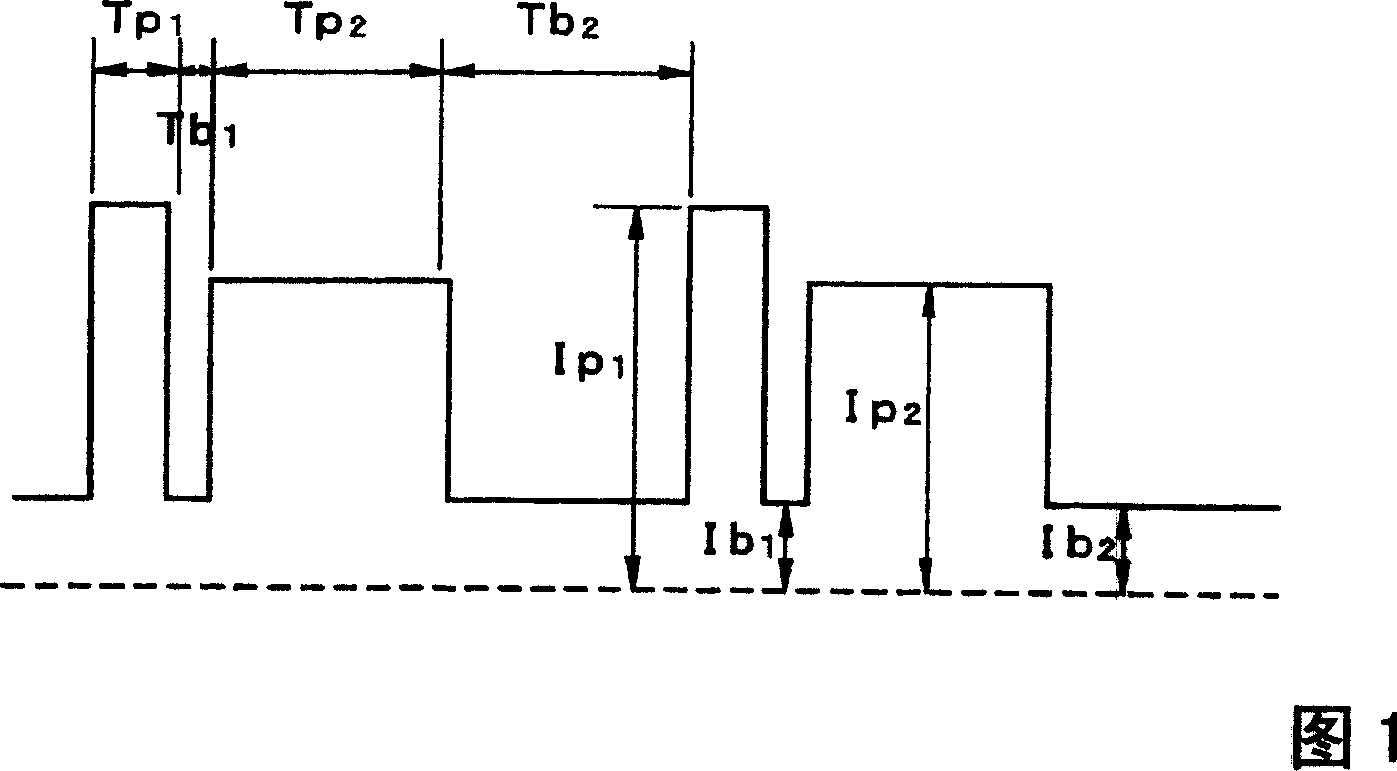
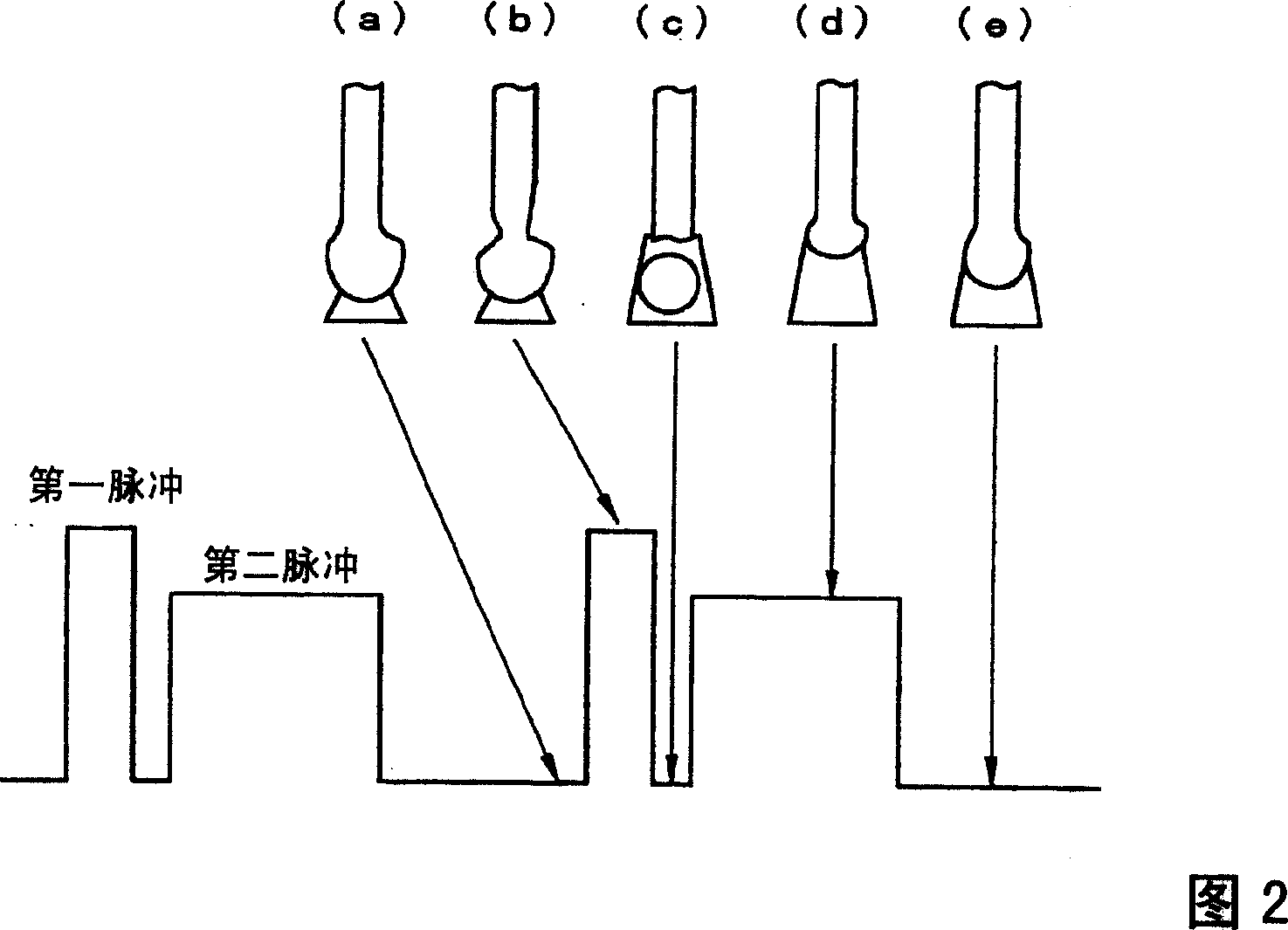
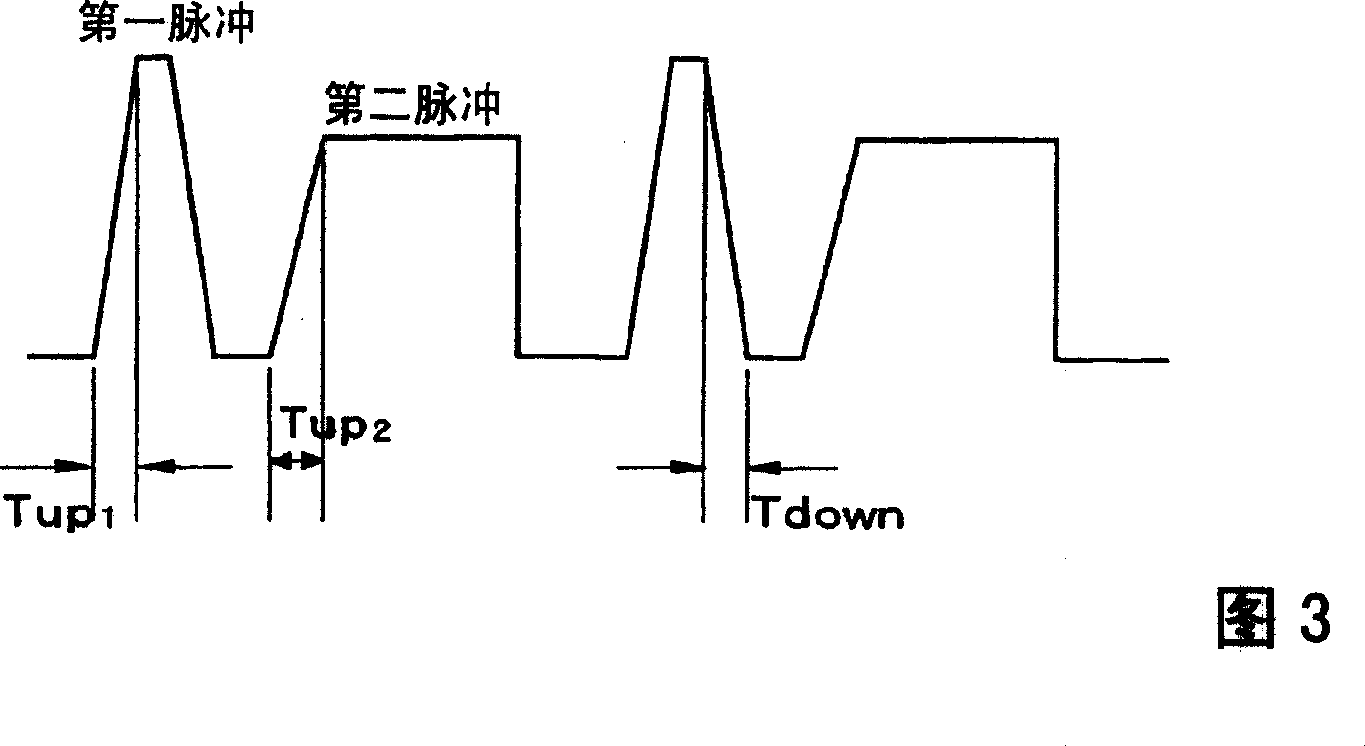
Pulsed arc welding method
A pulse and arc welding technology, which is applied in arc welding equipment, welding medium, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of frequent occurrence of large-grain spatter, inability to separate molten droplets, and difficult transition, so as to reduce small-grain spatter, reduce the occurrence of large-grain spatter and Effect of smoke generation and stabilization improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 41
[0128] Examples 41 to 42 are examples of the third embodiment. In Example 41, the detection of droplet detachment was implemented. In Example 42, after setting the slope period during the first and second pulse rising periods and the first pulse falling period, it was implemented. Droplet detachment detection.
[0129] Examples 43 to 47 are examples of the third embodiment. Examples 43 to 44 overlap high-frequency pulses. Example 45 overlaps after setting a slope period during the rising period of the first and second pulses and during the falling period of the first pulse. In Example 47, droplet detachment detection was performed after the first and second pulse rising periods and the first pulse falling period provided a slope period, and high-frequency pulses were superimposed.
[0130] Next, comparative examples shown in Table 6 will be described. However, these Comparative Examples 48 to 61 satisfy the scope of the present invention. In Comparative Example 48, there is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com