Reduction of time to first fix in an SATPS receiver
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
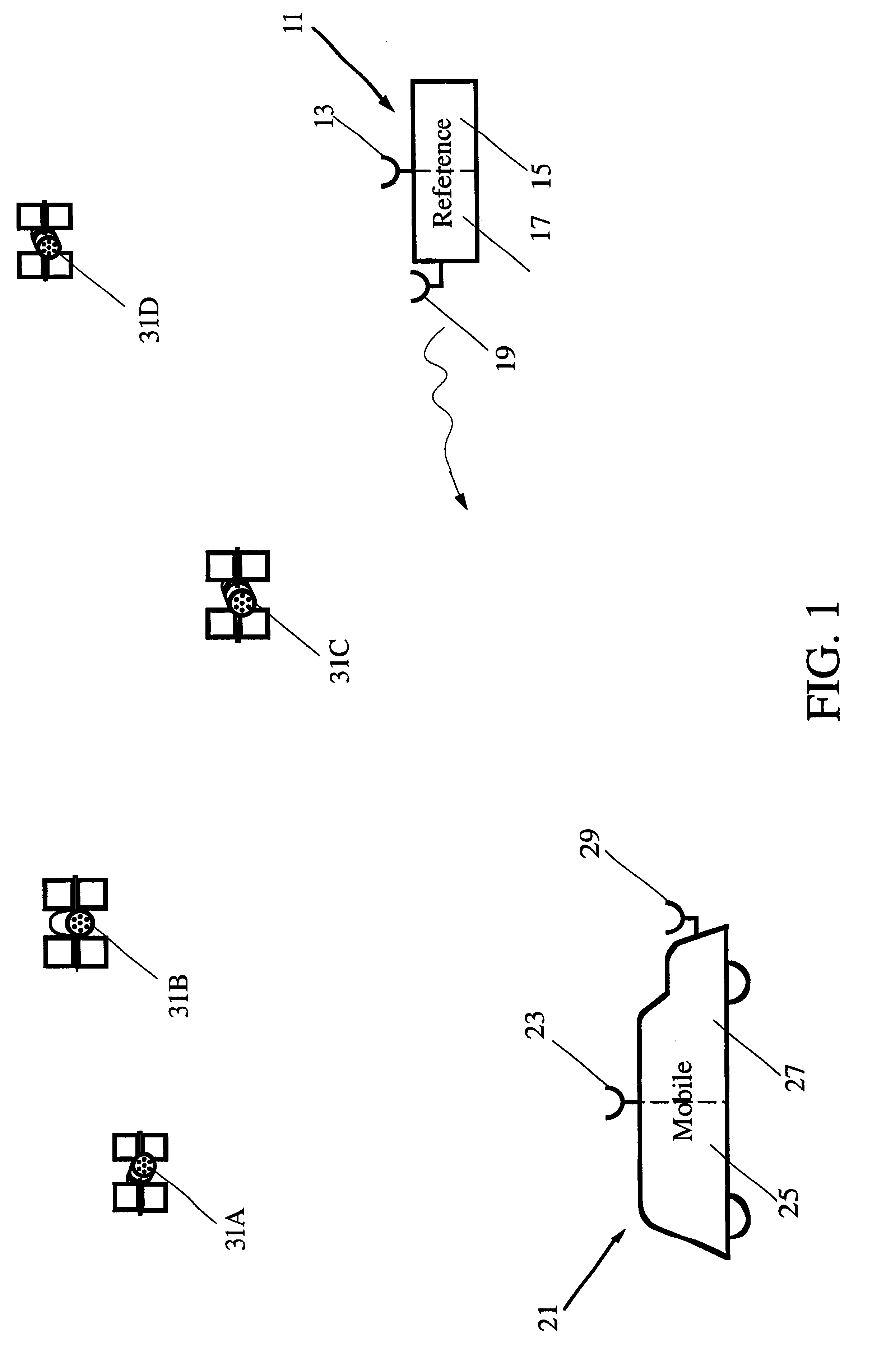
FIG. 1 illustrates operation of a differential satellite positioning system in simplified form. An SATPS reference station 11 includes an SATPS signal antenna 13 and associated SATPS receiver / processor 15, a DSATPS communications transmitter 17 and communications antenna 19, where the location of the SATPS antenna is known with high accuracy at any time. A roving or mobile SATPS station 21, including an SATPS antenna 23 and associated SATPS receiver / processor 25, a DSATPS communications receiver 27 and communications antenna 29, is spaced apart from the SATPS reference station 11 on or adjacent to the Earth's surface. Presently, an SATPS signal antenna is approximately omni-directional so that SATPS signals can be received from any area of the sky, except near the horizon, without requiring that the antenna be "pointed."
An SATPS antenna receives SATPS signals from a plurality (preferably three or more) of SATPS satellites and passes these signals to an SATPS signal receiver / processo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com