Tumor-homing cells engineered to produce tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
A technology of apoptosis-inducing ligand and tumor necrosis factor, applied in the direction of tumor necrosis factor, tumor/cancer cell, genetic engineering, etc., can solve problems that cannot be reasonably predicted
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1 - triggering apoptosis of lymphoma cell lines in vitro, wherein said lymphoma cell lines are co-cultured with CD34+ cells or NK cells expressing TRAIL after adenovirus-mediated gene transfer
[0034] This example evaluates the effect of co-culture of lymphoma cell lines with CD34+ cells or NK cells, which were engineered to express TRAIL after adenovirus-mediated gene transfer.
[0035] At the beginning of the in vitro experiment, an adenovirus vector expressing TRAIL (Ad-TRAIL) was used to establish the optimal conditions for adenovirus infection of CD34+ cells and NK cells. Then, the progress of TRAIL expression on the surface of CD34+ cells and NK cells was monitored using PE-conjugated anti-TRAIL monoclonal antibody (clone Rik-2). Finally, the ability of membrane-bound TRAIL to induce apoptosis of lymphoma cell lines was evaluated by co-culturing Ad-TRAIL / CD34+ cells or Ad-TRAIL / NK cells with lymphoma cell lines.
[0036] method
[0037] Adenovirus encod...
Embodiment 2
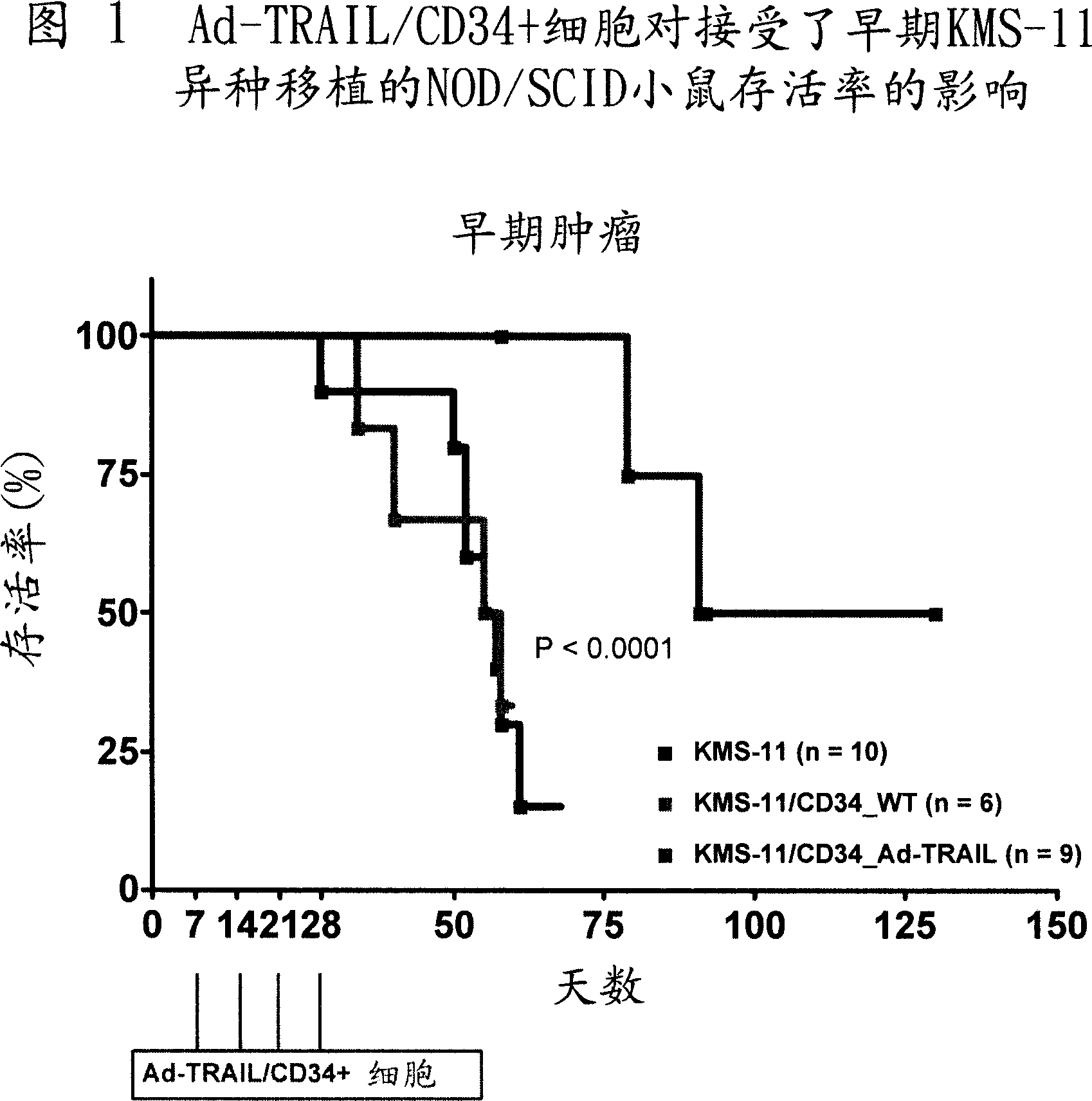
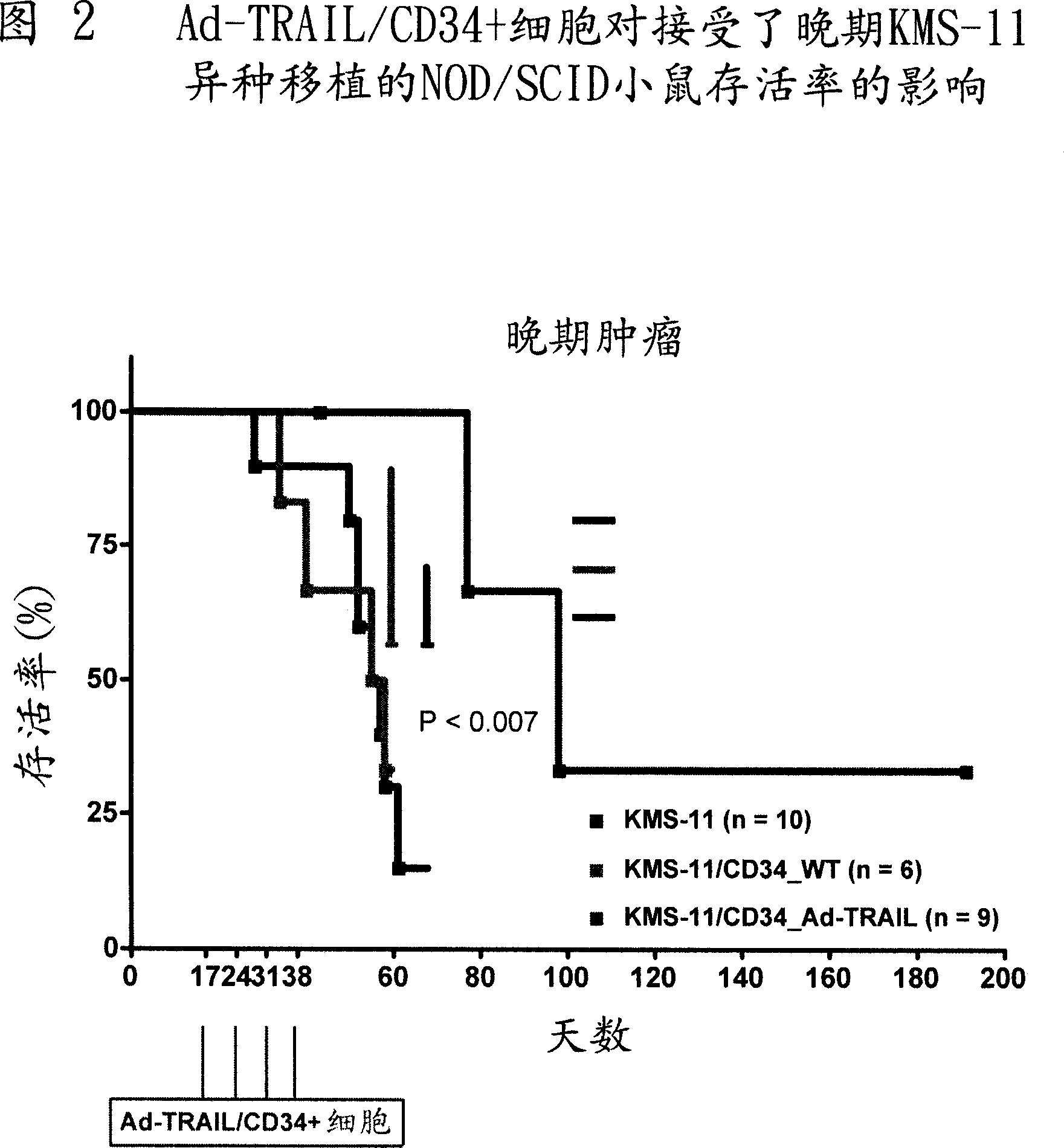
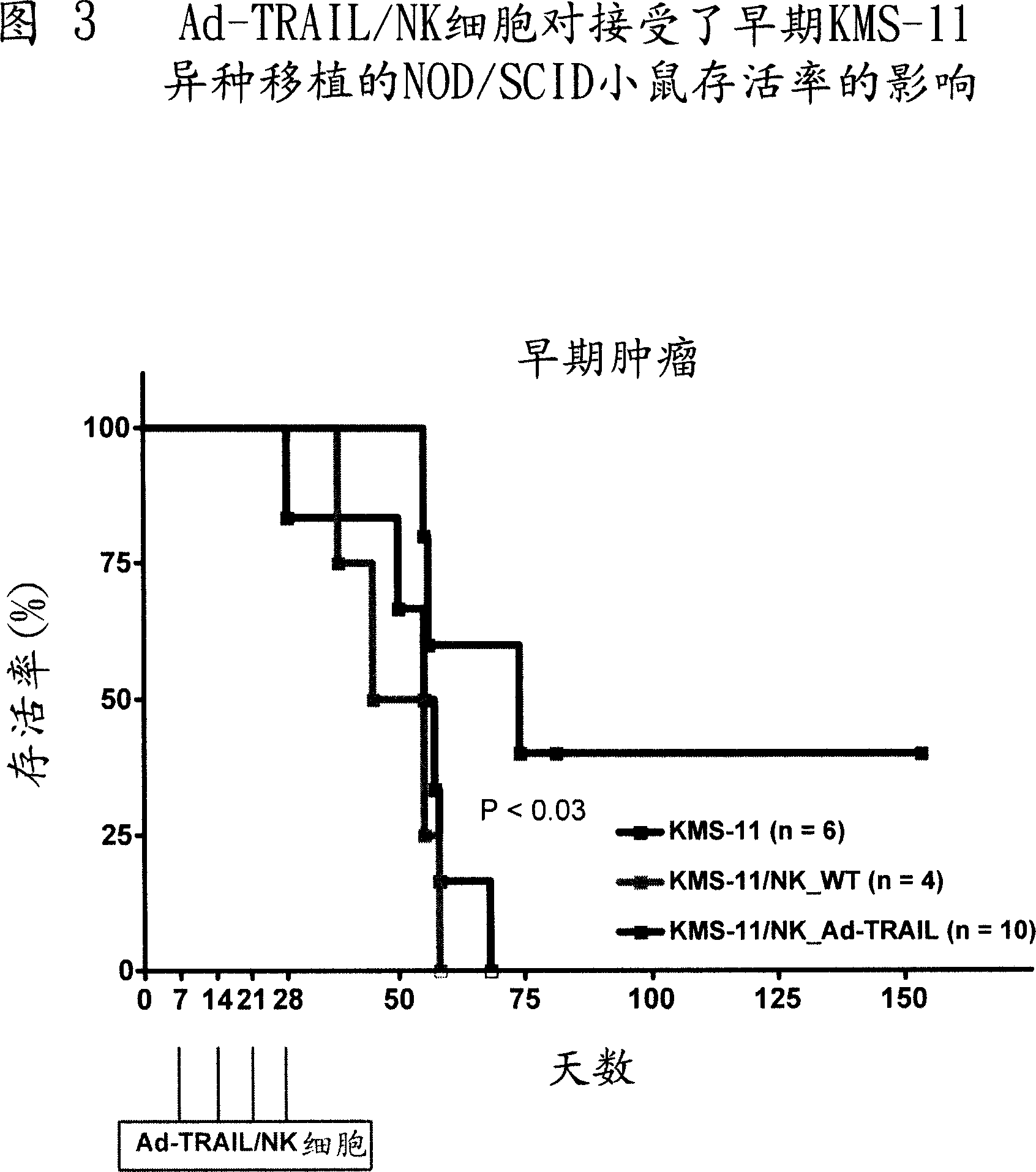
[0070] Example 2 - In vivo evaluation of anticancer activity of CD34+ cells or NK cells engineered to express TRAIL following adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in NOD / SCID mice
[0071] To study the therapeutic ability of Ad-TRAIL / CD34+ cells or Ad-TRAIL / NK cells, NOD / SCID mice were reperfused with TRAIL-sensitive KMS-11 multiple myeloma cell line. Mice were then injected with Ad-TRAIL / CD34+ cells or Ad-TRAIL / NK cells, and mouse survival was used as a readout for the antitumor efficacy of cell-based TRAIL delivery.
[0072] method
[0073] Evaluation of the antitumor activity of Ad-TRAIL / CD34+ cells or Ad-TRAIL / NK cells: 6- to 8-week-old female NOD / SCID mice weighing 20 to 25 g were purchased from Charles River (Milan, Italy). The animals were maintained under standard experimental conditions according to our guidelines. Experimental procedures on animals were approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of the Istituto Nazionale Tumori and performed in accordance...
Embodiment 3
[0081] In vitro anti-tumor activity of embodiment 3-CD34 / Ad-TRAIL cells against breast cancer cell lines
[0082] A large proportion of breast cancer cell lines are resistant to TRAIL-induced apoptosis due to multiple mechanisms, including TRAIL masking by TRAIL decoy receptors, loss of R1 and R2 receptor expression, FLIP overexpression, etc. [40] . Based on our previous results that sTRAIL-resistant lymphoma cell lines responded to TRAIL when exposed to mTRAIL, we investigated the sensitivity of two breast cancer cell lines to sTRAIL and mTRAIL.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com