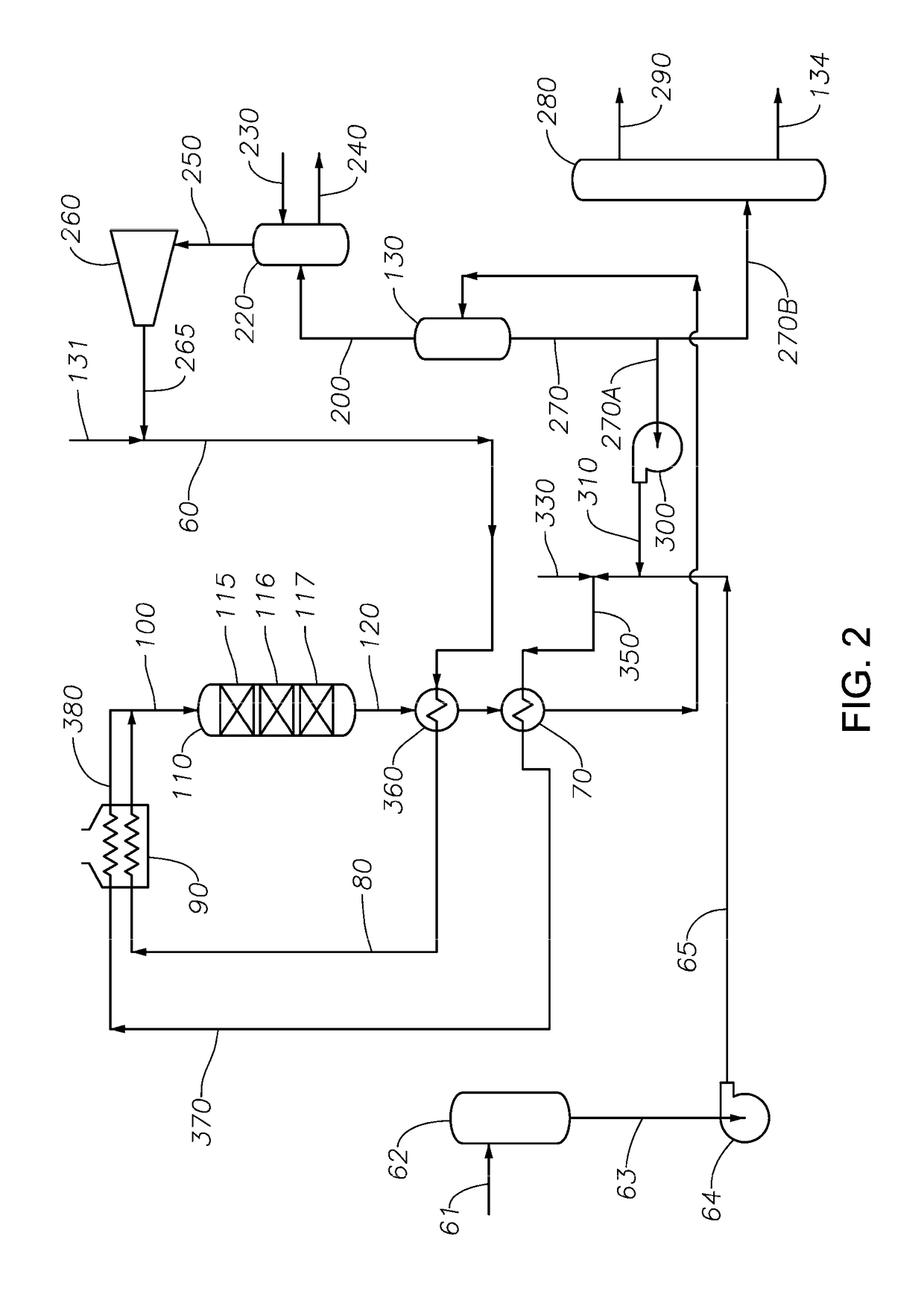
Process for the upgrading of the products of Fischer-Tropsch processes
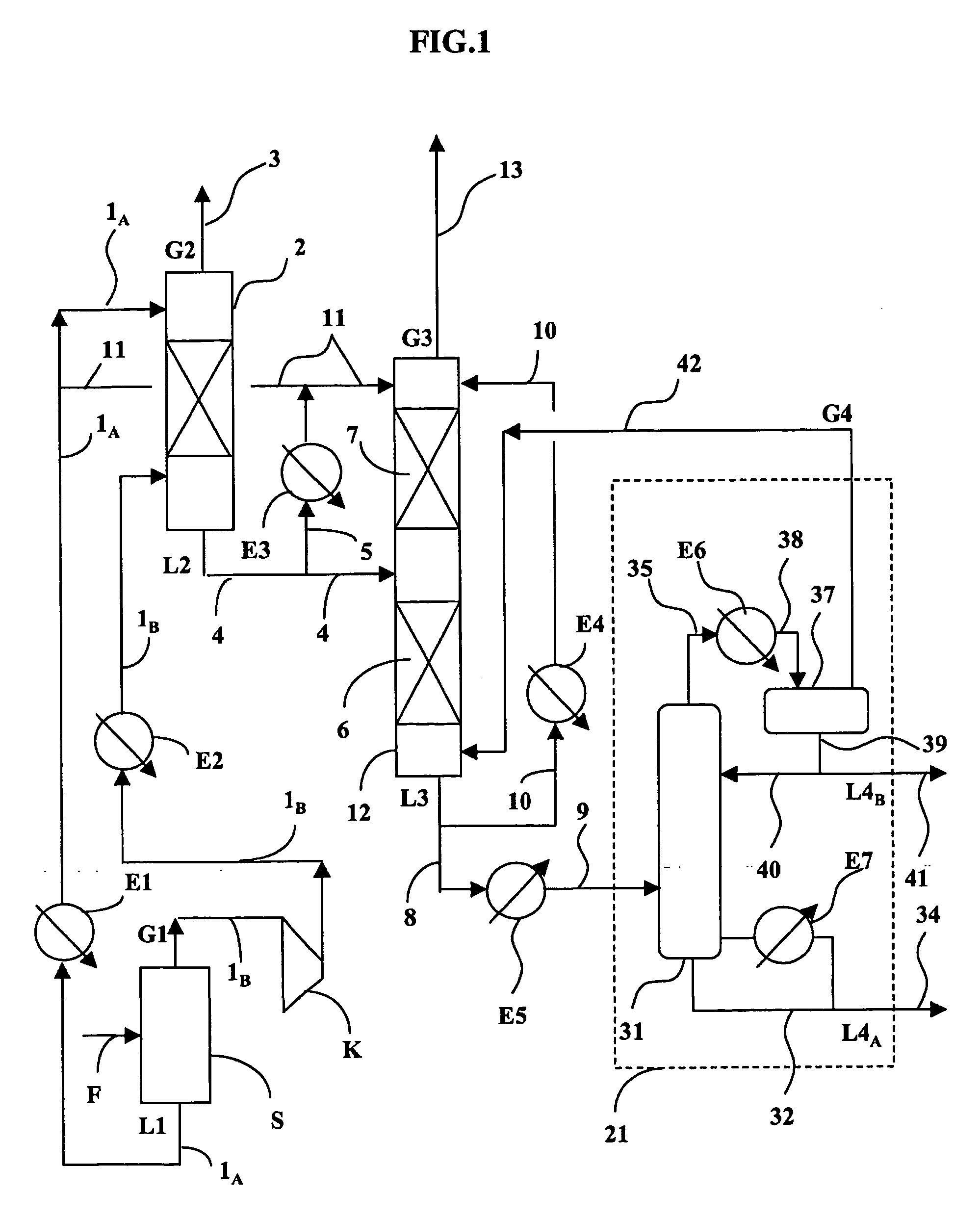
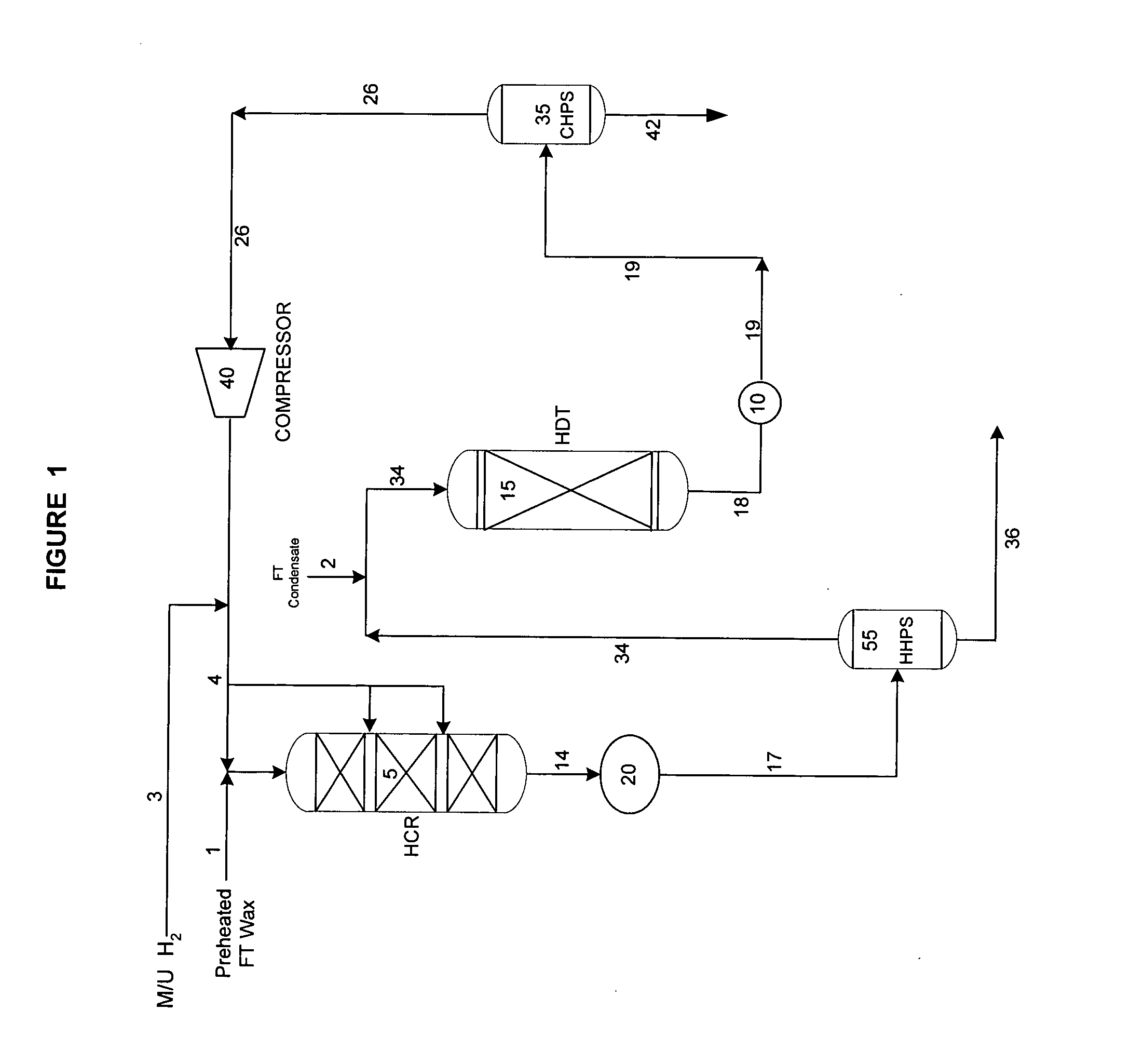
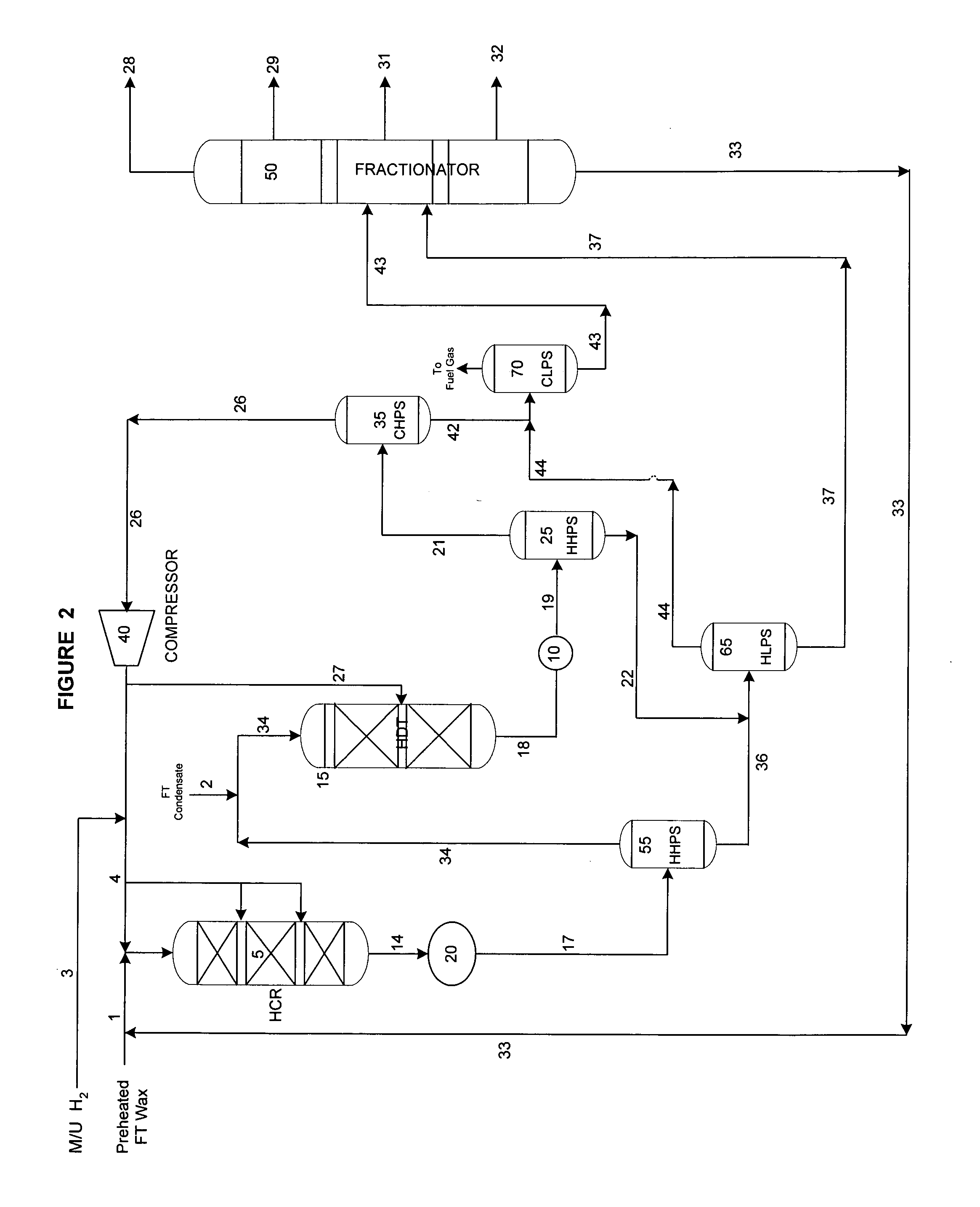
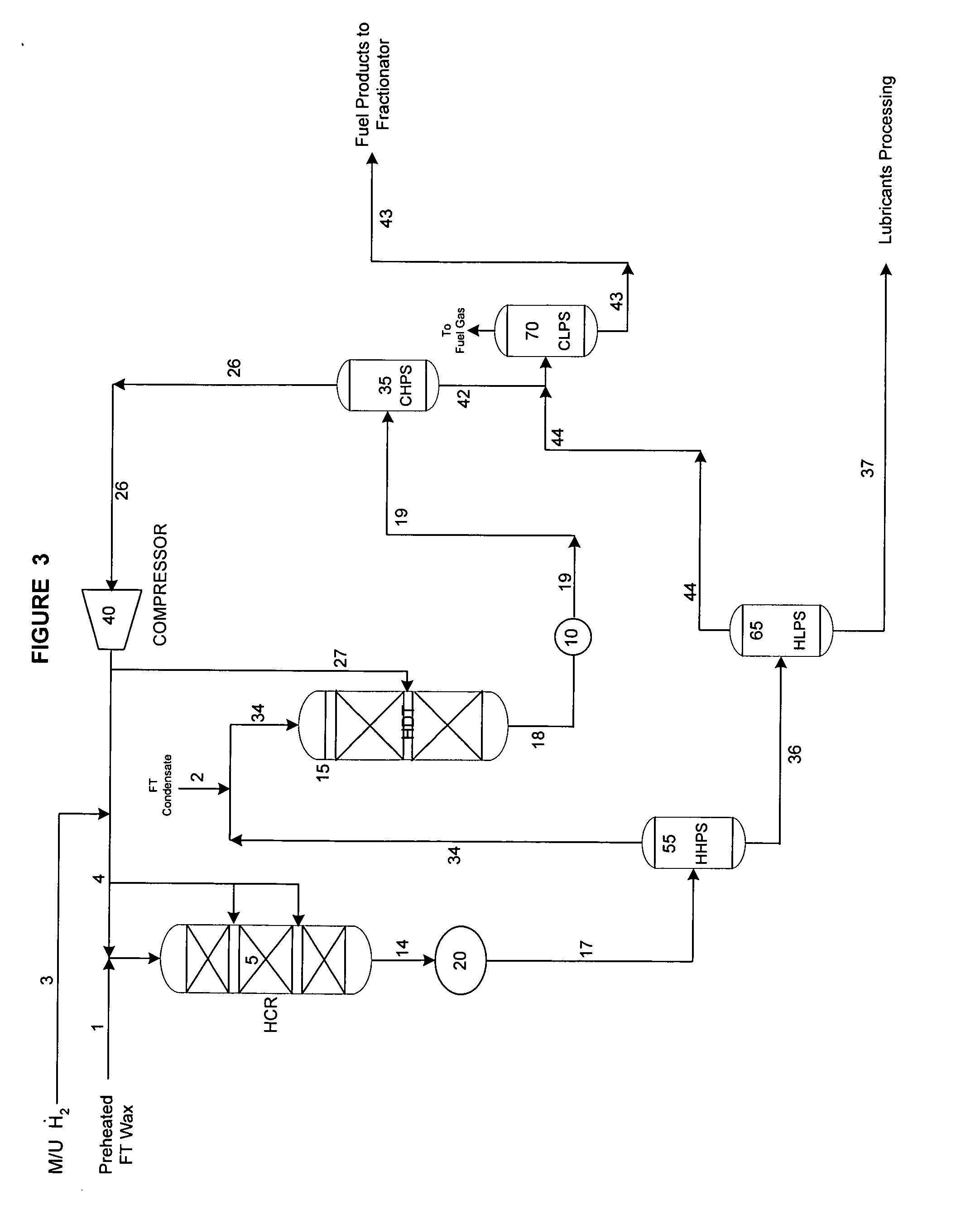
ActiveUS20050103683A1Reduce capital investmentIncrease productionThermal non-catalytic crackingOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOxygenateChain length
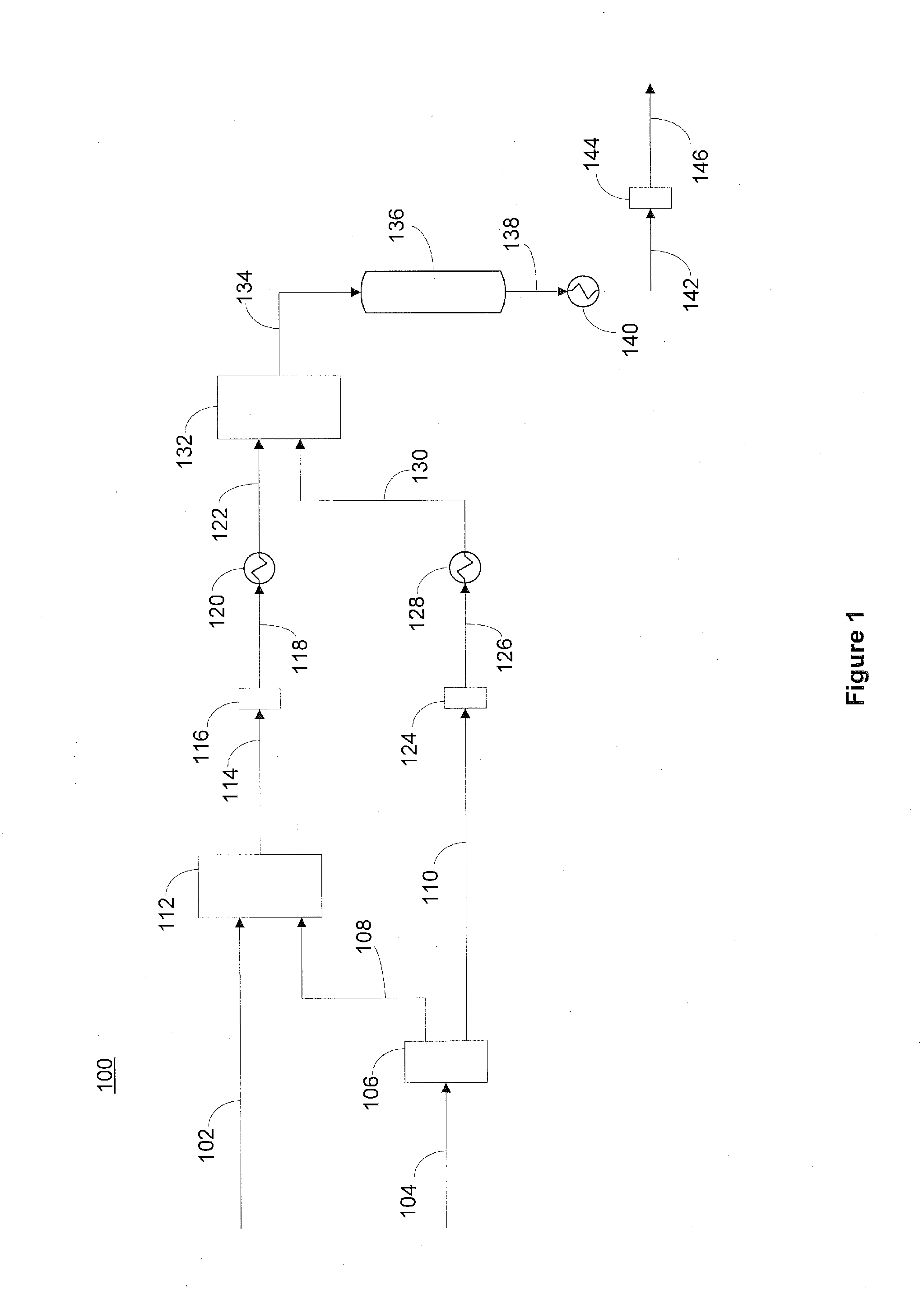
The present invention is directed to a method for hydroprocessing Fischer-Tropsch products. The invention in particular relates to an integrated method for producing liquid fuels from a hydrocarbon stream provided by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. The method involves separating the Fischer-Tropsch products into a light fraction (FT condensate) and a heavy fraction. The heavy fraction is subjected to hydrocracking conditions, preferably through multiple catalyst beds, to reduce the chain length. The products of the hydrocracking reaction following the last catalyst bed are subjected to a separation step. The lighter material is combined with the Fischer-Tropsch condensate and hydrotreated. The hydrotreatment conditions hydrogenate double bonds, reduce oxygenates to paraffins, and desulfurize and denitrify the products. The heavier material from the separation step is sent to the lube plant for hydroisomerization, or is subjected to subsequent fraction steps to produce fuels and middle distillates.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Pyrolysis Tar Upgrading Using Recycled Product
ActiveUS20150368570A1Pyrolysis tar hydroprocessing is improvedLesser rateRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonTreatment with plural serial stages onlyBoiling pointTar
The invention relates to a process for upgrading pyrolysis tar in the presence of a utility fluid. The utility fluid contains 1-ring and / or 2-ring aromatics and has a final boiling point ≦430° C. The invention also relates to the upgraded pyrolysis tar, and to the use of the upgraded pyrolysis tar, e.g., for fuel oil blending.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Pitch composition
ActiveUS20100326882A1Alleviate cokingReduce cracking concernWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumenWorking-up tarParticulatesSlurry
A process and apparatus is disclosed for converting heavy hydrocarbon feed into lighter hydrocarbon products. The heavy hydrocarbon feed is slurried with a particulate solid material to form a heavy hydrocarbon slurry and hydrocracked in a slurry hydrocracking unit to produce vacuum gas oil (VGO) and pitch. A first vacuum column separates VGO from pitch, and a second vacuum column further separates VGO from pitch. As much as 15 wt-% of VGO can be recovered by the second vacuum column and recycled to the slurry hydrocracking unit. A pitch composition is obtained which can be made into particles and transported without sticking together.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for selectively producing C3 olefins in a fluid catalytic cracking process with recycle of a C4 fraction to a secondary reaction zone separate from a dense bed stripping zone
InactiveUS7374660B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyPtru catalystNaphtha
A process for selectively producing C3 olefins from a catalytically cracked or thermally cracked naphtha stream is disclosed herein. The naphtha stream is introduced into a process unit comprised of a reaction zone, a stripping zone containing a dense phase, a catalyst regeneration zone, and a fractionation zone. The naphtha feedstream is contacted in the reaction zone with a catalyst containing from about 10 to about 50 wt. % of a crystalline zeolite having an average pore diameter less than about 0.7 nanometers at reaction conditions. Vapor products are collected overhead and the catalyst particles are passed through the stripping zone on the way to the catalyst regeneration zone. Volatiles are stripped with steam in the stripping zone and the catalyst particles are sent to the catalyst regeneration zone where coke is burned from the catalyst, and are then recycled to the reaction zone. Overhead products from the reaction zone are passed to a fractionation zone where a stream of C3 products is recovered and a stream rich in C4 olefins is recycled to a dilute phase reaction zone in the stripping zone separate from the dense phase of the stripping zone. The olefins can be further processed and polymerized to form a variety of polymer materials.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com