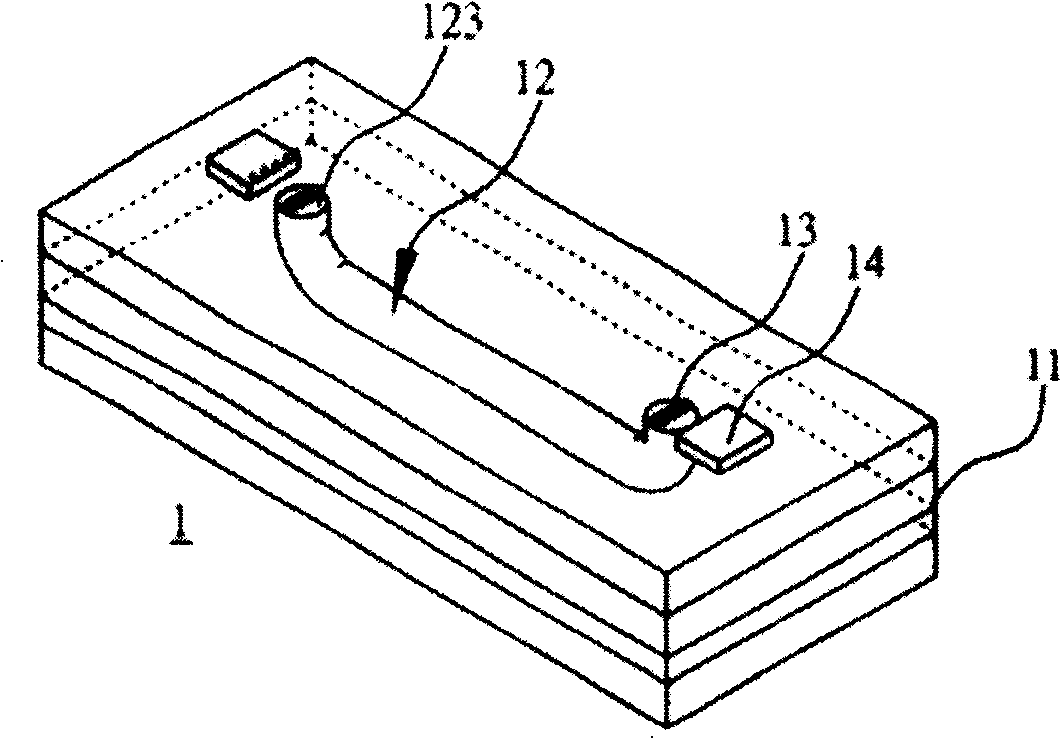
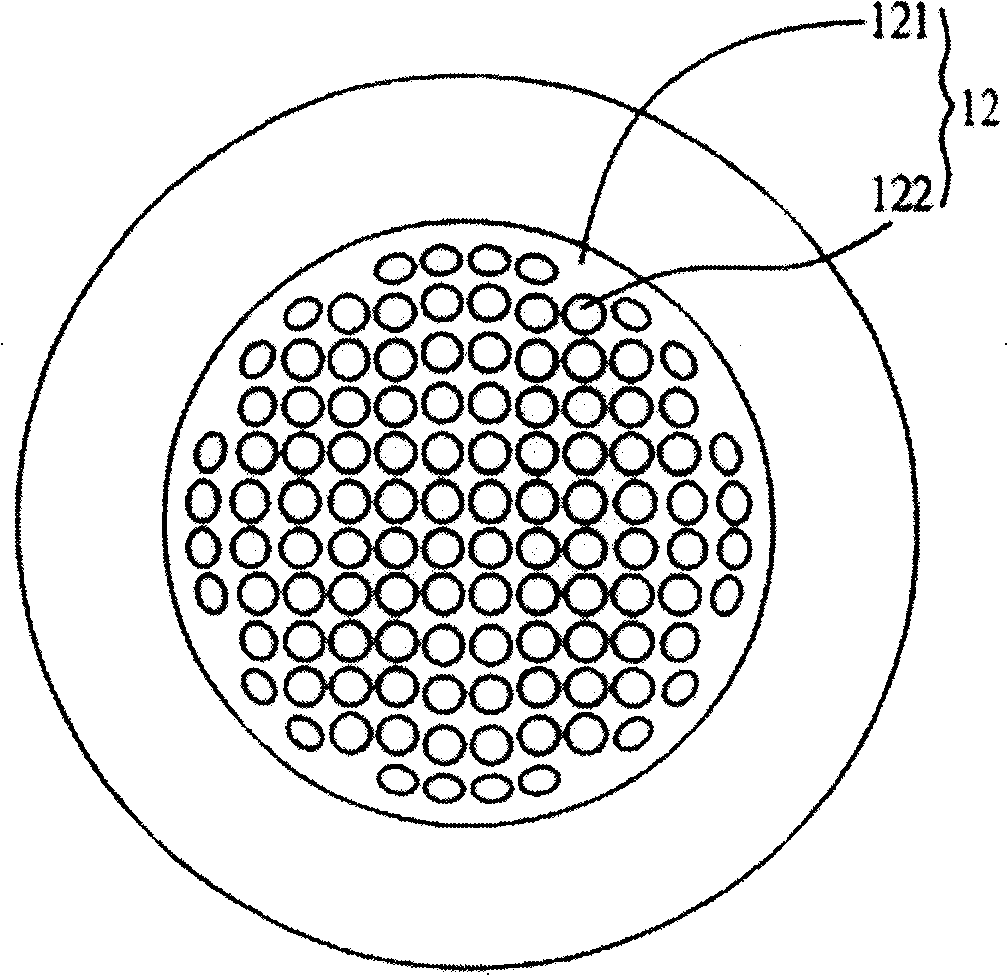
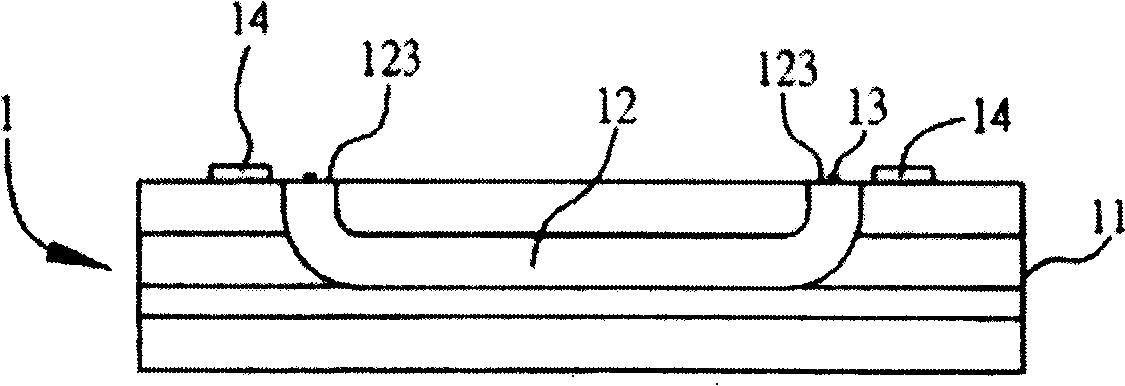
Photoelectric conversion substrate
A technology of photoelectric conversion and substrate, applied in the direction of optical waveguide and light guide, can solve the problem of incompatibility between photoelectric conversion substrate and printed circuit board process, and achieve the effect of improving displacement tolerance, high production cost, and increasing displacement tolerance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] image 3 It is a cross-sectional view of Embodiment 1 of the photoelectric conversion substrate 1 of the present invention. The two end faces 123 of the at least one honeycomb-shaped micro-optical waveguide 12 each have at least one alignment structure or alignment mark (not shown), wherein the at least one The alignment structure or the alignment mark is aligned and optically connected to the photoelectric element 13, so the displacement tolerance of the photoelectric element 13 on the photoelectric conversion substrate 1 package and the number of array channels can be increased, and in the honeycomb The end face 123 of the honeycomb-shaped micro-optical waveguide 12 has an asymmetric structure, which is beneficial to the alignment during wiring. Since this structure is applied in the structure of the M×N array, in order to avoid the structure of the honeycomb-shaped micro-optical waveguide 12 When the wiring is twisted, the 1-to-1 correspondence of the Tx Channel and ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of Embodiment 2 of the photoelectric conversion substrate 1 of the present invention, wherein the figure 1 The difference is that the photoelectric conversion substrate 1 of the present invention has a plurality of honeycomb-shaped micro-optical waveguides 12, wherein the honeycomb-shaped micro-optical waveguides 12 can span each other, it can realize a three-dimensional multi-channel structure, and due to the honeycomb-shaped micro-optical waveguides 12 The structure of the micro-optical waveguide 12 can allow more channel transmission per unit area, so it is not limited by the pitch of the optical fiber 250mm, so the pitch of the VCSEL element can be less than 250mm, in other words, within the unit area of the VCSEL Wafer Can have more VCSEL components.
Embodiment 3
[0041] see Figure 5 , which is a schematic diagram of Embodiment 3 of the photoelectric conversion substrate 1 of the present invention, wherein the Figure 4 The difference is that the present invention applies a plurality of optical element sub-modules 2 to the photoelectric conversion substrate 1 having a plurality of honeycomb-shaped micro-optical waveguides 12 of the present invention, wherein the optical element sub-module 2 integrates optoelectronic elements and IC drivers. element.
[0042] To sum up, the structure of the photoelectric conversion substrate 1 disclosed in the present invention is easy to manufacture and can reduce the production cost, overcomes the problem of incompatibility between the existing photoelectric conversion substrate and the printed circuit board in the manufacturing process, and can effectively increase the number of photoelectric elements on the photoelectric conversion substrate. Displacement tolerance on package.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com