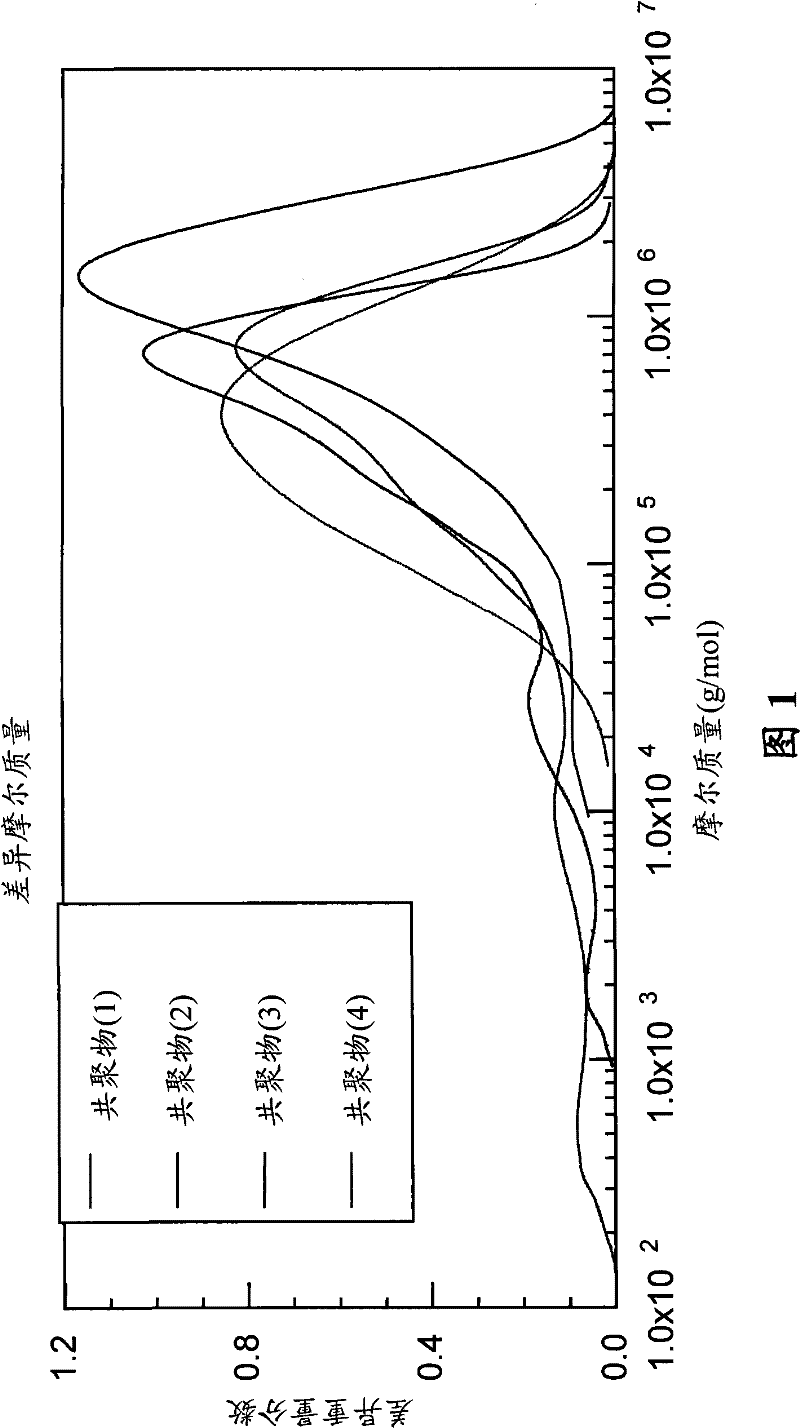
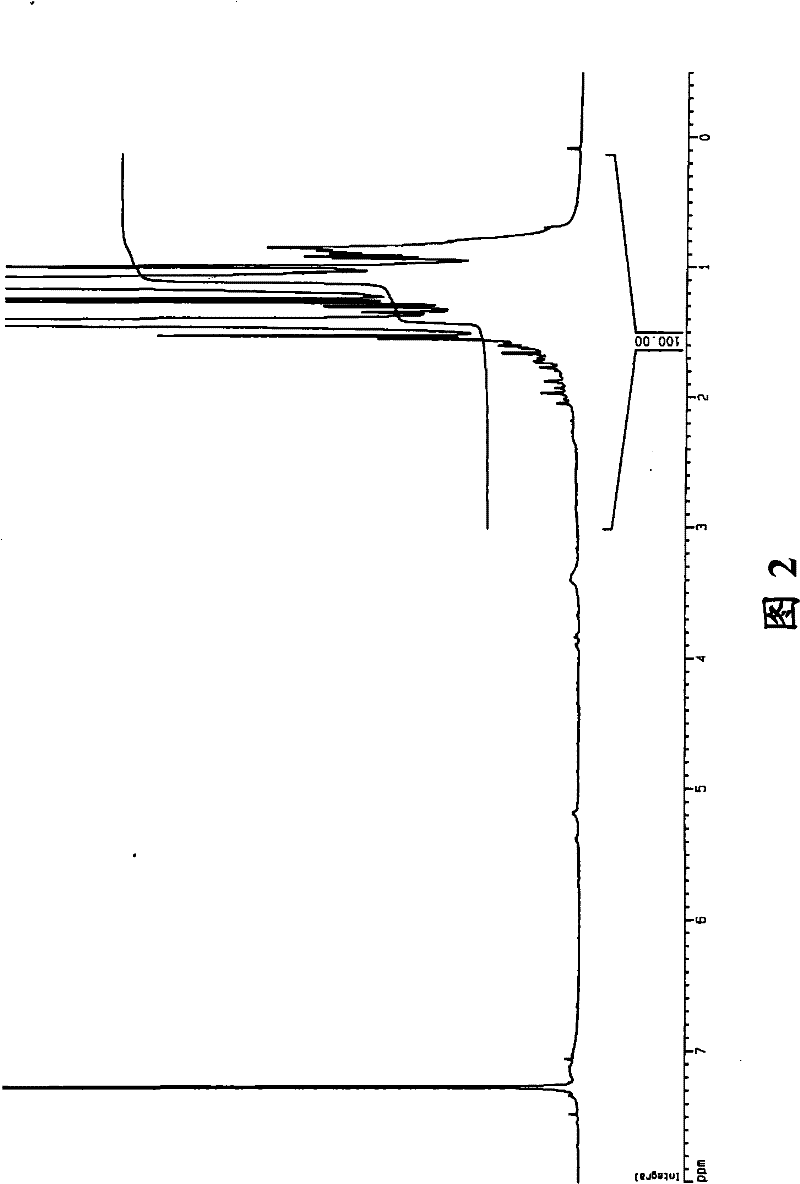
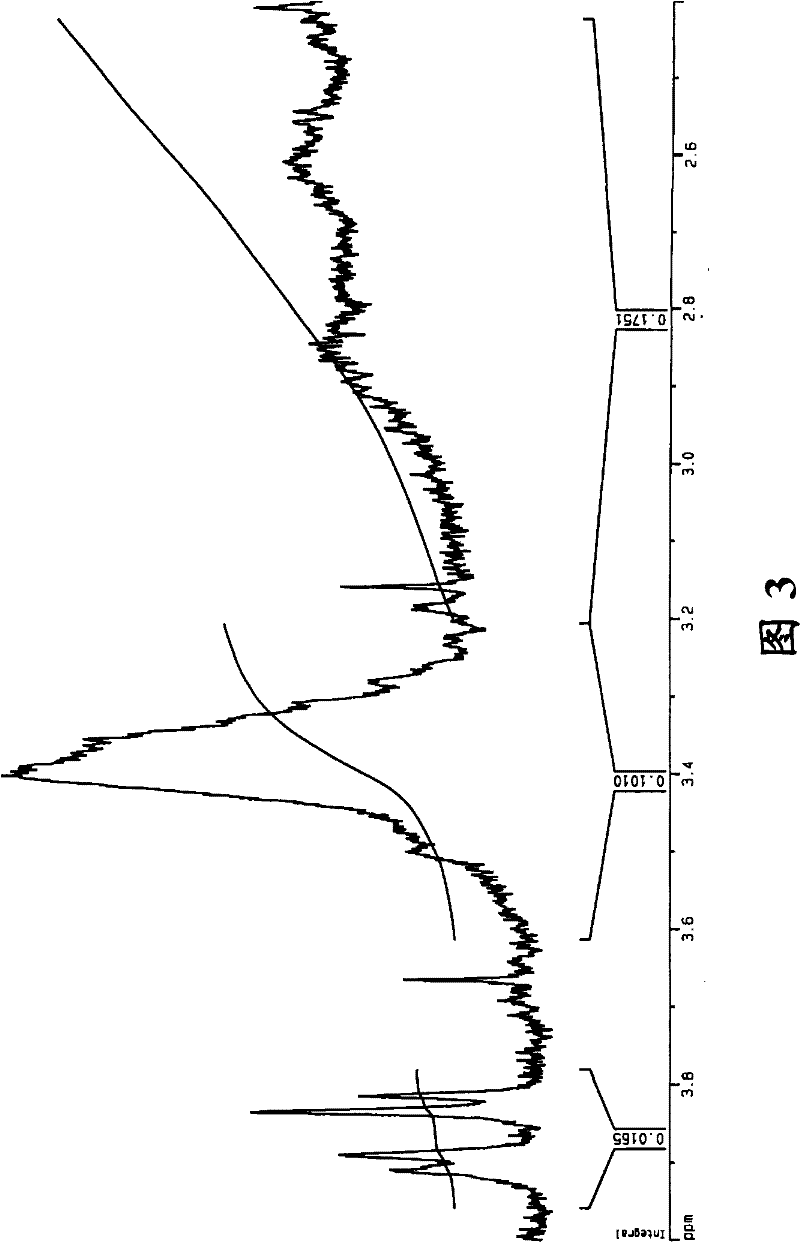
Co-polymerization of an isoolefin with a halogenated co-monomer
A comonomer, isoolefin technology, applied in the direction of rolling resistance optimization, road transportation emission reduction, etc., can solve problems such as undeveloped
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] Copolymers are not limited to specific isoolefins. However, preference is given to isoolefins in the range of 4 to 16 carbon atoms, especially 4 to 7 carbon atoms, such as isobutene, 2-methyl-1-butene, 3-methyl-1-butene, 2- Methyl-2-butene, 4-methyl-1-pentene and mixtures thereof. Most preferred is isobutene.
[0044] Halogenated comonomers may include any suitable monomer which, when copolymerized with an isoolefin monomer, produces a non-vinyl, non-allyl primary bromide with an adjacent tertiary carbon. Preferably, the comonomer comprises a straight chain C having an alkene group at one end and a halogen group at its opposite end. 4 main chain. More preferably, the comonomer comprises 4 Alkyl group on the third carbon of the main chain. Still more preferably, the halogenated comonomer is of the formula:
[0045]
[0046] in,
[0047] R 1 is C 1 -C 20 Alkyl, C 1 -C 20 Straight-chain or branched alkenyl, or substituted aromatic hydrocarbons,
[0048] R ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com