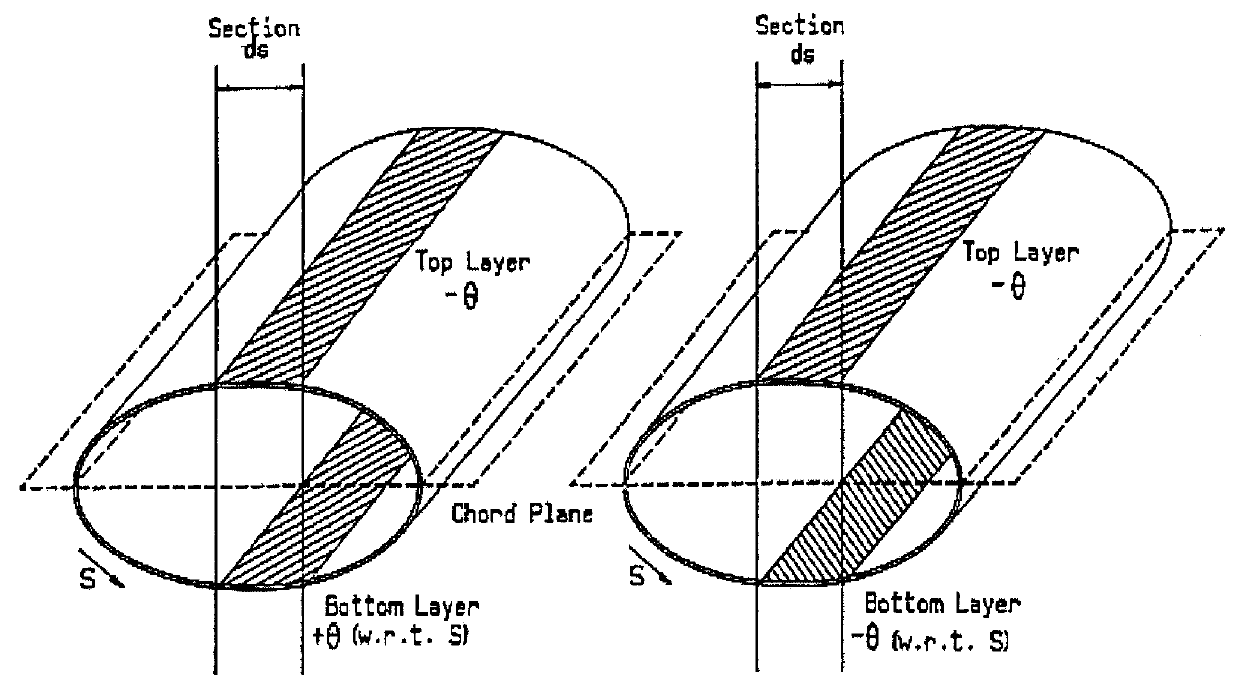
Load attenuating passively adaptive wind turbine blade
a passive adaptive, wind turbine technology, applied in passive/reactive control, vessel construction, marine propulsion, etc., can solve the problems of changing loads and affecting output power, affecting fatigue life throughout the system, and small twisting angles that can have significant impa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
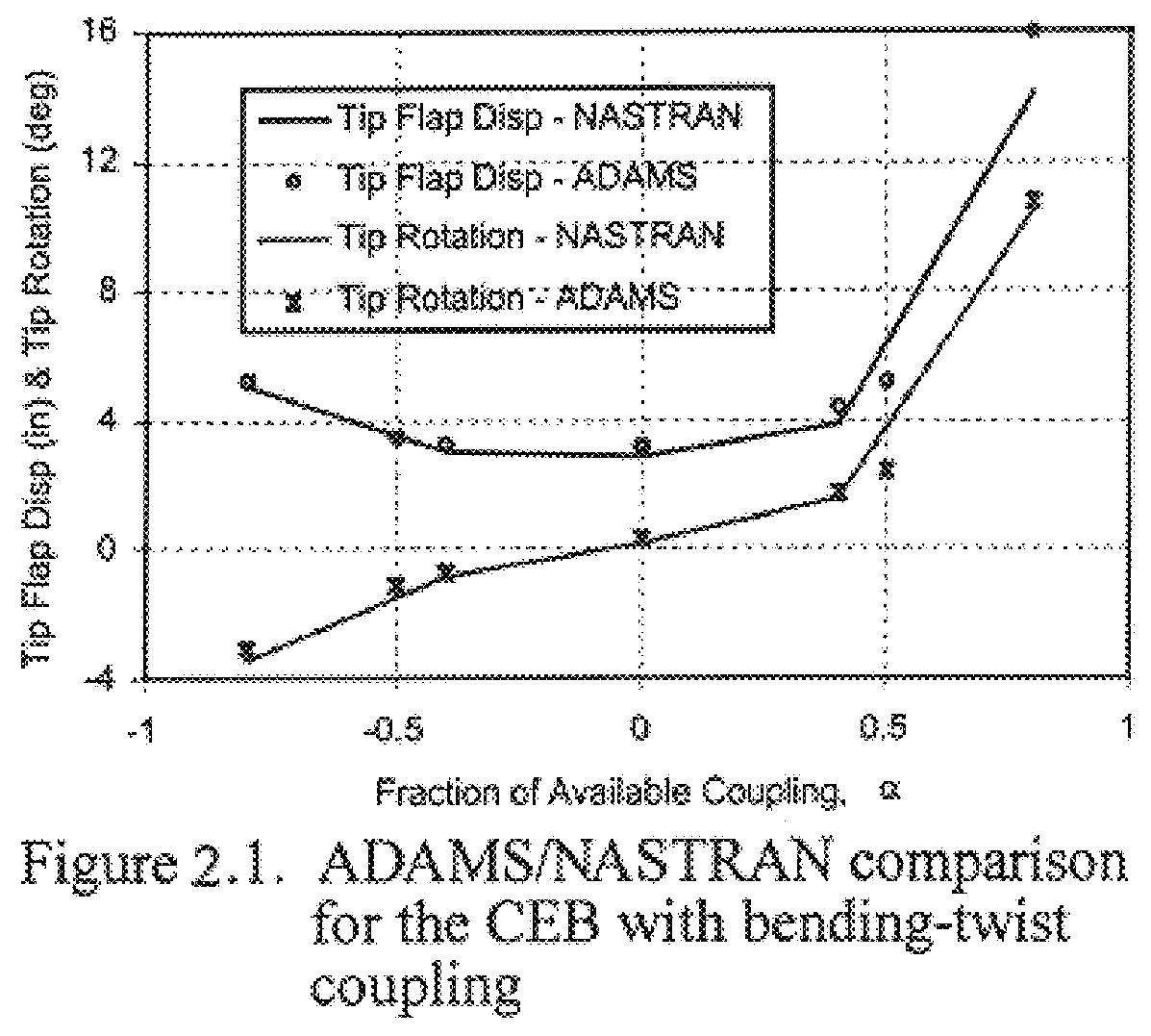
The analysis for the bending-twist coupled blade according to the invention was carried out within the confines of beam finite element theory. The coupling terms for the beam elements are generated starting with beam "stress- strain" relations. For bending-twist coupling the "stress-strain" relations at a point along the blade span are given by Equation 1: ##EQU1##
Here, .theta.=.delta..upsilon. / .delta.x is the flapwise slope of the blade, .upsilon. is the flapwise displacement, M.sub.b is the flapwise bending moment, .psi. is the blade twist, and M.sub.t is the twisting moment. The material parameters E and G are the Young's modulus and the shear modulus respectively; I represents the moment of inertia of the cross section and K the torsional moment of inertia (equal to the polar moment of inertia for circular sections). The quantity g, is the coupling term, and has a value of zero for the standard beam where no coupling is present. In order for this system to be positive definite (...
example 2
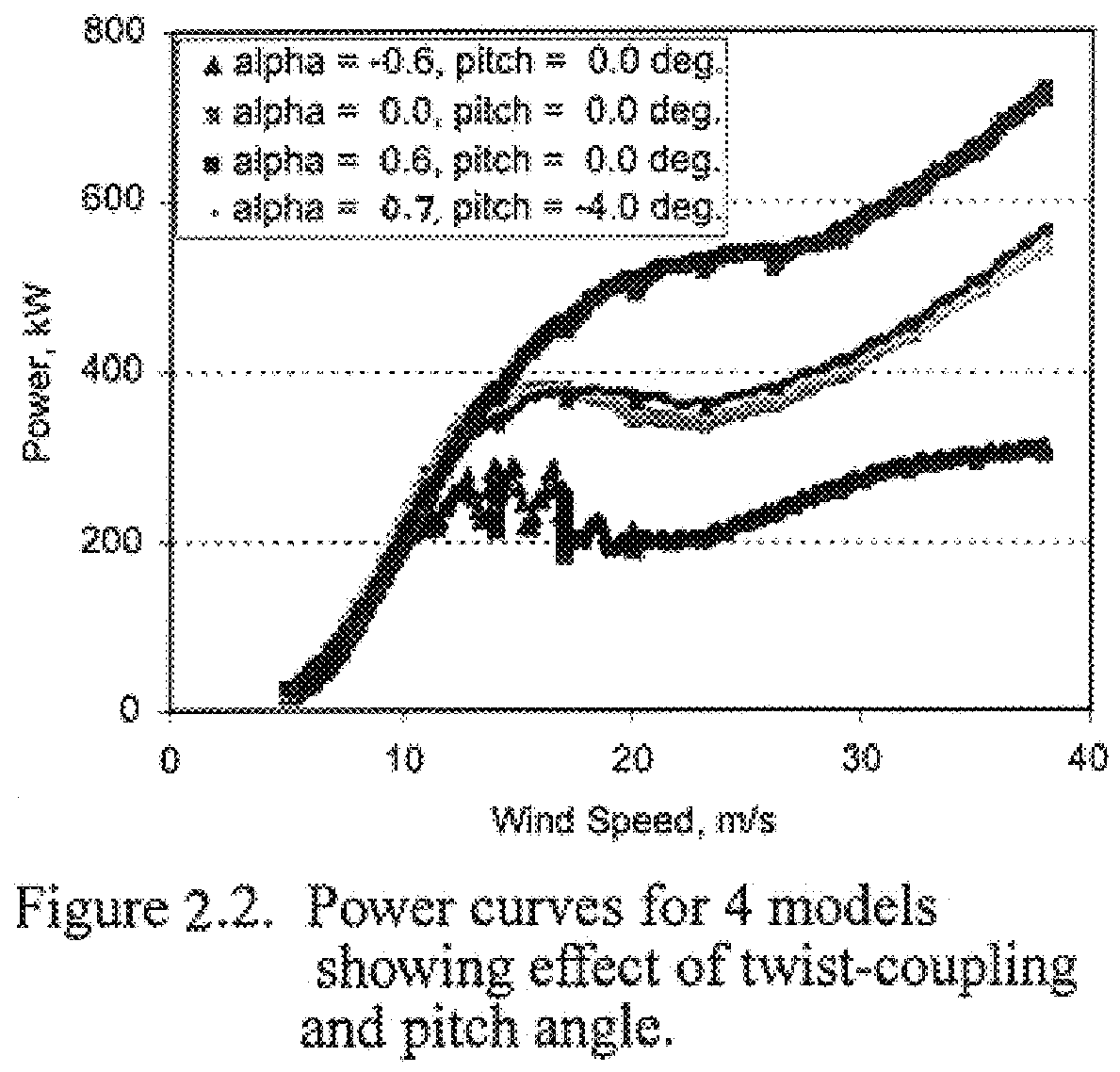
The present invention includes improved bending twist-coupled blades in rotors that use different power-control strategies. In confirming these alternative embodiments, a constant speed type stall-controlled rotor was included in the simulation as a baseline. Two of the more commonly accepted control strategies, variable speed stall-control and variable speed pitch-control, were used. The blades of each of these alternative embodiment rotors were first optimized mized by setting the pretwist such that a desirable twist distribution is achieved at rated power. In each case this procedure produced power curves for the twist-coupled rotors that were nearly identical to those of the uncoupled rotors to which they were compared.
A separate study for the variable speed stall-controlled rotor was performed wherein the twist-coupled rotor efficiency was compared to that of the uncoupled one in a steady wind environment. The peak rotor efficiency was determined at each windspeed by optimally ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com