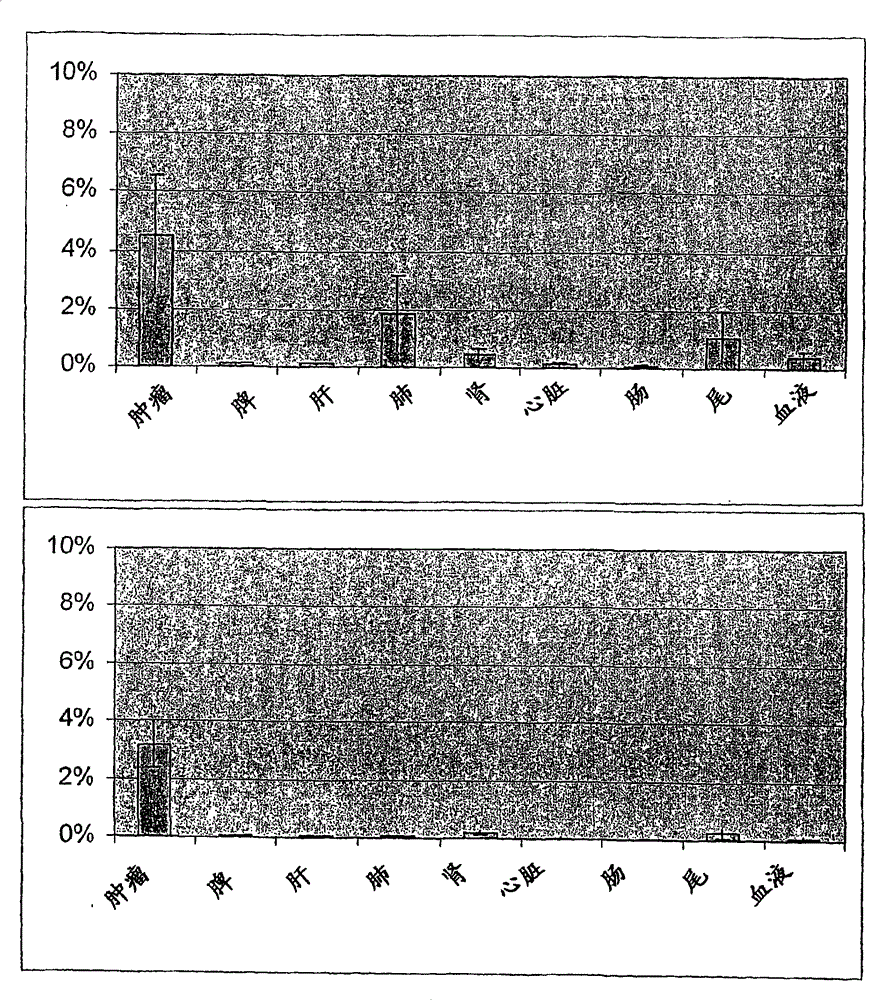
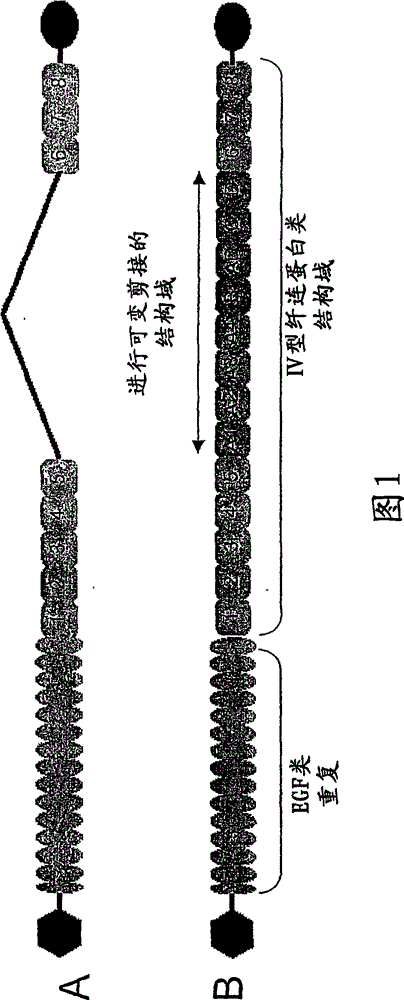
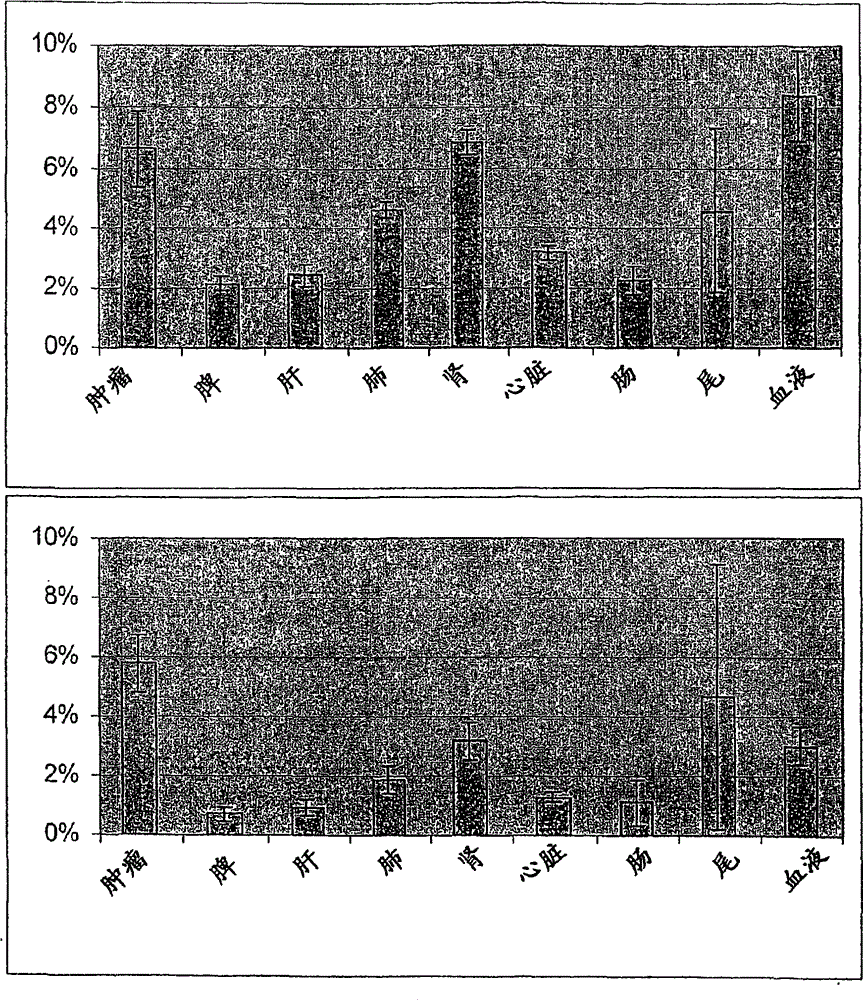
antibody against tenascin c
A tenascin and tenascin technology, applied in the field of human antibodies against tenascin C, can solve the problems of epitope and antibody specificity or insufficient stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0171] The gene encoding domain A1 of human tenascin C was cloned from mRNA by RT-PCR, specifically normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) cultured at pH 7.5 in the absence of serum [16], by PCR , the mRNA was isolated from the cells using oligomeric TnC-AlBamHIba (cgggatcctccactgaacaagcccctgag) and TnC-A1BglIIforggagatctttcccctgtggaggcctcagc). The gene was then cloned into the pQE12 bacterial expression vector (Qiagen) and expressed in E. coli TG-1. Purification was performed by His-tag using nickel-loaded Ni-NTA agarose resin (Qiagen).
[0172] Purified domain Al was biotinylated prior to selection using Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin (Pierce). Biopanning was performed as described (VitiF, et al. Methods Enzymol 2000; 326:480-505). Briefly, biotinylated proteins (final concentration 10 -7 M) Incubate with 600 [mu]l pre-blocked ETH-2 library phage for 30 minutes. By adding 5.3×10 -7 Streptavidin-coated magnetic beads (Dynal) capture bound phage. After strong washing, the selected ...
Embodiment 2
[0183] The gene encoding domain C of human tenascin C was cloned into the vector pQE12 (Qiagen) [Carnemolla B et al AmJ Pathol 1999; 154: 1345-1352, Balza E et al FEBS Lett 1993; 332: 39-43] and expressed in E. coli TG-1. Purification was performed by His-tag using nickel-loaded Ni-NTA (Qiagen).
[0184] Purified domain C was biotinylated prior to selection using Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin (Pierce). Bioscreens were performed as described [VitiF, et al. Methods Enzymol 2000; 326: 480-505], but using alternate screening protocols on streptavidin and avidin coated plates. Briefly, biotinylated proteins (final concentration 10 -7 M) Incubate with 600 [mu]l pre-blocked ETH-2 library phage for 30 minutes. Bound phage were captured on plastic microtiter plates coated with avidin (1st and 3rd incubation cycles) or streptavidin (2nd incubation cycle). After extensive washing, selected phage were eluted by reducing the disulfide bond in the biotin linker. Isolated phage were amplified in T...
Embodiment 3
[0189] Using a similar protocol as described in Example 2, scFvs against the C domain of tenascin C were further isolated and named F4 and G11, respectively. F4 and G11 have two VL domains that differ in amino acids and have the same VH domain. The VH and VL domains are connected by a peptide linker having an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 37 or SEQ ID NO: 39 encoded by SEQ ID NO: 36 or SEQ ID NO: 38, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com