Vector ECG instrument and carrying out method thereof
A technology of electrocardiograph and implementation method, which is applied in the fields of instruments, diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, etc., and can solve the problems that electrocardiograms cannot be converted to each other, lead systems are different, and it is difficult to improve diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. , to achieve the effect of improving the diagnostic level of electrocardiology and correcting wrong ideas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
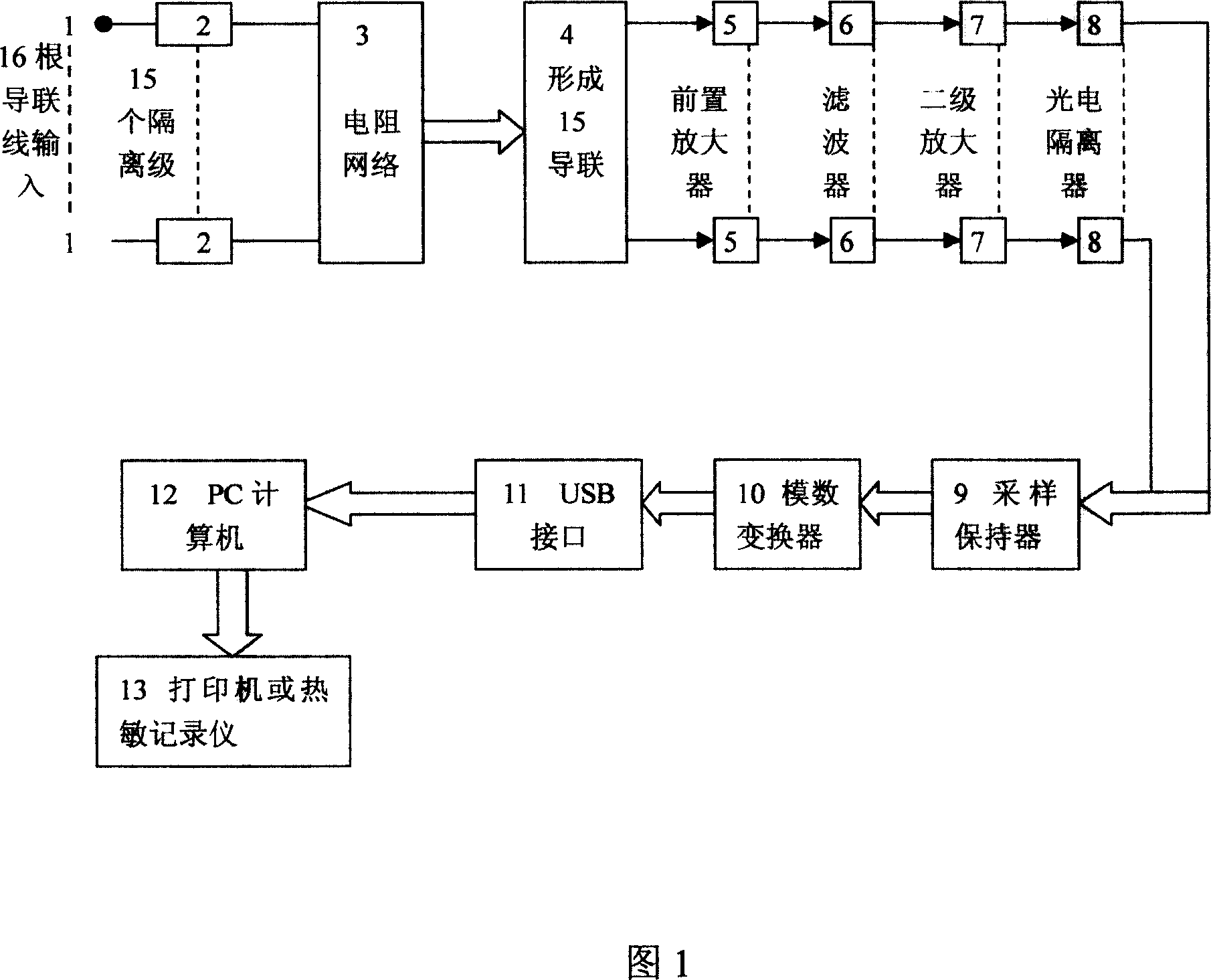
[0049] Embodiment 1: A vector electrocardiograph, 16 electrode wires / 15 channels, space-time domain. Real-time homologous simultaneous conversion observation and tracing of 1D, 2D and 3D ECG.
[0050] 16 electrode lines, parallel 15-channel input Einthoven-Goldberger-Wilson and Frank lead system; 15 isolation stages; resistor network; 15-lead system; preamplifier; filter; secondary amplifier; photoelectric isolator; sample and hold device; analog-to-digital conversion (A / D); USB interface; PC computer; plotter or thermal recorder.
[0051] The signal processing unit includes:
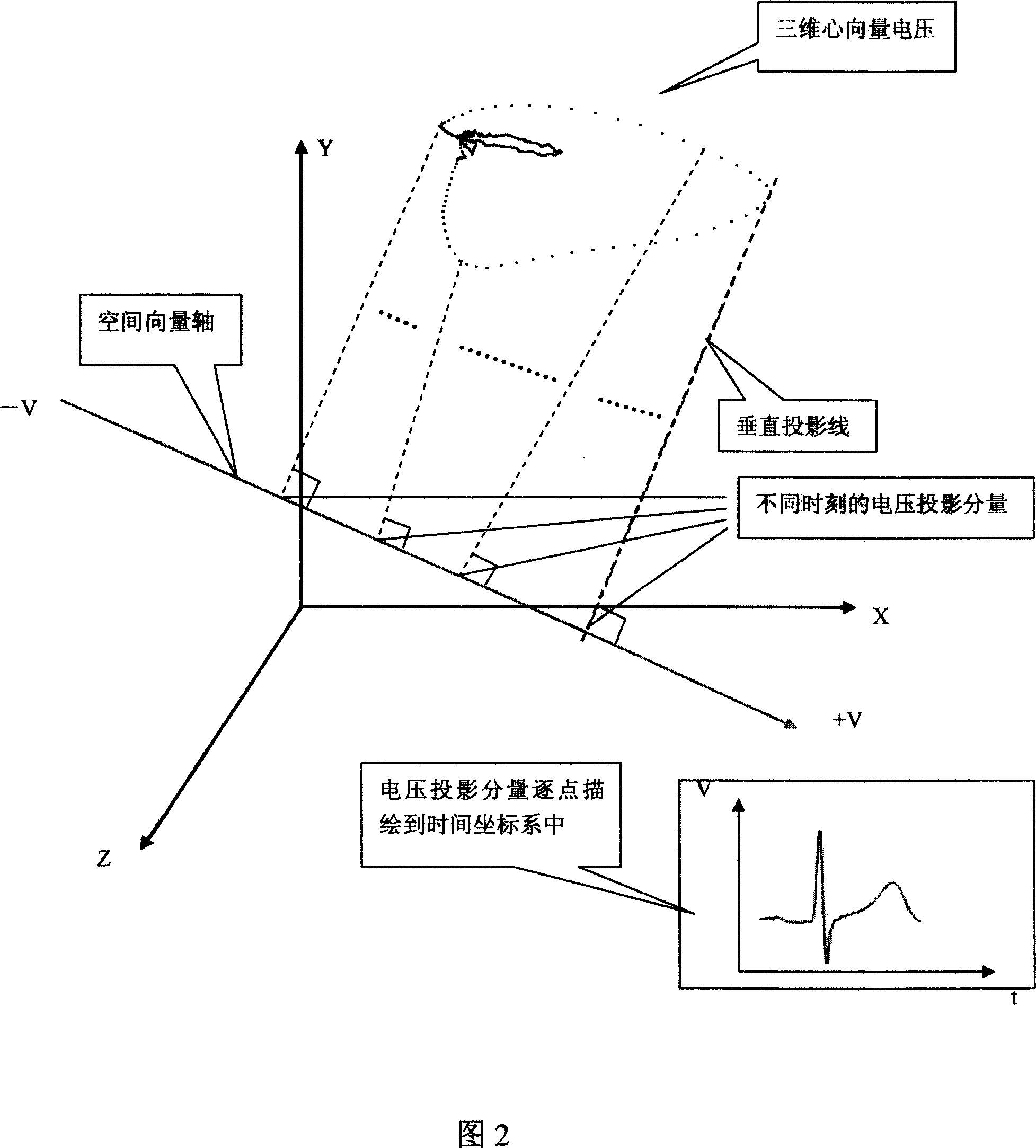
[0052] Perform spatial domain processing on each heart vector signal output by the electrical signal acquisition device, including a three-dimensional heart vector model composed of three mutually perpendicular intersections of X, Y, and Z, and draw the corresponding trajectory curve through the output device A heart vector three-dimensional space processing unit;
[0053] Perform plane processing on...
Embodiment 2
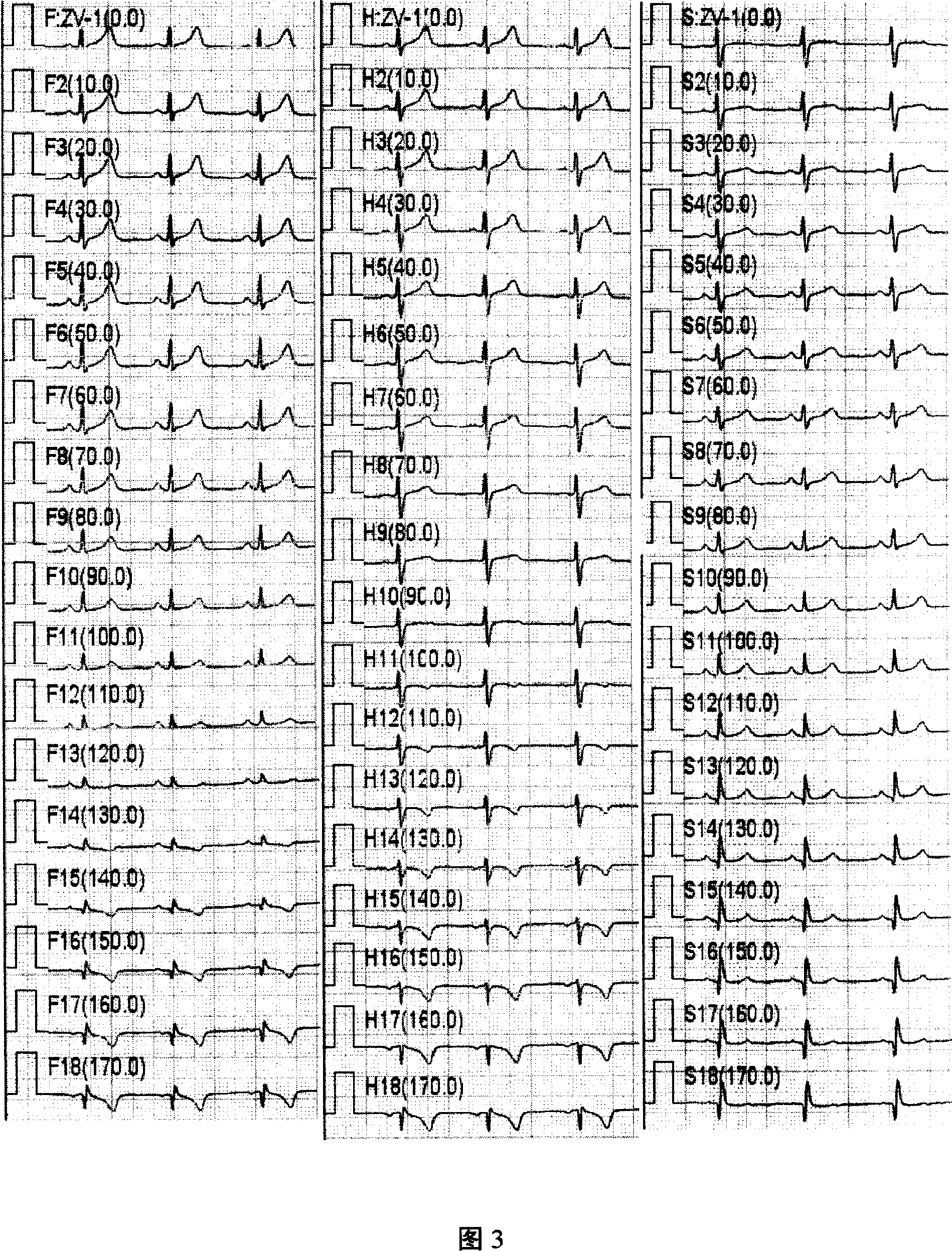
[0064] As shown in Figure 3, the lead of the vector electrocardiogram is a virtual lead realized by computer software. Each virtual lead has a plane attribute, an angle attribute and after determining the direction of the lead, the computer can calculate and trace the corresponding electrocardiogram according to the lead axis.
[0065] The virtual lead axis provided by this system is to set 0 to 18 lead axes within the range of 0 to 360 degrees on the frontal plane, transverse plane and side surface respectively. There are 54 virtual lead axes on the three sides. The minimum degree between the lead shafts is 0.5 degrees, and the angle of each lead shaft can be set as required. The vector electrocardiogram (z-VECG) can display the tracing synchronously with the traditional 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG), and can also observe the tracing synchronously with other two-dimensional or three-dimensional ECG.
Embodiment 3
[0067] The vector electrocardiograph also provides a teaching demonstration function module, which is helpful to understand the interrelationship between the first, second and three-dimensional electrocardiograms. For example: Figure 4. Shows the vector ECG generated when the frontal mid-lead axis angle is 30°. Figure 5 is a demonstration of the instantaneous generation of a horizontal multi-lead vector ECG, which is a dynamic display process for a cardiac cycle, that is, from the beginning (starting point) of the plane VCG to the end (end point). While depicting point by point along with the instantaneous time, each lead axis synchronously displays and depicts the corresponding vector electrocardiogram according to their respective angles in the coordinate system. Figure 6. The projection of the "lead free axis" is a way of displaying z-VECG in contrast to VCG. The free lead axis is a lead axis whose angle can be changed freely by the user. The axis is a vector line with a d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com