Transimpedance amplifier with negative impedance compensation function
A transimpedance amplifier, negative impedance technology, applied in the field of amplifiers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
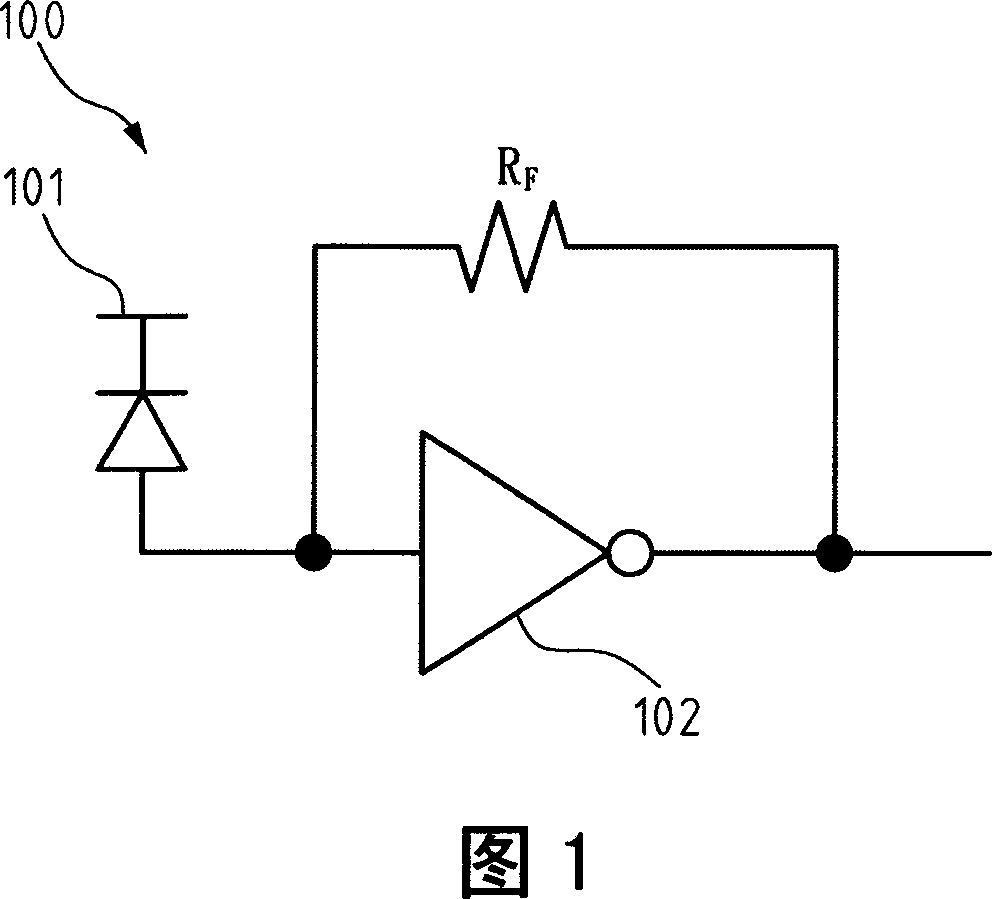
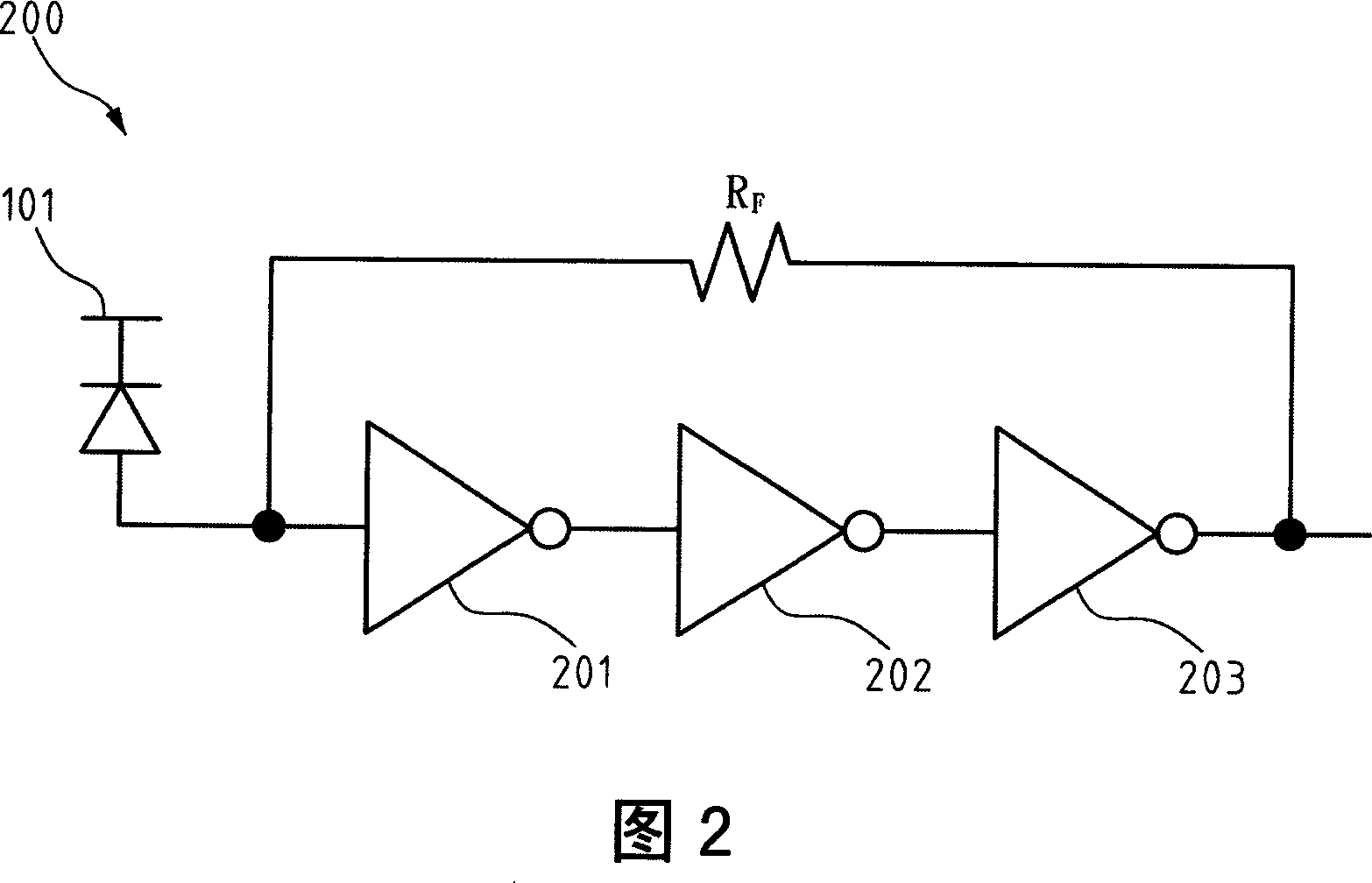
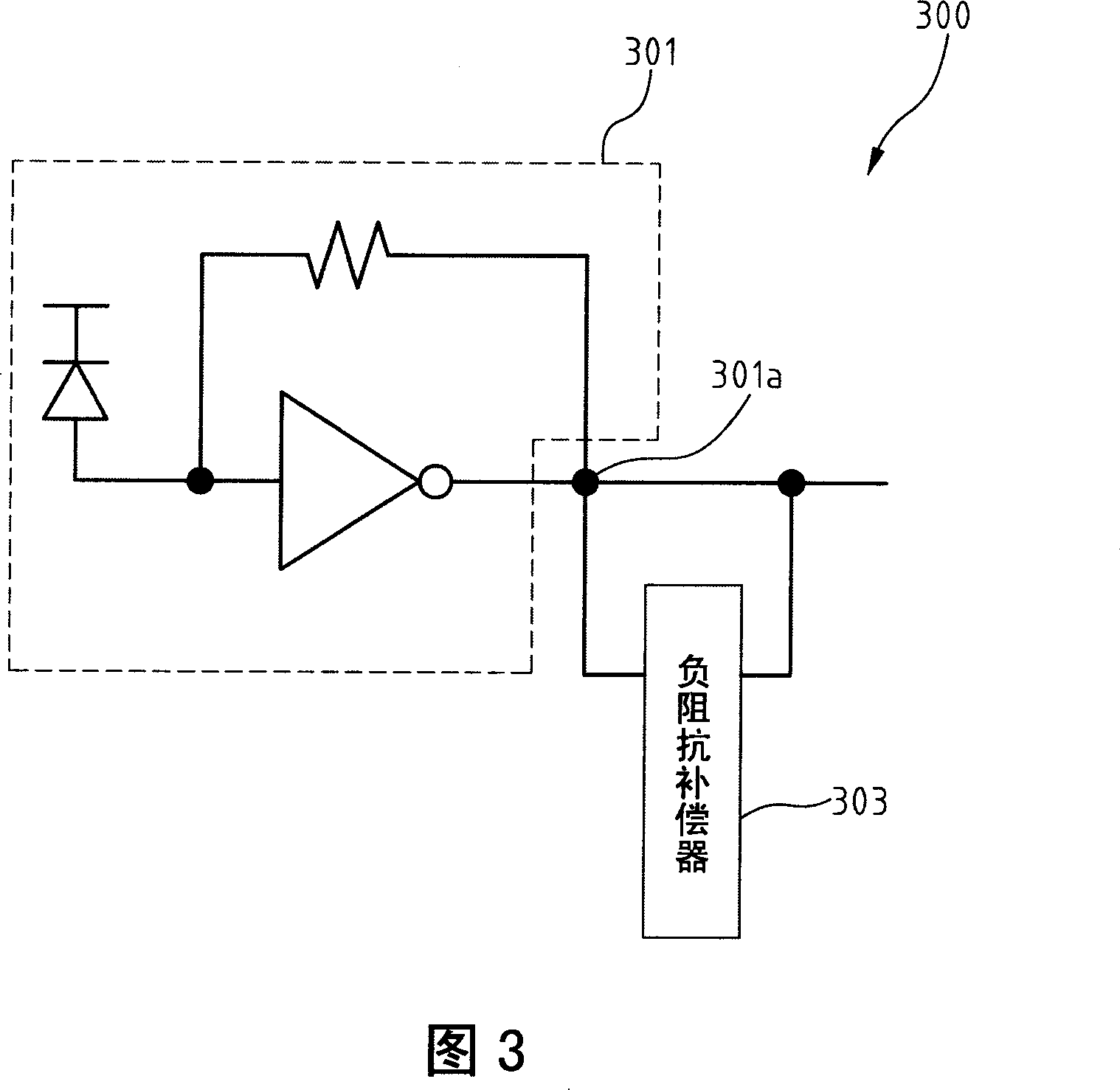
[0048] FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating the architecture of the first embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 3 , the transimpedance amplifier 300 mainly includes a single-stage transimpedance amplifier element 301 and a negative impedance compensator (negativeimpedance compensator) 303 . The single-stage transimpedance amplifier element 301 has an output terminal 301a to generate an equivalent ground impedance. The negative impedance compensator 303 is connected to the output end 301a of the single-stage transimpedance amplifier element 301, which changes the equivalent ground impedance generated by the output end 301a from low to high, and compensates the parasitic capacitance effect generated by the output end 301a .
[0049] The negative impedance compensator 303 can be realized by various circuit architectures, mainly including a negative resistance element composed of a positive feedback circuit and a compensation circuit for the parasitic capacitan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com