Apparatus for making nonwoven fabrics having raised portions
a technology for nonwoven fabrics and accessories, applied in the direction of pattern making, manufacturing tools, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of complex product creation, high cost, and inability to meet the needs of customers, and achieve the effect of reducing labor intensity, reducing labor intensity, and increasing production cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
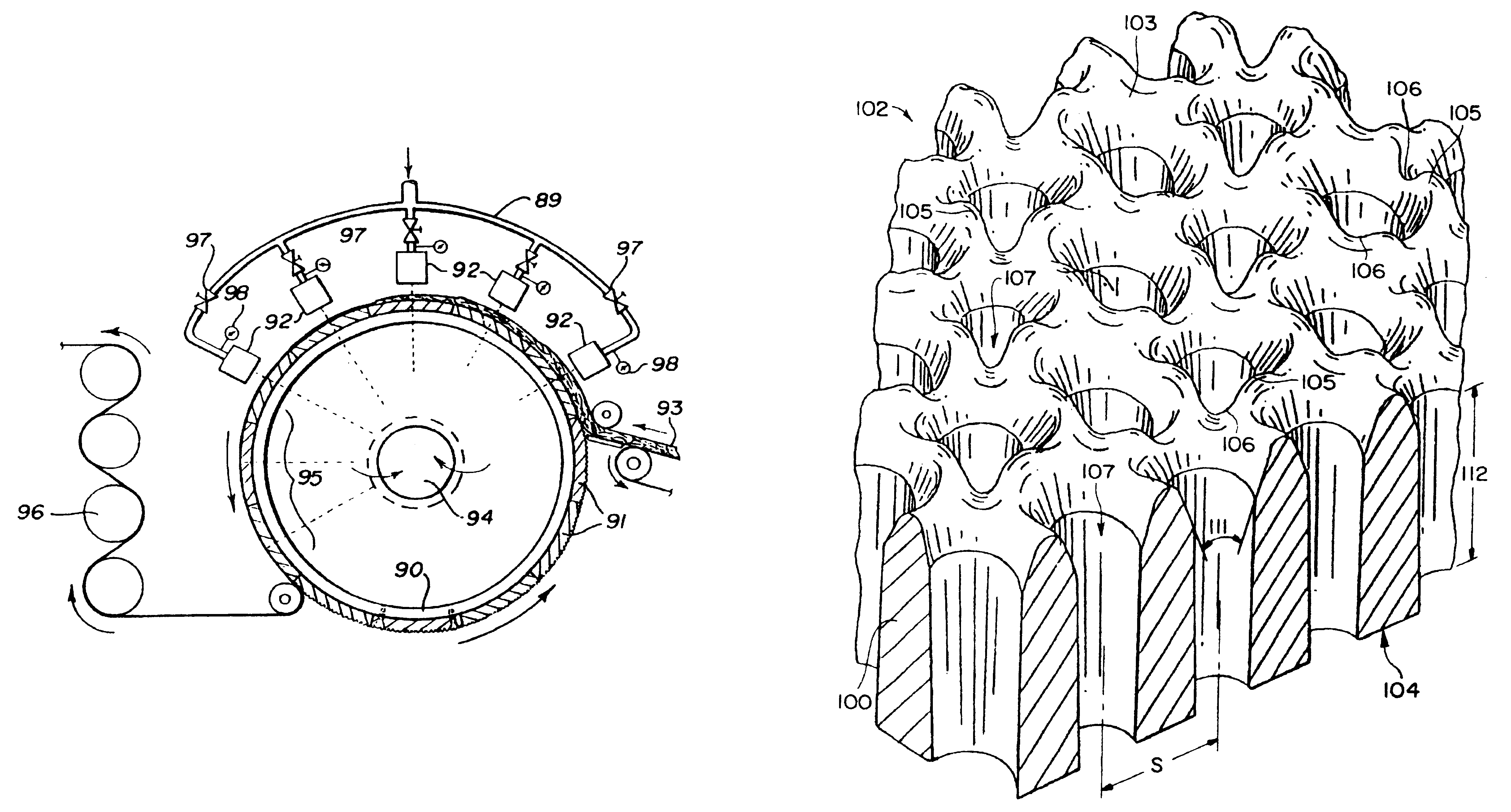
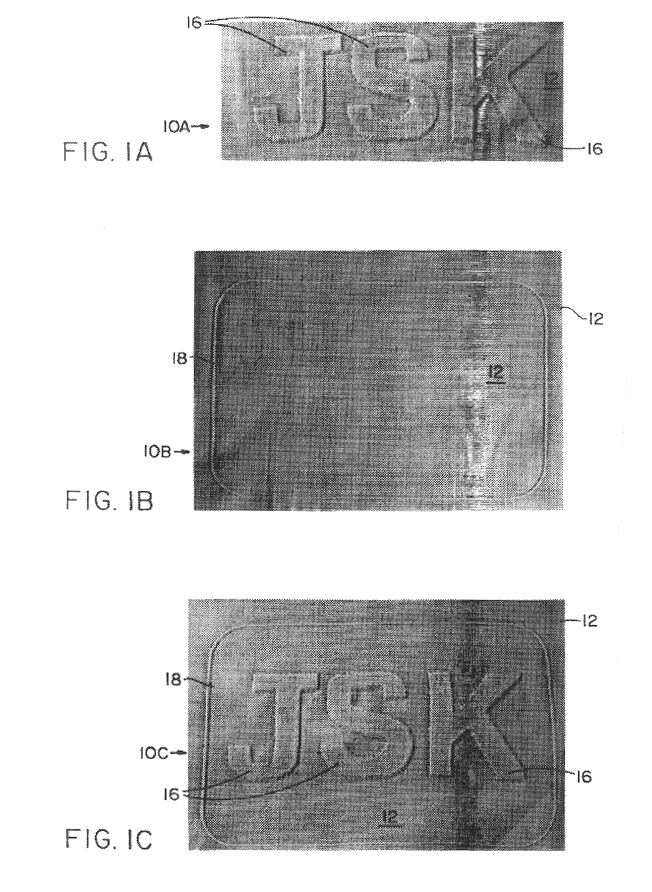
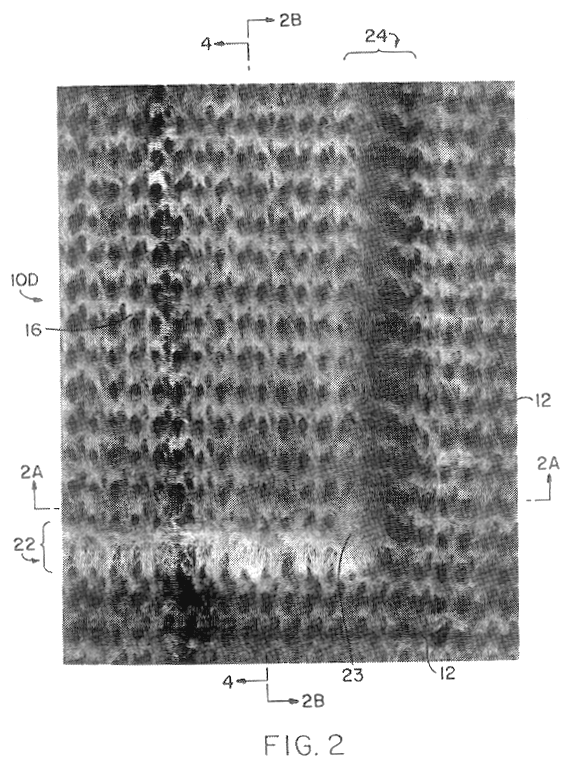
This example shows the production of a topographical support member which can be used to produce nonwoven fabric 10C of FIG. 1C. The precursor topographical support member is made of acetal and has the topographical pattern of peaks, valleys and apertures shown in FIG. 13 of the accompanying drawings. The precursor topographical support member was made by the laser drilling process disclosed in commonly assigned copending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 08 / 307,203, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,585,017, filed Sep. 16, 1994, the title of which is "Defocused Laser Drilling Process For Making Fabric Forming Device" and the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference. The support member of this Example 1 was made on the apparatus of FIG. 16 using the precursor support member just mentioned and the laser ablation process described hereinabove. The precursor support member was mounted on mandrel 821. The computer graphic file used to control the laser ablation process was that shown in...
example 2
This example illustrates the production of nonwoven fabric 10C shown in FIG. 1C using the topographical support member made in accordance with Example 1. The topographical support member of Example 1 was removed from mandrel 821 of the apparatus shown in FIG. 16 and was mounted on drum 90 of the apparatus shown in FIG. 12.
A fibrous web consisting entirely of staple-length cotton fibers and weighing 1.2 ounces per square yard was made by combining a 0.6 ounce per square yard 100% cotton web made by a conventional carding process and a 0.6 ounce per square yard 100% cotton web made by a conventional air laying process. In the specific example being discussed, the carded web and the air laid web were combined by positioning the air laid web on top of the carded web. It will be understood that the carded web could, if desired, be positioned on top of the air laid web.
The aforementioned 1.2 oz / sq yd 100% cotton web was lightly pre-entangled using a conventional flat-belt entangling appar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com