Monoclonal antibodies against human colon carcinoma-associated antigens and uses therefor
a human colon carcinoma and antibody technology, applied in the field of immunology and medicine, can solve the problem that none of the sakamoto mabs has the degree of colon tumor specificity, and achieve the effect of improving the survival rate of cancer patients and enhancing the host anti-tumor immunity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Preparation and Characterization of the Colon Carcinoma-Associated Antigen (CCAA)
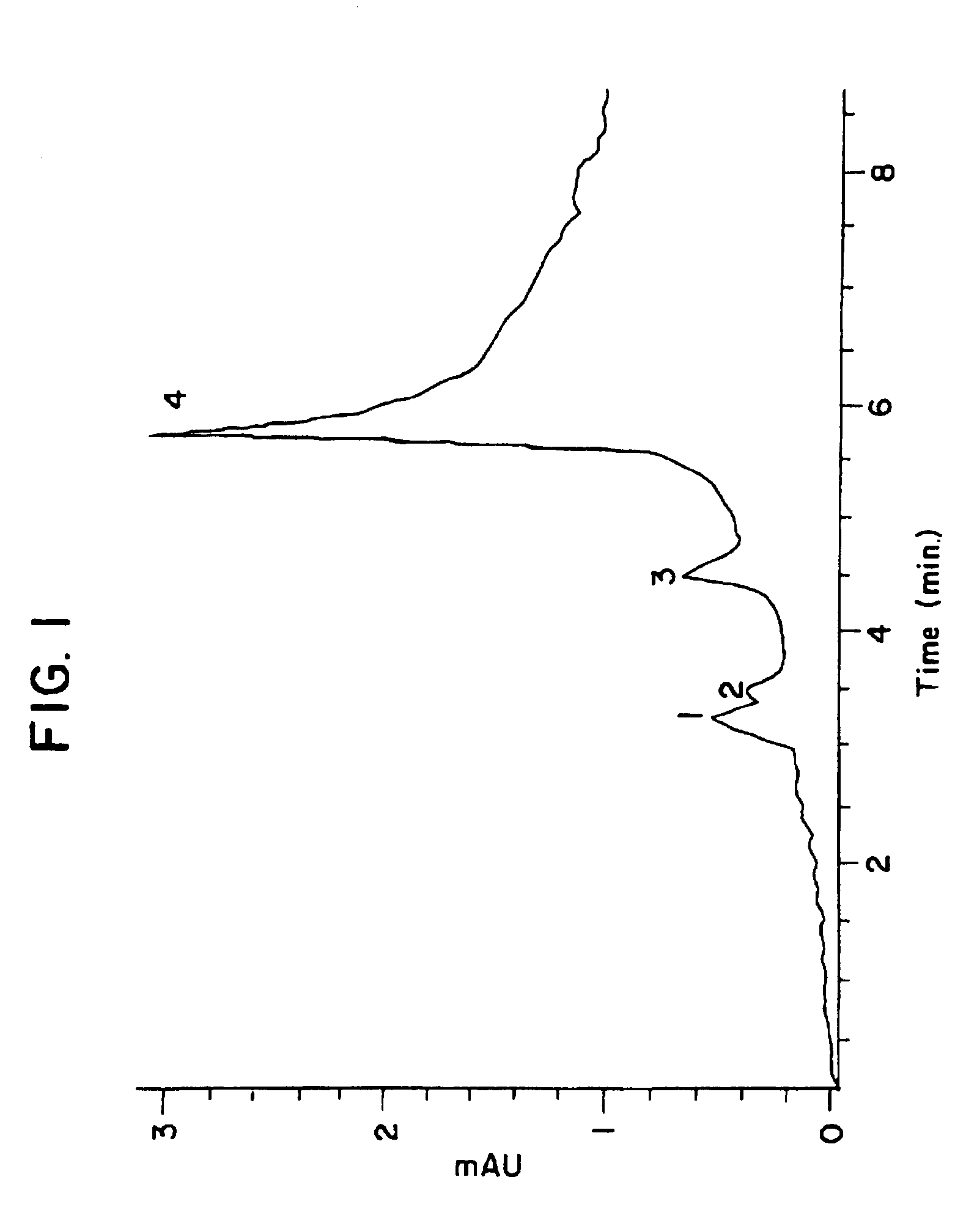
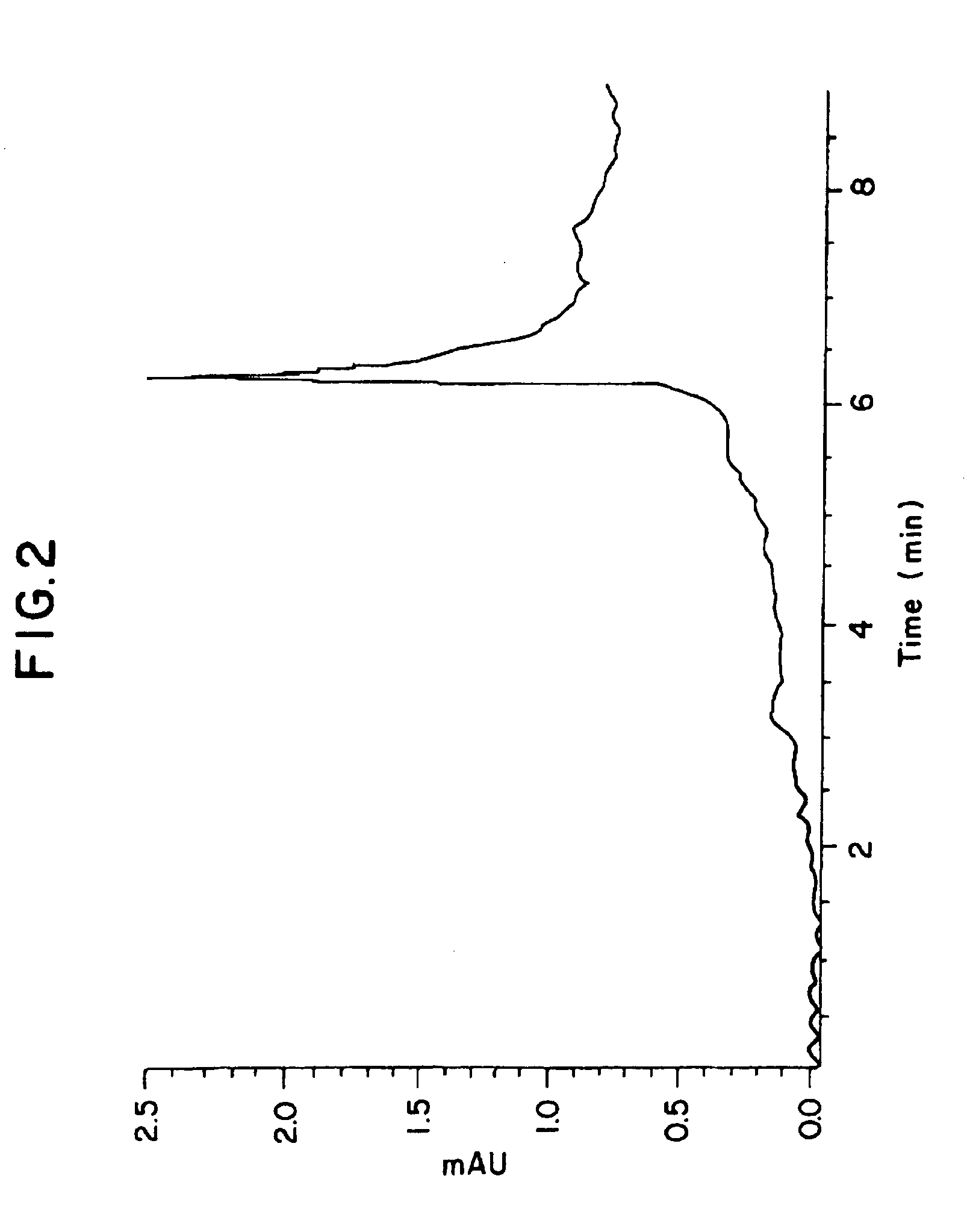
[0168]The antigenic preparation was obtained from pooled colon carcinoma membranes according to the method described by Hollinshead et al., Cancer 56:480 (1985). This antigenic material was purified to the extend that the membrane fractions were free of HL-A antigens and were separated from much of the non-immunogenic glycoprotein fractions. In its final form the antigenic preparation was shown to be immunogenic in a specific manner in humans as evidenced by its capability of eliciting a delayed hypersensitivity reaction only in patients with active colon, breast, and ovary carcinoma.
[0169]Tumor cell suspensions in saline were prepared from fresh operating room specimens. Single cell suspensions, obtained by conventional means, were centrifuged for 10 minutes at about 400×g and the supernatant was retained. The cell pellet was resuspended and recentrifuged. The membrane material was examined by electron...
example ii
Preparation and Screening of Monoclonal Antibodies
[0172]Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against human colon carcinoma-associated antigens (CCAA) were obtained by the production and cloning of hybrids resulting from the fusion of mouse myeloma cells Sp2 / 0-Ag14 with spleen cells from BALB / c mice which had been immunized with the CCAA described above.
[0173]Five hybrid clones were established, as described below, and designated as 31.2, 31.1, 77, 33.23 and 33.28. All five mAbs reacted strongly with the CCAA and with two colon carcinoma cell lines (SW480 and SW620) when assayed by ELISA. Two of the mAbs, 31.1. and 33.28, were studied in greatest detail.
A. Immunization and Cell Fusion
[0174]BALB / c mice were immunized by intrapertioneal injection of 50 μg of the CCAA described above emulsified in complete Freud's adjuvant, as described by Hollinshead in clinical trials (Hollinshead et al., supra). Ten days later the mice received an intravenous booster injection of the same amount of CCAA in s...
example iii
Analysis of Monoclonal Antibodies and their Reactivity
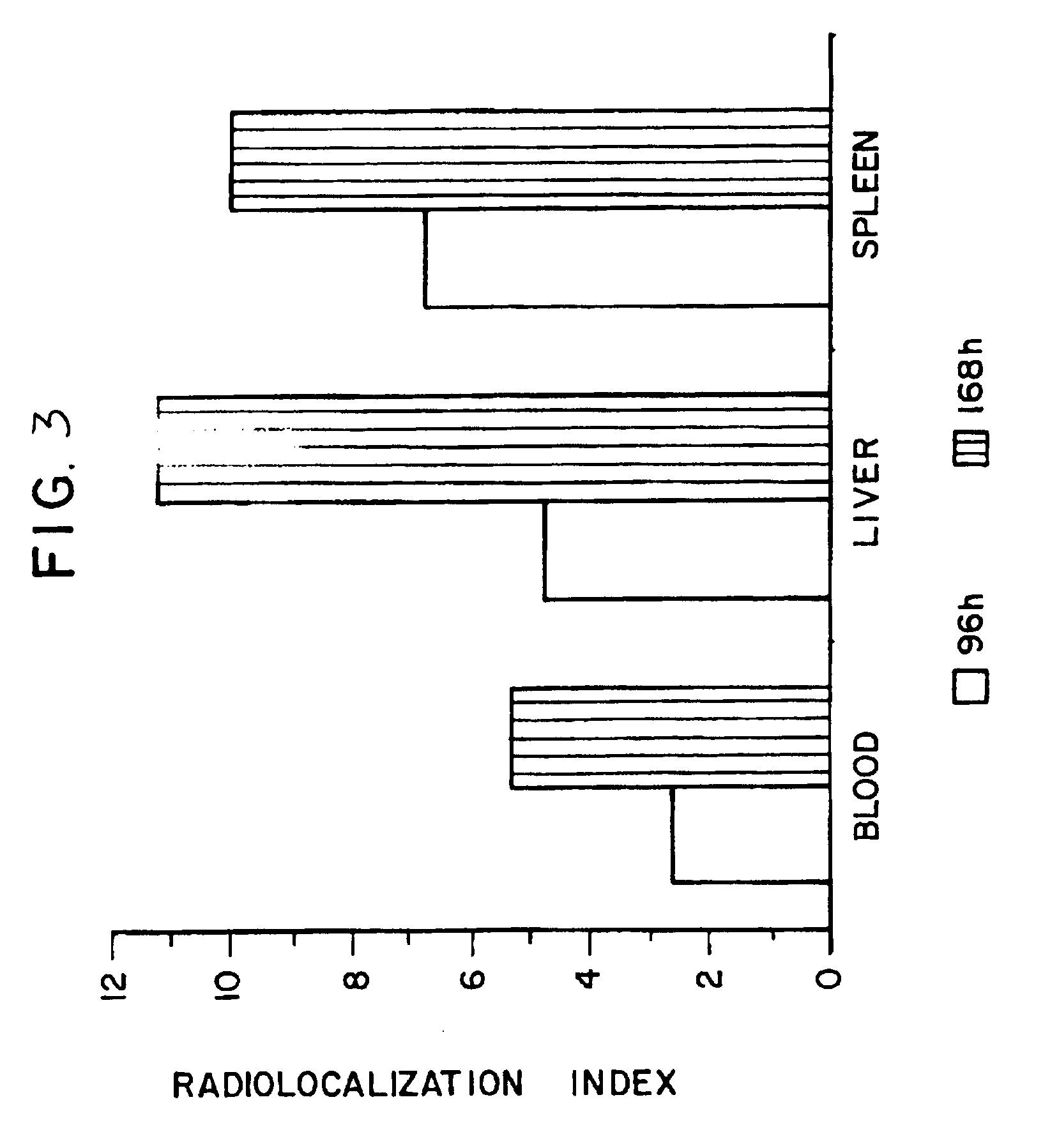
[0178]The anti-CCAA mAbs produced and detected as above were also tested for reactivity with fresh human tissue. Cryostat sections of the tissue types listed in Table 2, below, were fixed with 3.5% formaldehyde in PBS and then washed three times with PBS. For indirect immunofluorescence studies, the sections were incubated with the mAbs and then stained with a fluorescein-labelled second antibody as above.
[0179]As is shown in Table 2, mAbs 31.1 and 33.28 were highly specific for colon carcinoma cells. This indicates that an antigen (CCAA) which was highly specific for colon carcinoma and, furthermore, was immunogenic in colon carcinoma patients (positive DH reactions), and served as a successful immunogen in mice for the devnd phycoerythrin excitation was used. Trigger regions were established by examining cells by forward versus 90° light scatter. As shown in Table 4, both 31.1 and 33.28 bound to colon carcinoma cells; neither m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Atomic weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com