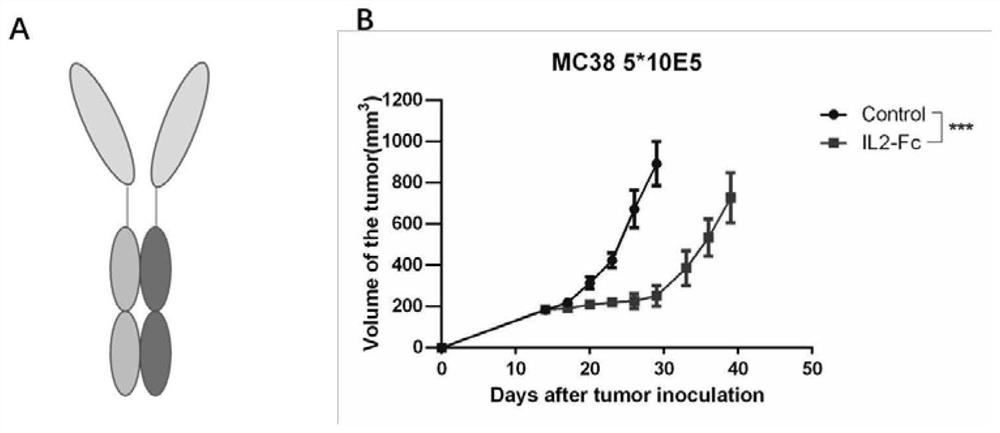
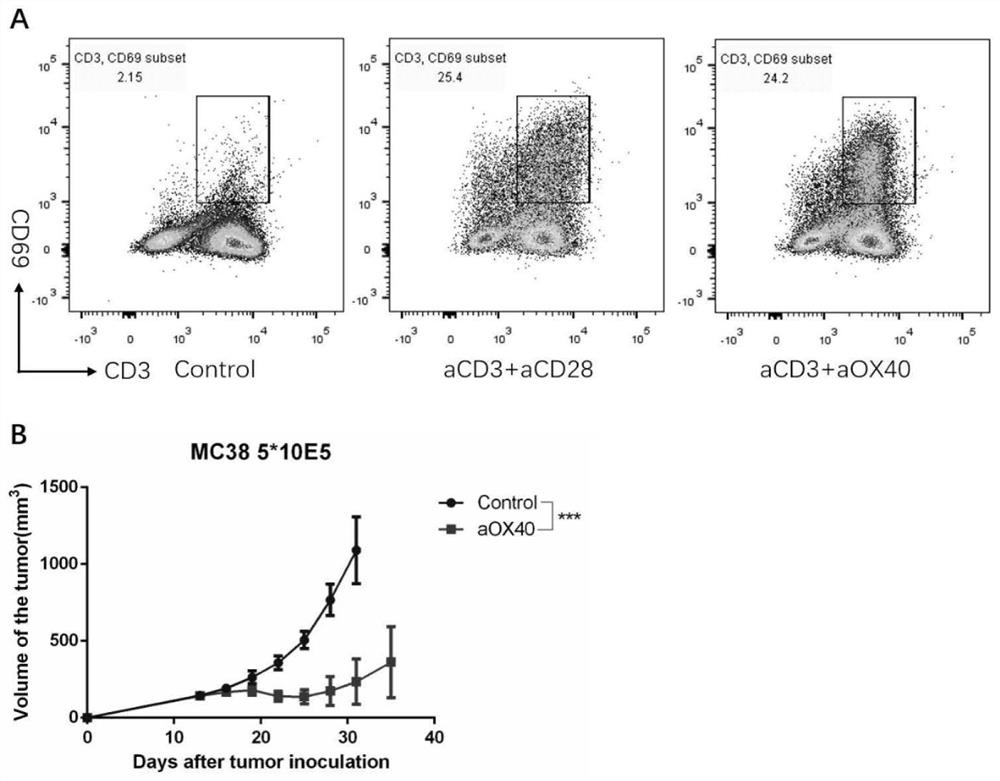
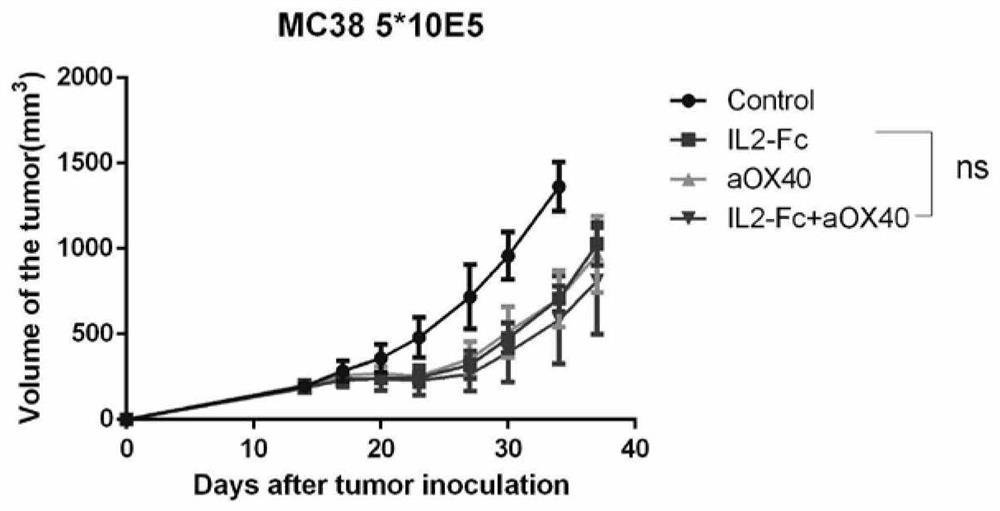
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Tnf family" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
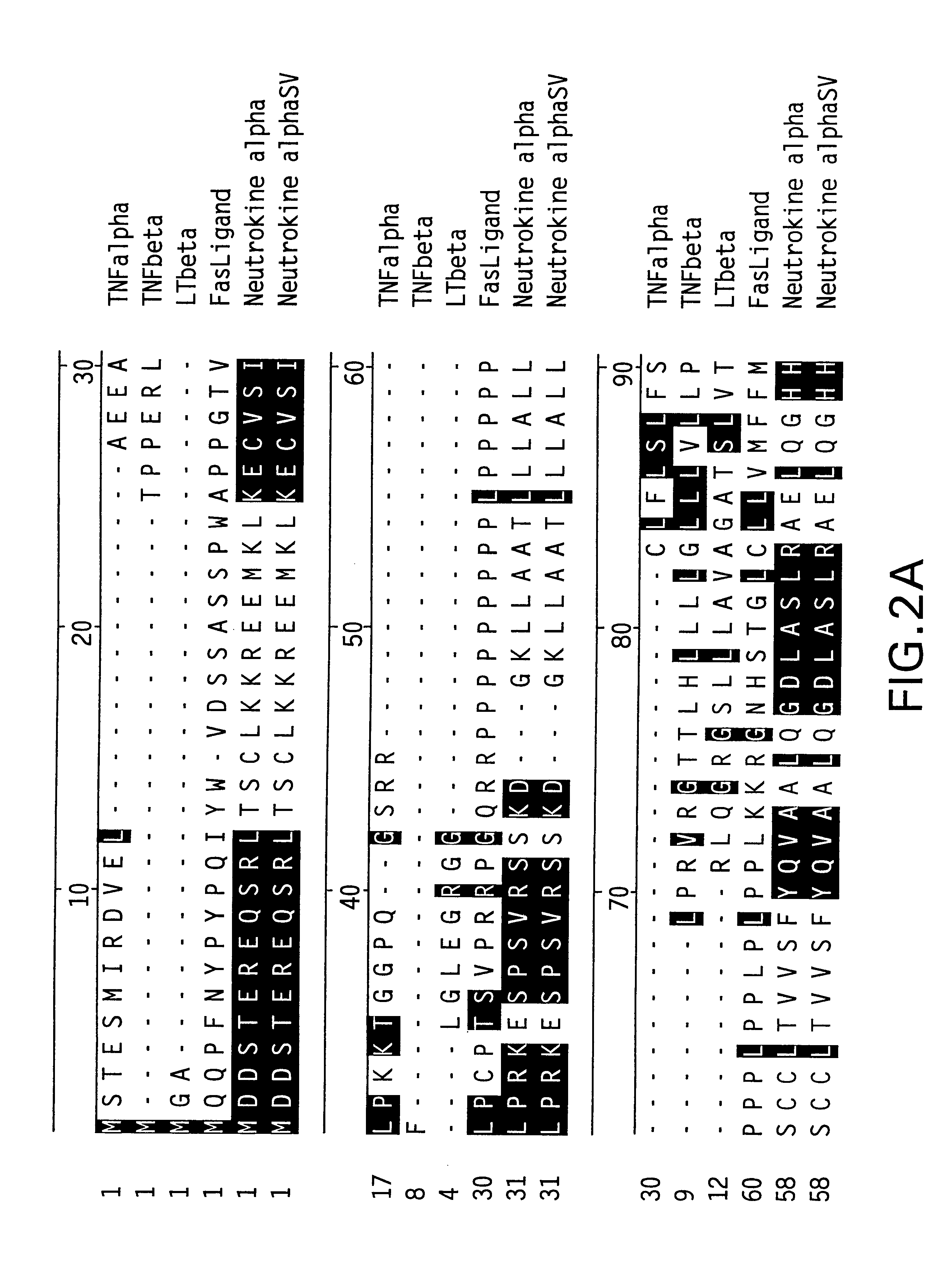
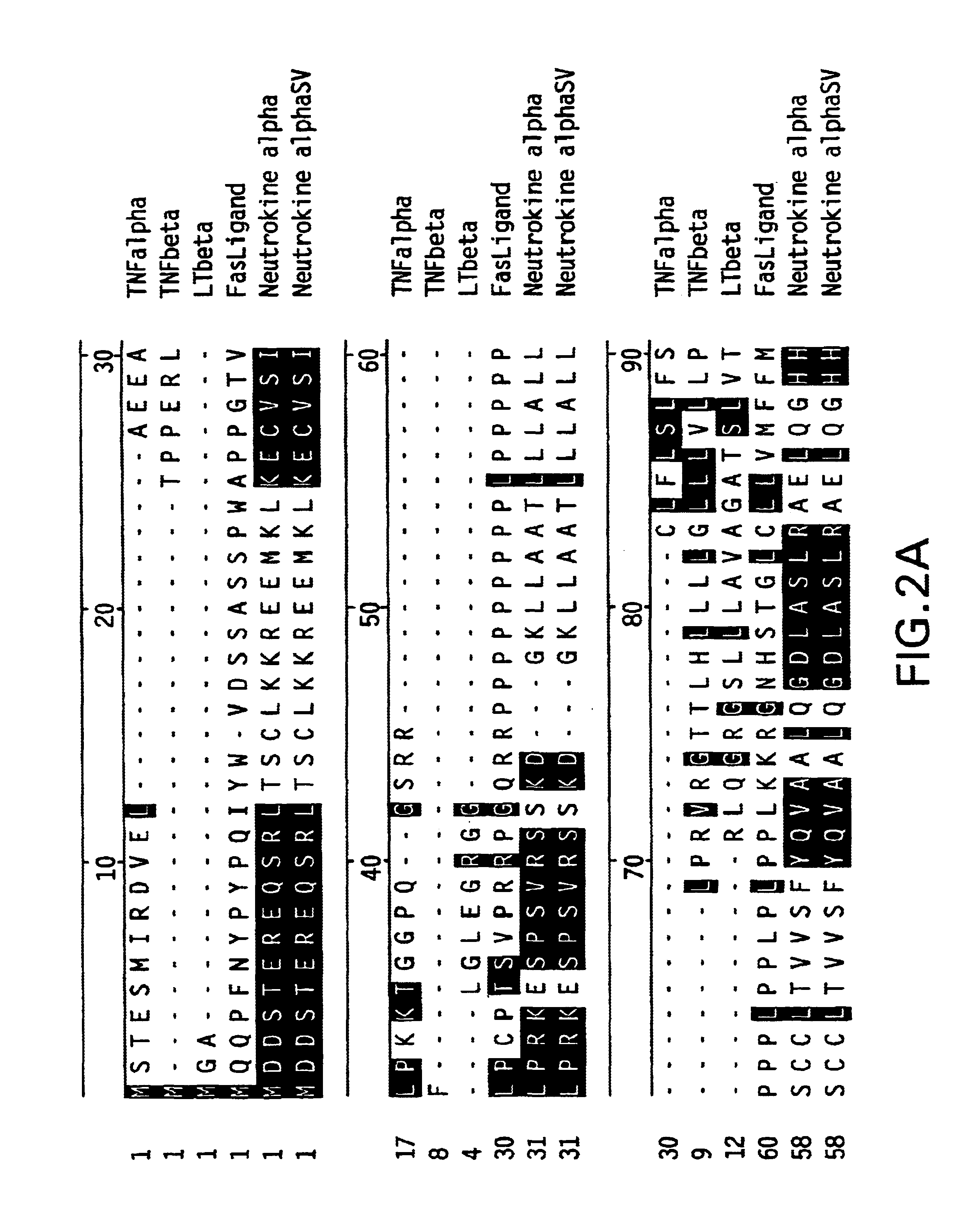
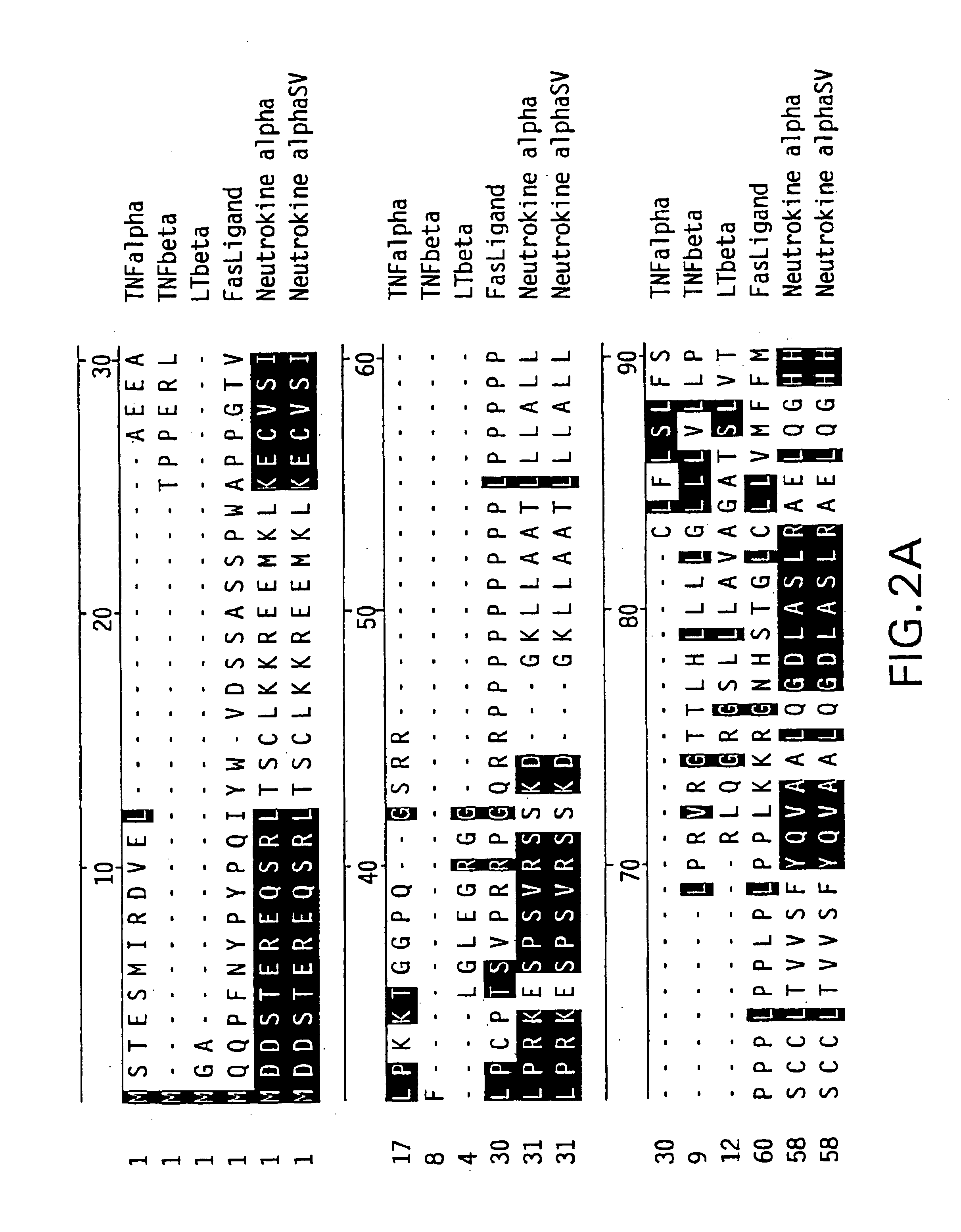
TNF family. The tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily refers to a superfamily of cytokines that can cause cell death (apoptosis). The first two members of the family to be identified were: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNFα or TNF alpha, is the best-known member of this class.
Antibodies to neutrokine-alpha
InactiveUS6403770B1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsScreening methodTnf family
The present invention relates to a novel Neutrokine-alpha, and a splice variant thereof designated Neutrokine-alphaSV, polynucleotides and polypeptides which are members of the TNF family. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding the human Neutrokine-alpha and / or Neutrokine-alphaSV polypeptides, including soluble forms of the extracellular domain. Neutrokine-alpha and / or Neutrokine-alphaSV polypeptides are also provided as are vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of Neutrokine-alpha and / or Neutrokine-alphaSV activity. Also provided are diagnostic methods for detecting immune system-related disorders and therapeutic methods for treating immune system-related disorders.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Method of assaying Neutrokine-alpha mRNA level
The present invention relates to a novel Neutrokine-a, and a splice variant thereof designated Neutrokine-aSV, polynucleotides and polypeptides which are members of the TNF family. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding the human Neutrokine-a and / or Neutrokine-aSV polypeptides, including soluble forms of the extracellular domain. Neutrokine-a and / or Neutrokine-aSV polypeptides are also provided as are vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of Neutrokine-a and / or Neutrokine-aSV activity. Also provided are diagnostic methods for detecting immune system-related disorders and therapeutic methods for treating immune system-related disorders.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Neutrokine-alpha polypeptides
The present invention relates to a novel Neutrokine-alpha, and a splice variant thereof designated Neutrokine-alphaSV, polynucleotides and polypeptides which are members of the TNF family. In particular isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding the human Neutrokine-alpha and / or Neutrokine-alphaSV polypeptides, including soluble forms of the extracellular domain. Neutrokine-alpha and / or Neutrokine-alphaSV agonists and antagonists of Neutrokine-alpha and / or Neutrokine-alphaSV activity. Also producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of Neutrokine-alpha and / or Neutrokine-alphaSV activity. Also provided are diagnostic methods for detecting immune system-related disorders and therapeutic methods for treating immune system-related disorders.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Methods of modulating the ox40 receptor to treat cancer
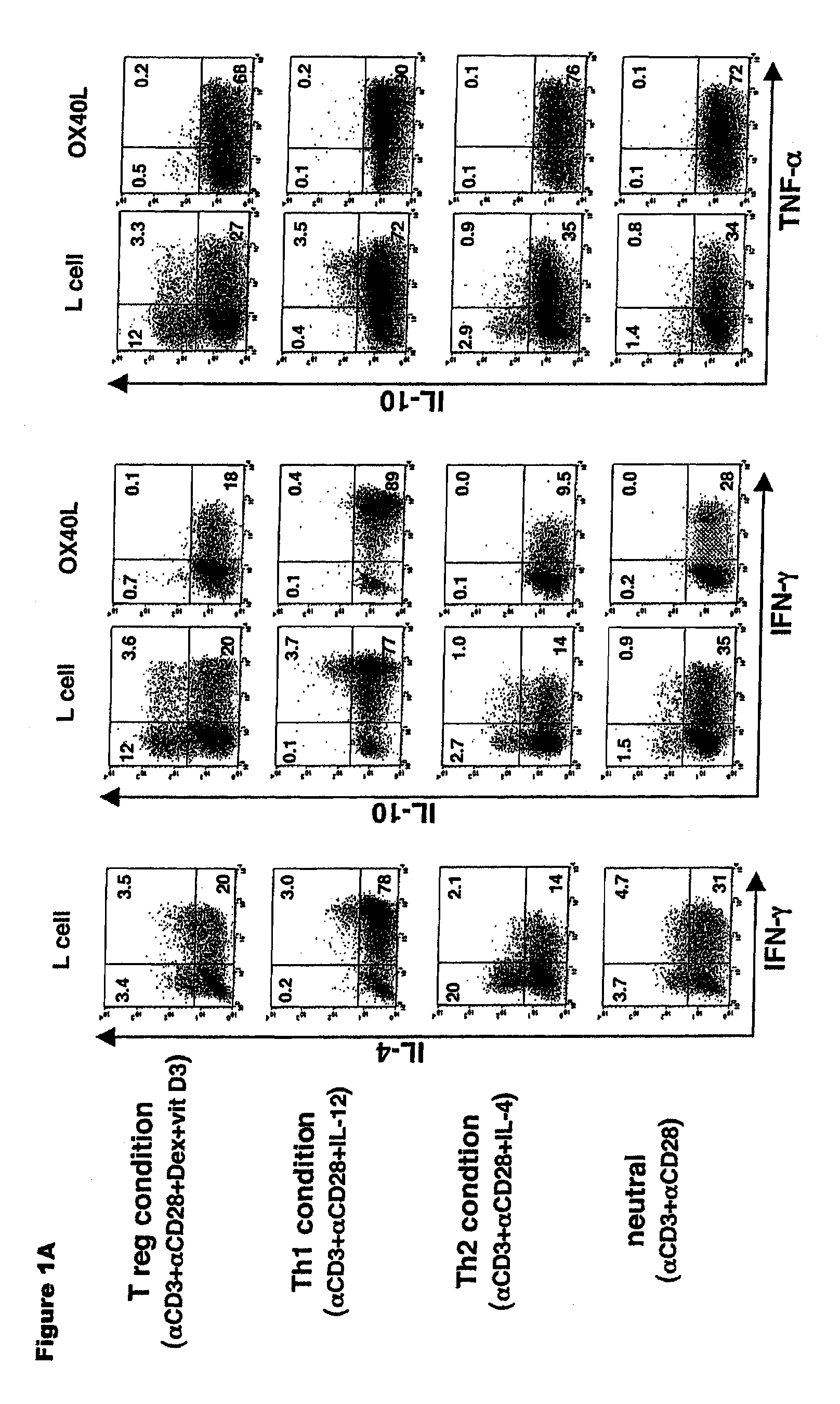
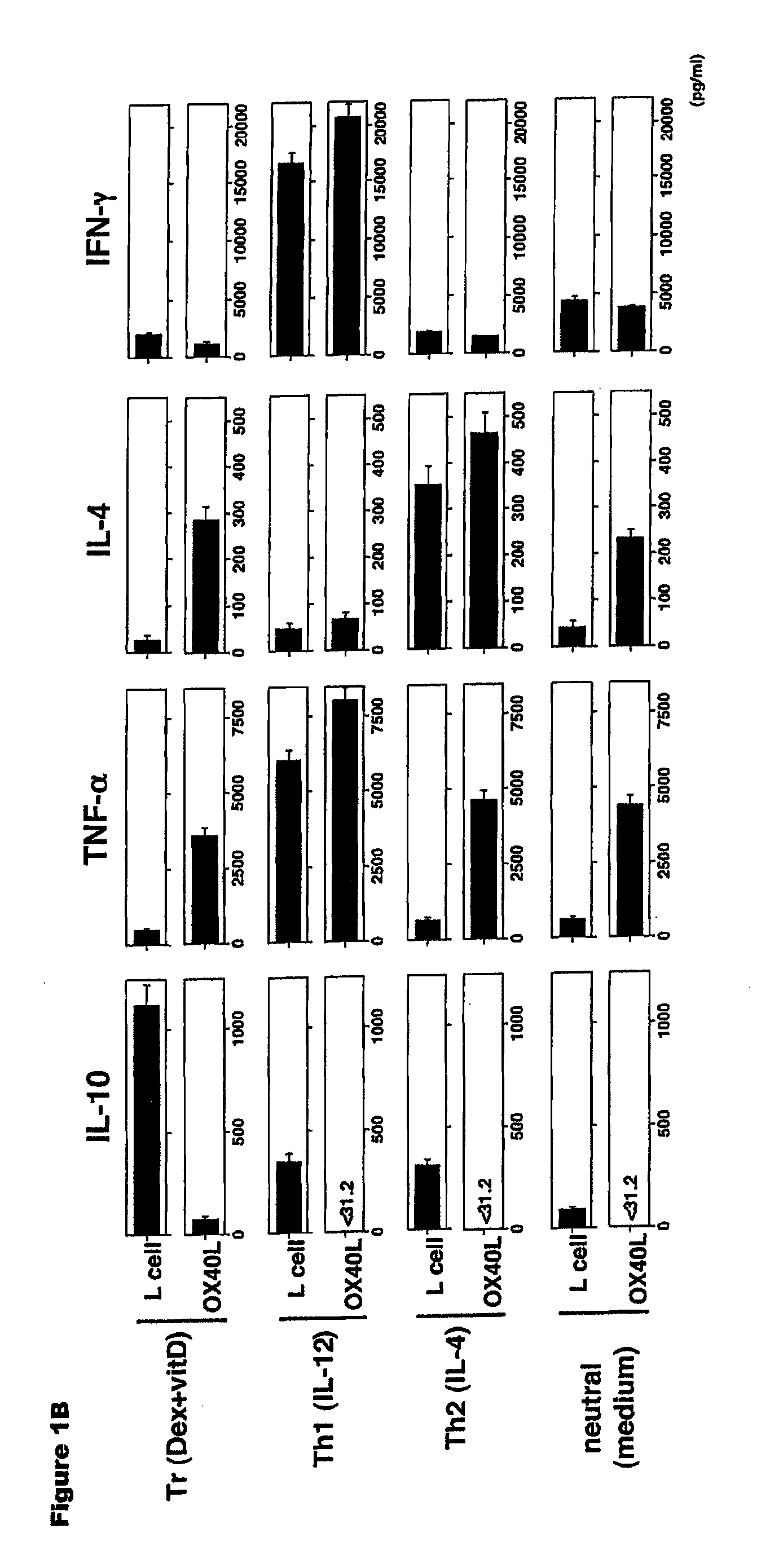
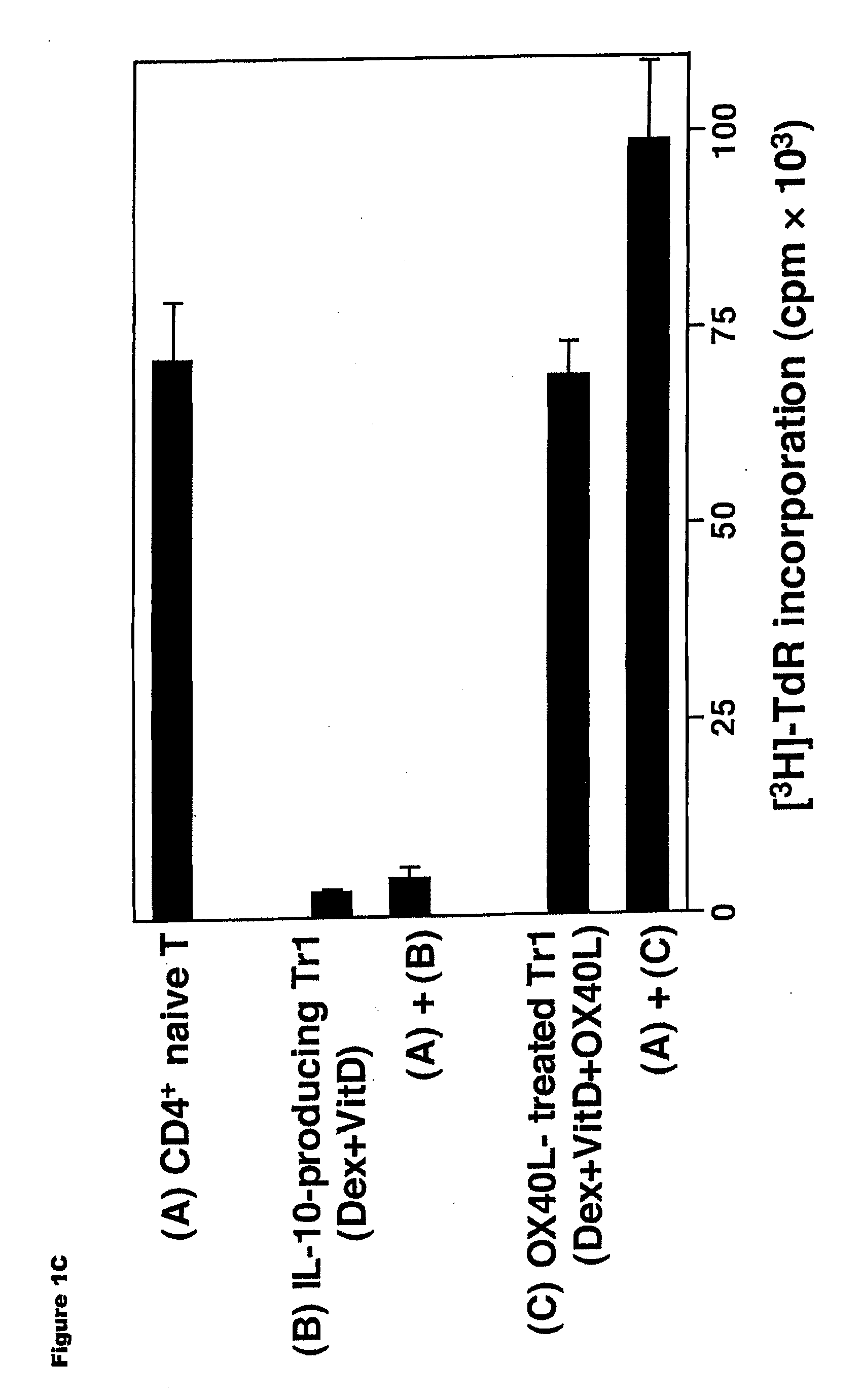
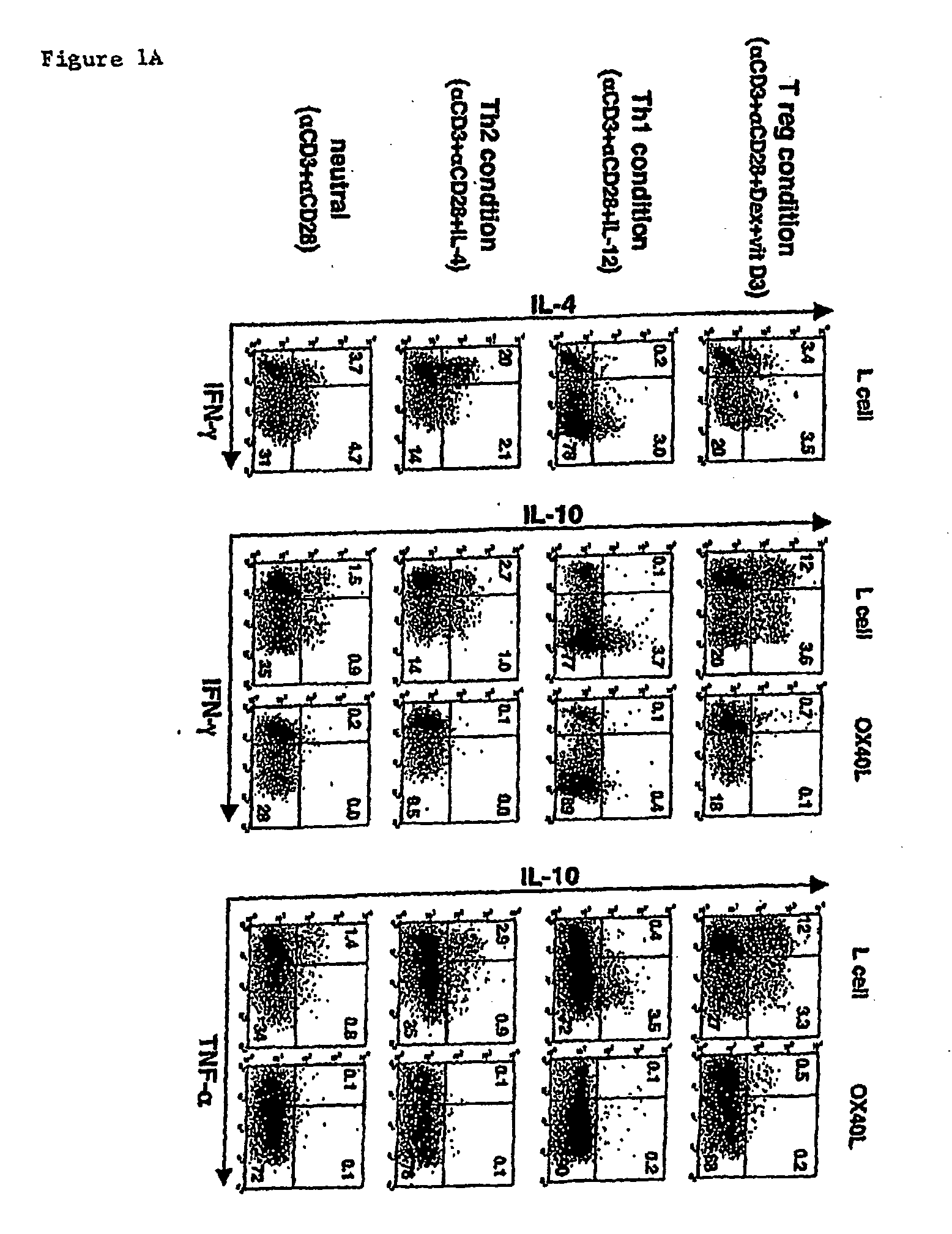
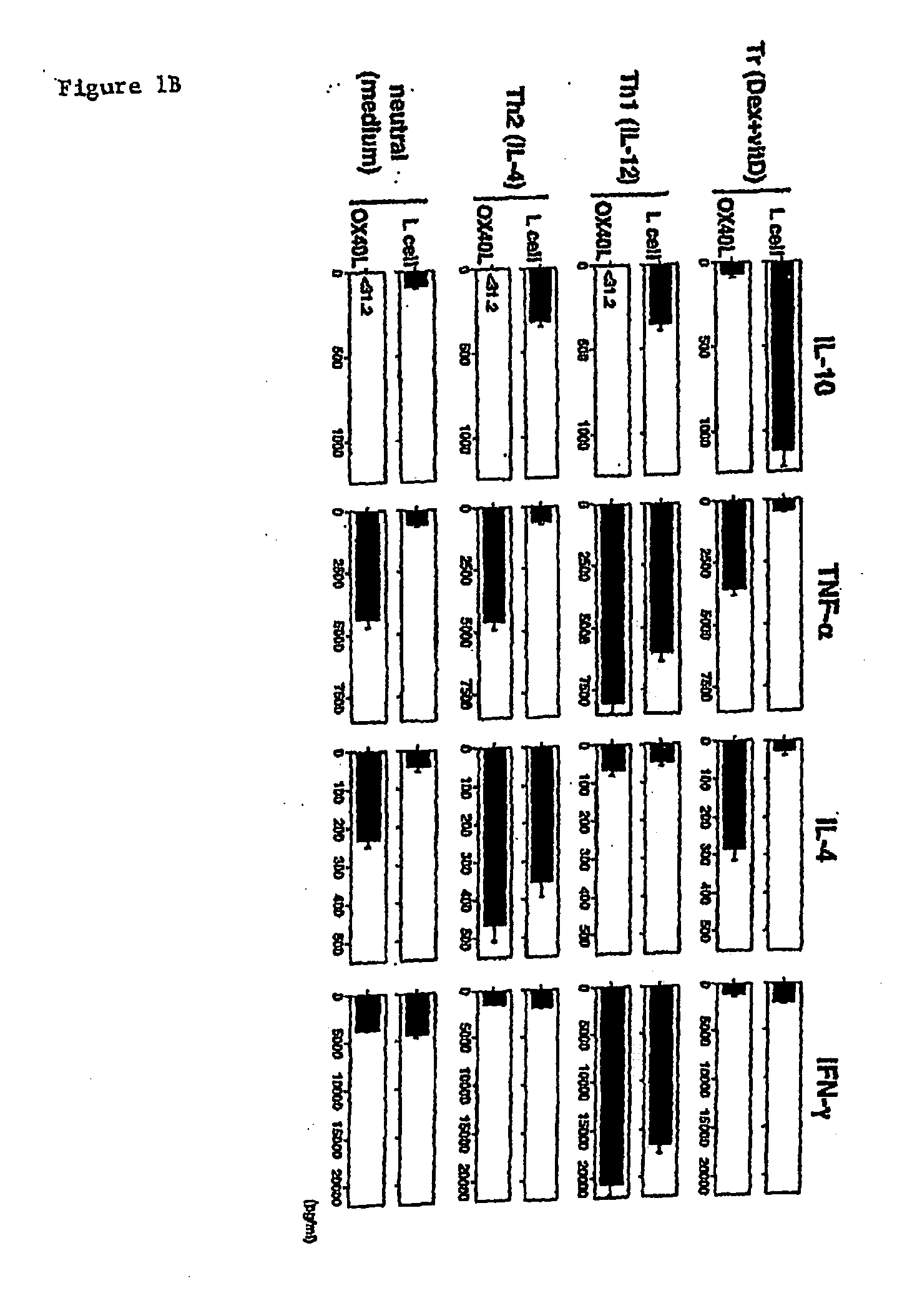
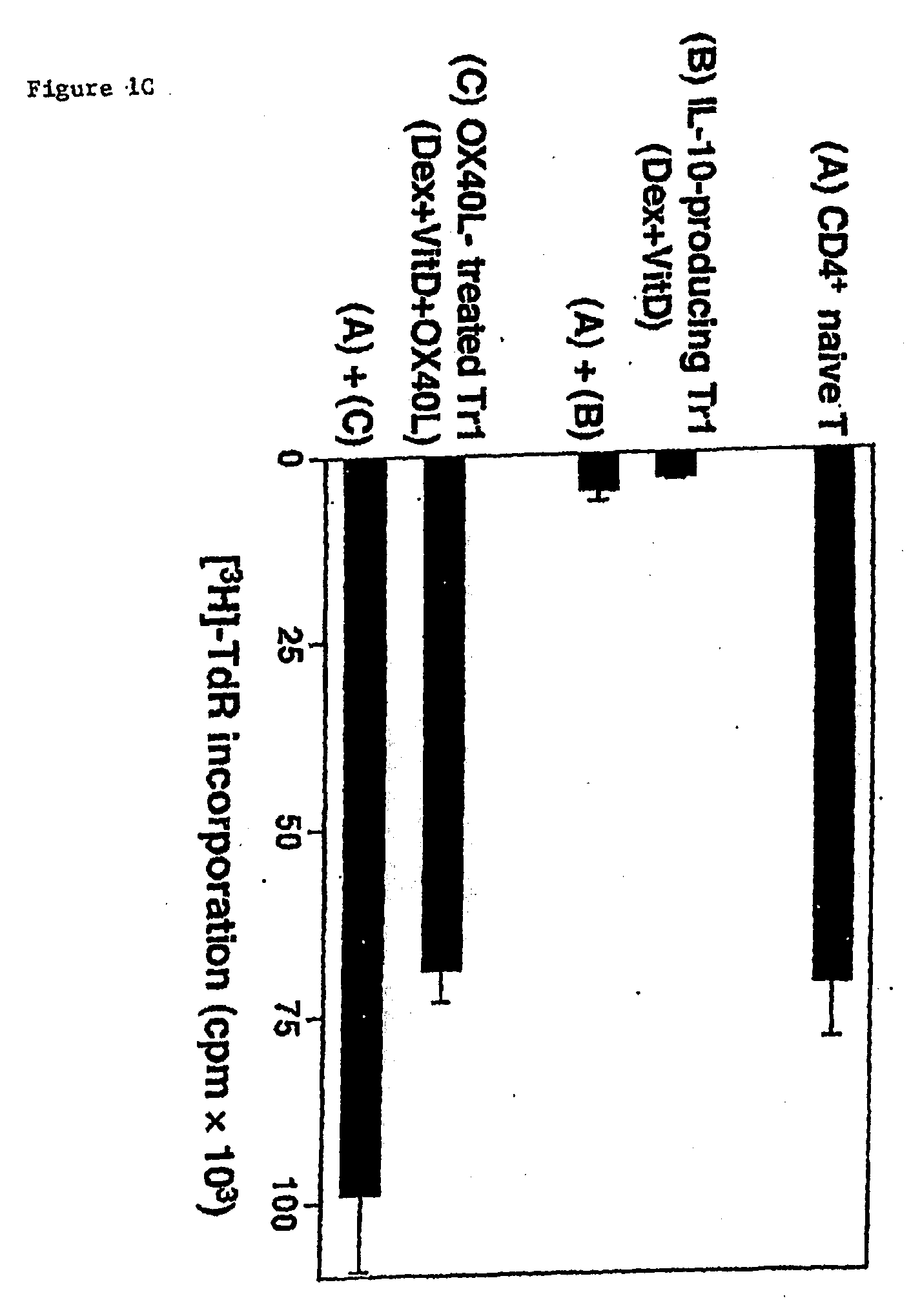
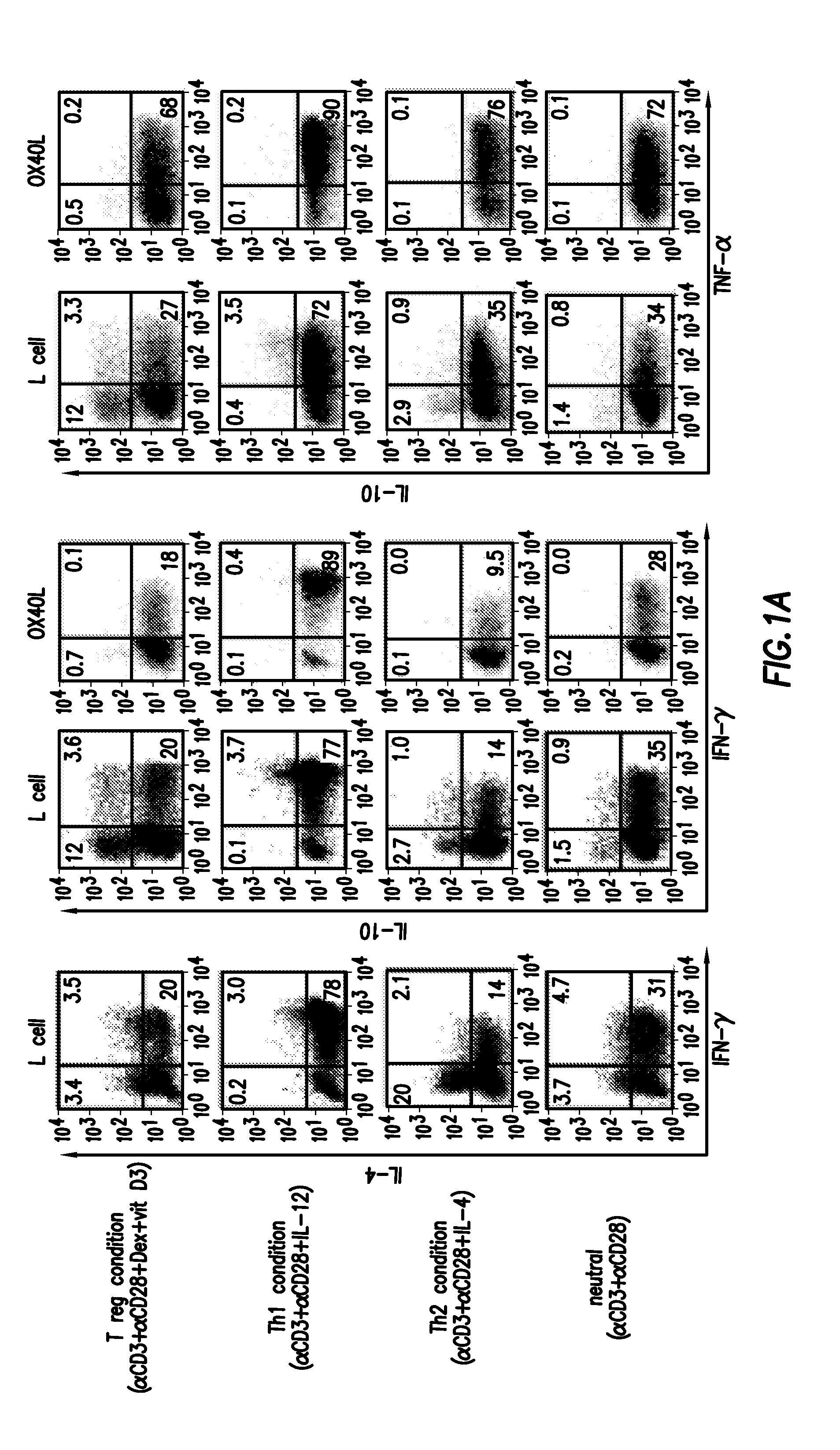
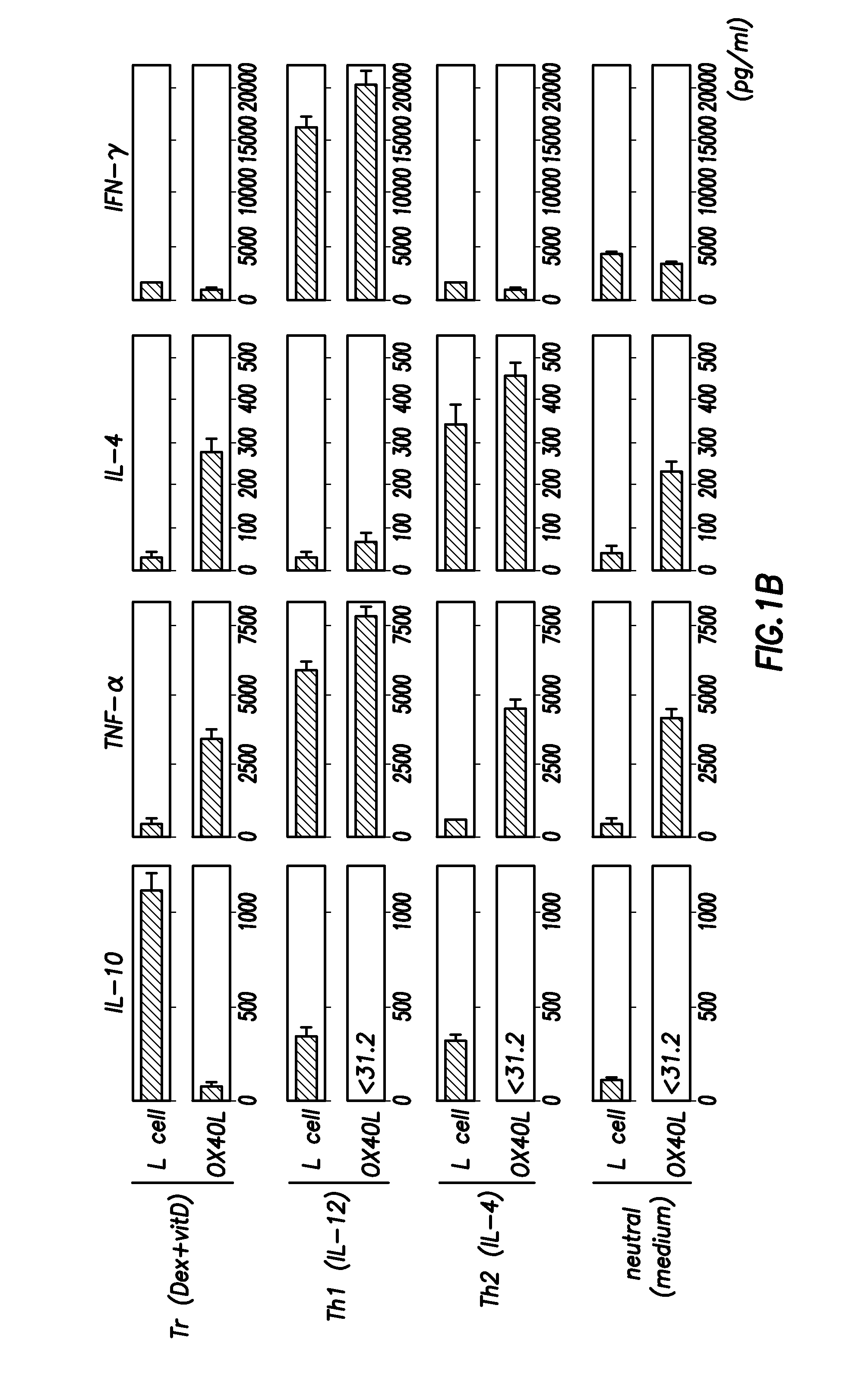
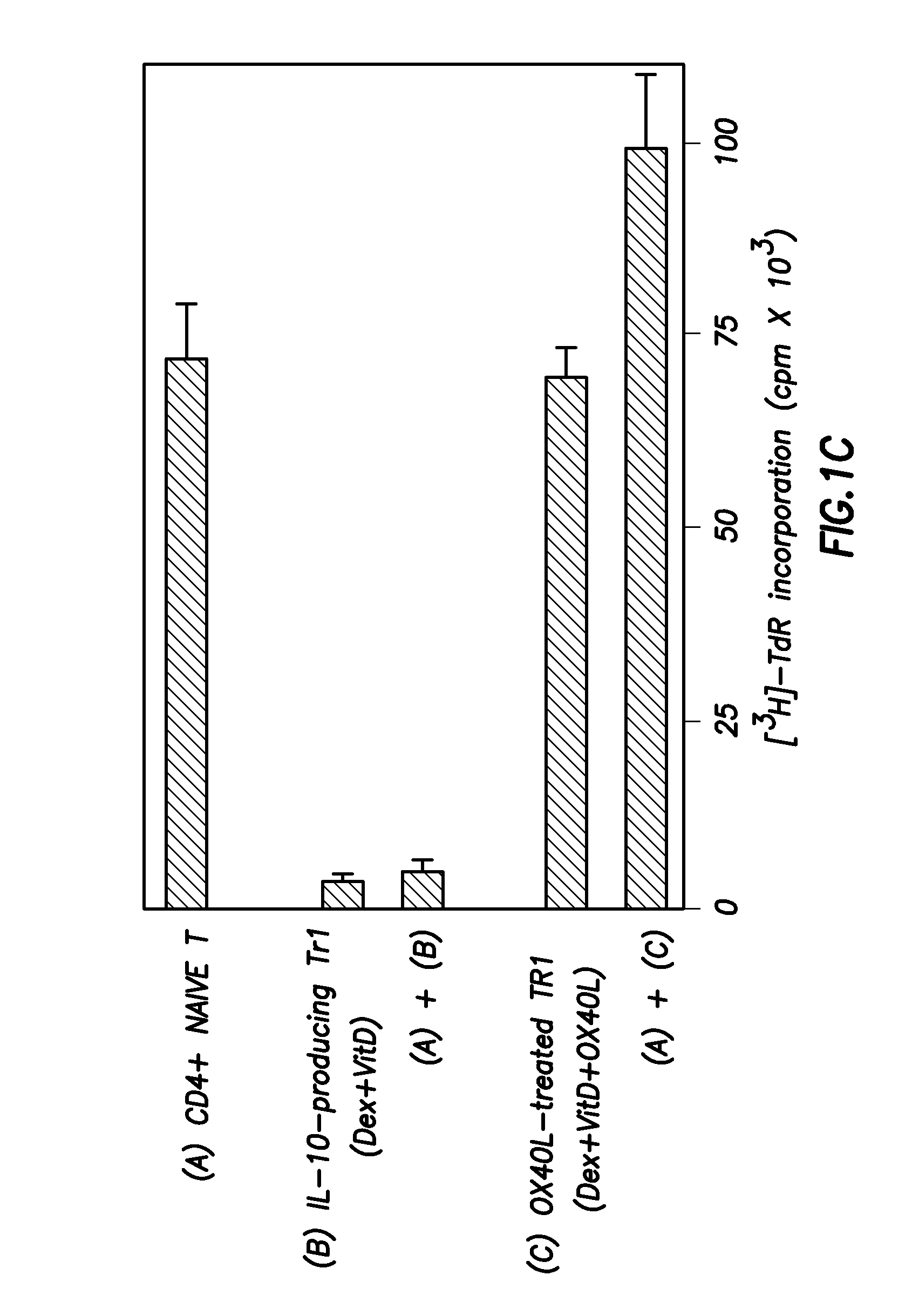
Numerous disease states, such as human allergic, autoimmune, and autoimmune diseases, and cancer, may be treated by targeting OX40 / OX4OL. OX4OL inhibits the generation of Tr1 cells from naïve and memory CD4+ T cells. This unique function of OX4OL is not shared by two other costimulatory TNF-family members, GITR-ligand and 4-1BB-ligand. It has been shown that signaling the OX40-receptor on human T cells by antibodies, small molecules, or the OX4OL modulates the generation and function of IL-10 producing Foxp3+ Treg immunosuppressive T cells and blocks Foxp3+ Treg function. Further, provided are high throughput methods for identifying compounds that can inhibit the immunosuppressive function of IL-10 producing Tr1 cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods to Treat Disease States by Influencing the Signaling of Ox-40-Receptors and High Throughput Screening Methods for Identifying Substances Therefor
InactiveUS20080286286A1Peptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisDiseaseRegulatory T cell
OX40L inhibits the generation of IL-10-producing Tr1 cells from naïve and memory CD4+ T cells induced by the immunuosuppressive drugs dexamethasone and vitamin D3. This unique function of OX40L is not shared by two other costimulatory TNF-family members, GITR-ligand and 4-1BB-ligand. OX40L also strongly inhibits the generation of IL-10-producing Tr1 cells induced by two physiological stimuli provided by inducible costimulatory ligand and immature DCs and inhibits the production of IL-10 by regulatory T cells. It has thus been shown that signaling the OX40-receptor on human T cells by monoclonal antibodies, small molecules, or OX40L regulates the generation and function of IL-10 producing immunosuppressive T cells. Also provided are high throughput methods for identifying substances that promote or inhibit the generation and function of IL-10 producing T cells. Numerous disease states, such as human allergic, autoimmune, and autoimmune diseases, and cancer, may be treated by targeting OX40 / OX40L.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods of modulating the ox40 receptor to treat cancer
Numerous disease states, such as human allergic, autoimmune, and autoimmune diseases, and cancer, may be treated by targeting OX40 / OX40L. OX40L inhibits the generation of Tr1 cells from naïve and memory CD4+ T cells. This unique function of OX40L is not shared by two other costimulatory TNF-family members, GITR-ligand and 4-1BB-ligand. It has been shown that signaling the OX40-receptor on human T cells by antibodies, small molecules, or the OX40L modulates the generation and function of IL-10 producing Foxp3+ Treg immunosuppressive T cells and blocks Foxp3+ Treg function. Further, provided are high throughput methods for identifying compounds that can inhibit the immunosuppressive function of IL-10 producing Tr1 cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
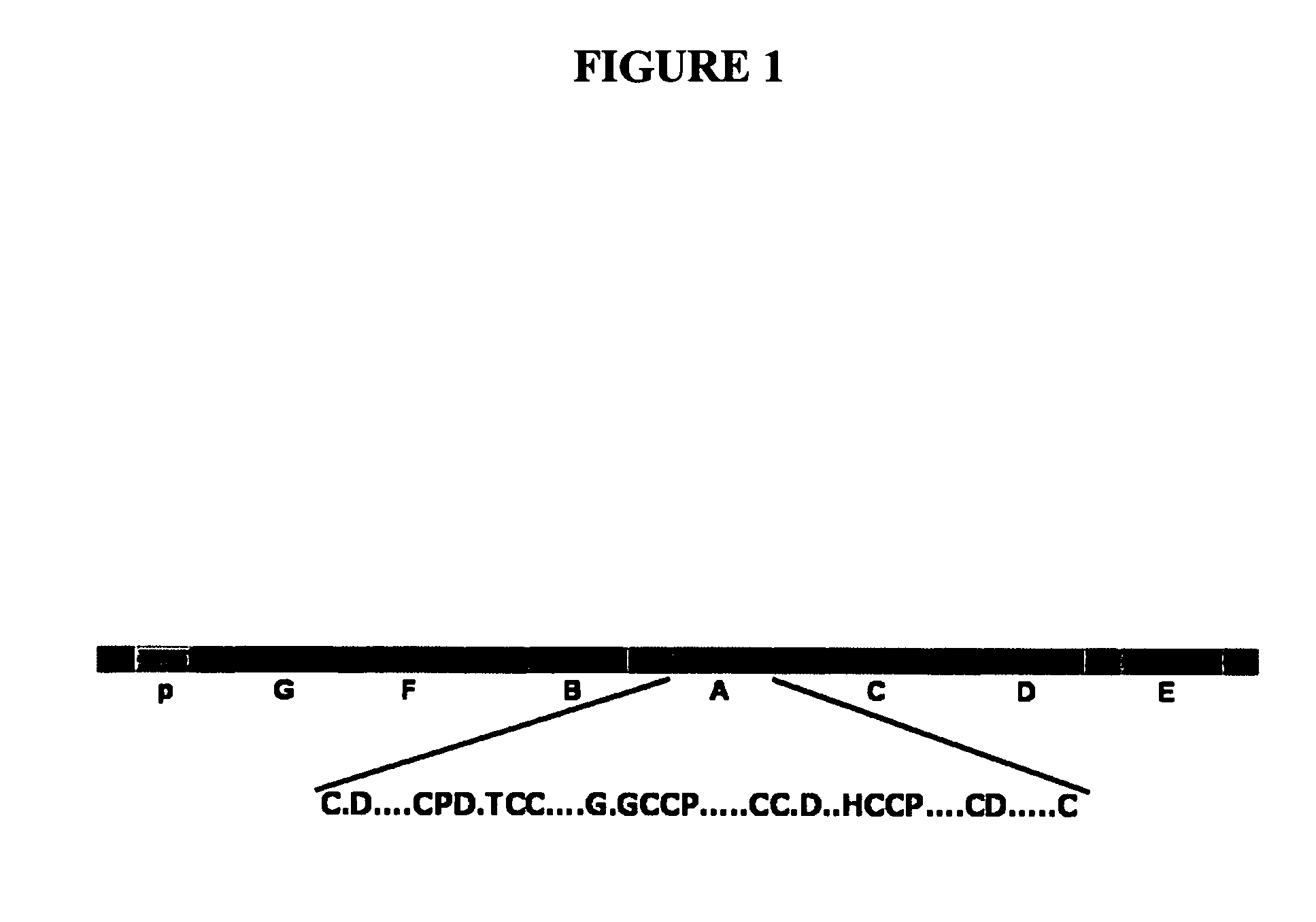
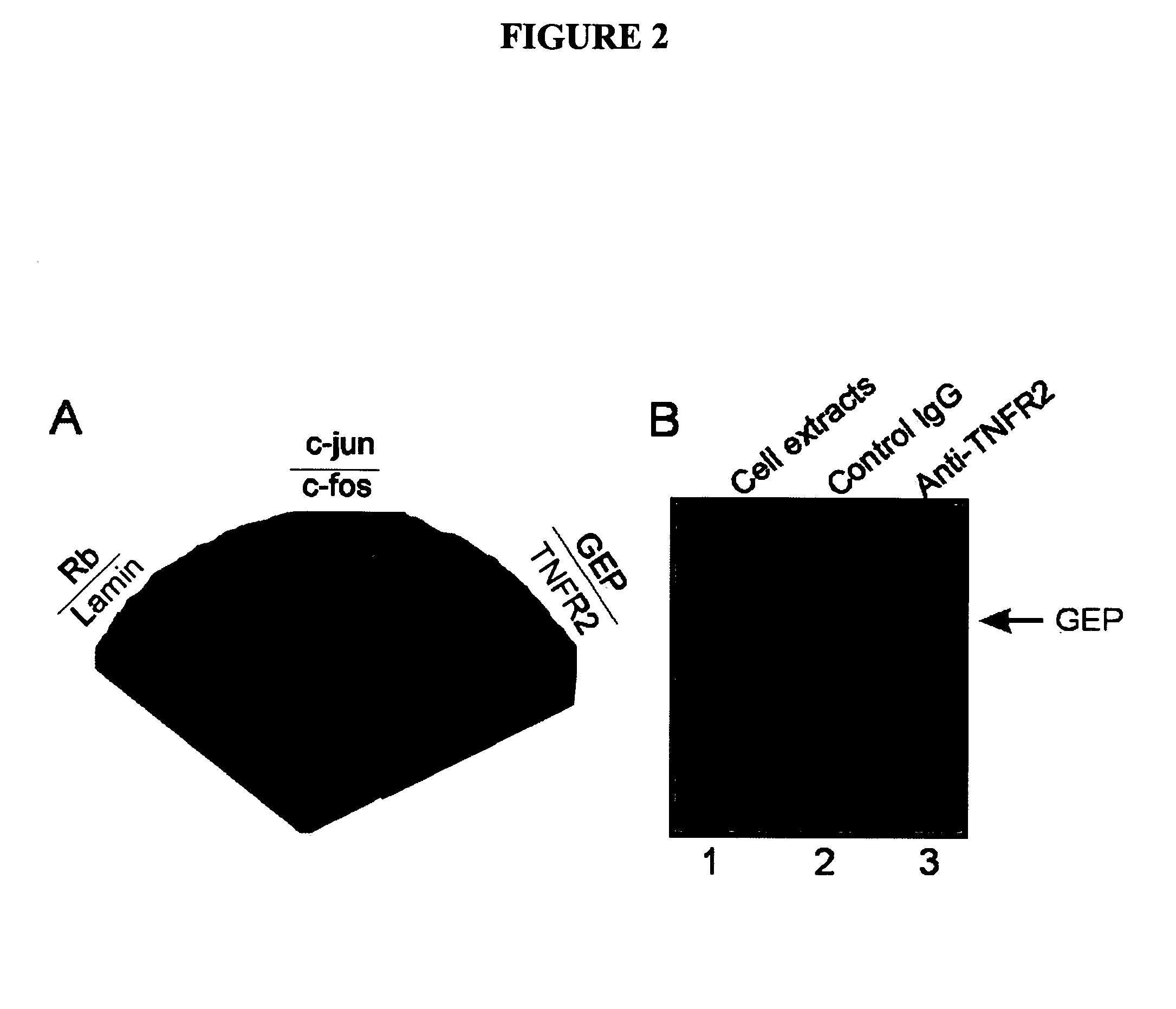
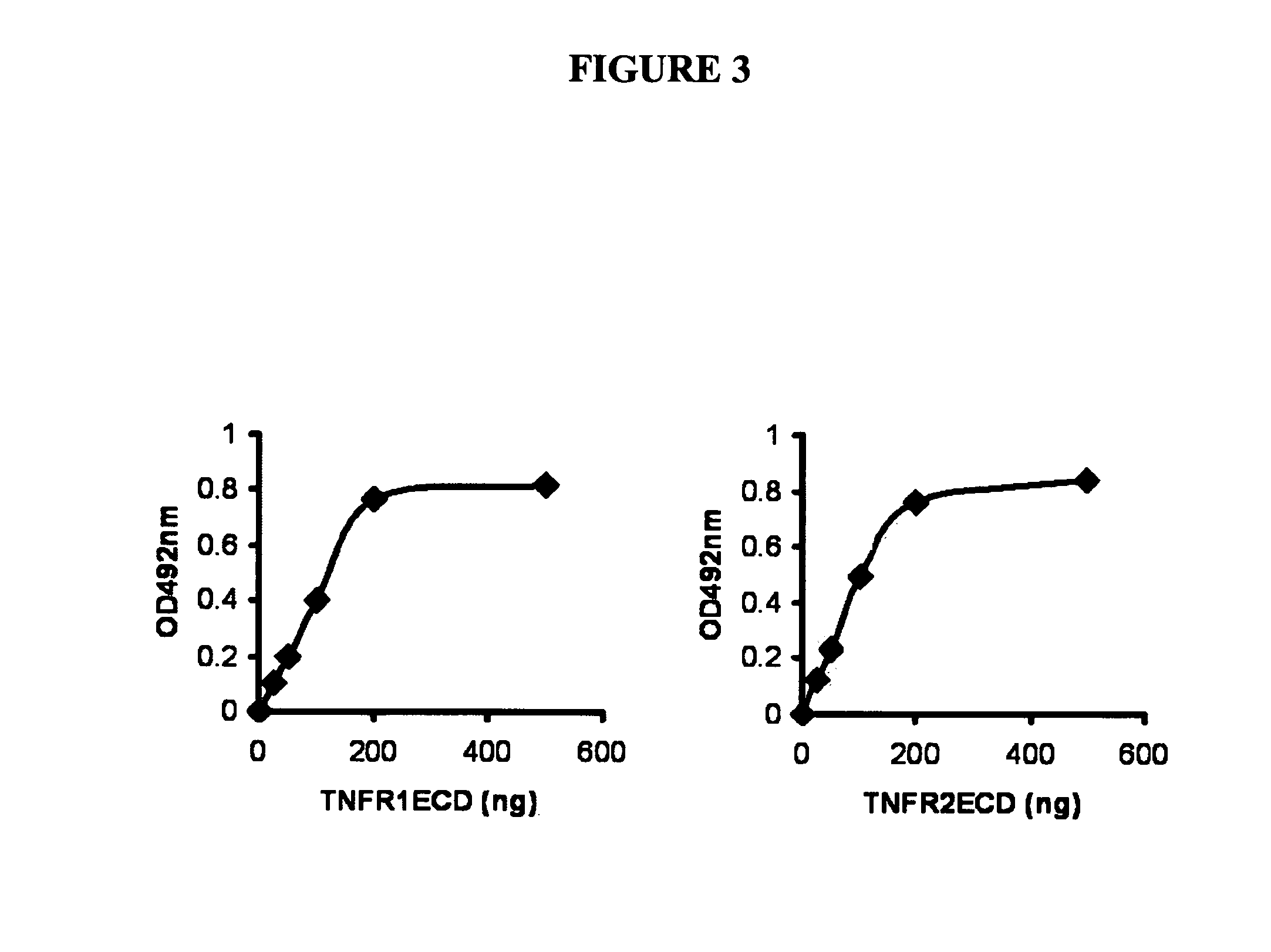
Peptides targeting TNF family receptors and antagonizing TNF action, compositions, methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100298232A1Easy to manageRemissionCompounds screening/testingSenses disorderUveitisUlcerative colitis
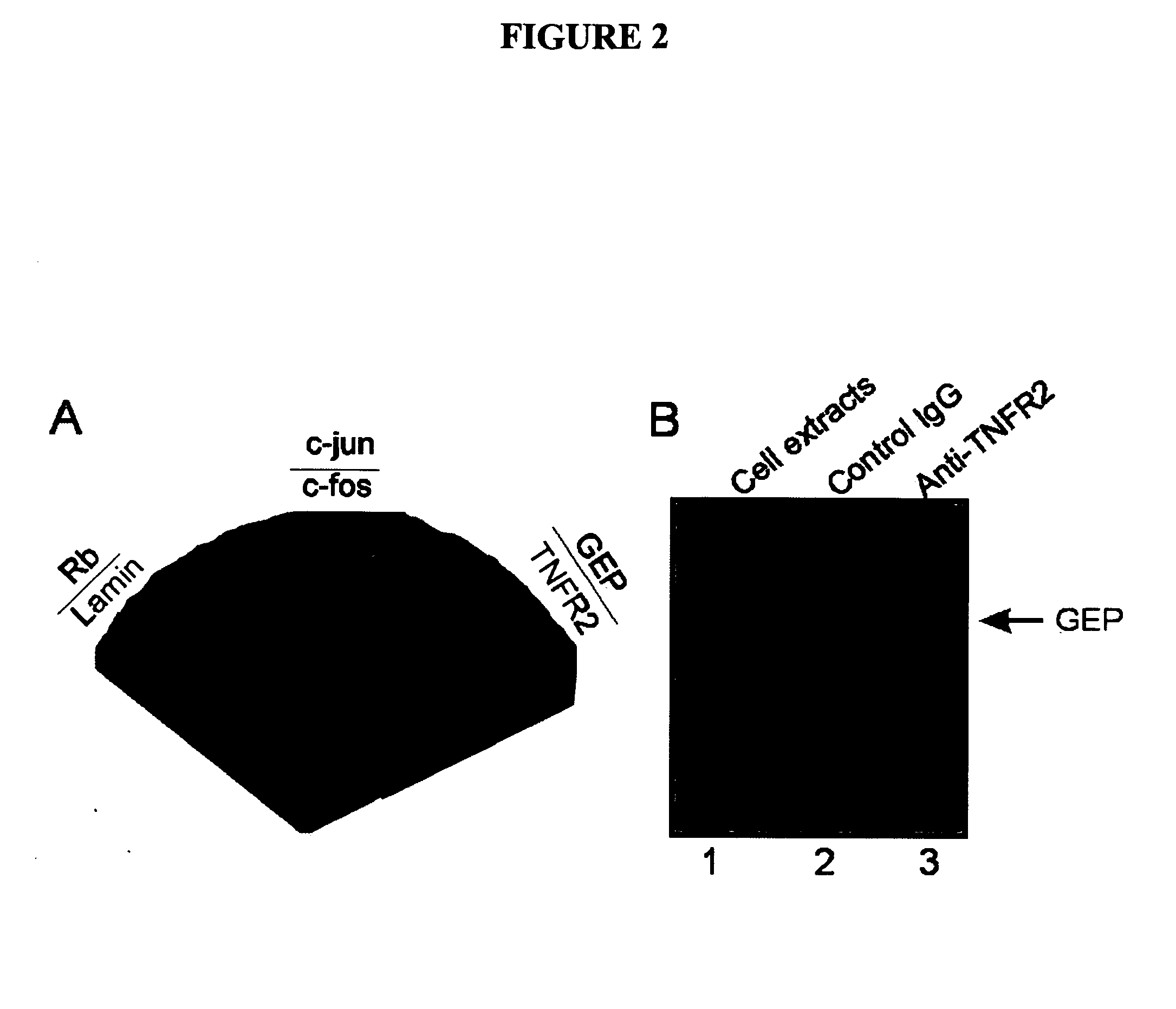
The present invention provides modulators of TNF, particularly peptides and their derivatives, particularly GEP peptides, which antagonize TNF and TNF-mediated responses, activity or signaling. The invention provides methods of antagonizing TNF and the modulation of TNF-mediated diseases or responses, including inflammatory diseases and conditions. Compositions of GEP peptides, including in combination with other inflammatory mediators, are provided. Methods of treatment, alleviation, or prevention of TNF-mediated diseases and inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel diseases, Chrohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, uveitis, inflammatory lung diseases, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are provided.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
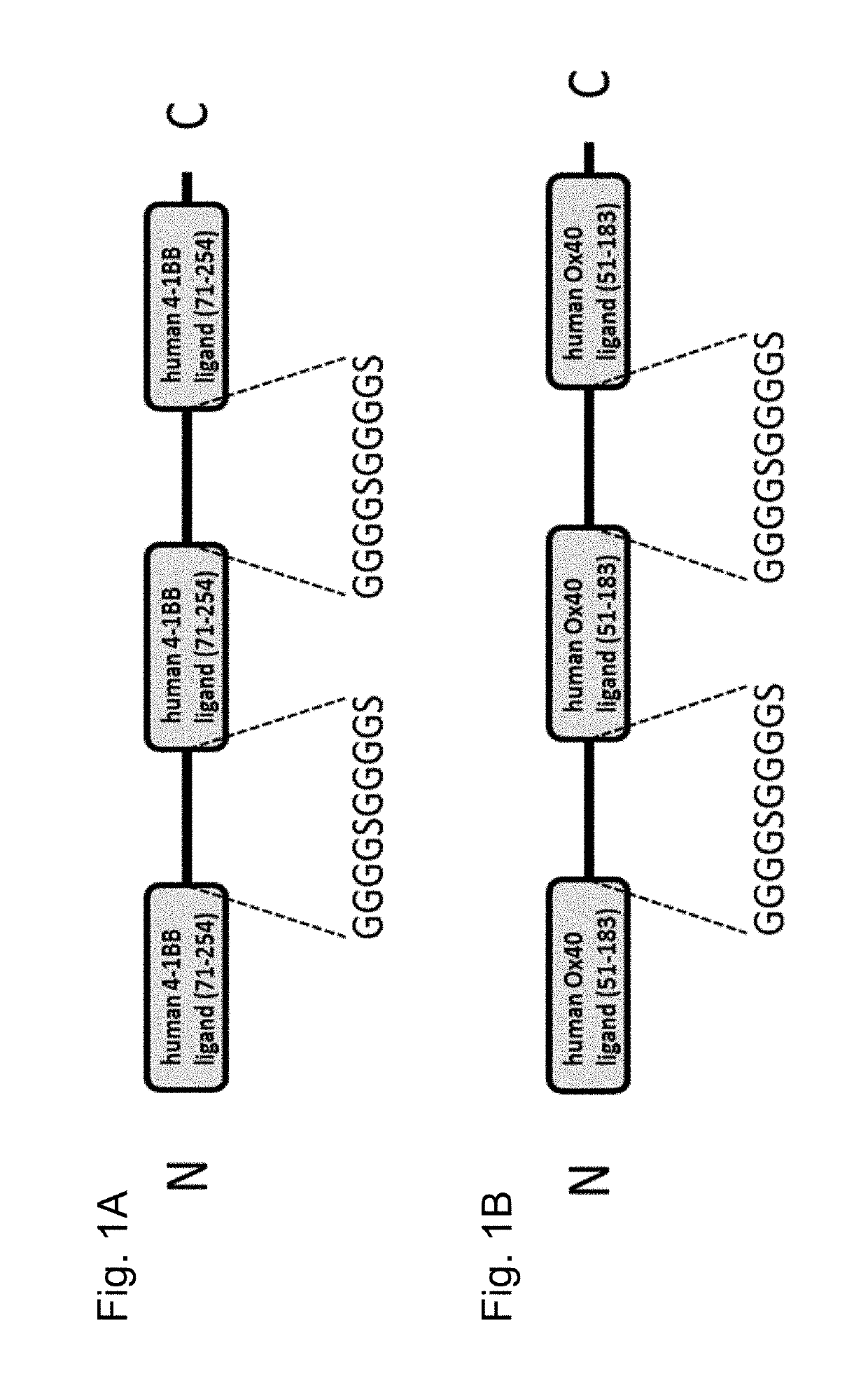
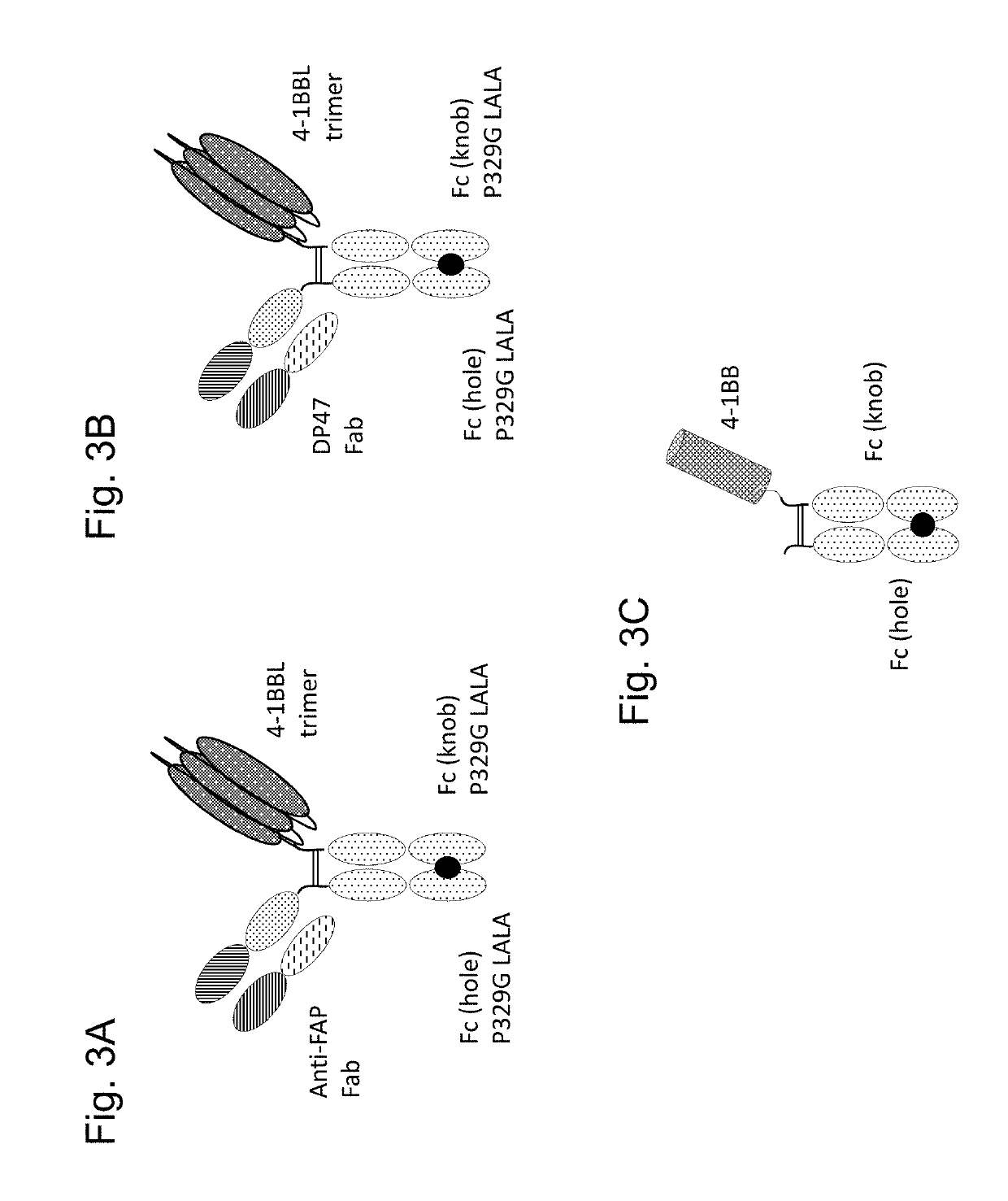
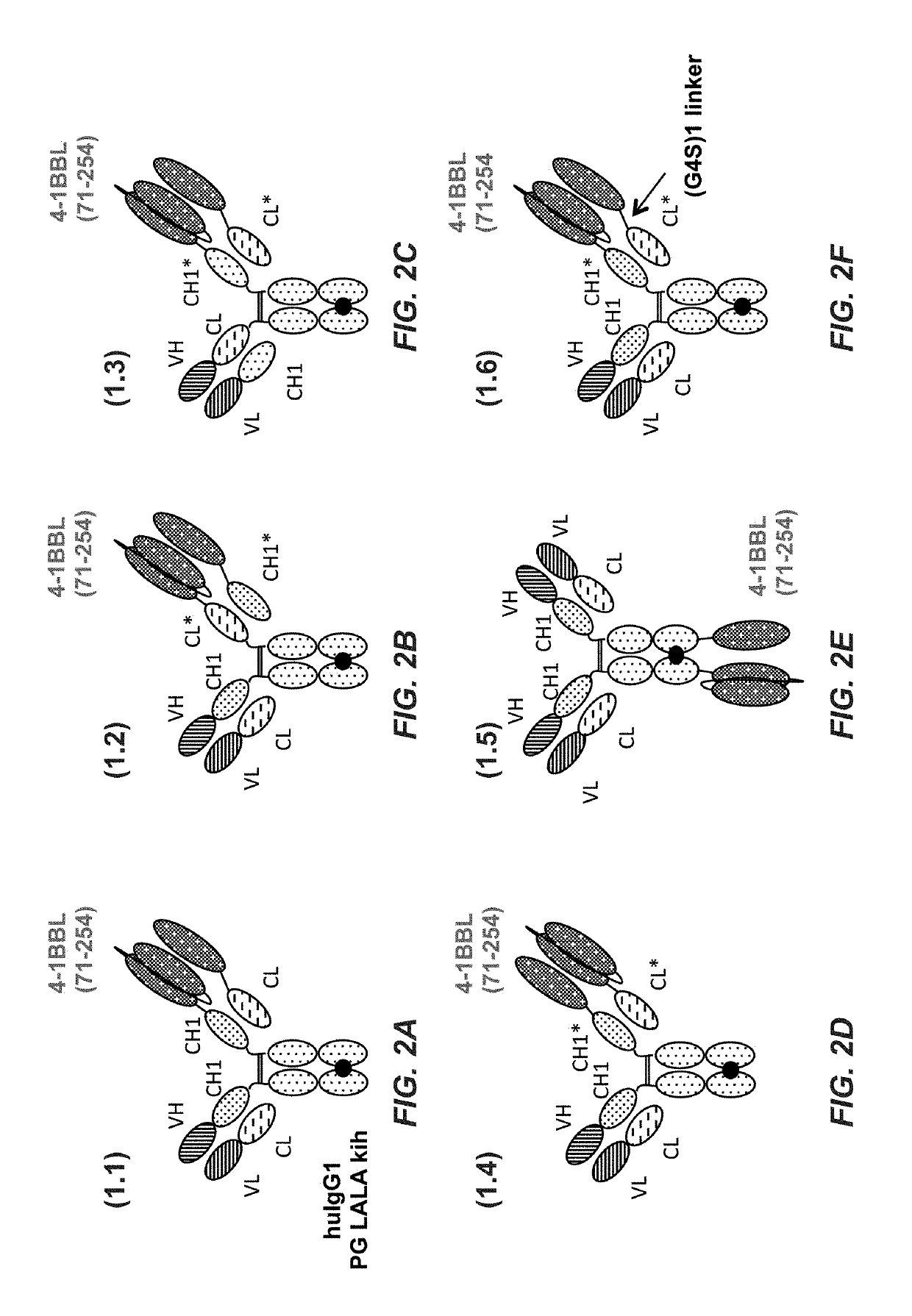
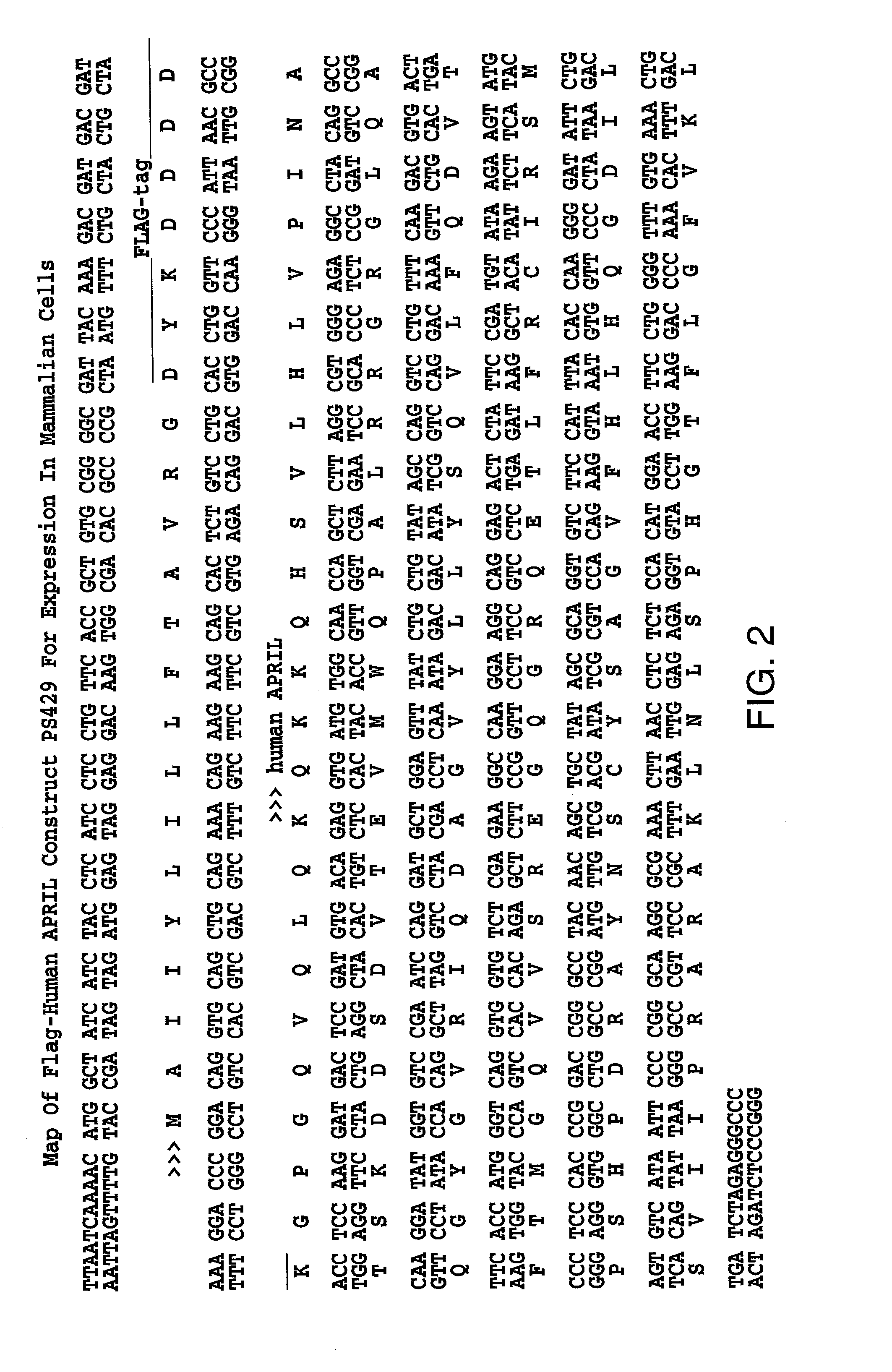
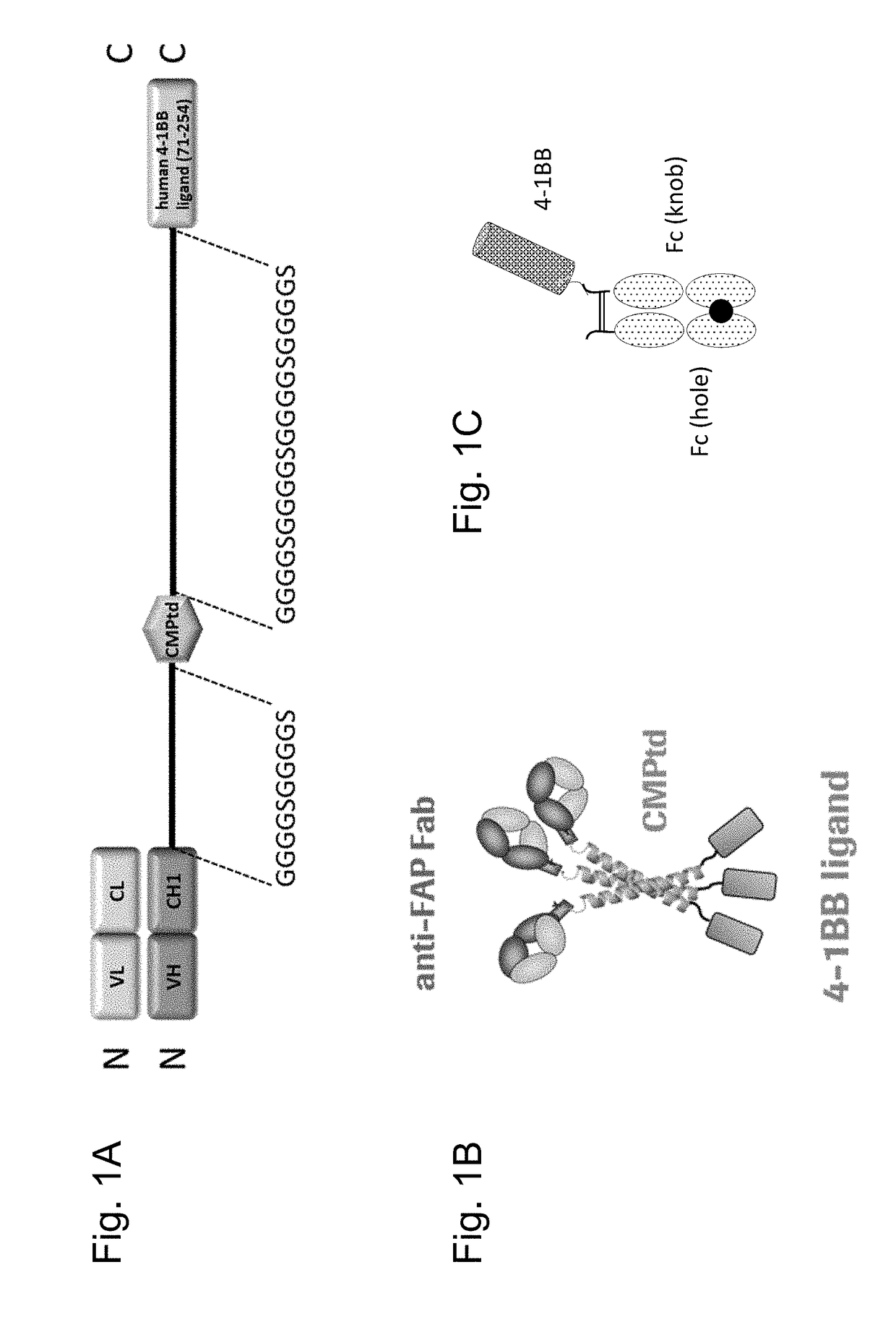
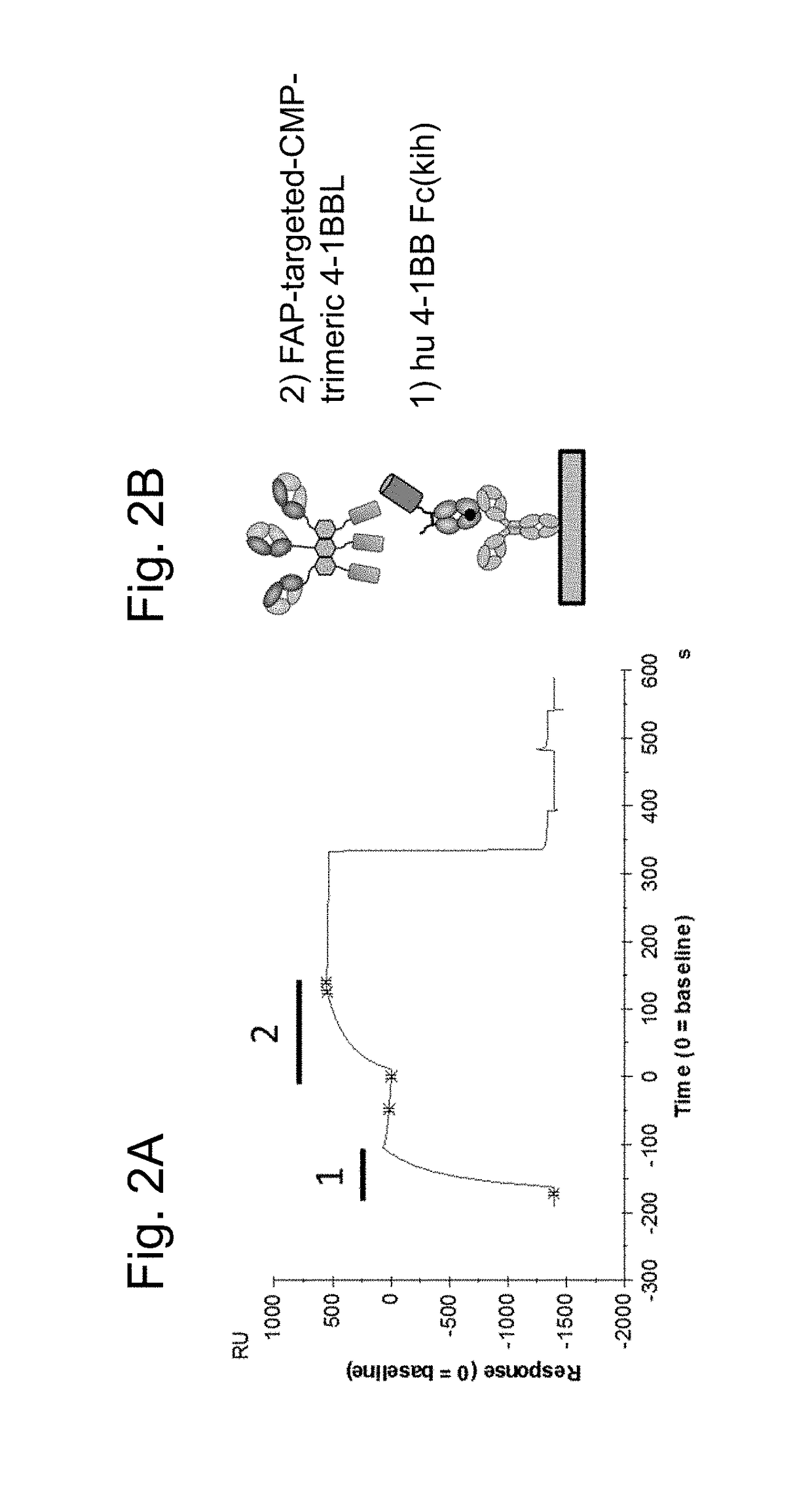
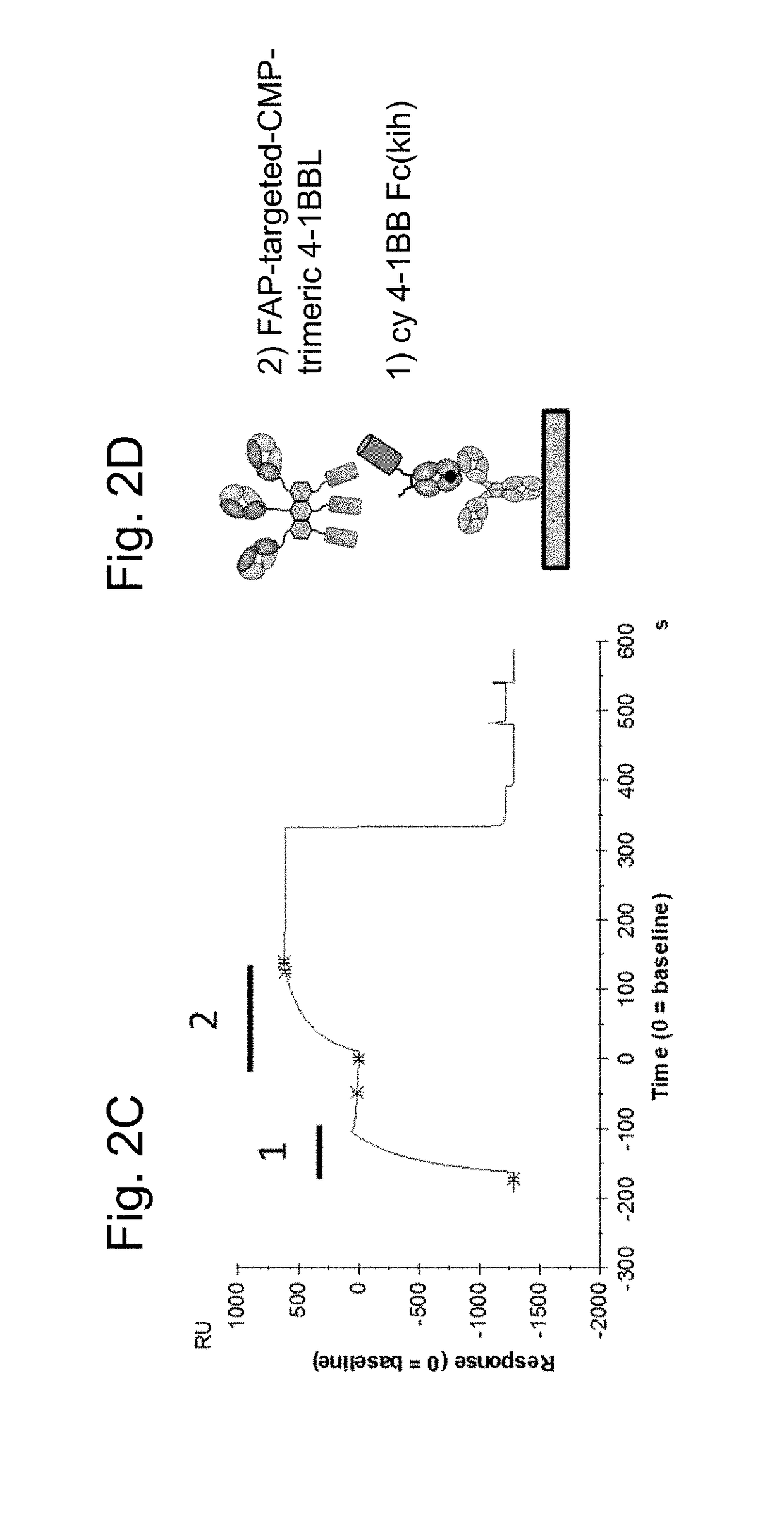
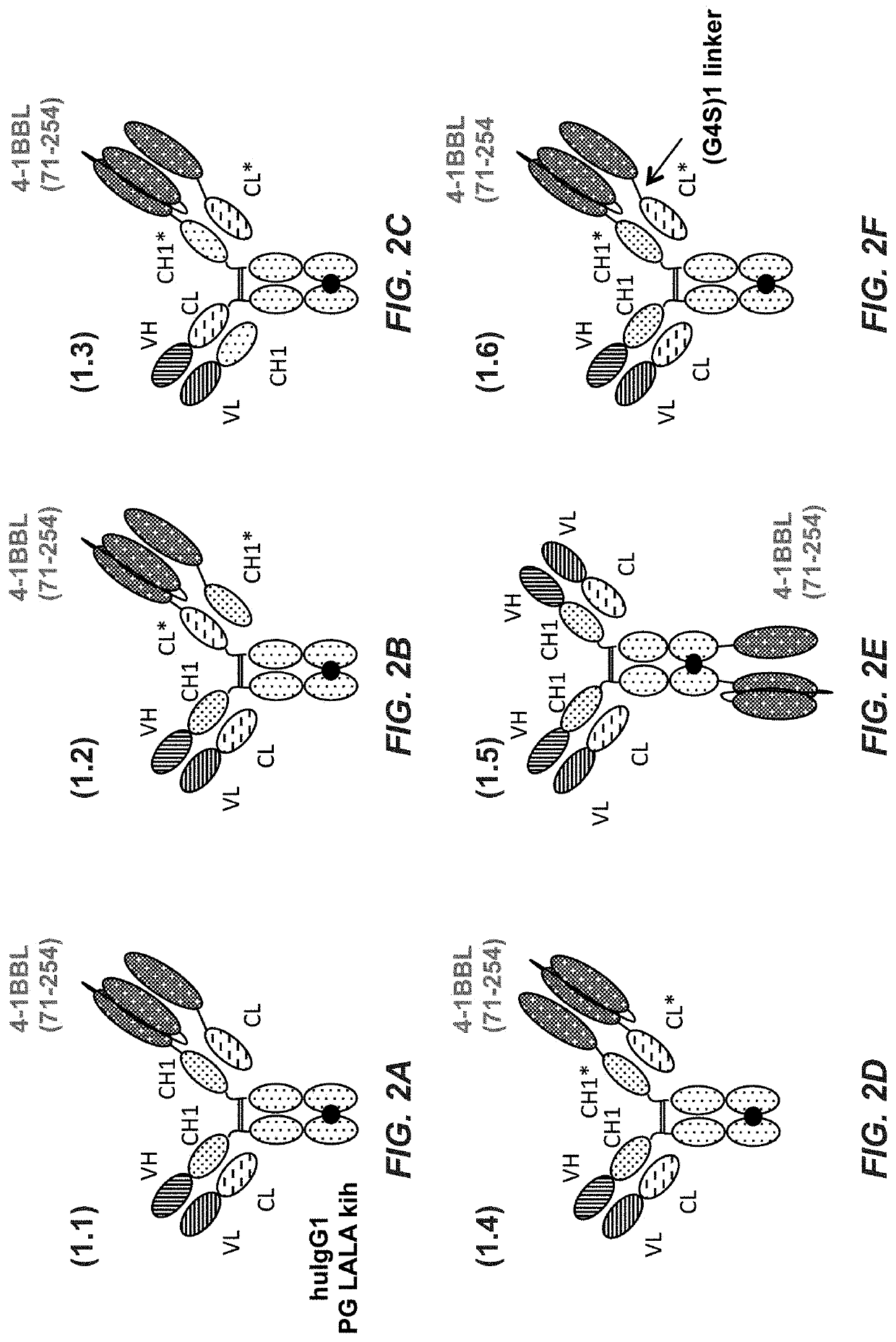
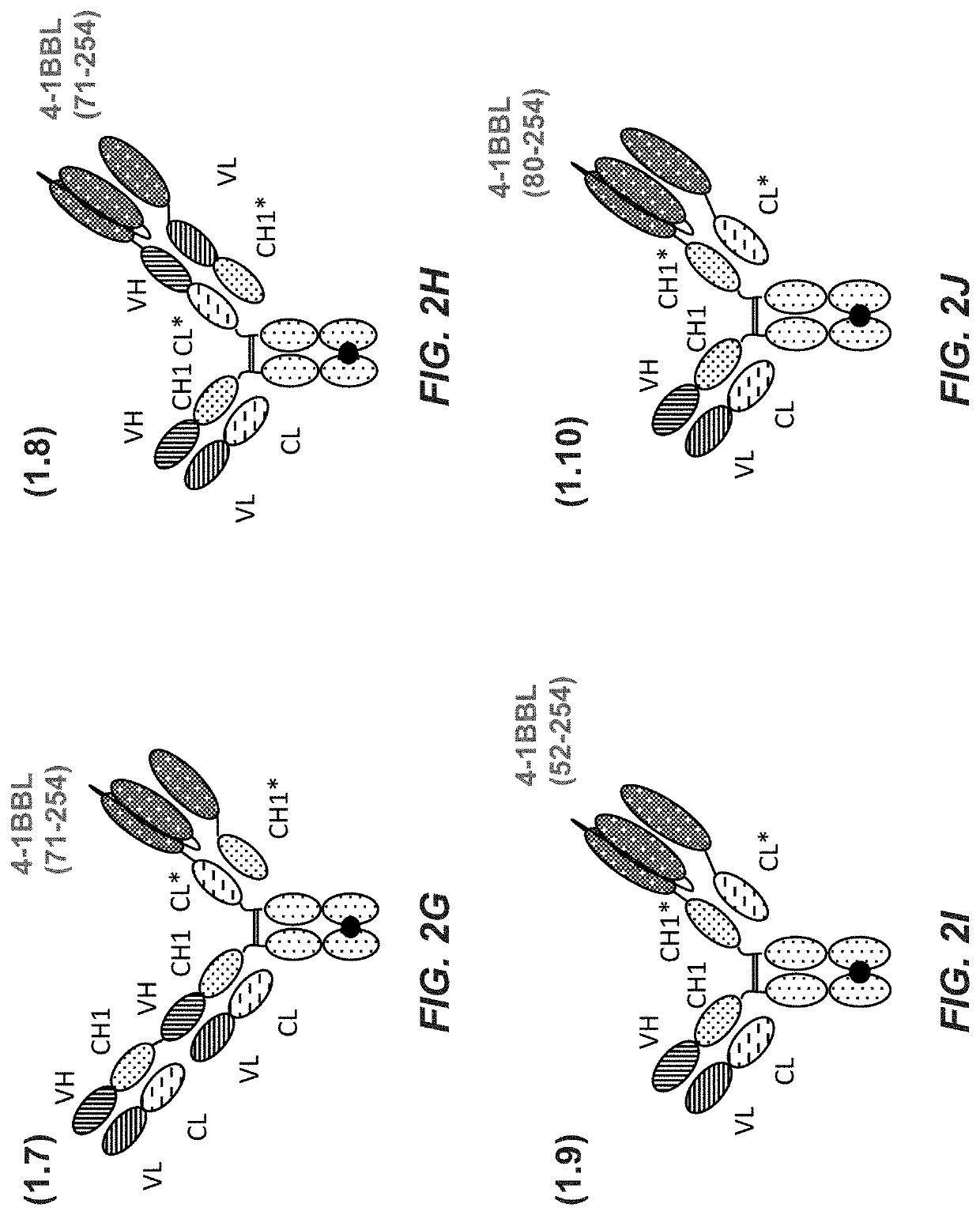
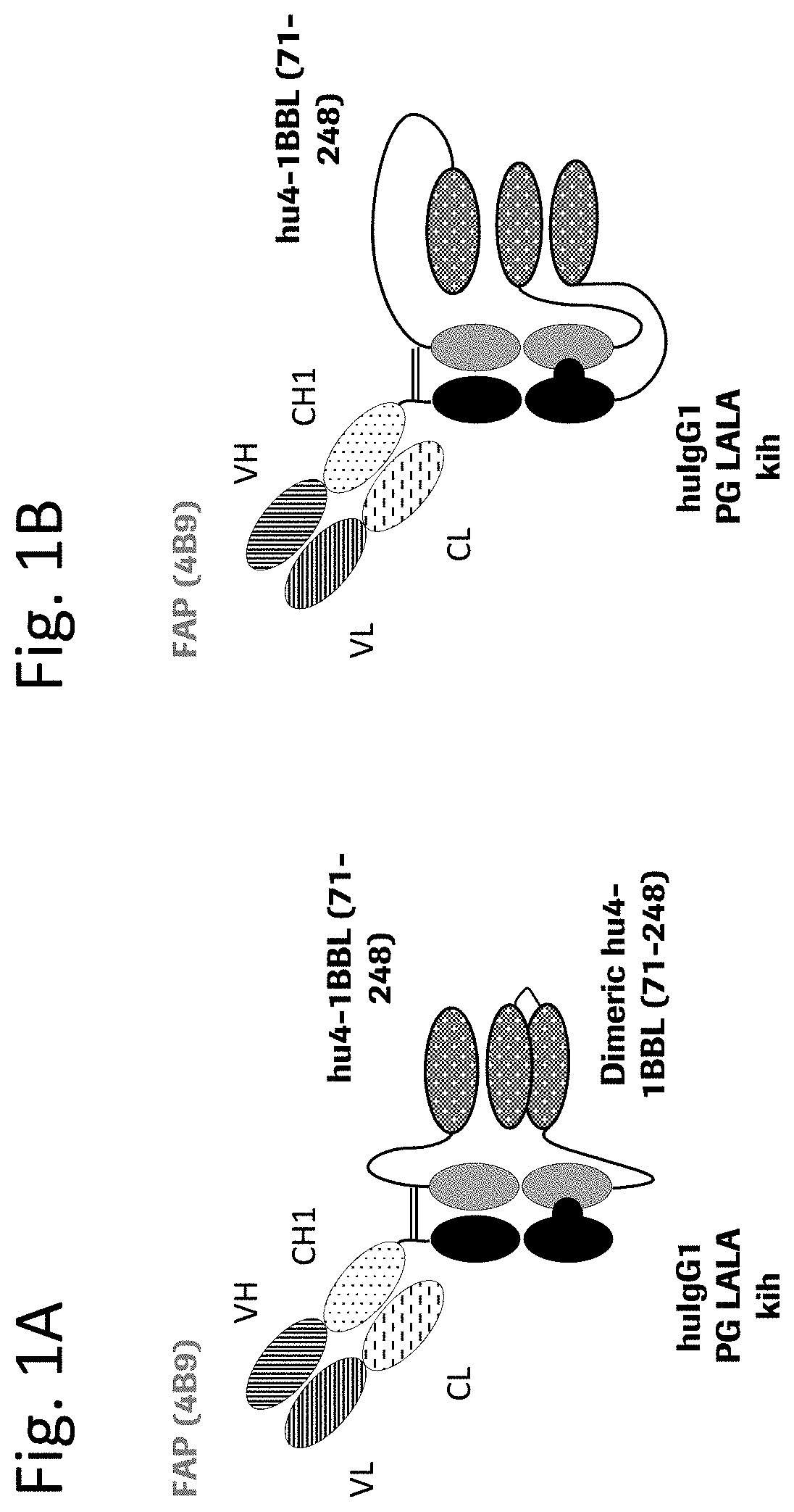
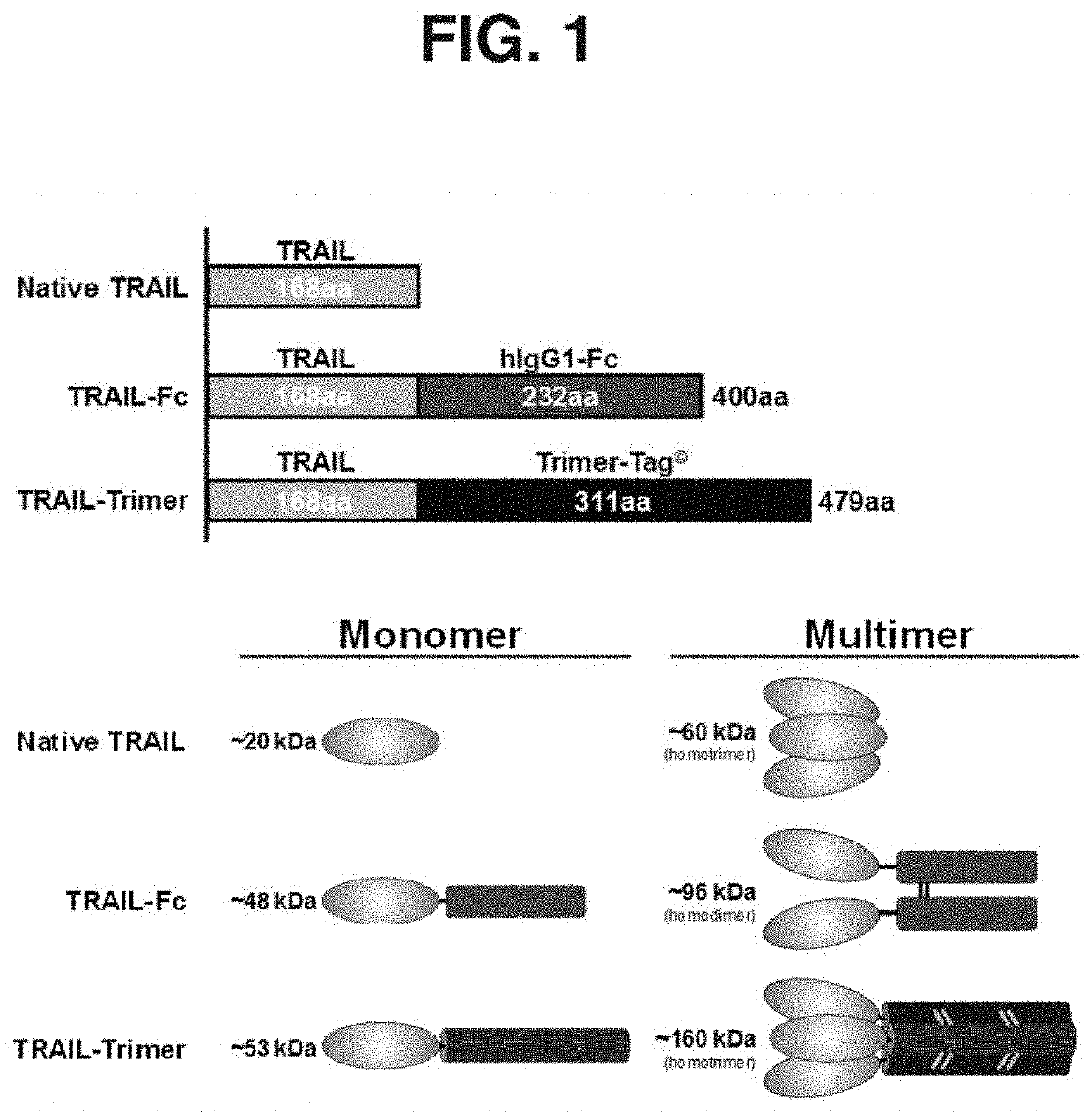
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family ligand trimer-containing antigen binding molecules
ActiveUS10464981B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsCellular antigensFc domain
The invention relates to novel TNF family ligand trimer-containing antigen binding molecules comprising (a) at least one moiety capable of specific binding to a target cell antigen, (b) a polypeptide comprising three ectodomains of a TNF ligand family member or fragments thereof that are connected to each other by peptide linkers and (c) a Fc domain composed of a first and a second subunit capable of stable association, and to methods of producing these molecules and to methods of using the same.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
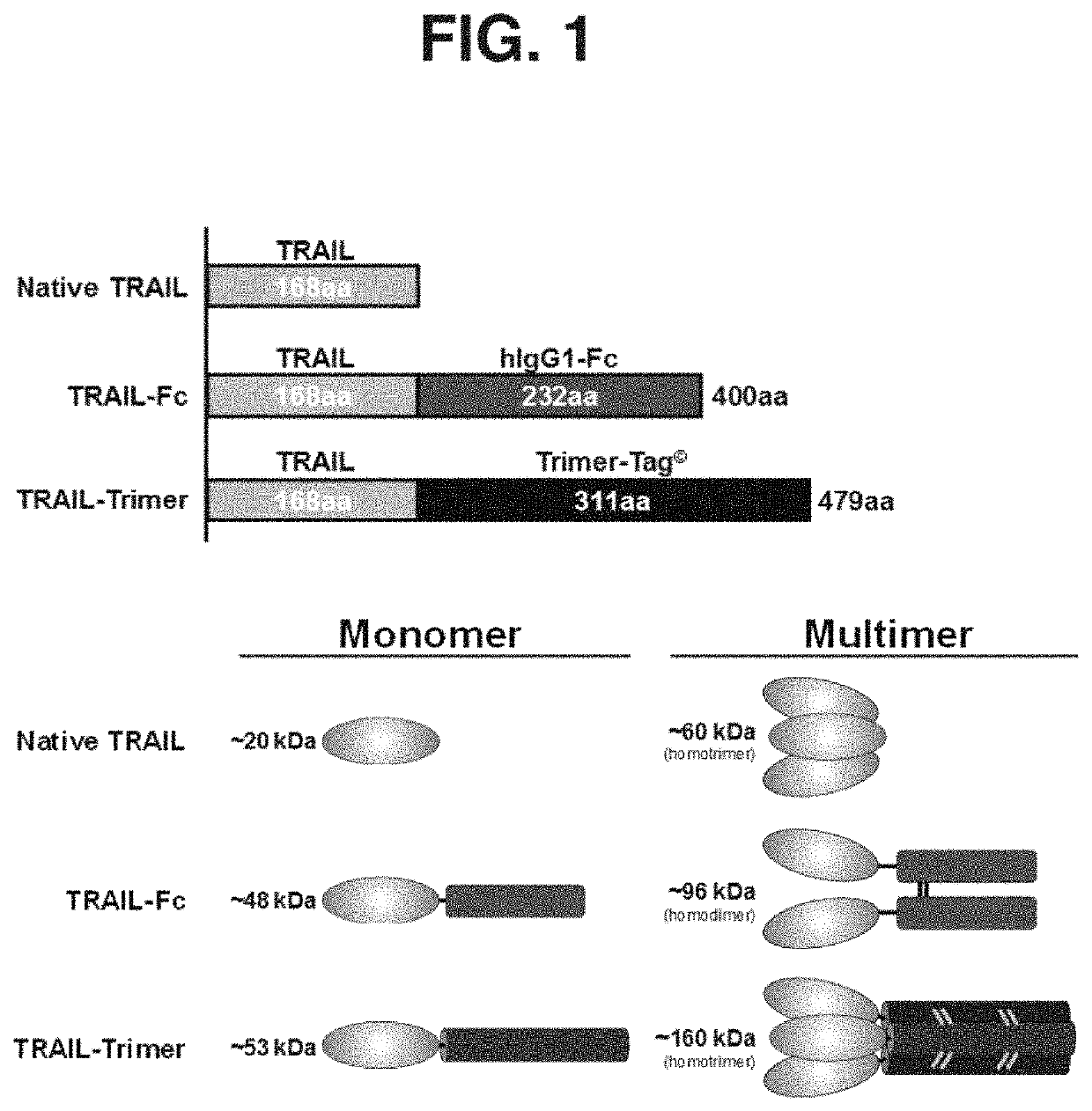
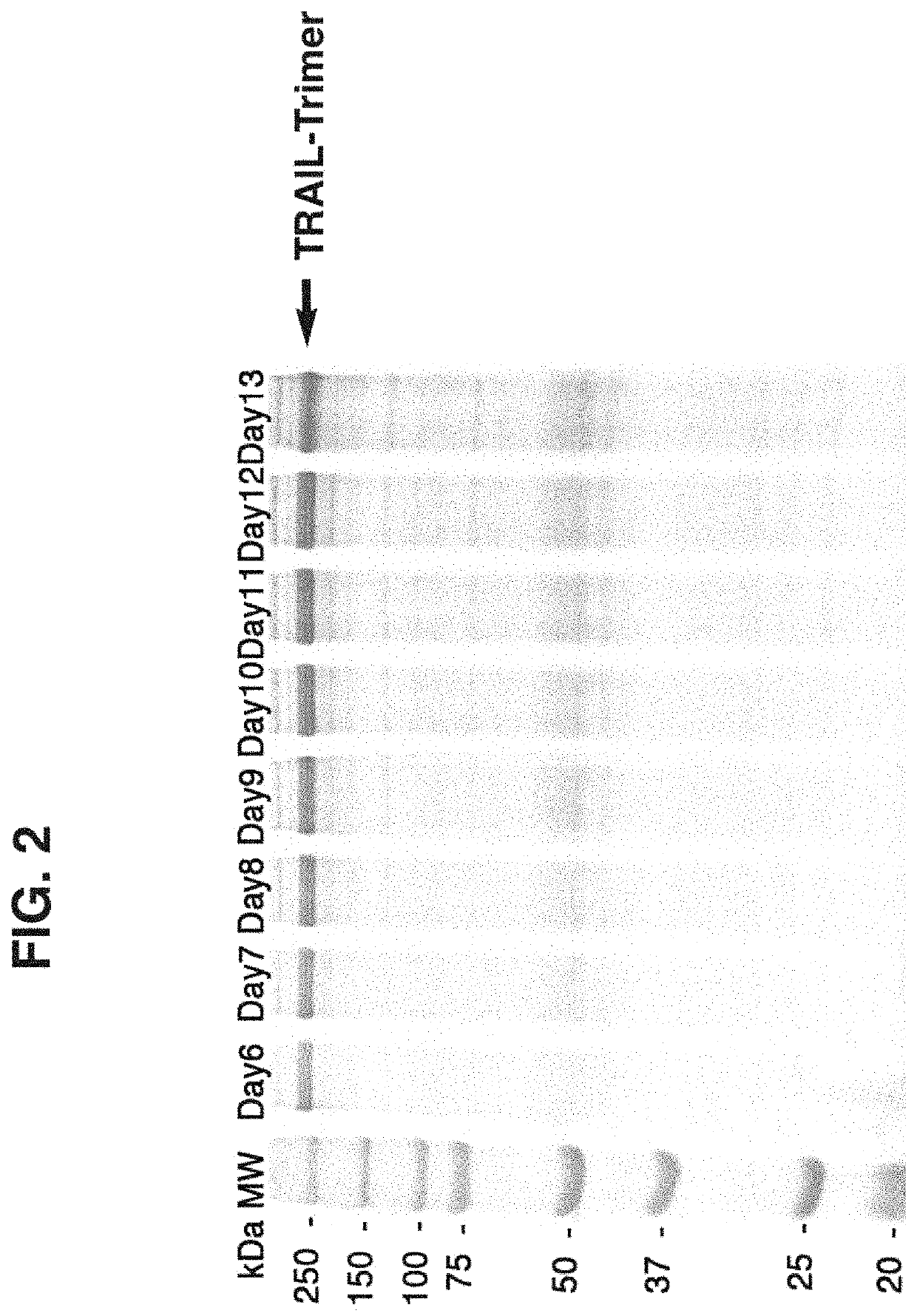
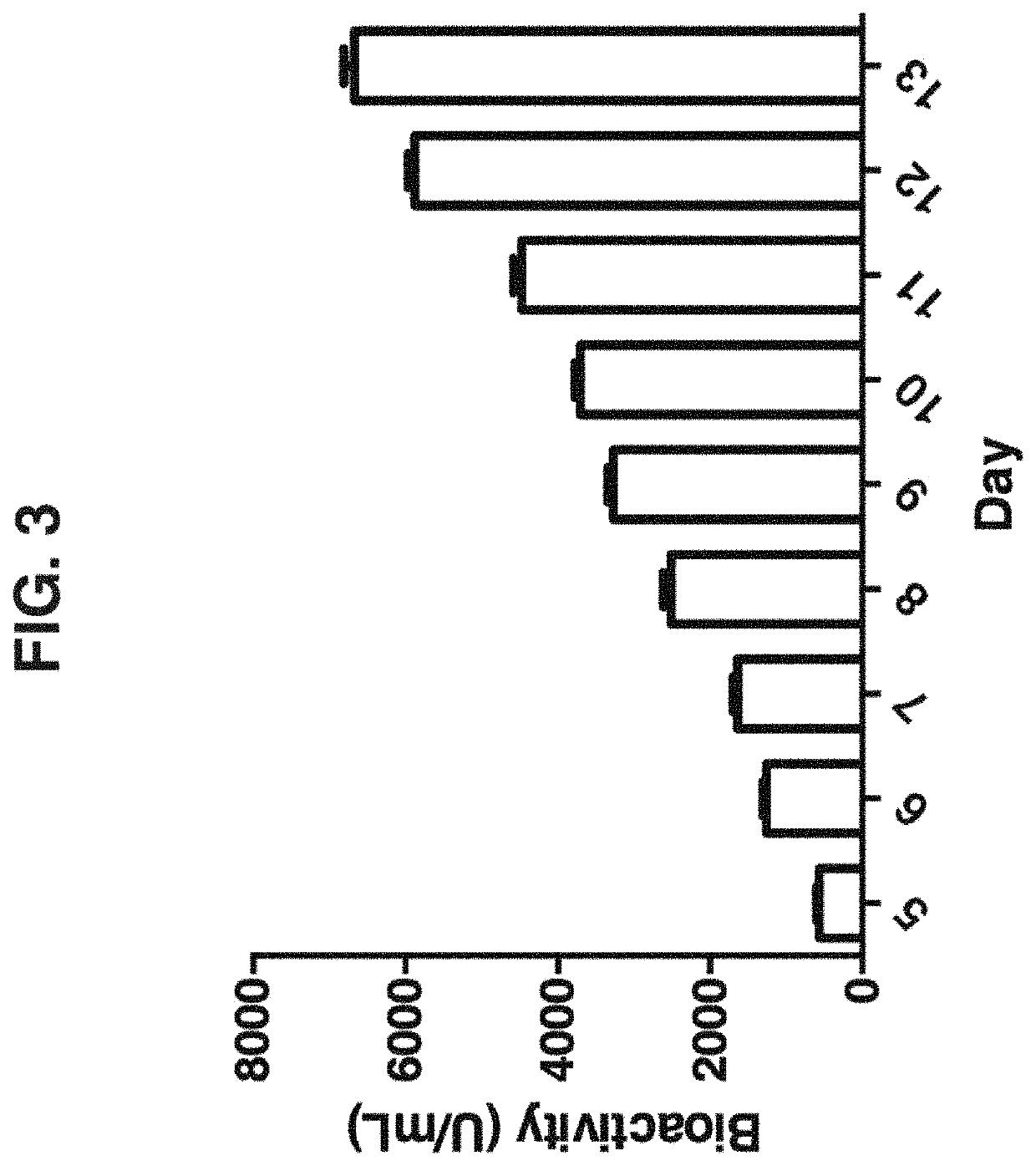
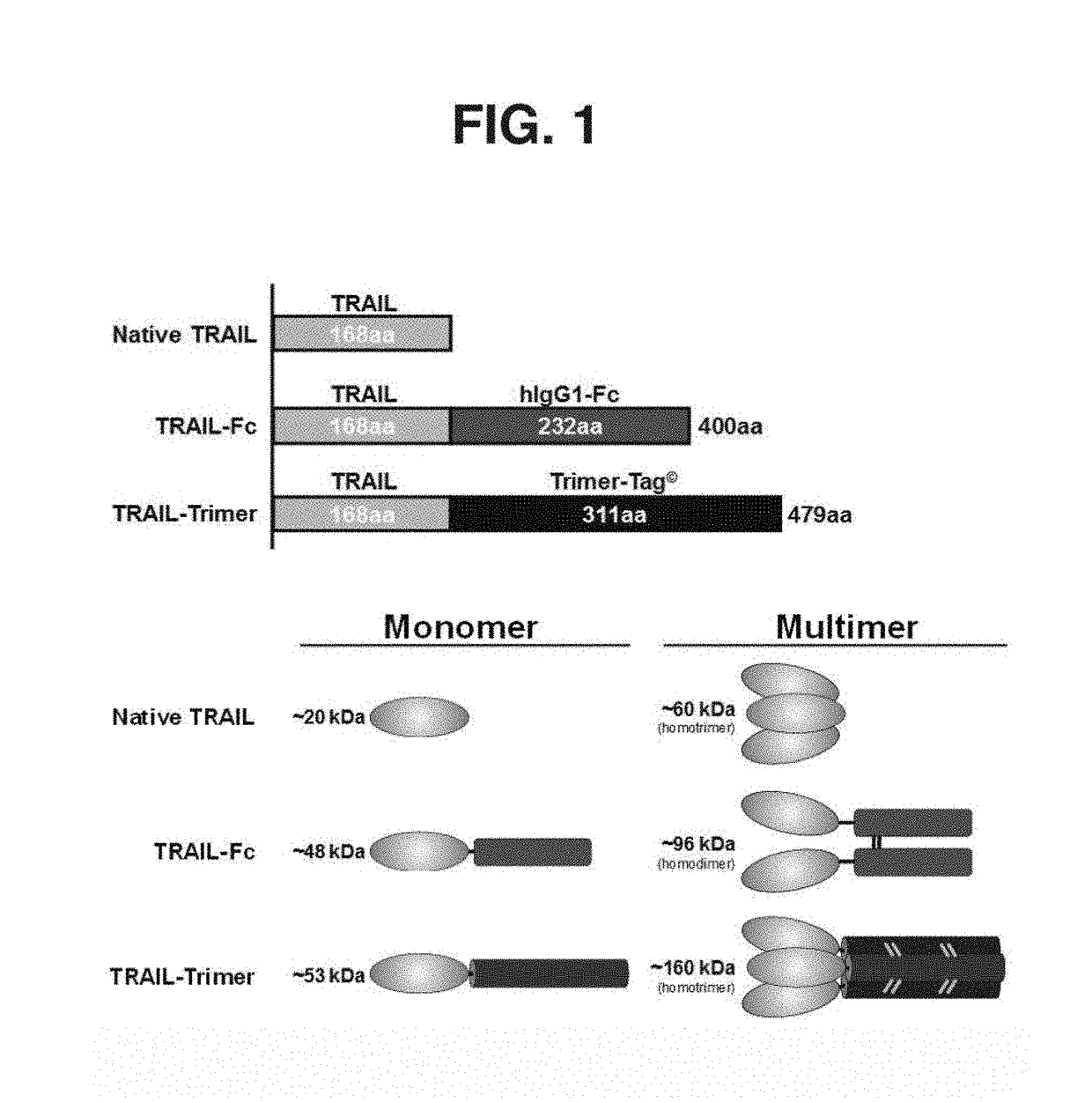
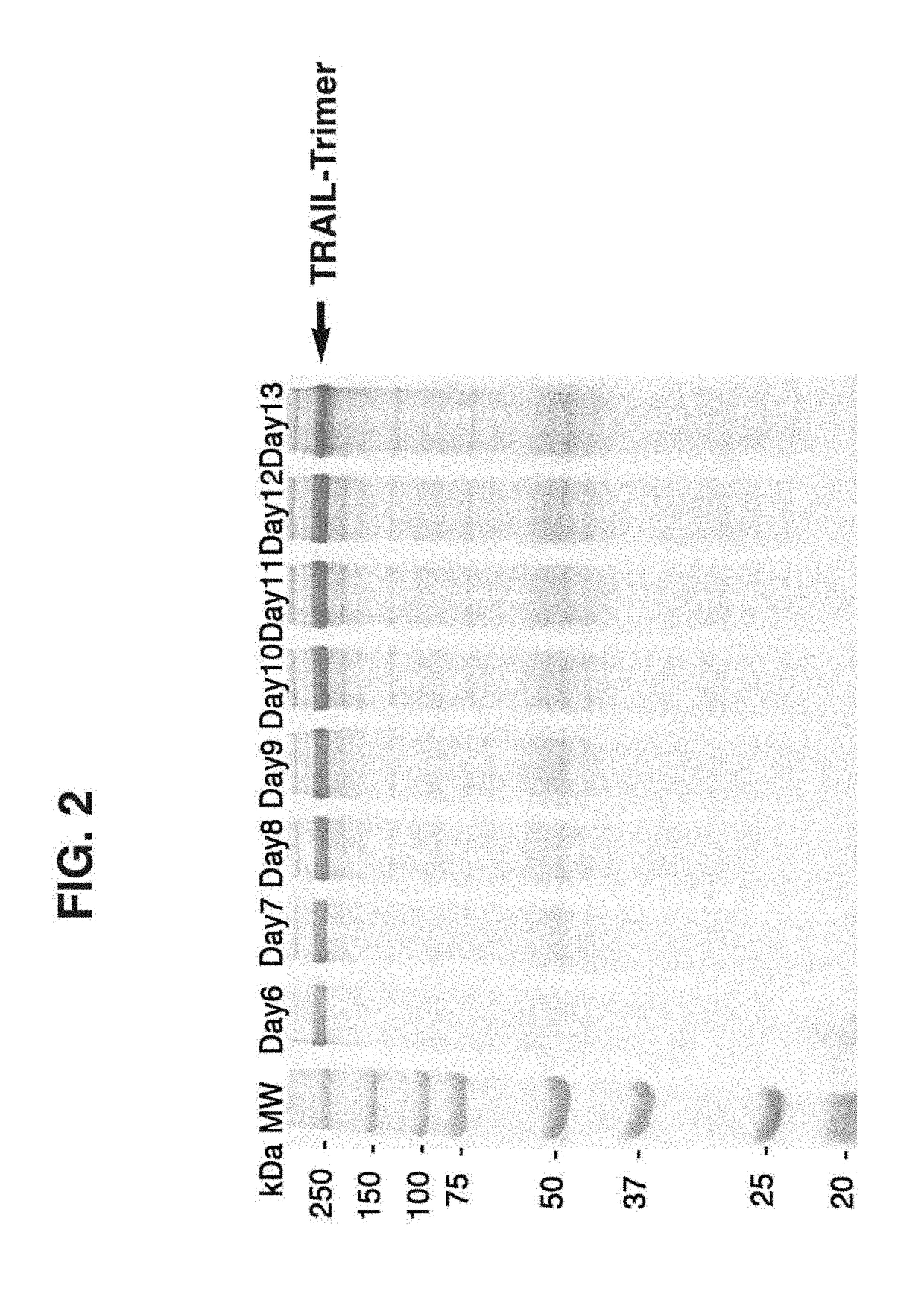
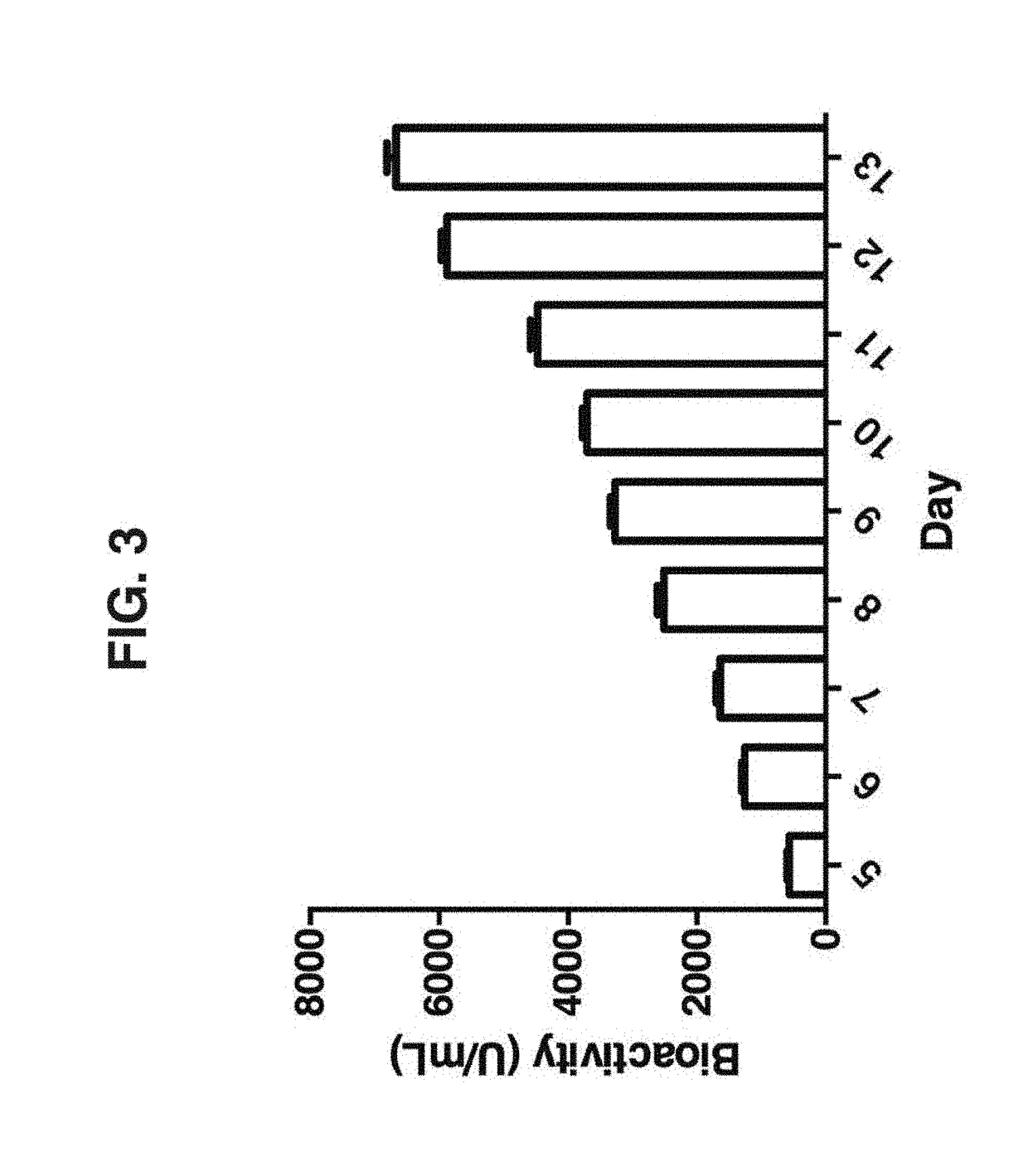
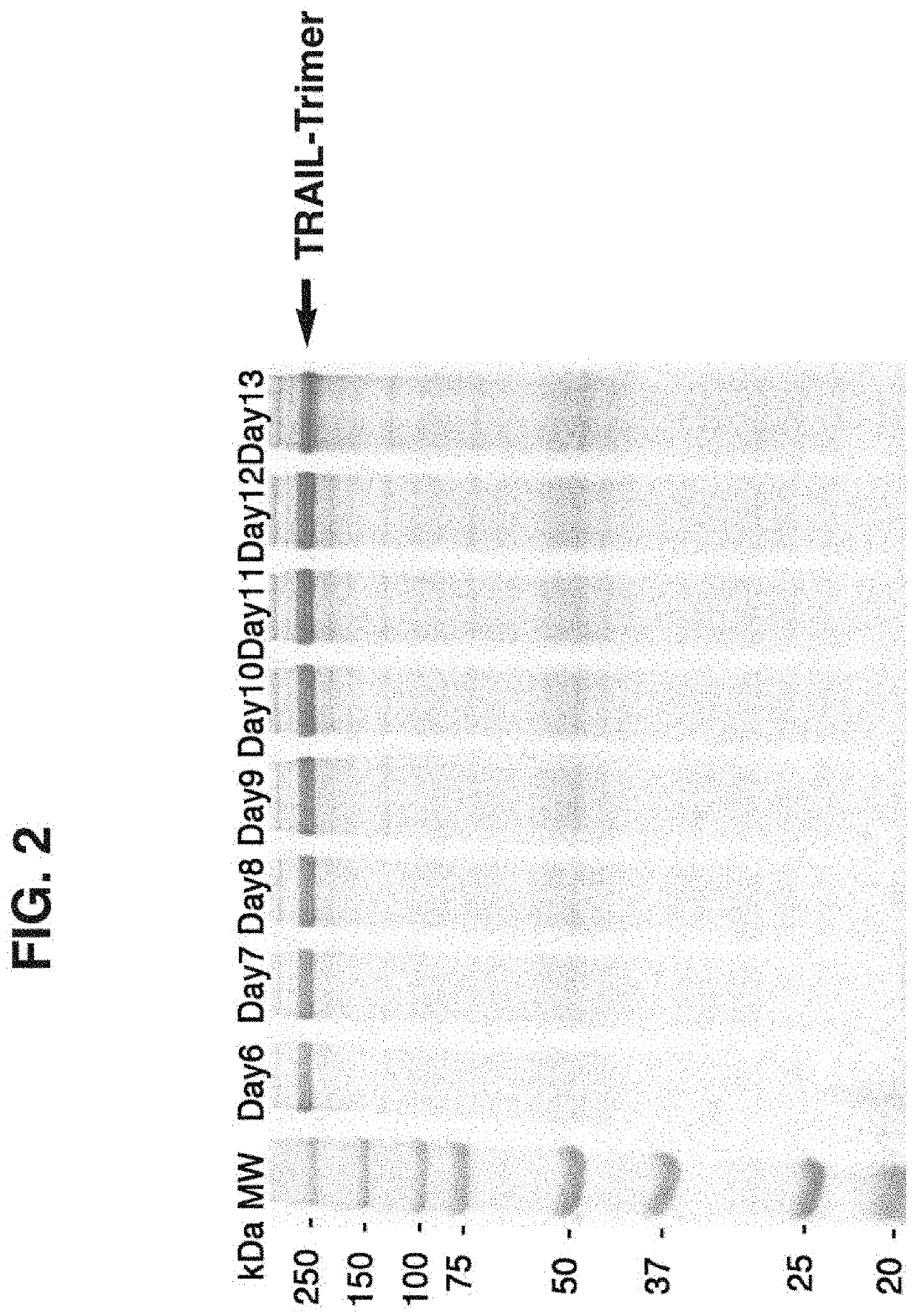
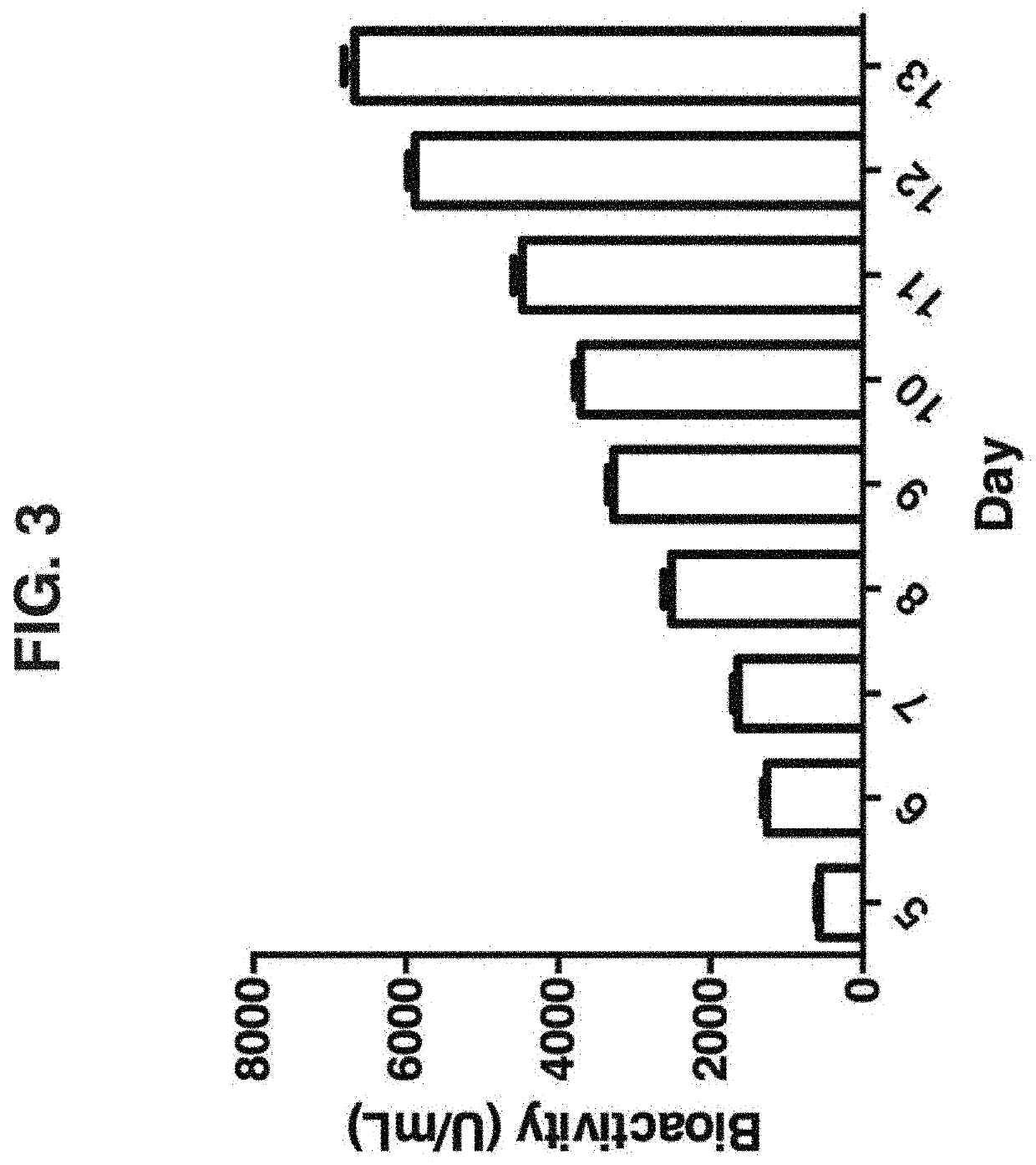
Method and compositions for producing disulfide-linked trimeric TNF family of cytokines and their use
ActiveUS10618949B2Avoid disruptionImprove biological activityConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsDisulfide bondingTnf family
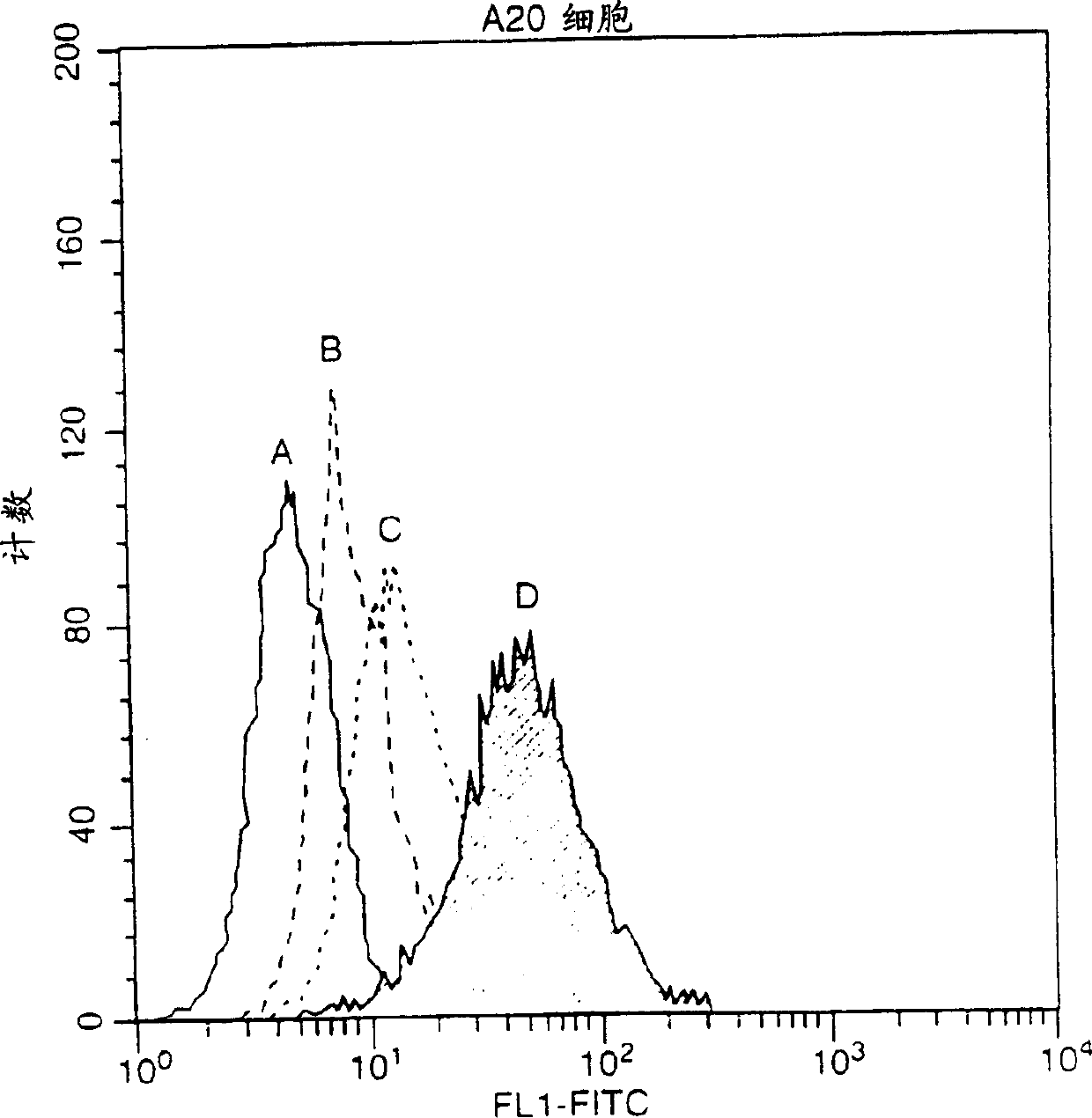
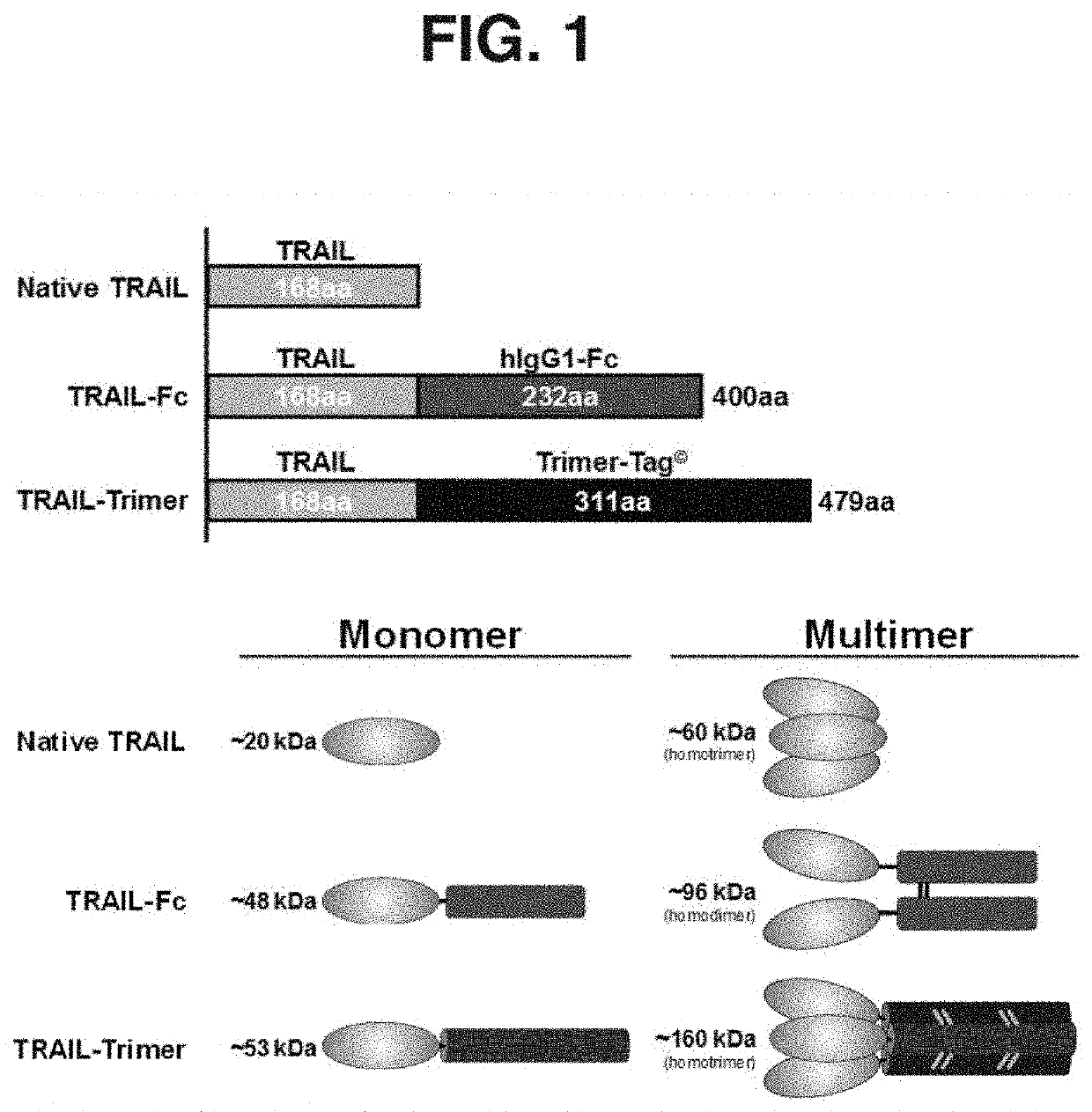
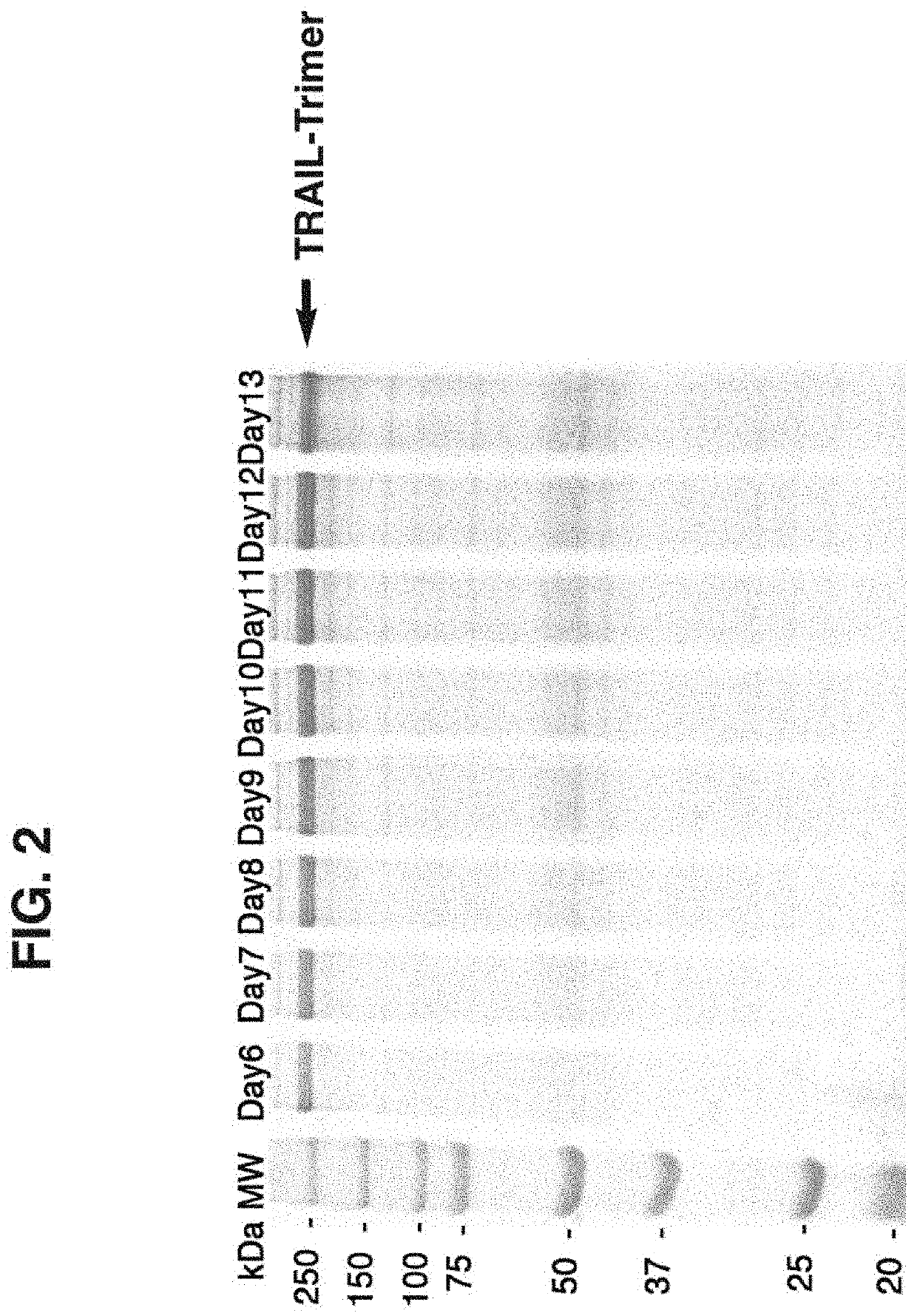
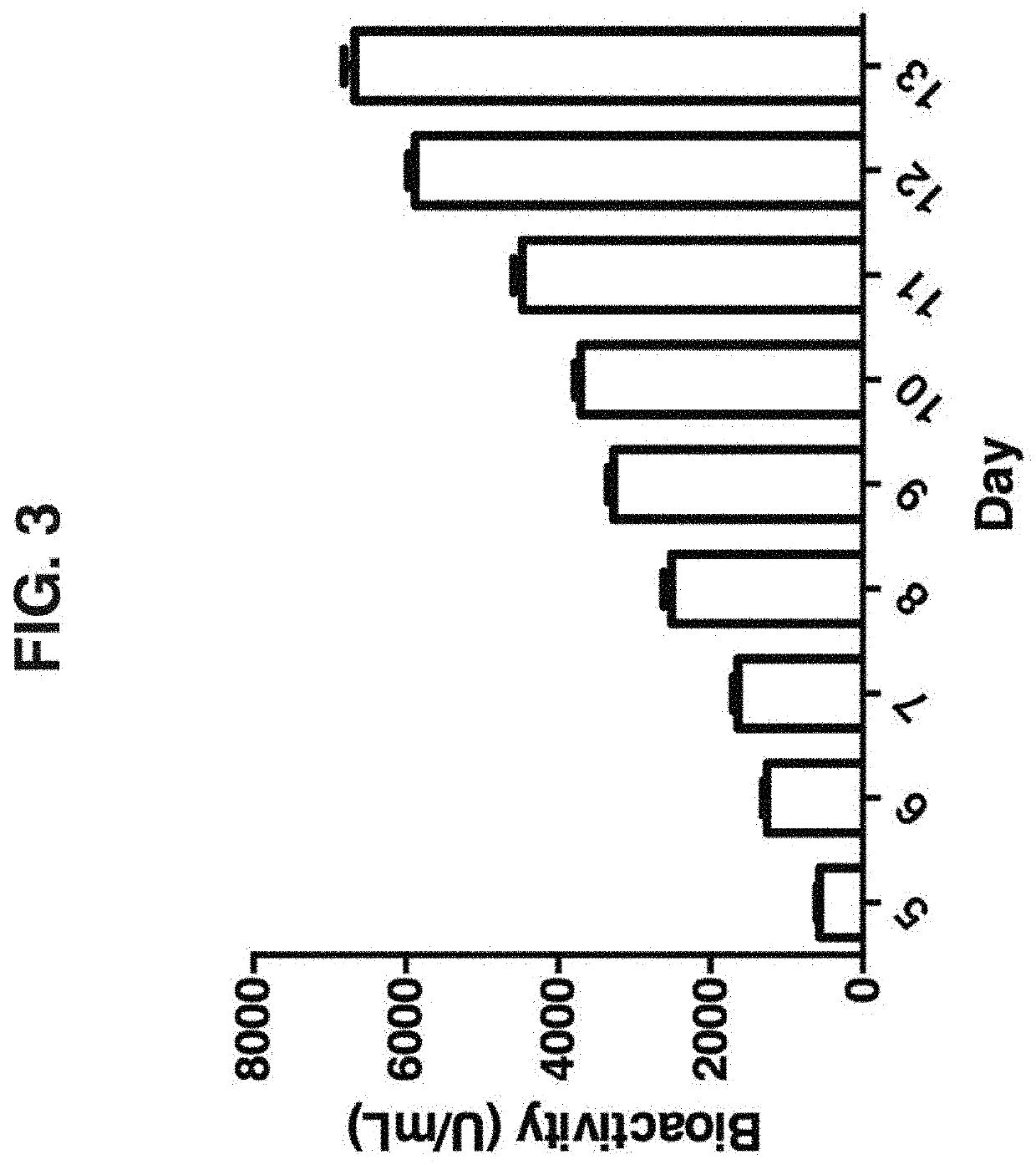
Compositions of TNF family of cytokines in covalently linked trimeric forms are disclosed. The resulting fusion proteins are secreted as disulfide bond-linked homotrimers, which are more stable in structure and therapeutically more efficacious than their native counterparts.
Owner:SICHUAN CLOVER BIOPHARM INC
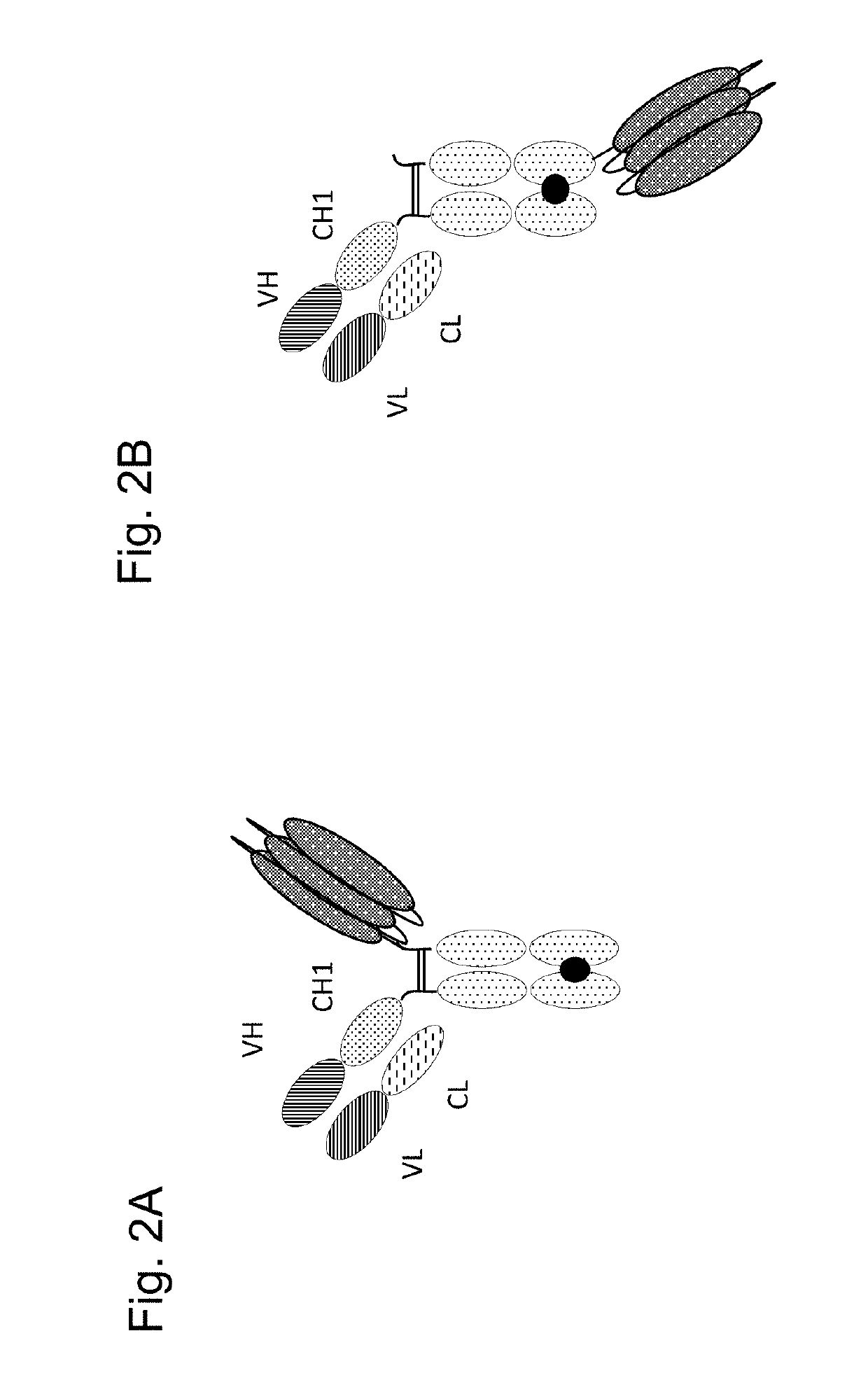
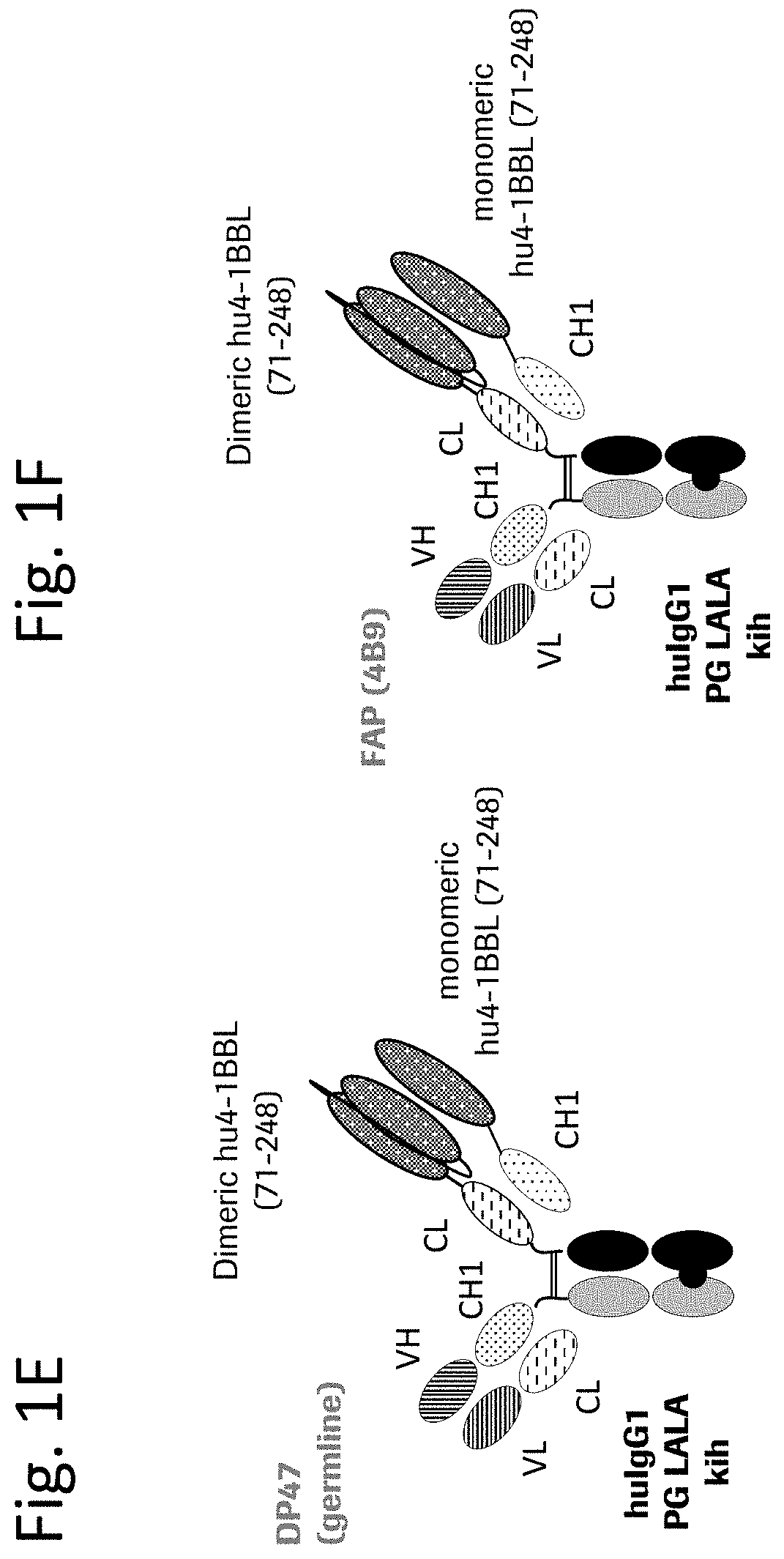
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family ligand trimer-containing antigen-binding molecules
The invention relates to novel TNF family ligand trimer-containing antigen binding molecules comprising (a) at least one moiety capable of specific binding to a target cell antigen and (b) a first and a second polypeptide that are linked to each other by a disulfide bond, characterized in that the first polypeptide comprises two ectodomains of a TNF ligand family member or fragments thereof that are connected to each other by a peptide linker and in that the second polypeptide comprises only one ectodomain of said TNF ligand family member or a fragment thereof.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Methods of treating a tumor that expresses APRIL by administering BCMA
InactiveUS7276241B2Prolong lifeImprove the quality of lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTnf familyReceptor for activated C kinase 1
A novel receptor in the TNF family is provided: APRIL-R. Chimeric molecules and antibodies to APRIL-R and methods of use thereof are also provided.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
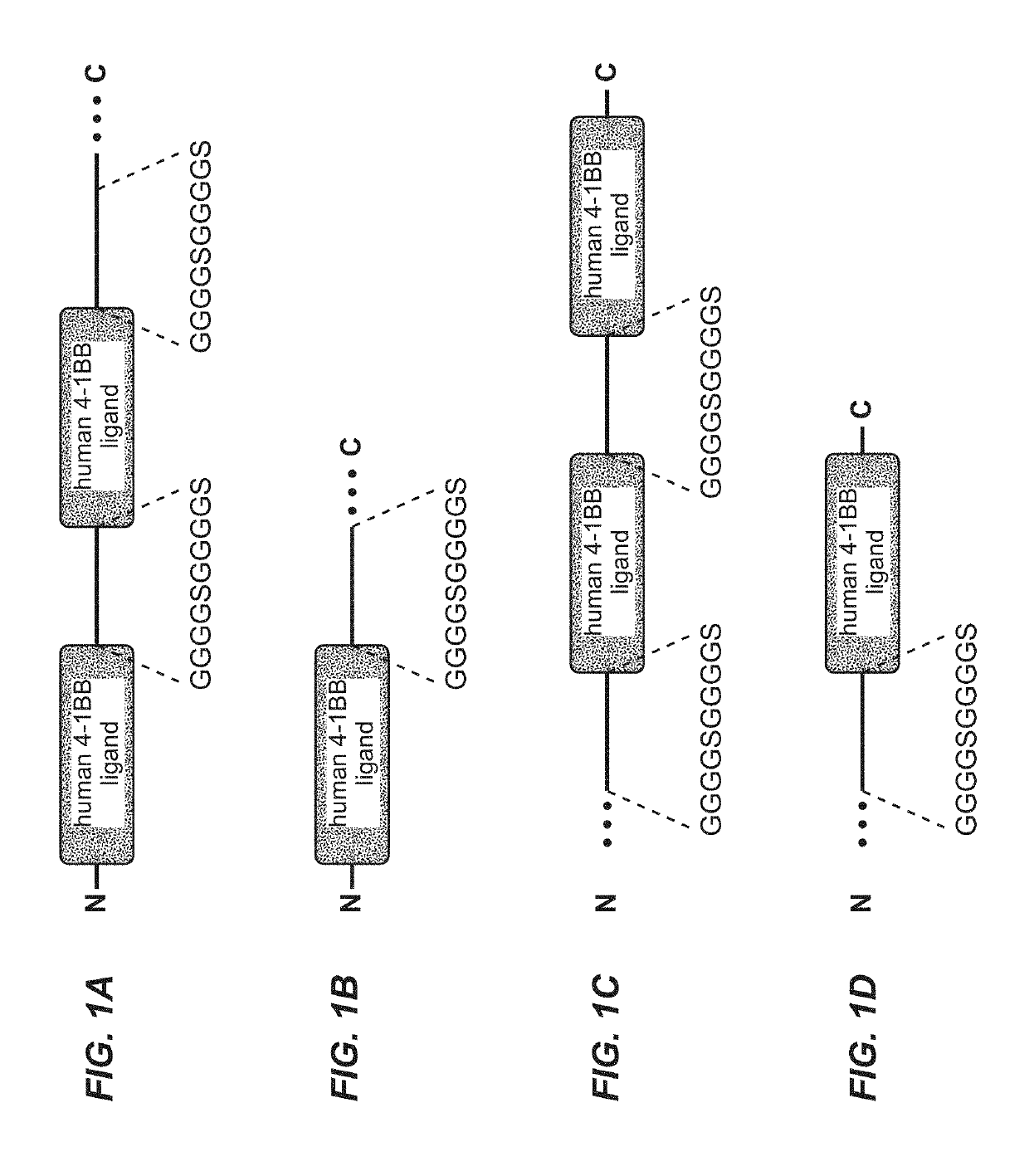
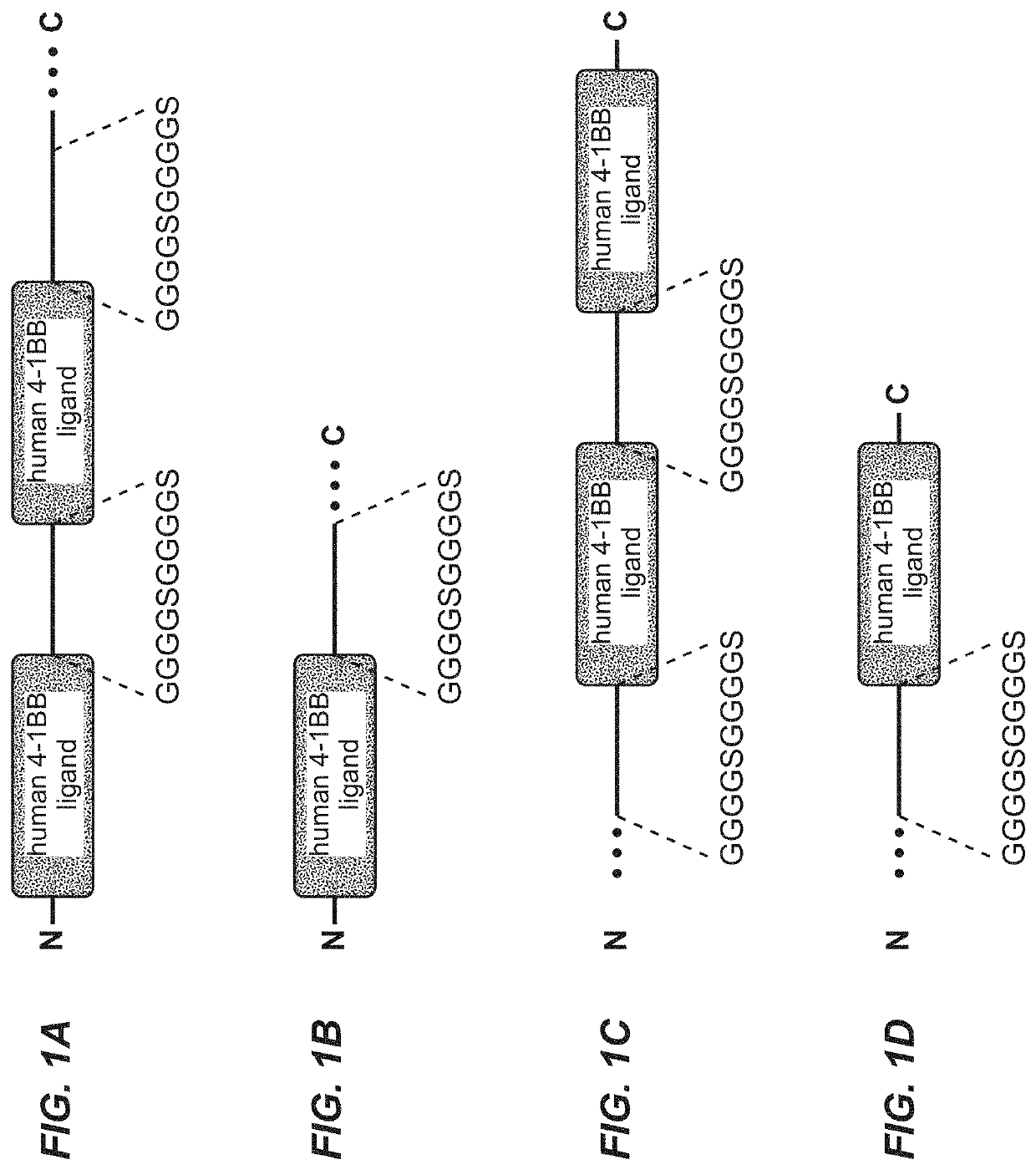
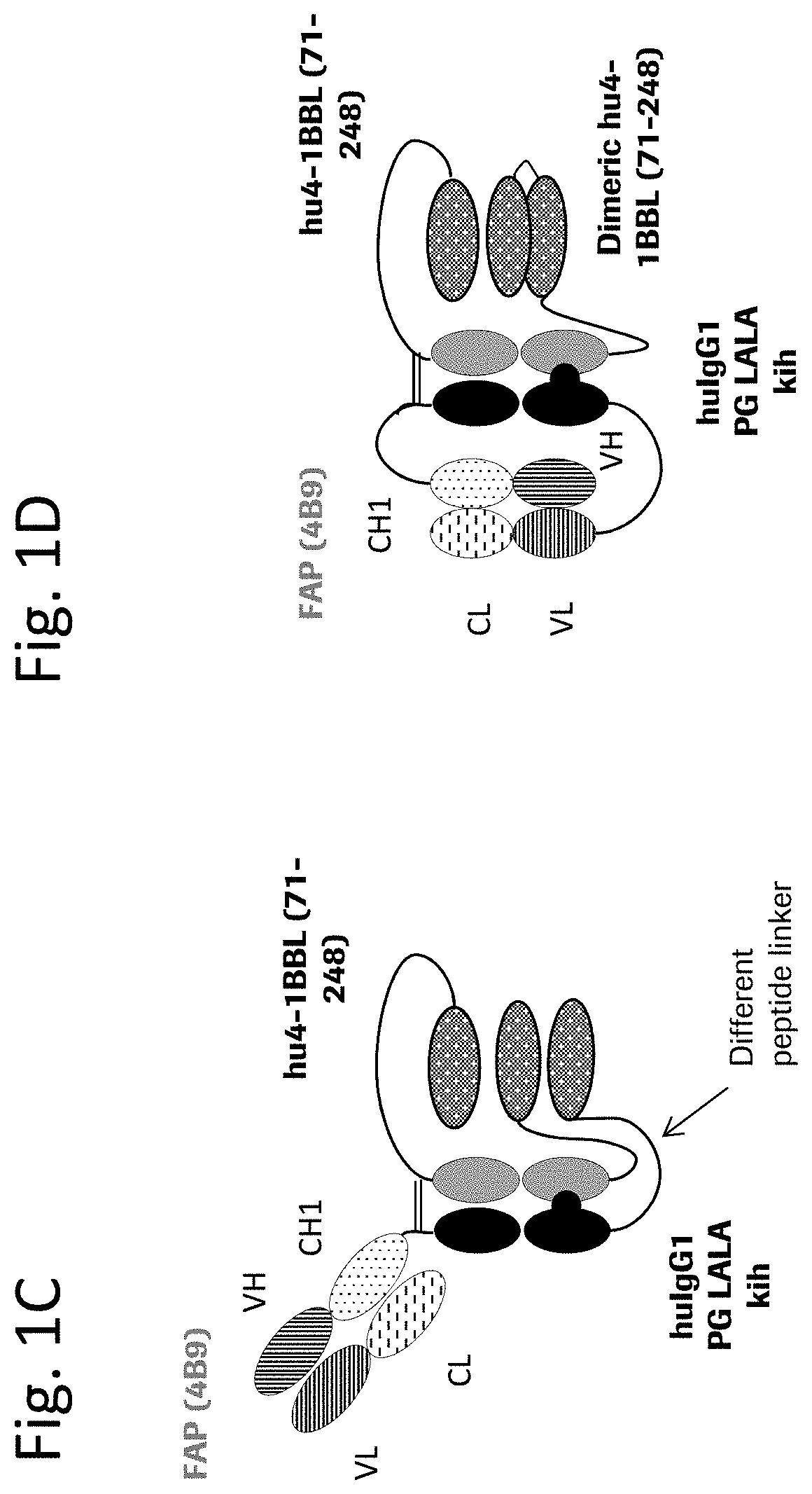
Trimeric costimulatory TNF family ligand-containing antigen binding molecules
InactiveUS20190016771A1Connective tissue peptidesHybrid immunoglobulinsCellular antigensAntigen binding
The invention relates to novel trimeric costimulatory TNF family ligand-containing antigen binding molecules comprising three fusion polypeptides, each of the three fusion polypeptides comprising (a) an ectodomain of a costimulatory TNF family ligand selected from the group consisting of 4-1BBL, OX40L and GITRL or fragments thereof, (b) a trimerization domain, in particular a trimerization domain derived from human cartilage matrix protein (huCMP) of SEQ ID NO:1, and (c) a moiety capable of specific binding to a target cell antigen, and to methods of producing these molecules and to methods of using the same.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
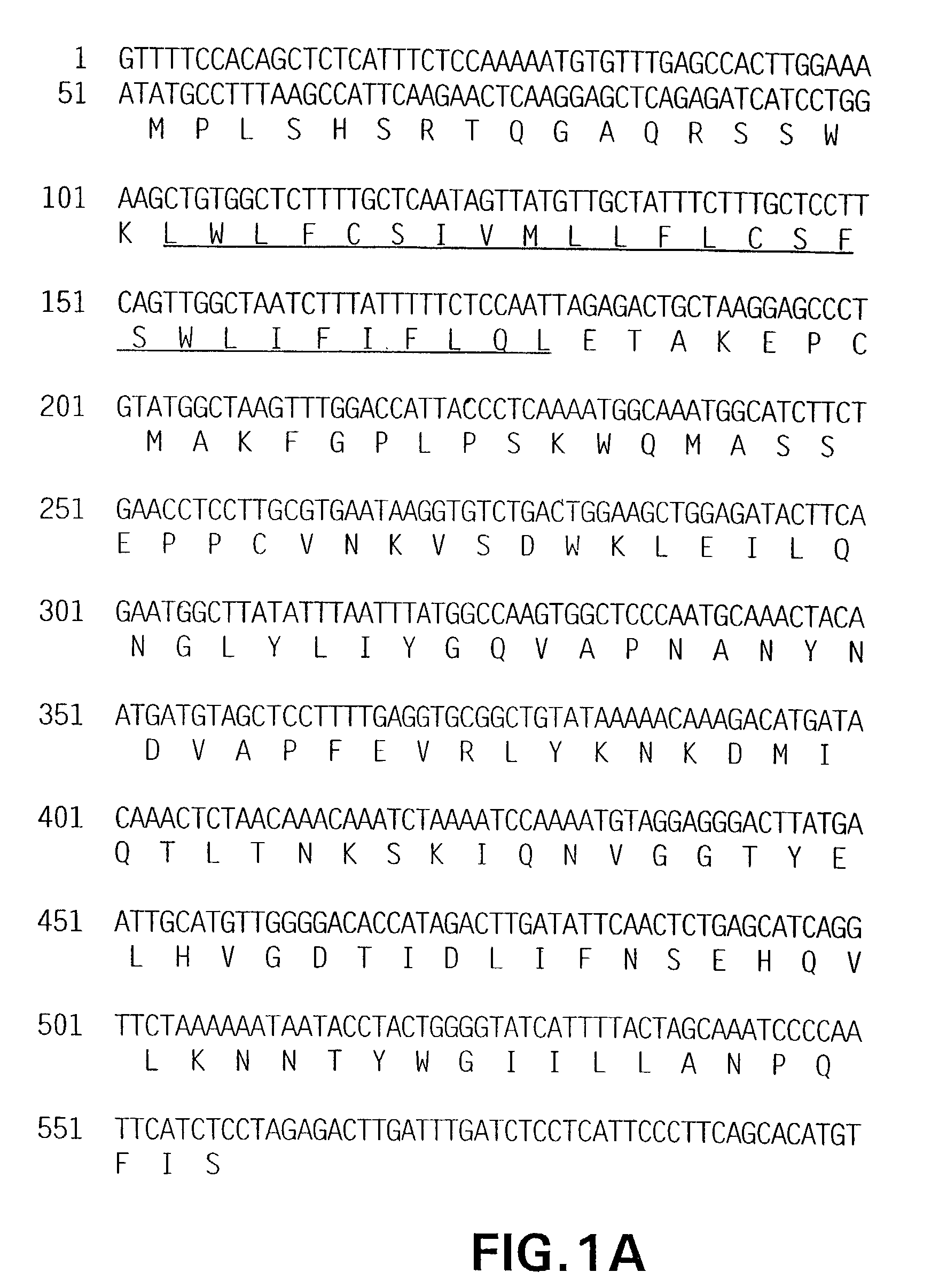
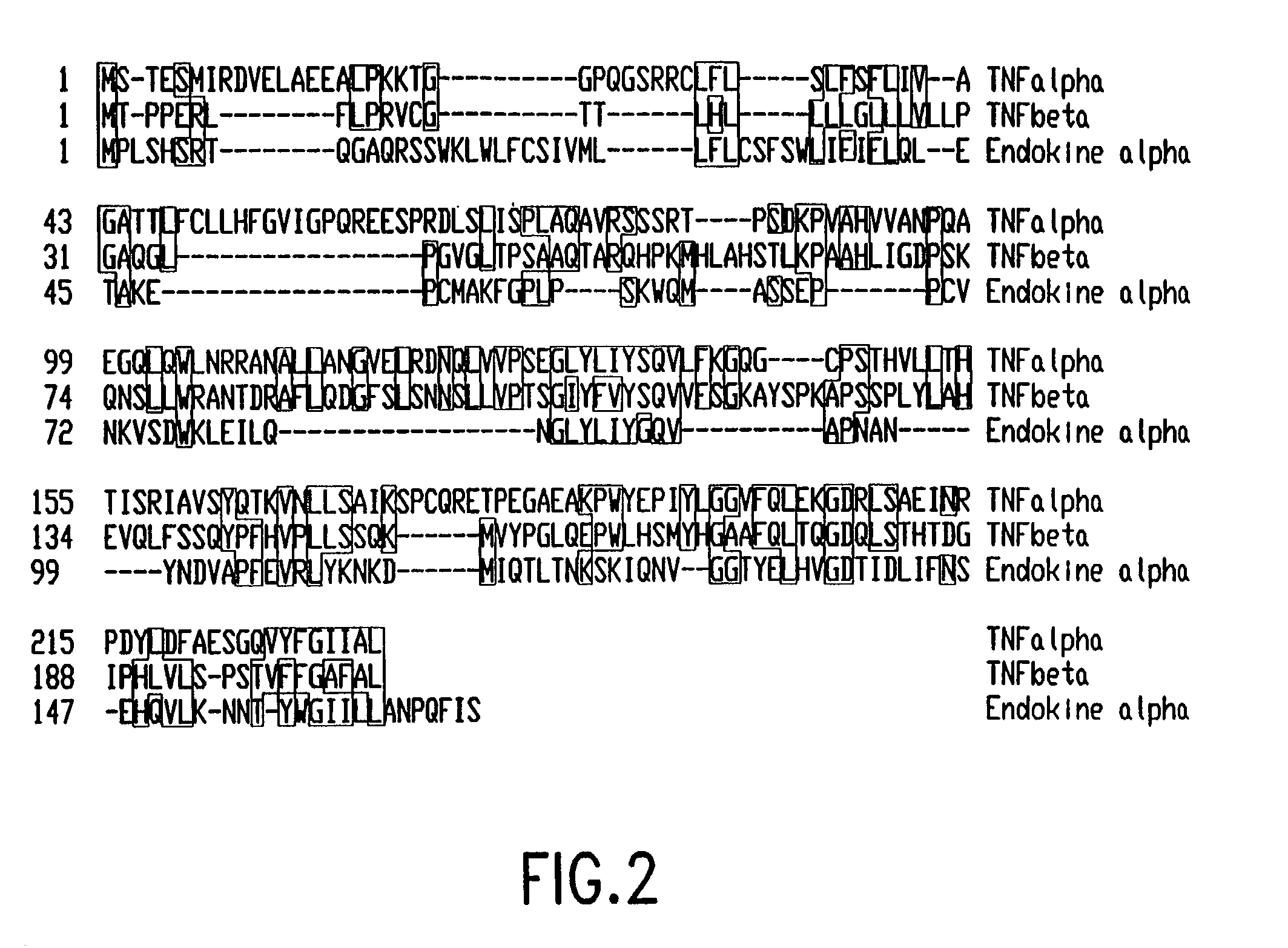
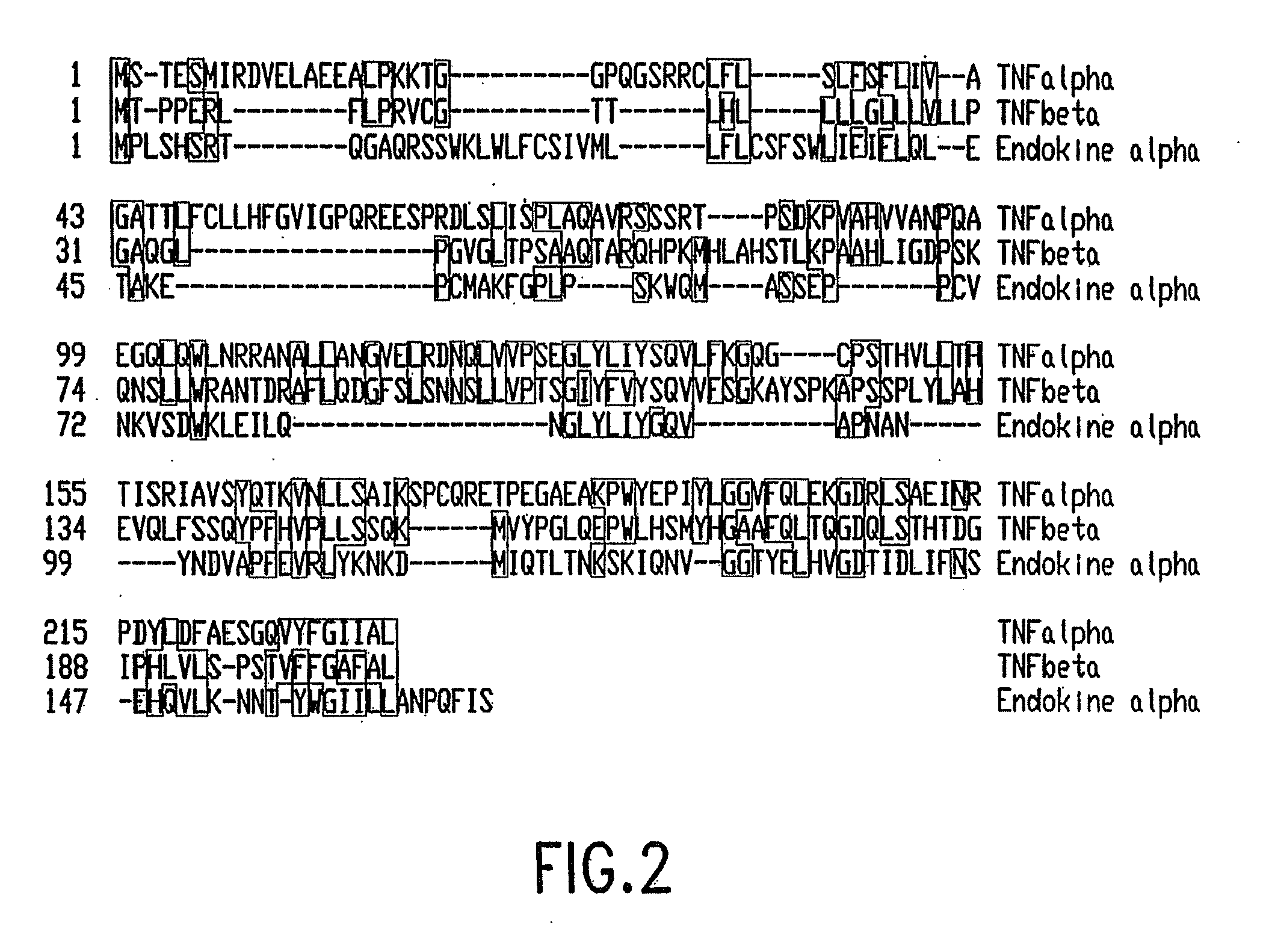
Human endokine alpha
The present invention concerns a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of cytokines. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding the endokine alpha protein. Endokine alpha polypeptides are also provided, as are vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same. Also provided are diagnostic and therapeutic methods concerning TNF family-related disorders.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Peptides targeting TNF family receptors and antagonizing TNF action, compositions, methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS8362218B2Improve the level ofReduced responseCompounds screening/testingSenses disorderUveitisUlcerative colitis
The present invention provides modulators of TNF, particularly peptides and their derivatives, particularly GEP peptides, which antagonize TNF and TNF-mediated responses, activity or signaling. The invention provides methods of antagonizing TNF and the modulation of TNF-mediated diseases or responses, including inflammatory diseases and conditions. Compositions of GEP peptides, including in combination with other inflammatory mediators, are provided. Methods of treatment, alleviation, or prevention of TNF-mediated diseases and inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel diseases, Chrohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, uveitis, inflammatory lung diseases, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are provided.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Antigen binding molecules comprising a TNF family ligand trimer
ActiveUS20190382507A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsCellular antigensAntigen binding
The invention relates to novel TNF family ligand trimer-containing antigen binding molecules comprising (a) at least one moiety capable of specific binding to a target cell antigen and (b) a first and a second polypeptide that are linked to each other by a disulfide bond, characterized in that the first polypeptide comprises two ectodomains of a TNF ligand family member or fragments thereof that are connected to each other by a peptide linker and in that the second polypeptide comprises only one ectodomain of said TNF ligand family member or a fragment thereof.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Nucleic acids encoding TRAIN-R: a cysteine rich member of the TNF-receptor family
The present invention relates to novel receptors in the TNF family. A novel receptor has been identified, referred to herein as TRAIN. The invention relates to DNA sequences encoding TRAIN receptors. The invention also contemplates recombinant DNAs comprising a sequence encoding TRAIN receptors or fragments thereof, as well as hosts with stably integrated TRAIN-R sequences introduced into their genome, or possessing episomal elements.
Owner:APOXIS
Train-R: a cysteine rich member of the TNF-receptor family
InactiveUS20060233792A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTnf familyReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Novel TNF family ligand trimer-containing antigen binding molecules
InactiveUS20200347115A1Efficient fusionImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyTnf familyAntigen binding
The invention relates to novel TNF family ligand trimer-containing antigen binding molecules comprising two different fusion polypeptides that comprise a spacer domain, an antigen binding domain and three ectodomains of a TNF ligand member or fragments thereof, wherein two of said ectodomains are separated from each other by a spacer domain comprising at least 25 amino acids and wherein the two fusion polypeptides are covalently associated to each other in the spacer domain
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG +1
Targeting-enhanced activation of galectins
InactiveUS20080234177A1Enhancing vivo efficacyHigh in vivo efficacyNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsArthritisTnf family
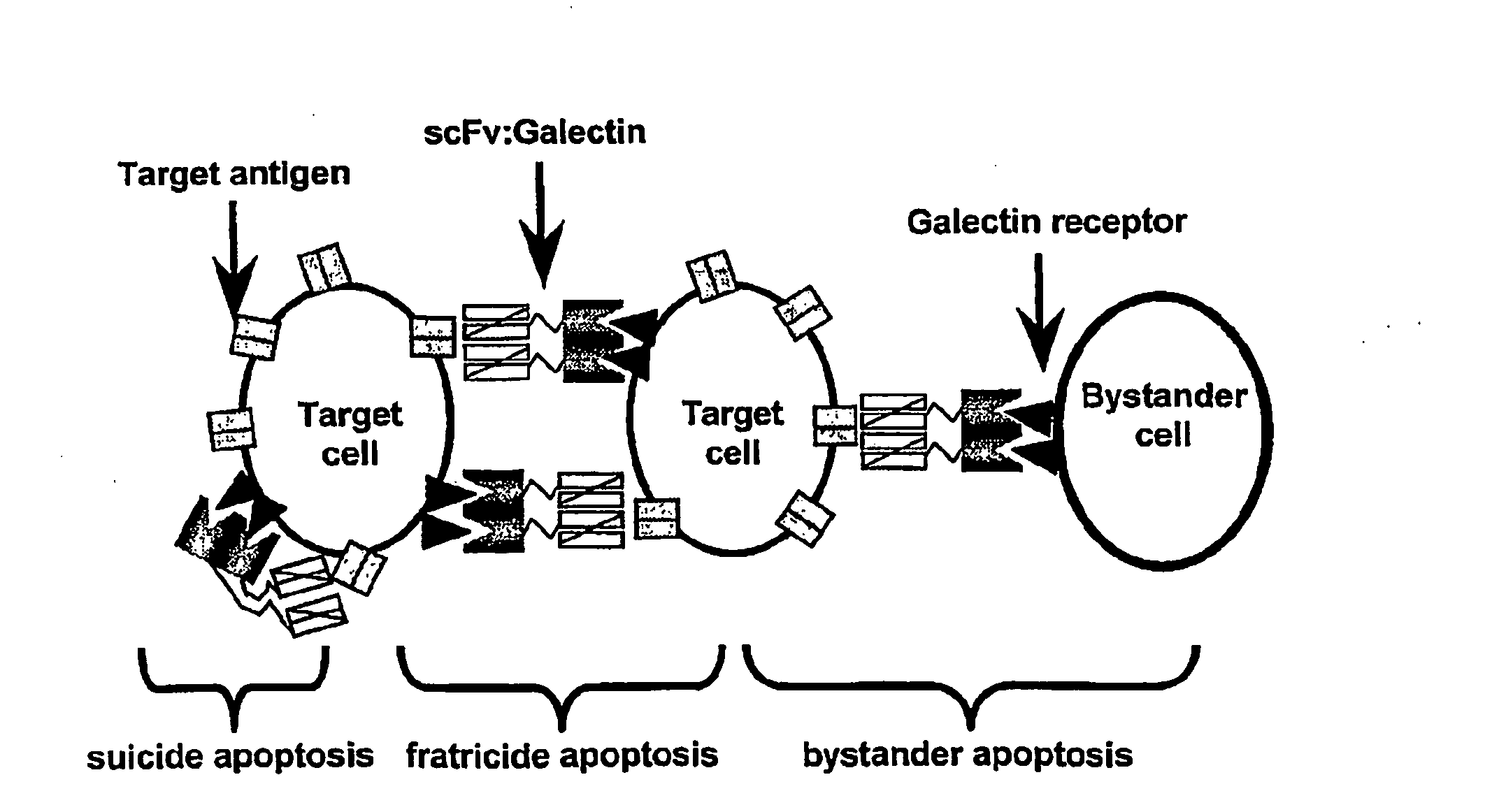
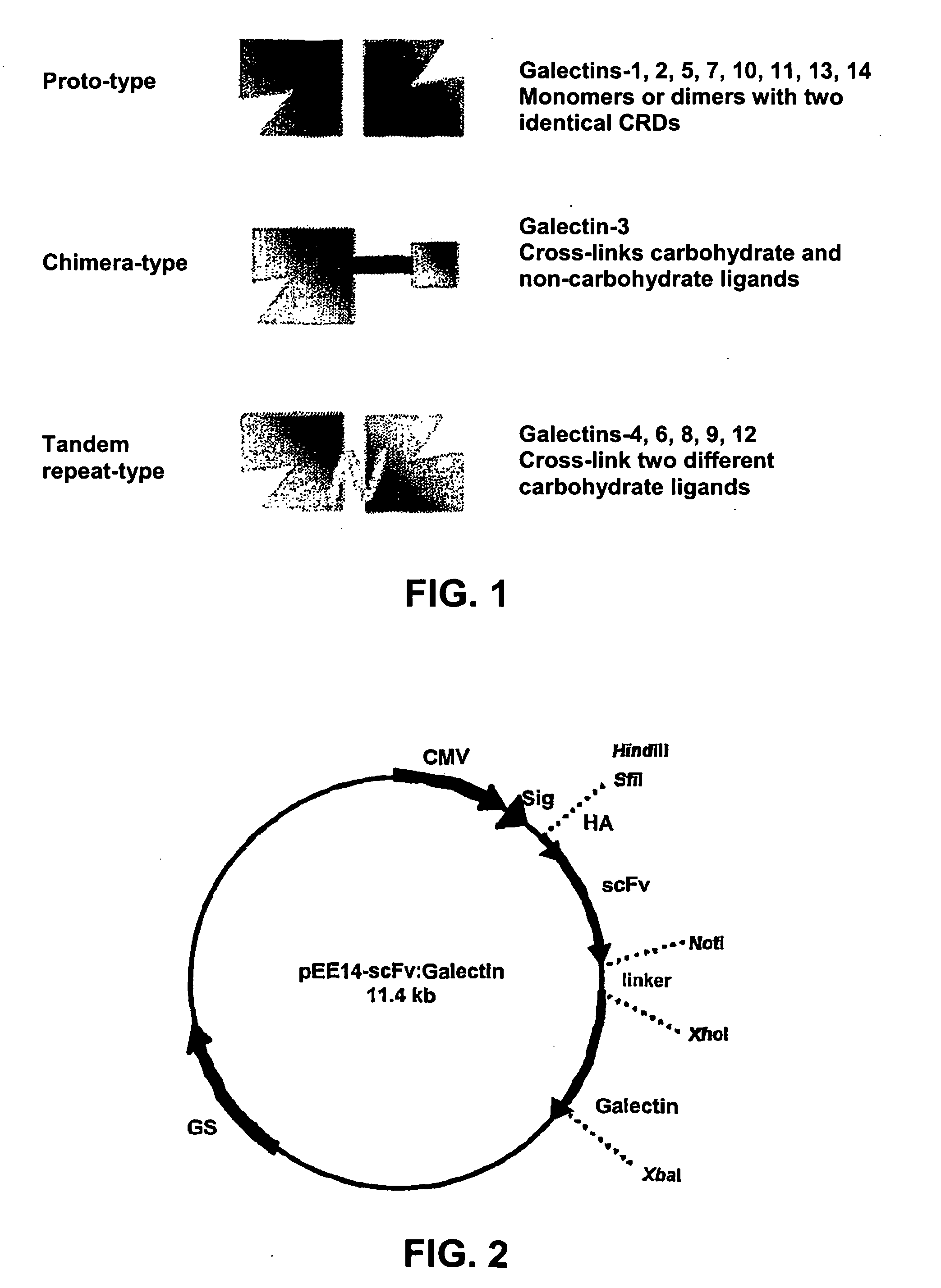
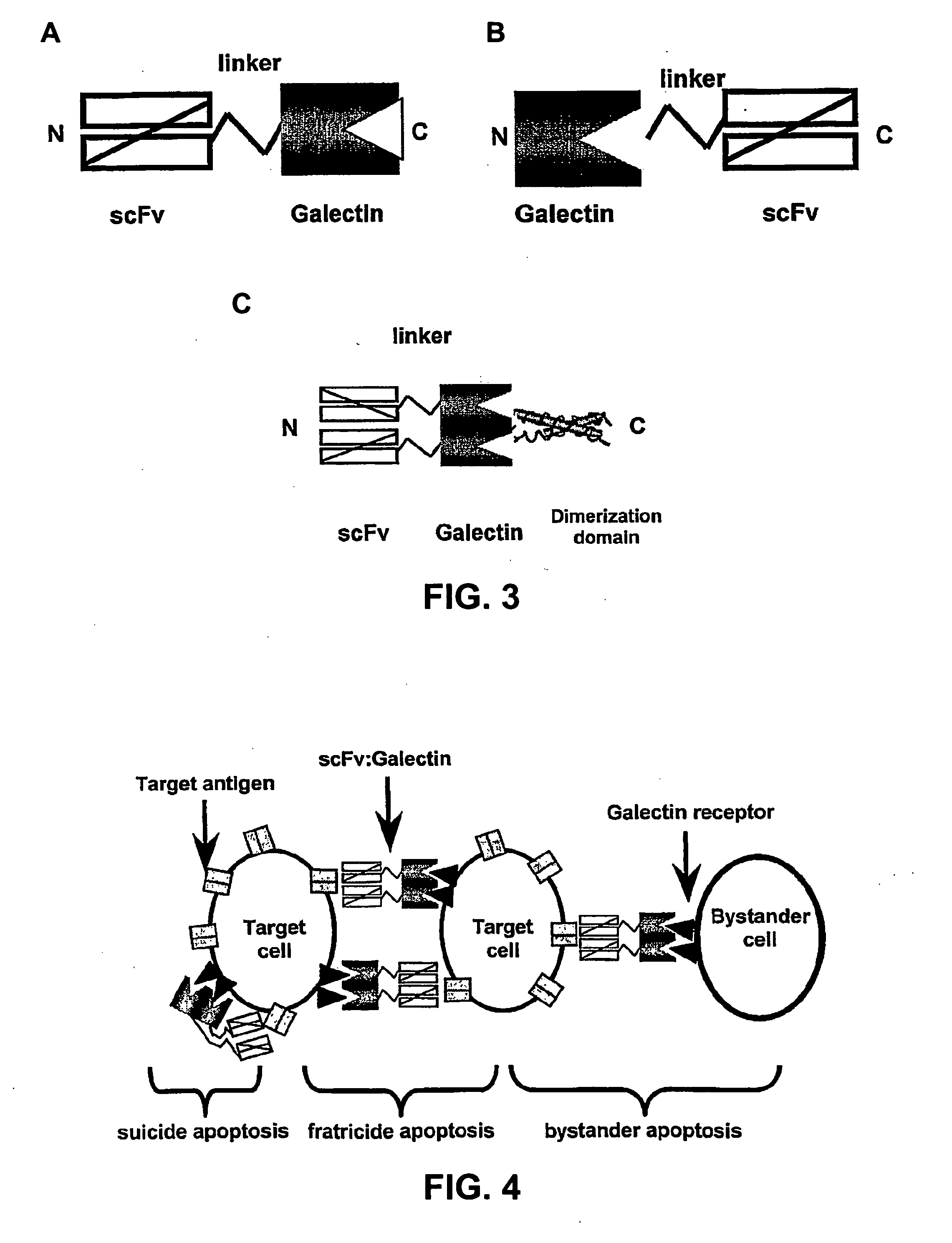
Lectin-binding proteins and their therapeutic use. In particular, described are the targeting and targeting-enhanced multimerization and activation of galectins. Provided is a galectin-conjugate including at least one galectin molecule conjugated to a non-galectin cell targeting means. Exemplary targeting means include targeting means able to bind EGP2, a pancarcinoma-associated cell surface target antigen, CD antigen, such as CD7 or CD38, or a TNF family member, such as TRAIL-R. The targeting means may comprise an antibody or a functional fragment thereof, such as a single chain variable antibody fragment (scFv). Also provided is the use of a galectin-conjugate for treating a disease, like cancer or an immune disorder, such as auto-immune disease, allergic disorder, auto-immune encephalomyelitis, arthritis, colitis, hepatitis, asthma, multiple sclerosis, transplant rejection, Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and / or inflammatory bowel disease.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN
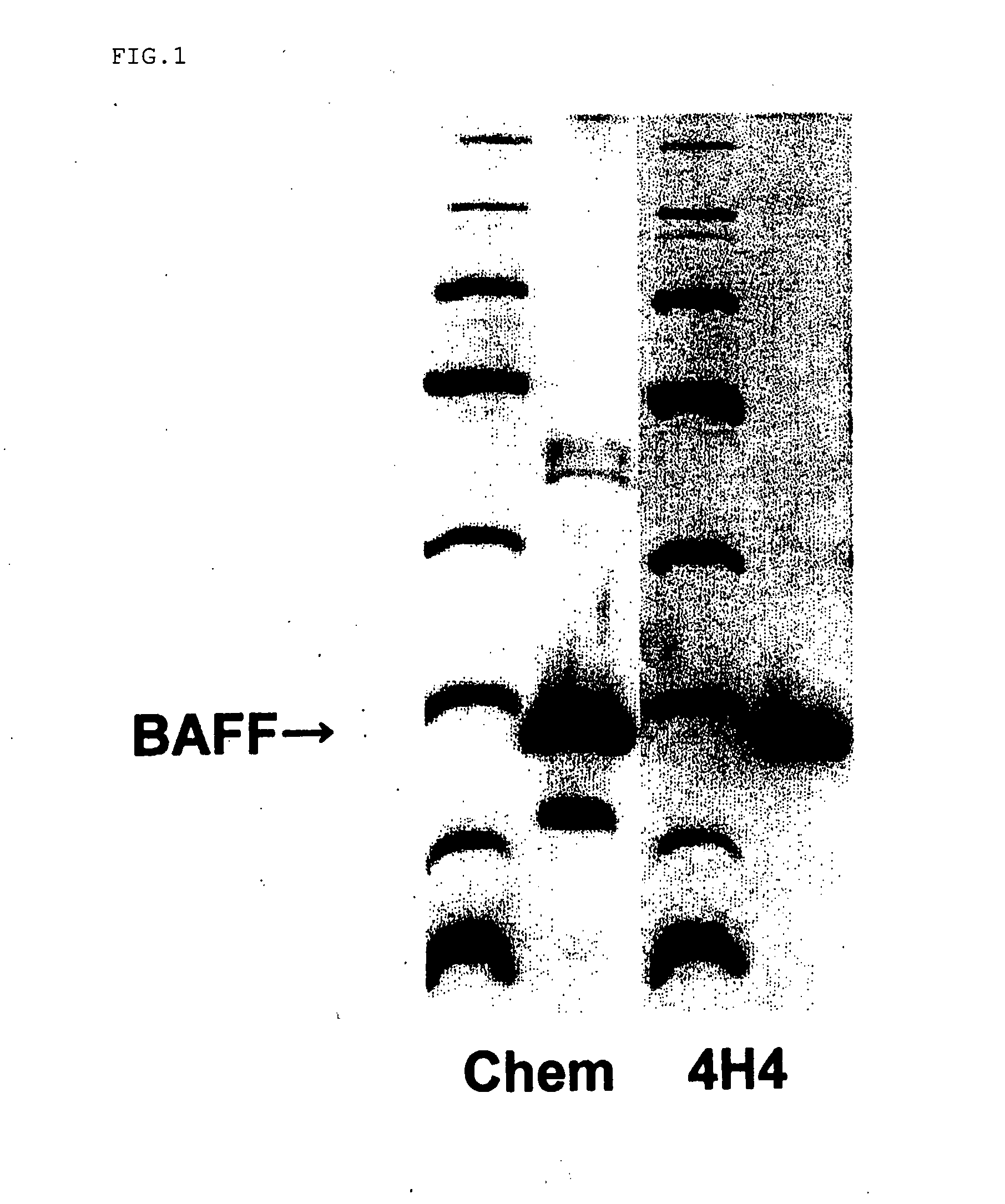
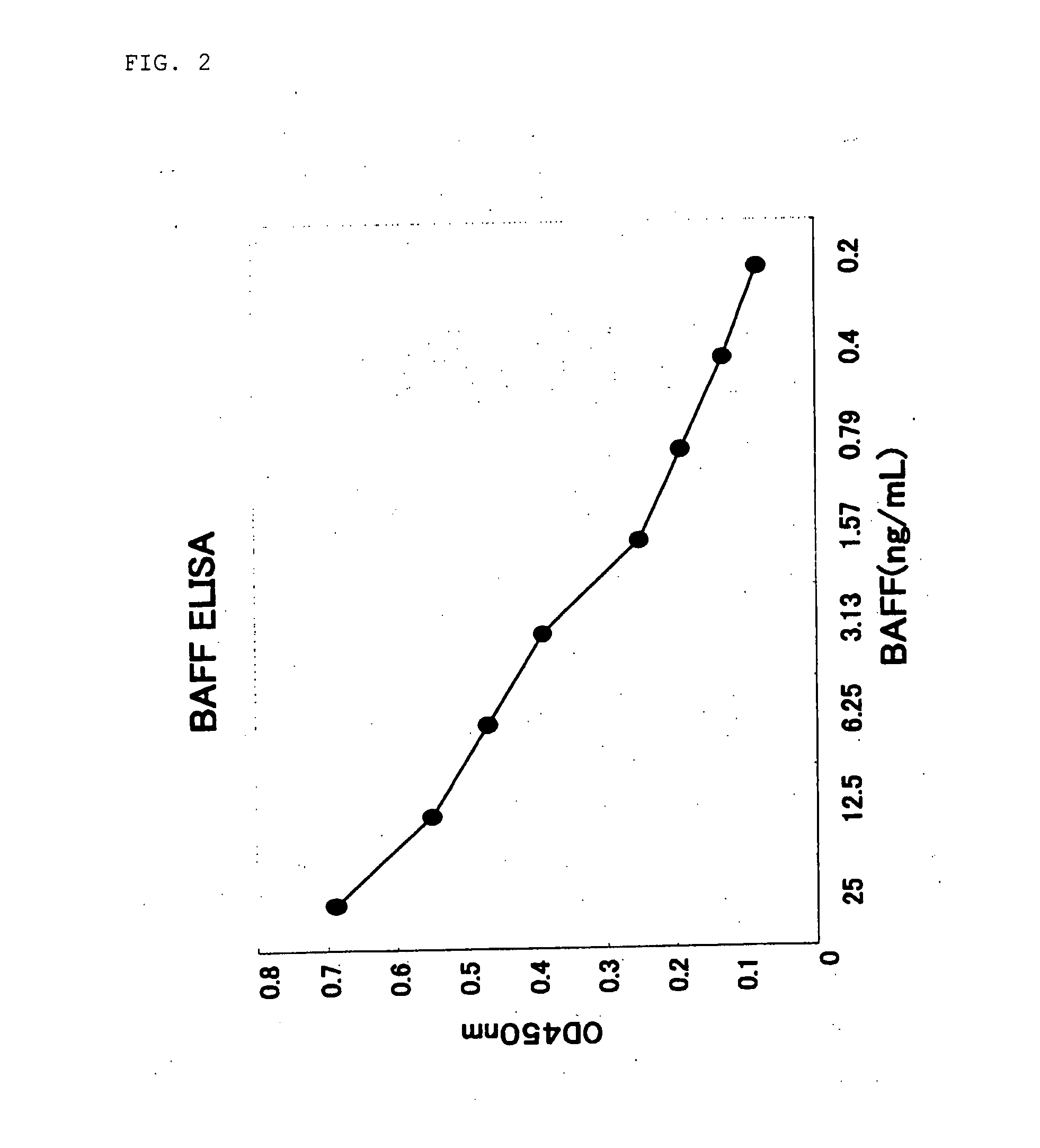
Antihuman Baff Antibody
InactiveUS20080050381A1High sensitivityEffective preventionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMonoclonal antibodyTnf family
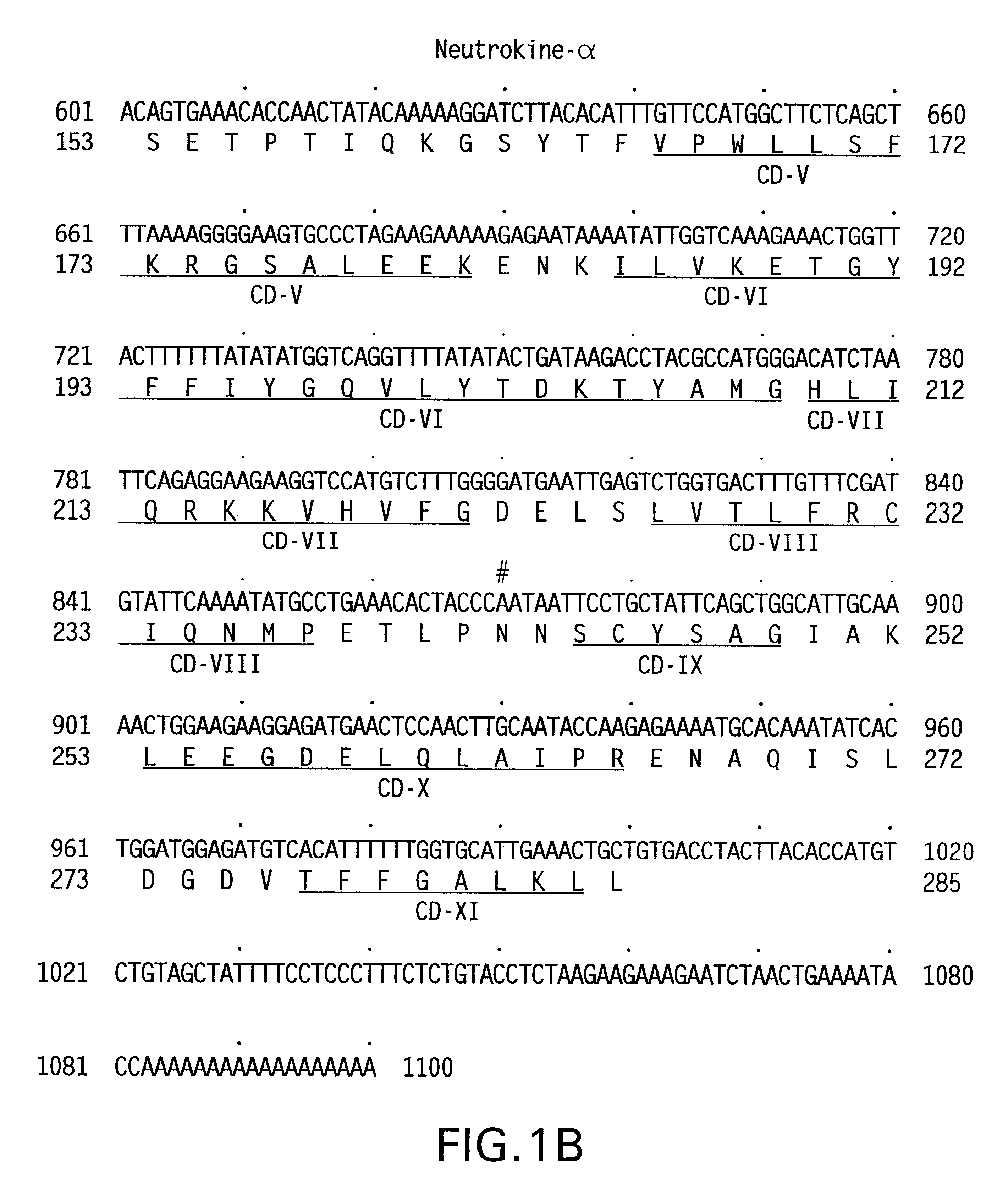
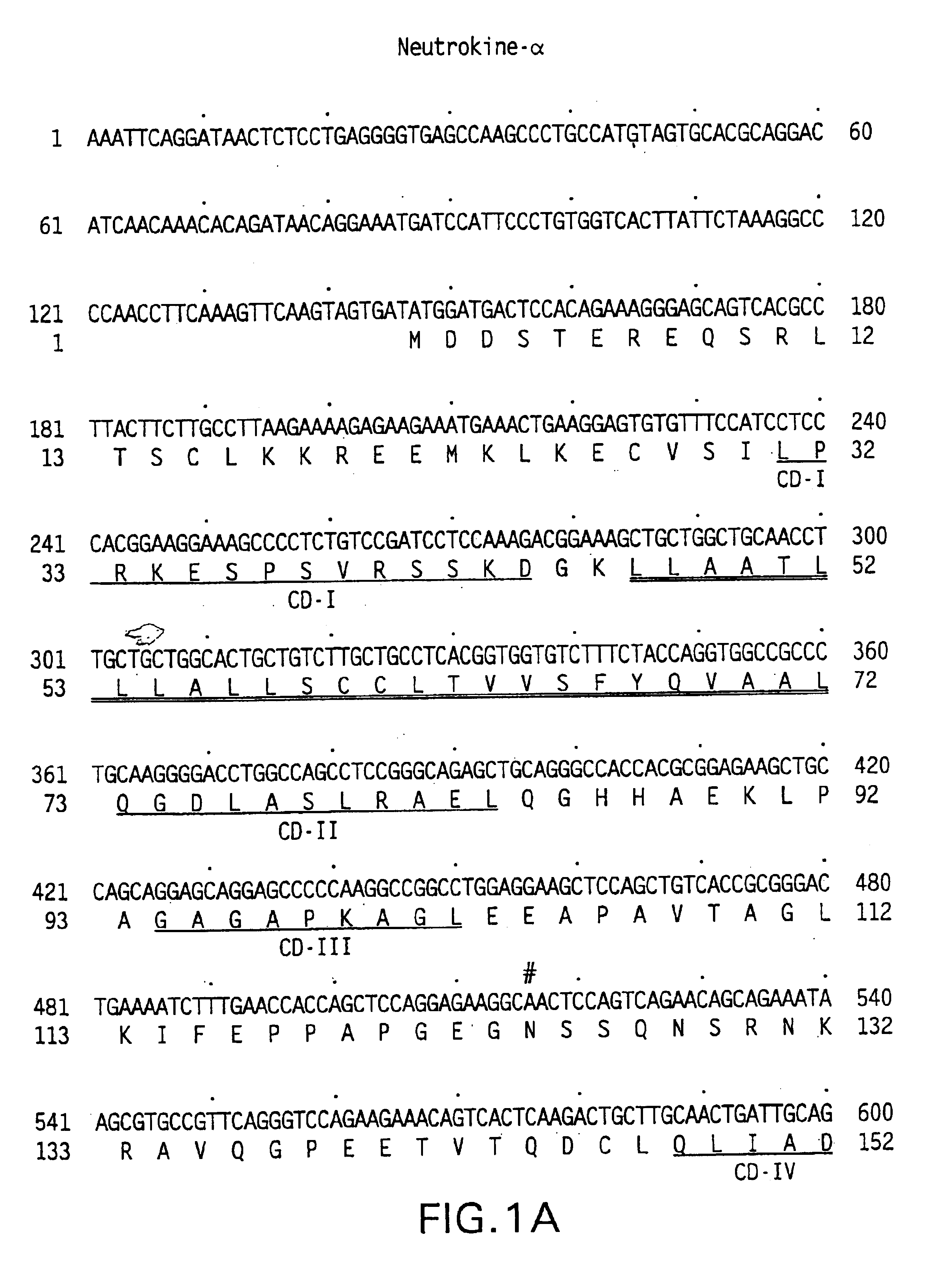
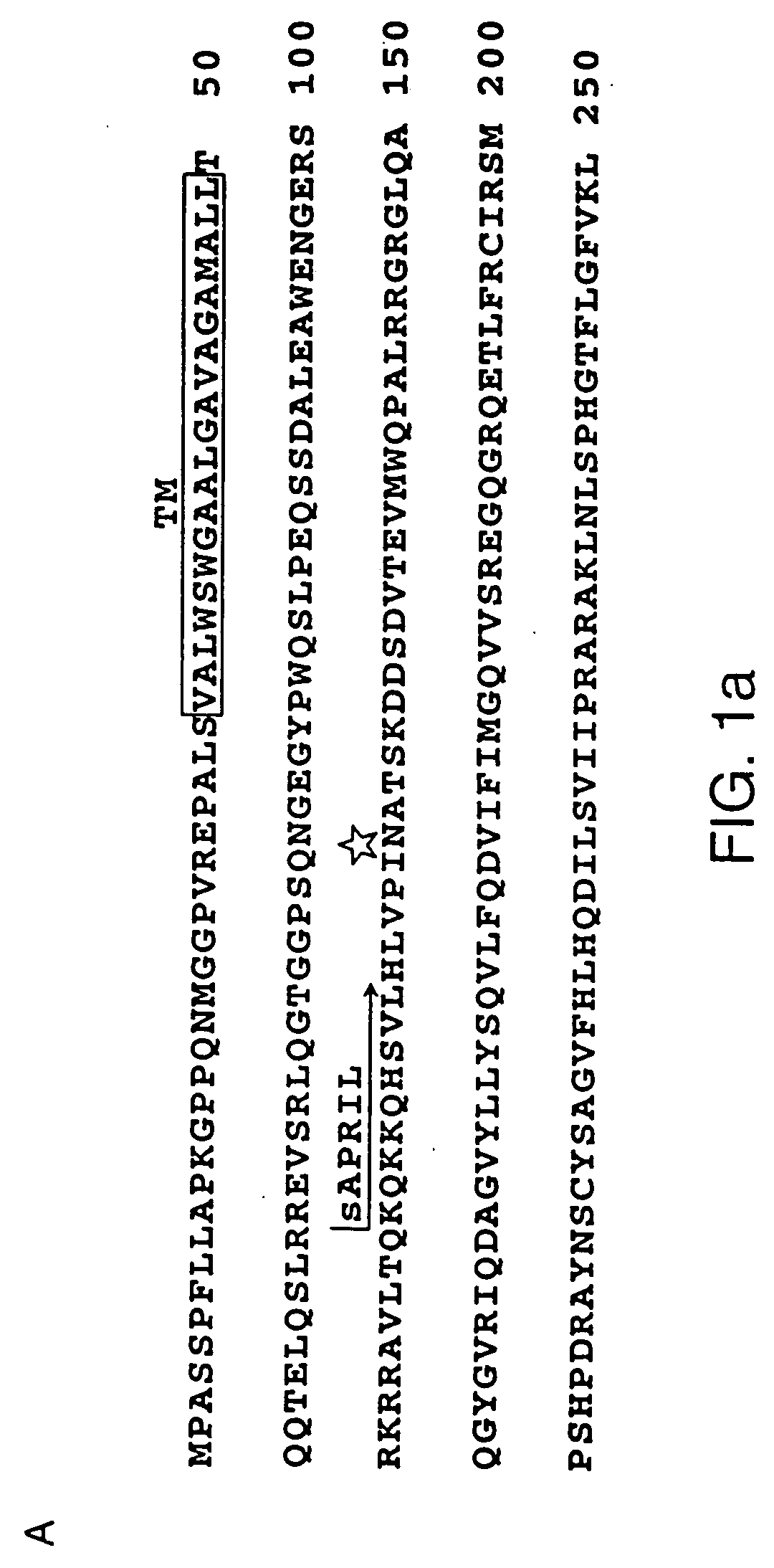
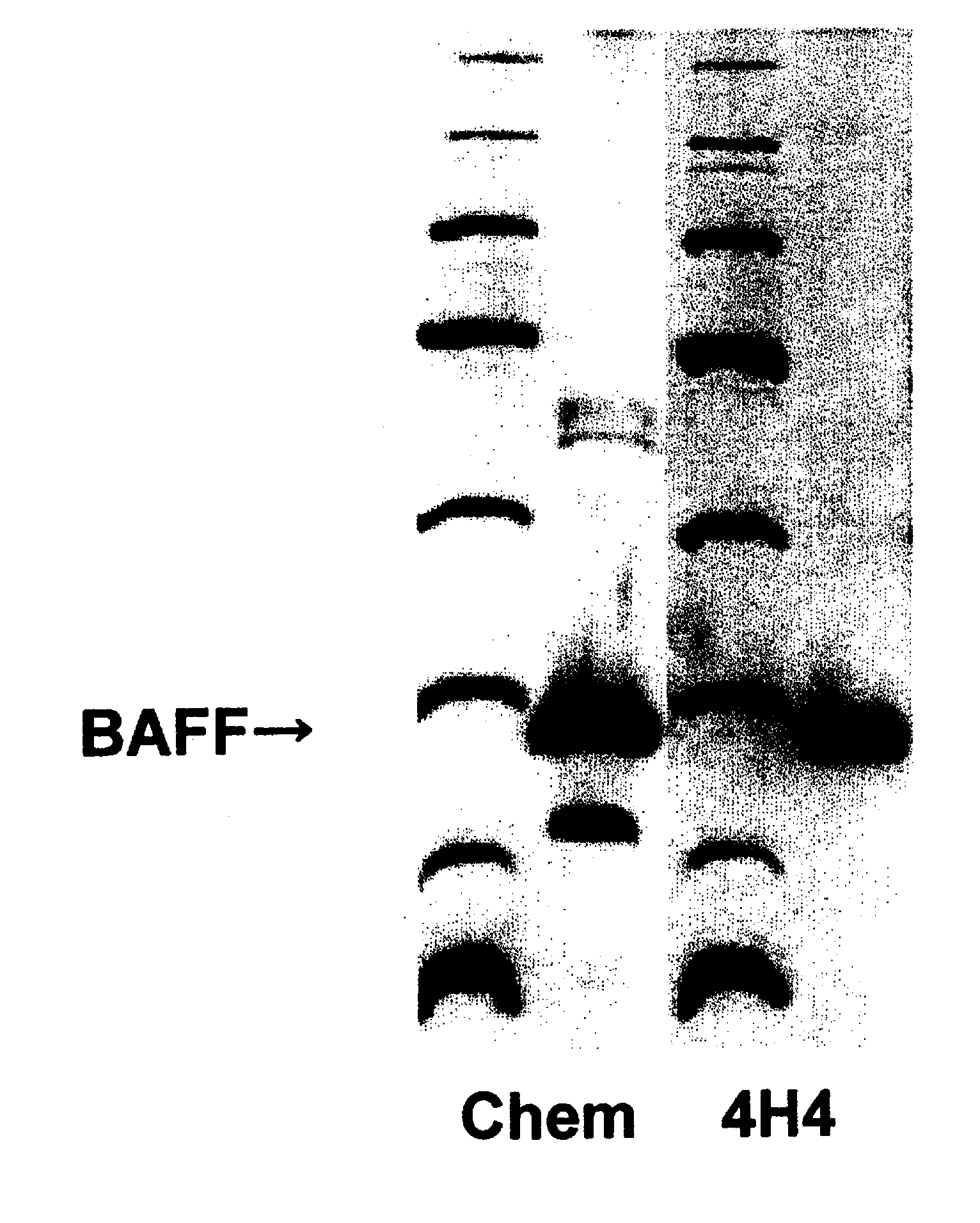
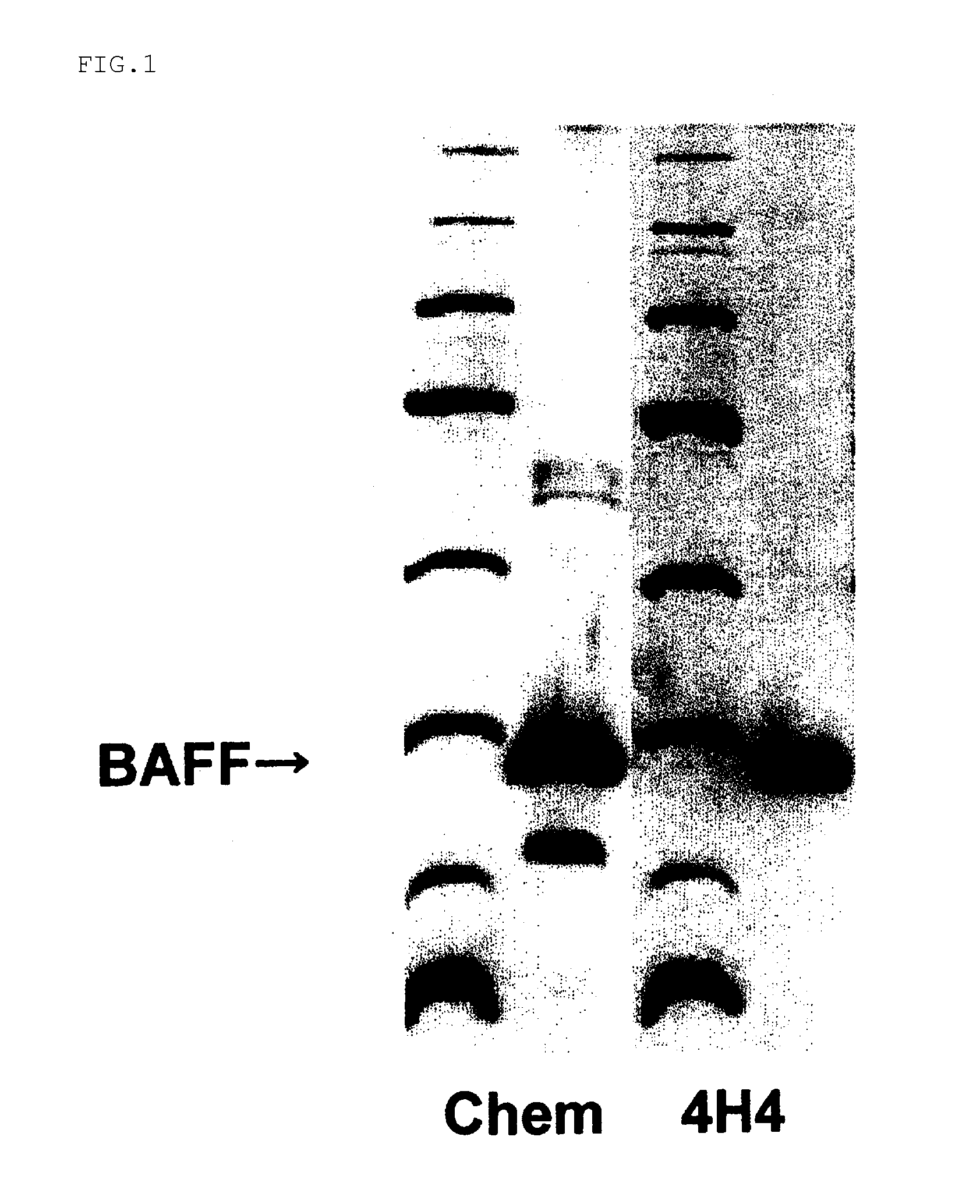
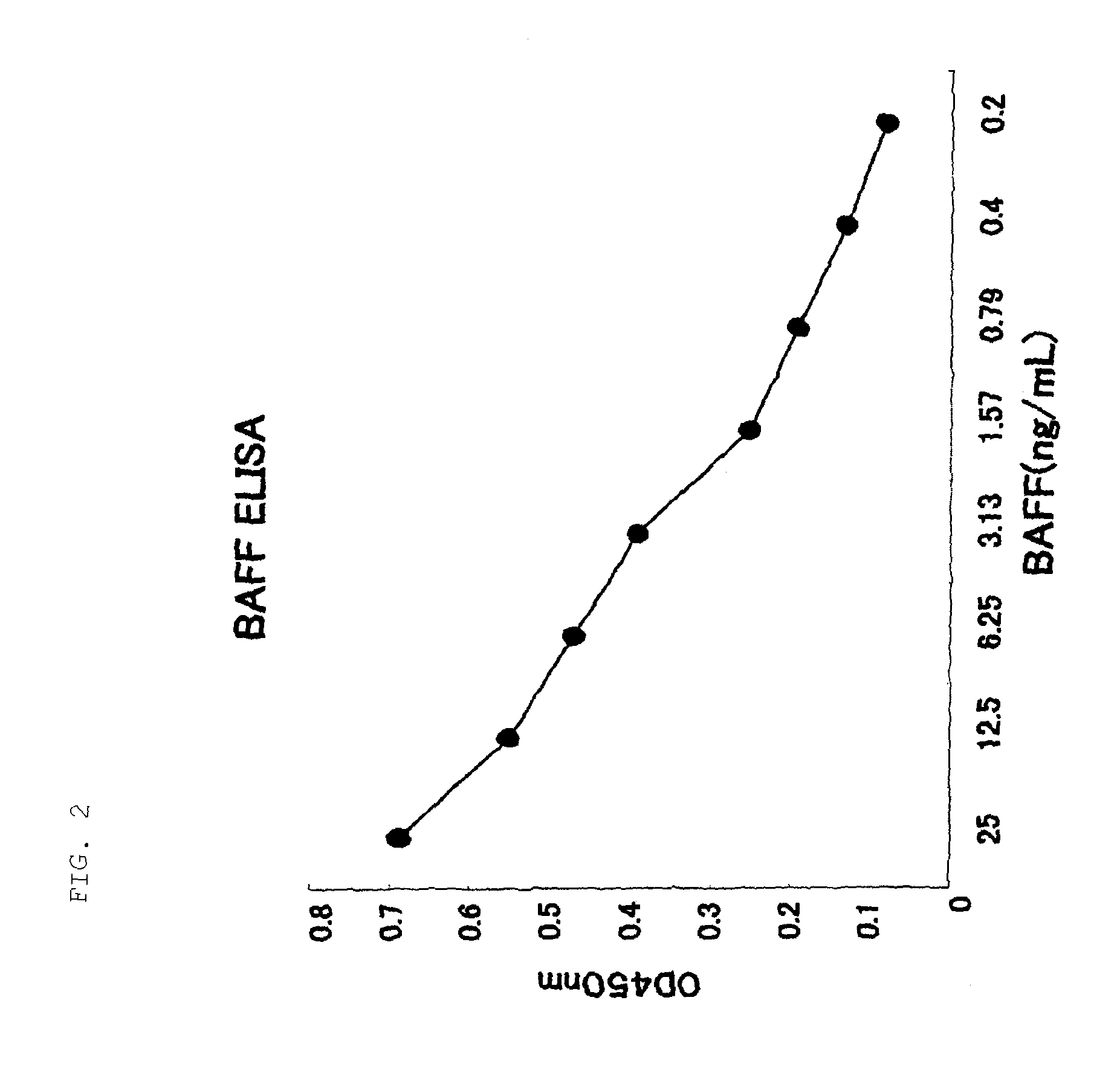
An antibody against a peptide having an amino acid sequence AVQGPEETVT QDC (expressed in single letter amino acid code) corresponding to the 134- to 146-positions in human BAFF (B cell activating factor belonging to the TNF family) protein which is preferably a monoclonal antibody; a method of producing the above antibody; a medicinal composition containing the antibody; utilization of the antibody; and a method of screening an inhibitory effect or an activating effect on BAFF with the use of the antibody.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD +2
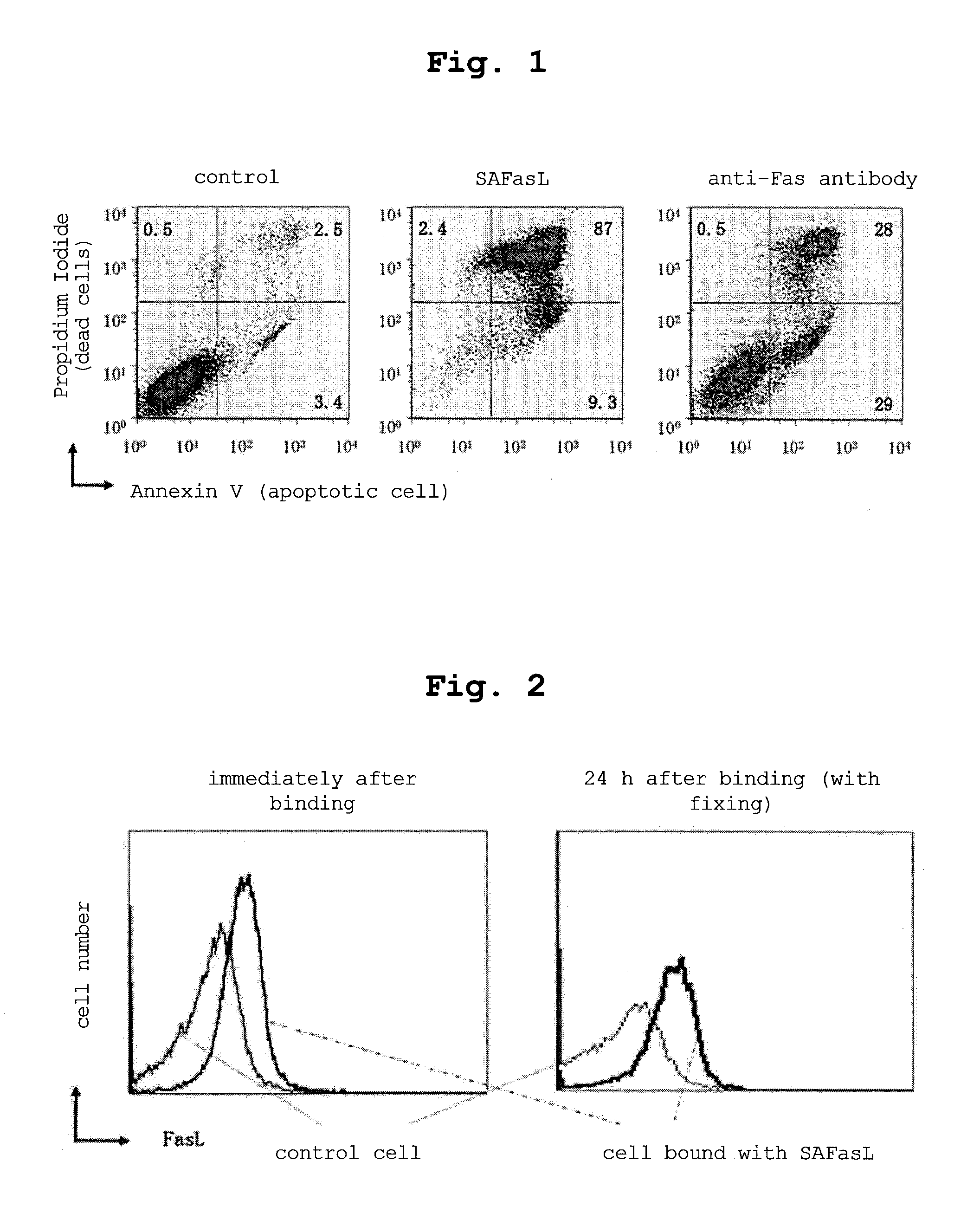
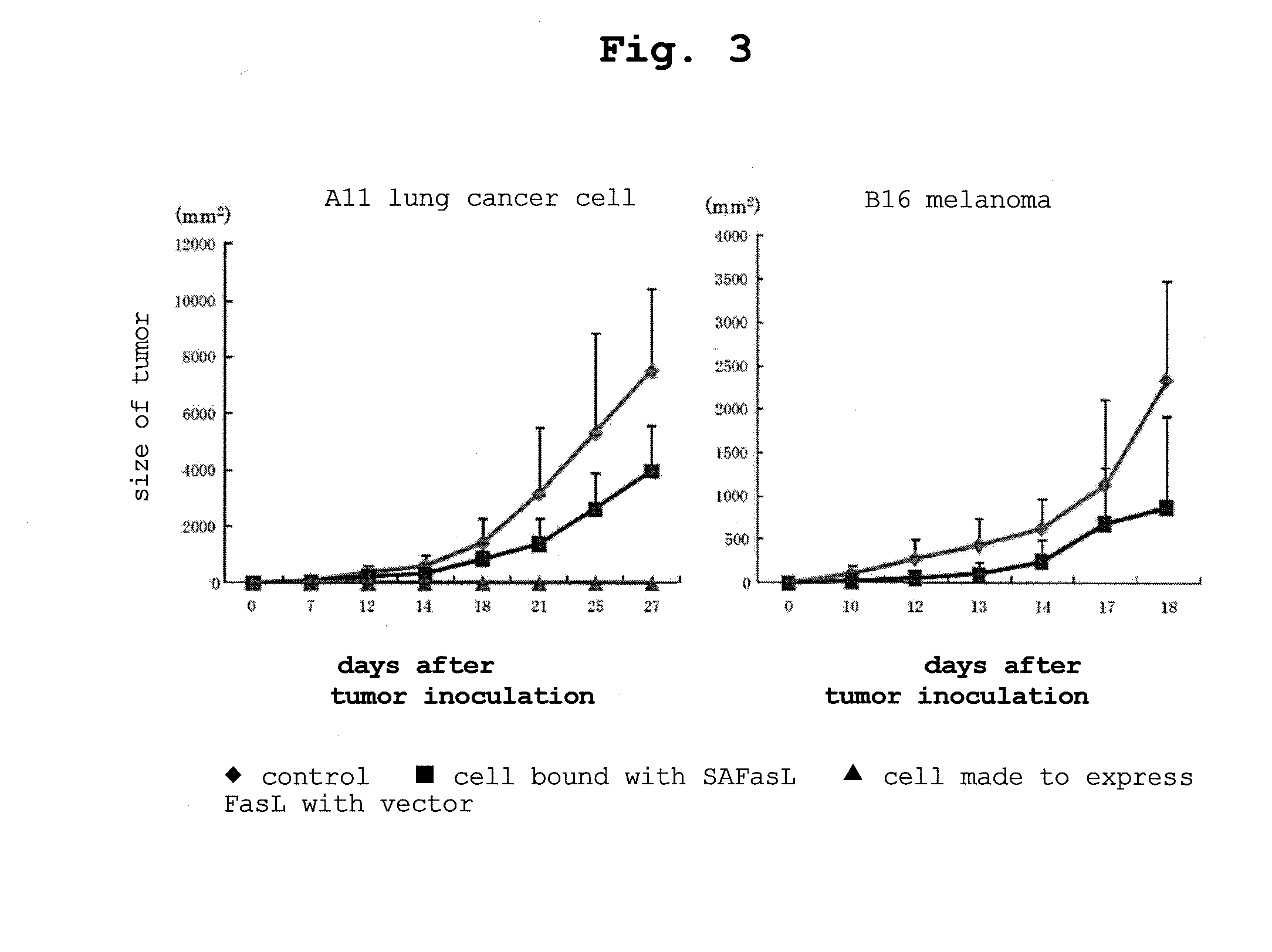
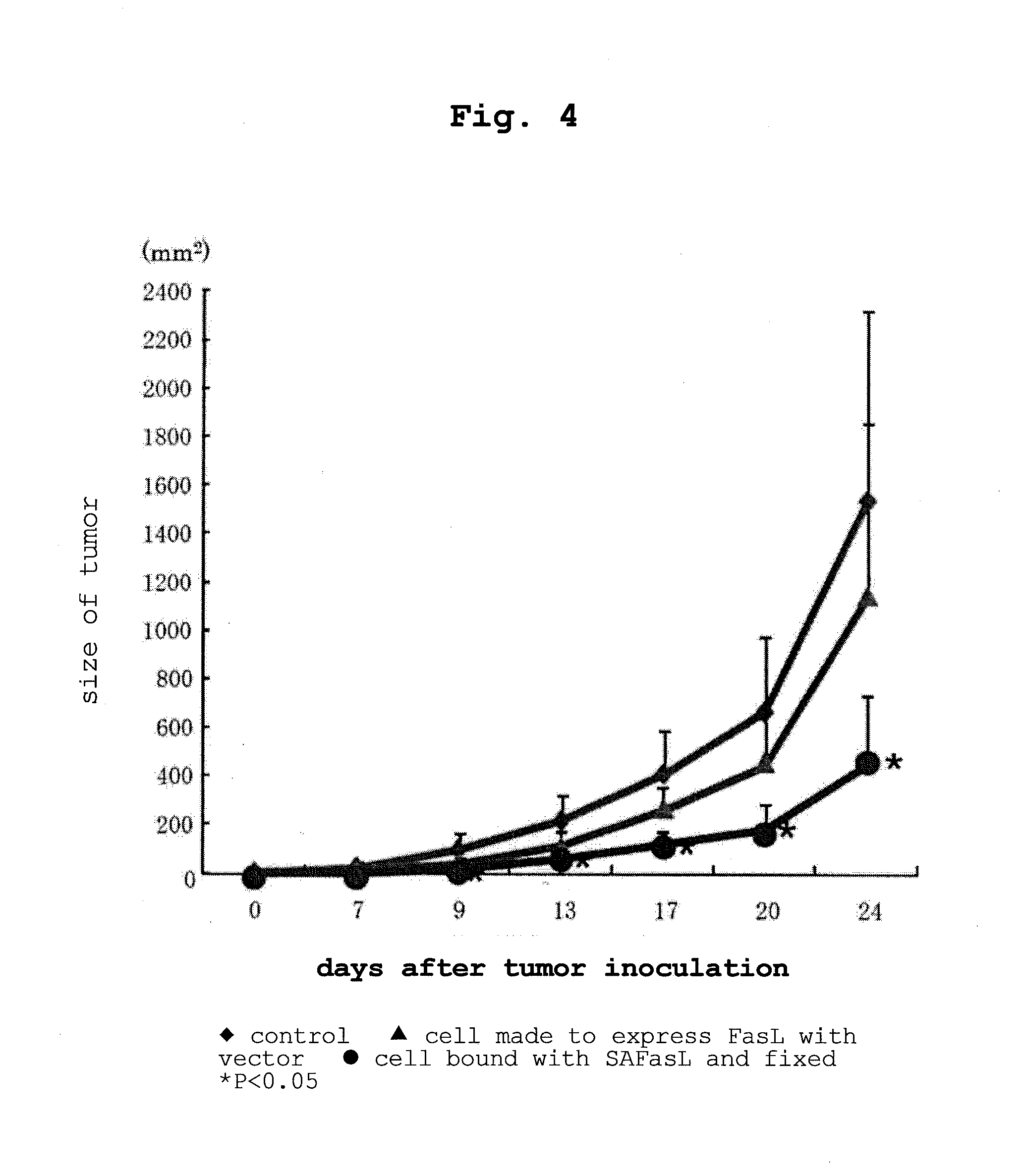
Complex having tumor vaccine effect, and use thereof
InactiveUS20130224145A1Effectively preventedEffectively treatedTumor necrosis factorVaccinesTnf familyWilms' tumor
The present invention provides a tumor cell-soluble TNF family member molecule complex containing a tumor cell and an isolated soluble TNF family member molecule, wherein the soluble TNF family member molecule is bound on a surface of the tumor cell such that it binds to a receptor of the TNF family member expressed on a surface of a cell other than the tumor cell, and stimulates the cell other than the tumor cell via the receptor, and a composition and a tumor vaccine, each containing the complex.
Owner:RIKEN
Method and Compositions for Producing Disulfide-Linked Trimeric TNF Family of Cytokines and Their Use
ActiveUS20180346549A1Avoid disruptionImprove biological activityConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsTnf familyCytokine
Compositions of TNF family of cytokines in covalently linked trimeric forms are disclosed. The resulting fusion proteins are secreted as disulfide bond-linked homotrimers, which are more stable in structure and therapeutically more efficacious than their native counterparts.
Owner:SICHUAN CLOVER BIOPHARM INC
Method and Compositions for Producing Disulfide-Linked Trimeric TNF Family of Cytokines and Their Use
ActiveUS20200199187A1Efficiently containedAvoid disruptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDisulfide bondingTnf family
Compositions of TNF family of cytokines in covalently linked trimeric forms are disclosed. The resulting fusion proteins are secreted as disulfide bond-linked homotrimers, which are more stable in structure and therapeutically more efficacious than their native counterparts.
Owner:SICHUAN CLOVER BIOPHARM INC
APRIL receptor (BCMA) and uses thereof
InactiveCN1399556AInhibit or slow growthProlong lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTnf familyChimeric molecules
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Method and Compositions for Producing Disulfide-Linked Trimeric TNF Family of Cytokines and Their Use
ActiveUS20200190181A1Efficiently containedAvoid disruptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDisulfide bondingTnf family
Compositions of TNF family of cytokines in covalently linked trimeric forms are disclosed. The resulting fusion proteins are secreted as disulfide bond-linked homotrimers, which are more stable in structure and therapeutically more efficacious than their native counterparts.
Owner:SICHUAN CLOVER BIOPHARM INC
Heterologous polypeptide of the TNF family
InactiveUS20050124543A1Stimulating B-cellInhibit tumor cell growthPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticHeterologousTnf family
A newly identified heteromeric ligand of the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-family, referred to hereinafter as “APBF” has been identified.
Owner:RENNERT PAUL +3
Antihuman baff antibody
InactiveUS20110081351A1High sensitivityEffective preventionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMonoclonal antibodyTnf family
An antibody against a peptide having an amino acid sequence AVQGPEETVT QDC (expressed in single letter amino acid code) as represented by SEQ ID: NO. 1 corresponding to the 134- to 146-positions in human BAFF (B cell activating factor belonging to the TNF family) protein which is preferably a monoclonal antibody; a method of producing the above antibody; a medicinal composition containing the antibody; utilization of the antibody; and a method of screening an inhibitory effect or an activating effect on BAFF with the use of the antibody.
Owner:TAKEUCHI +2
Human Endokine Alpha and Methods of Use
The present invention concerns a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of cytokines. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding the endokine alpha protein. Endokine alpha polypeptides are also provided, as are vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same. Also provided are diagnostic and therapeutic methods concerning TNF family-related disorders.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
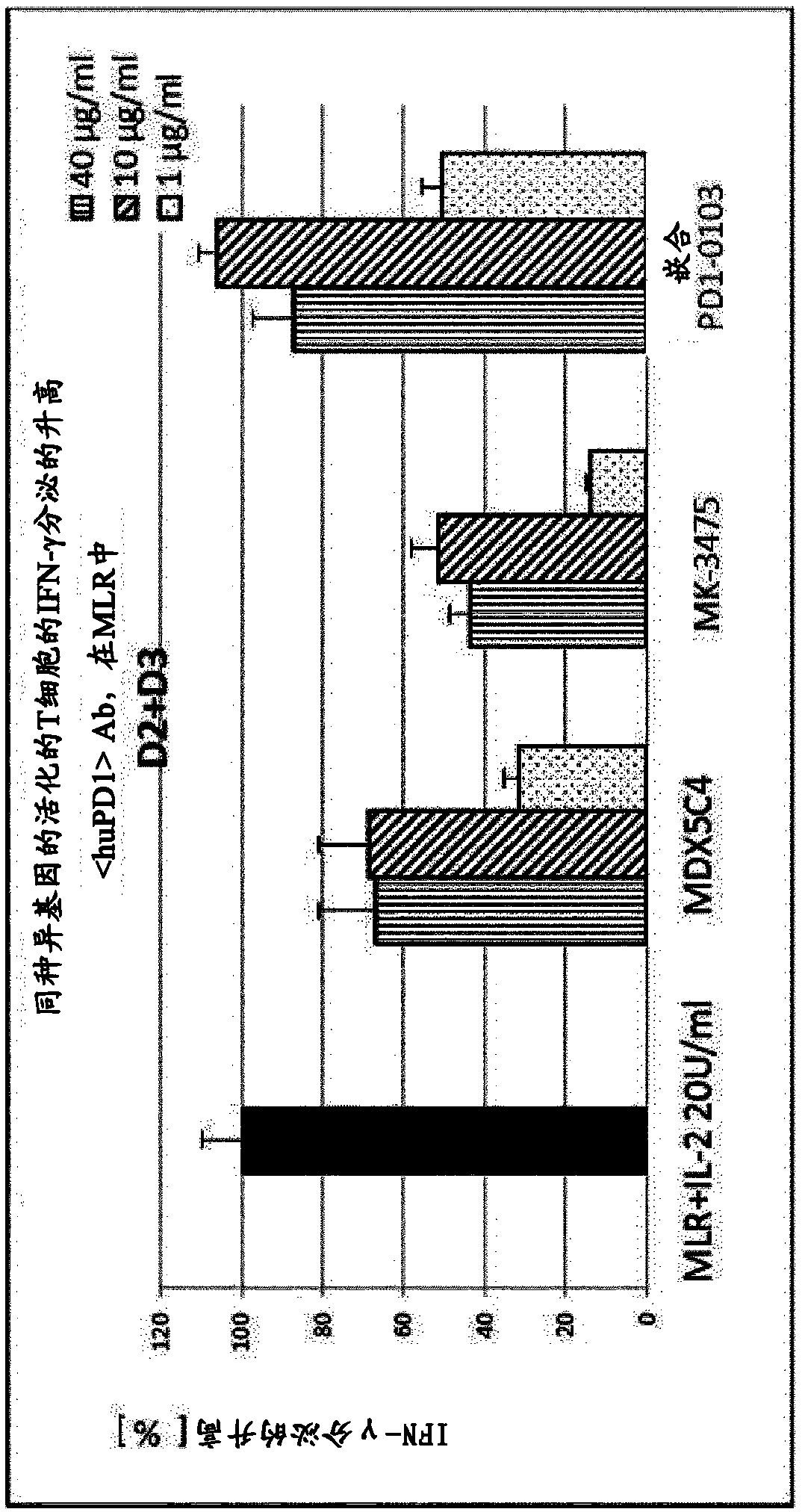
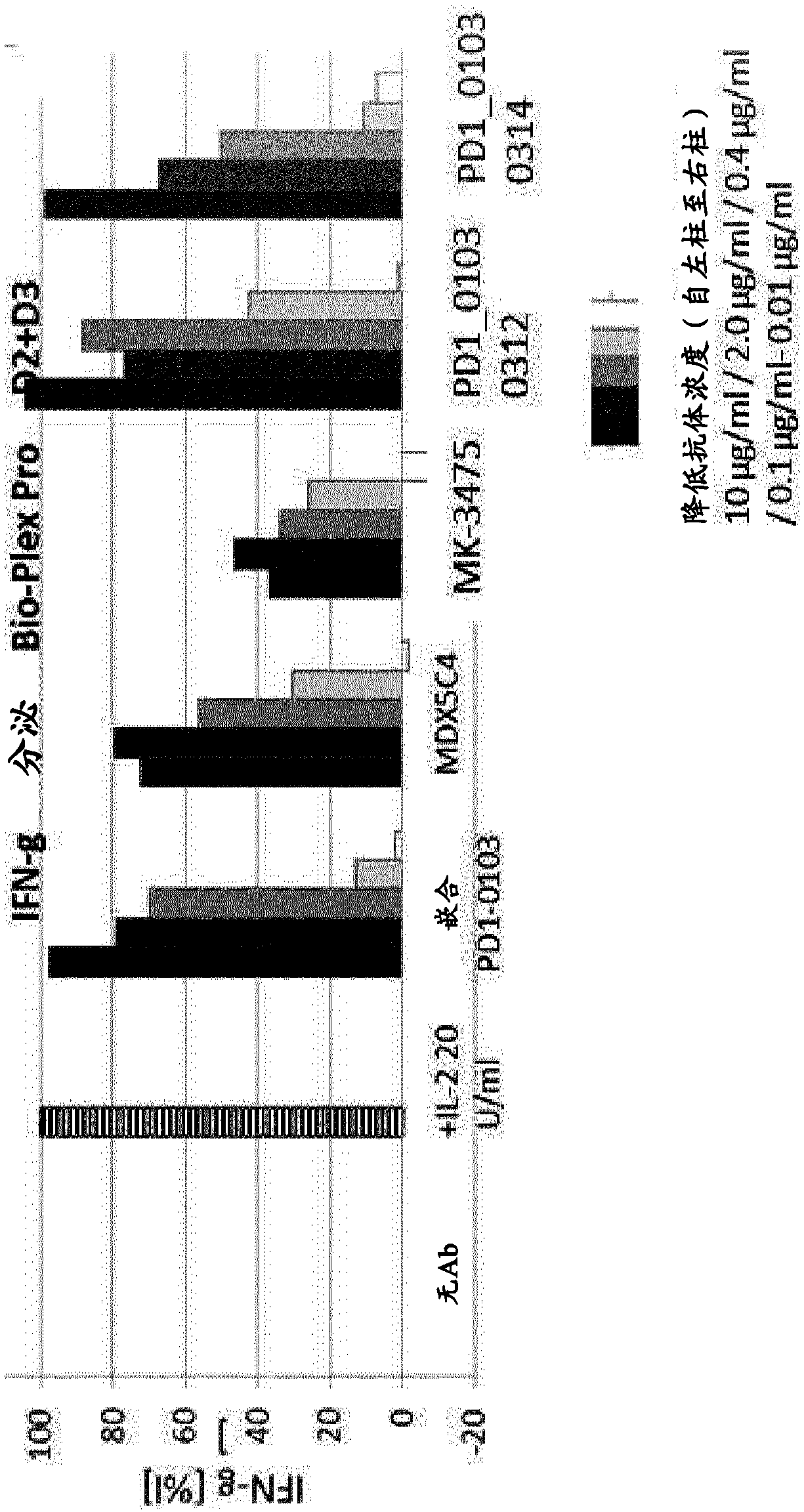
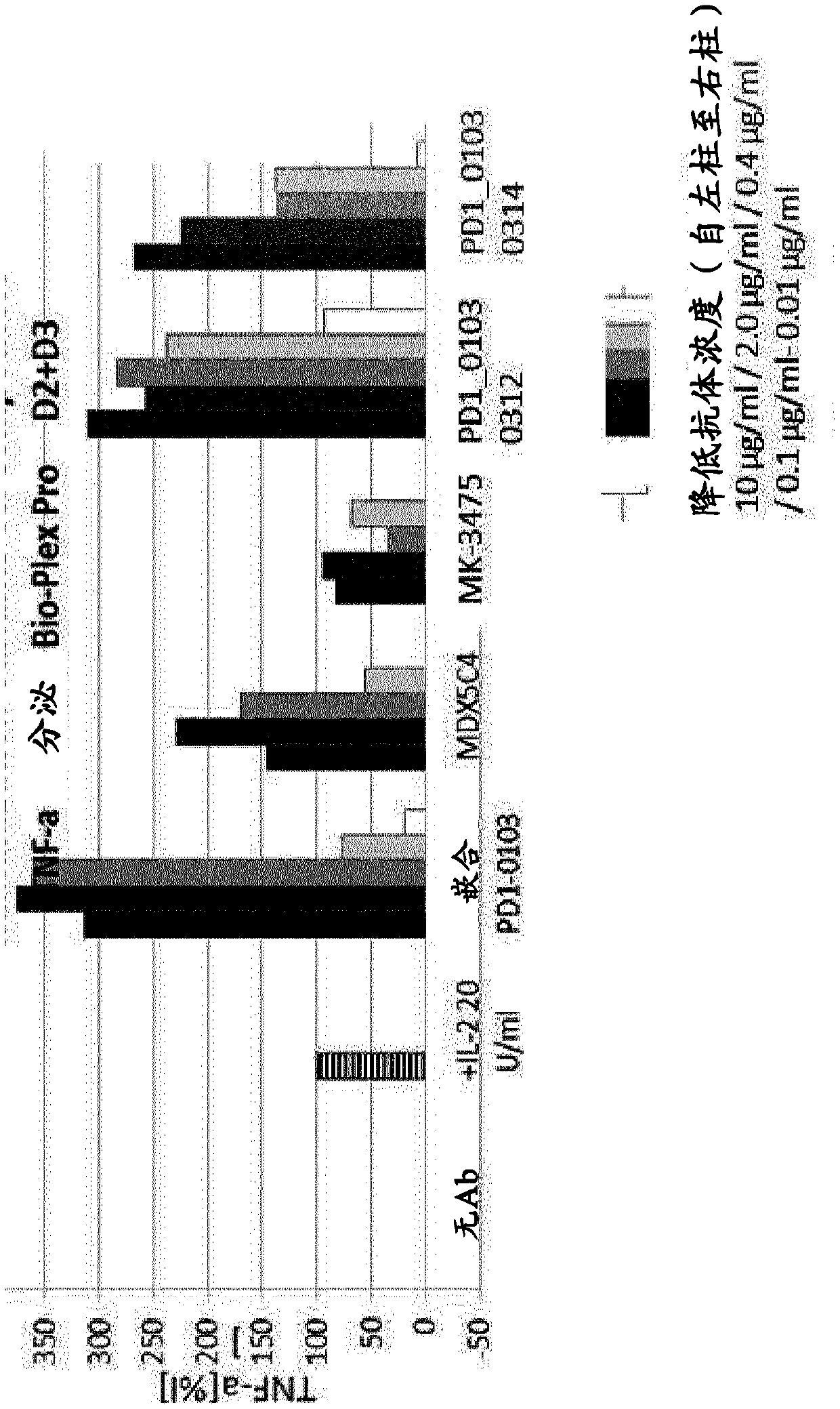
Antigen binding molecules comprising a TNF family ligand trimer and pd1 binding moiety
The invention relates to novel TNF family ligand trimer-containing antigen binding molecules comprising (a) at least one moiety capable of specific binding to PD1 and (b) a first and a second polypeptide that are linked to each other by a disulfide bond, characterized in that the first polypeptide comprises two ectodomains of a TNF ligand family member or fragments thereof that are connected to each other by a peptide linker and in that the second polypeptide comprises only one ectodomain of said TNF ligand family member or a fragment thereof.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Bifunctional fusion protein composed of IL-2 and antibody subunit
PendingCN114437228AAvoid disadvantagesOvercome resistancePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDimerHeterologous
The invention relates to a bifunctional fusion protein composed of IL-2 and an antibody subunit. The bifunctional fusion protein comprises a heterodimer composed of the following first monomer and second monomer: (1) the first monomer formed by connecting interleukin 2 (IL-2) and an immune globulin Fc single chain; and (2) a second monomer obtained by linking an Fc single chain to Fab / ScFv of an antibody of a TNF family co-stimulatory or co-inhibitory molecule or a CTLA4 molecule. The bifunctional fusion protein also comprises a homodimer, and the homodimer monomer comprises: (1) an IL-2 functional block; and (2) a monomer of an antibody or a monomer formed by connecting Fab / ScFv of the antibody with an Fc single chain, wherein the antibody is a TNF family co-stimulatory or co-inhibitory molecule or a CTLA4 molecule antibody. The invention also relates to application of the bifunctional fusion protein in preparation of antitumor drugs.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com