Nonwovens and machining method thereof
A technology of non-woven fabrics and processing methods, which is applied in the direction of non-woven fabrics, textiles, papermaking, adhesives, etc., and can solve problems such as poor heat absorption, expensive equipment investment and maintenance costs, and reinforcement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
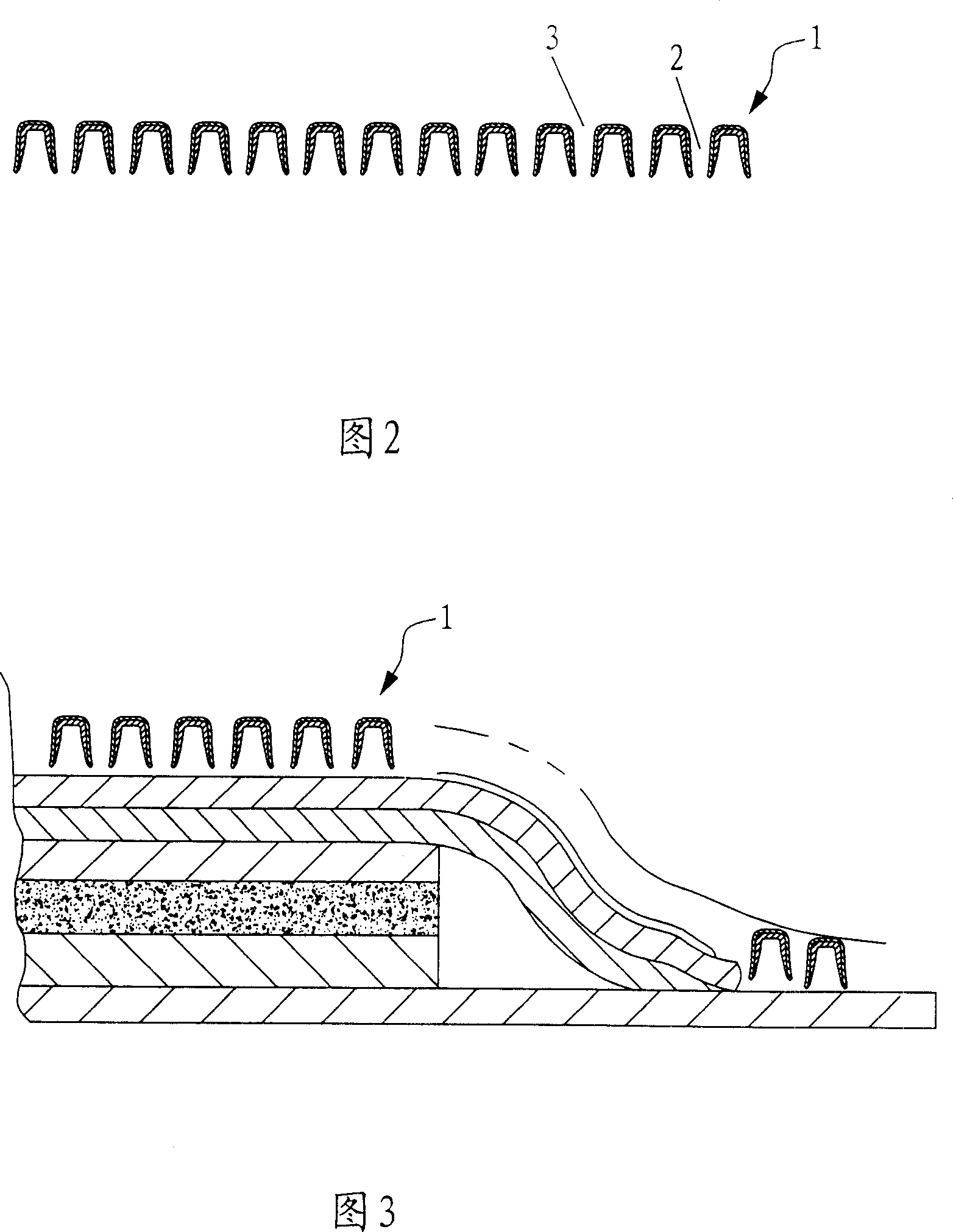
[0024] As shown in Figure 1, the nonwoven fabric of the present invention is made of hot-melt synthetic fiber staple fibers including but not limited to at least one of polypropylene staple fibers, polyethylene staple fibers, ES fibers, polyester staple fibers, and nylon staple fibers. It is mixed with at least one of non-thermofusible staple fiber with a content of not less than 30% by weight, including but not limited to cotton fiber, viscose staple fiber, vinylon staple fiber, bamboo fiber, soybean fiber, hemp fiber, etc. , wherein the proportion by weight of the non-heat-meltable short fiber is 30% to 90%, especially 40% to 80%. Heat-melt synthetic fiber staple and non-heat-melt staple fiber enter the mixing and opening equipment in proportion to mix and open the fibers, and enter the carding and web forming equipment through the cotton feeder for carding and web forming. After laying the web, the resulting fiber web enters the thermal bonding and strengthening equipment f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com