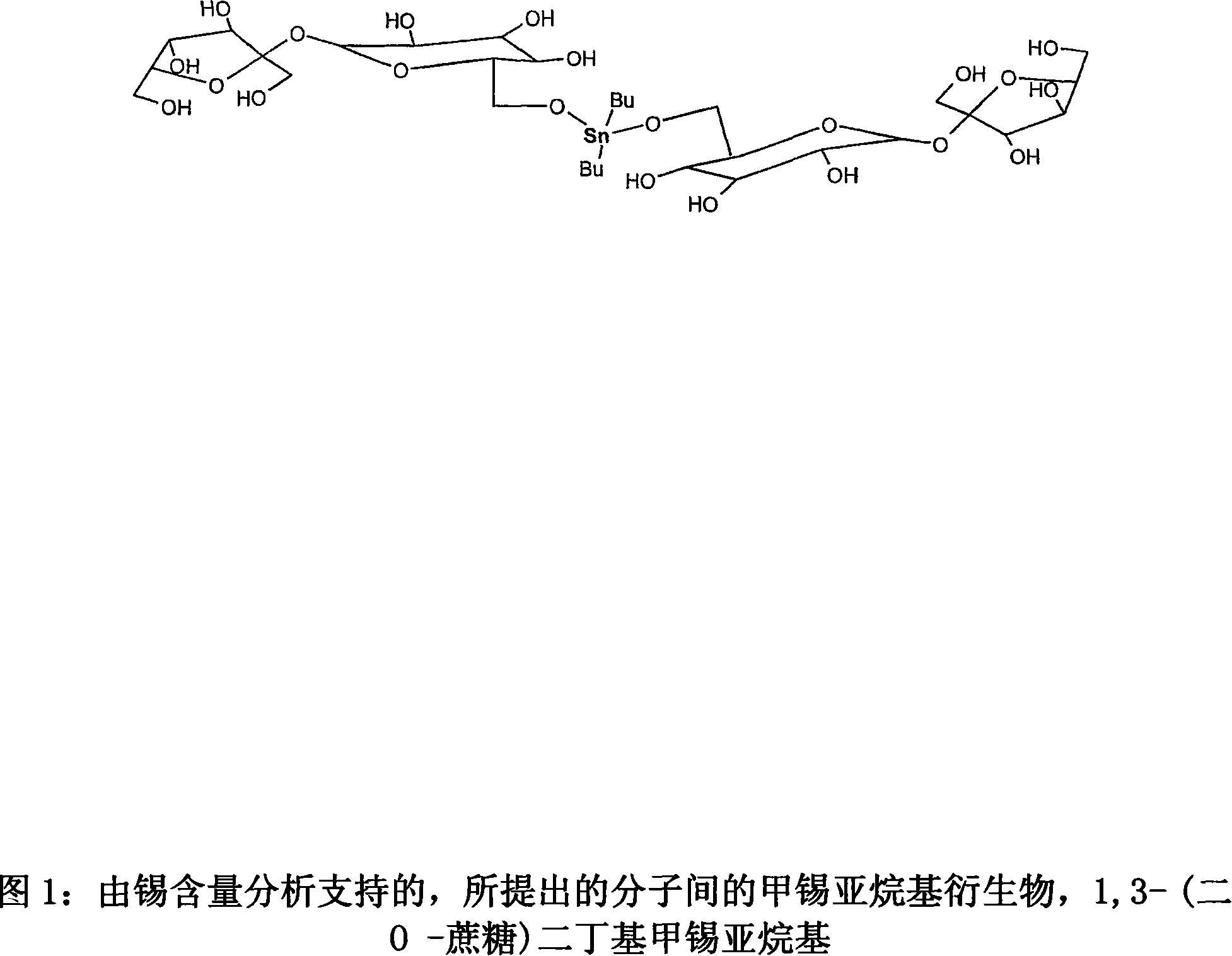
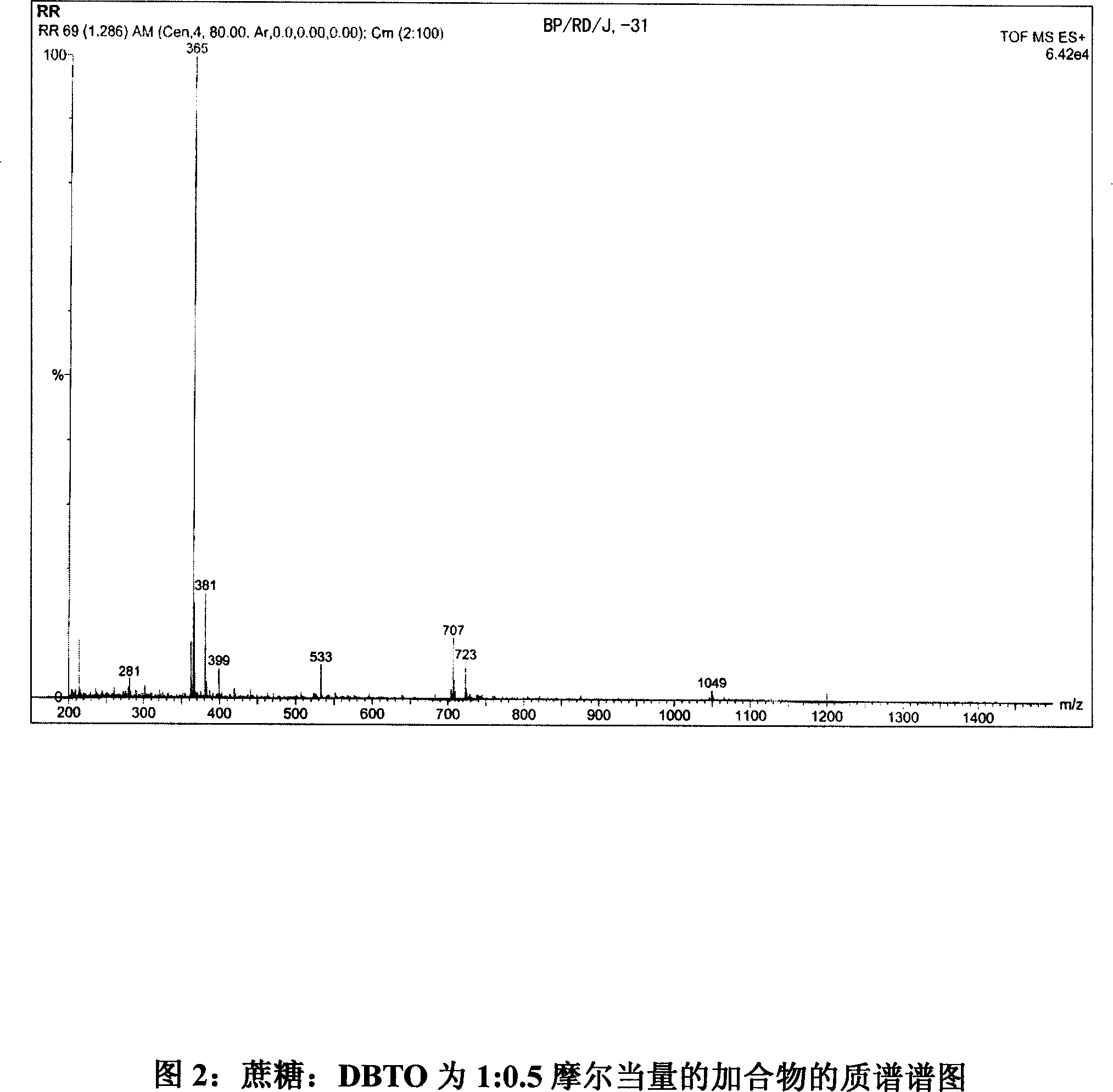
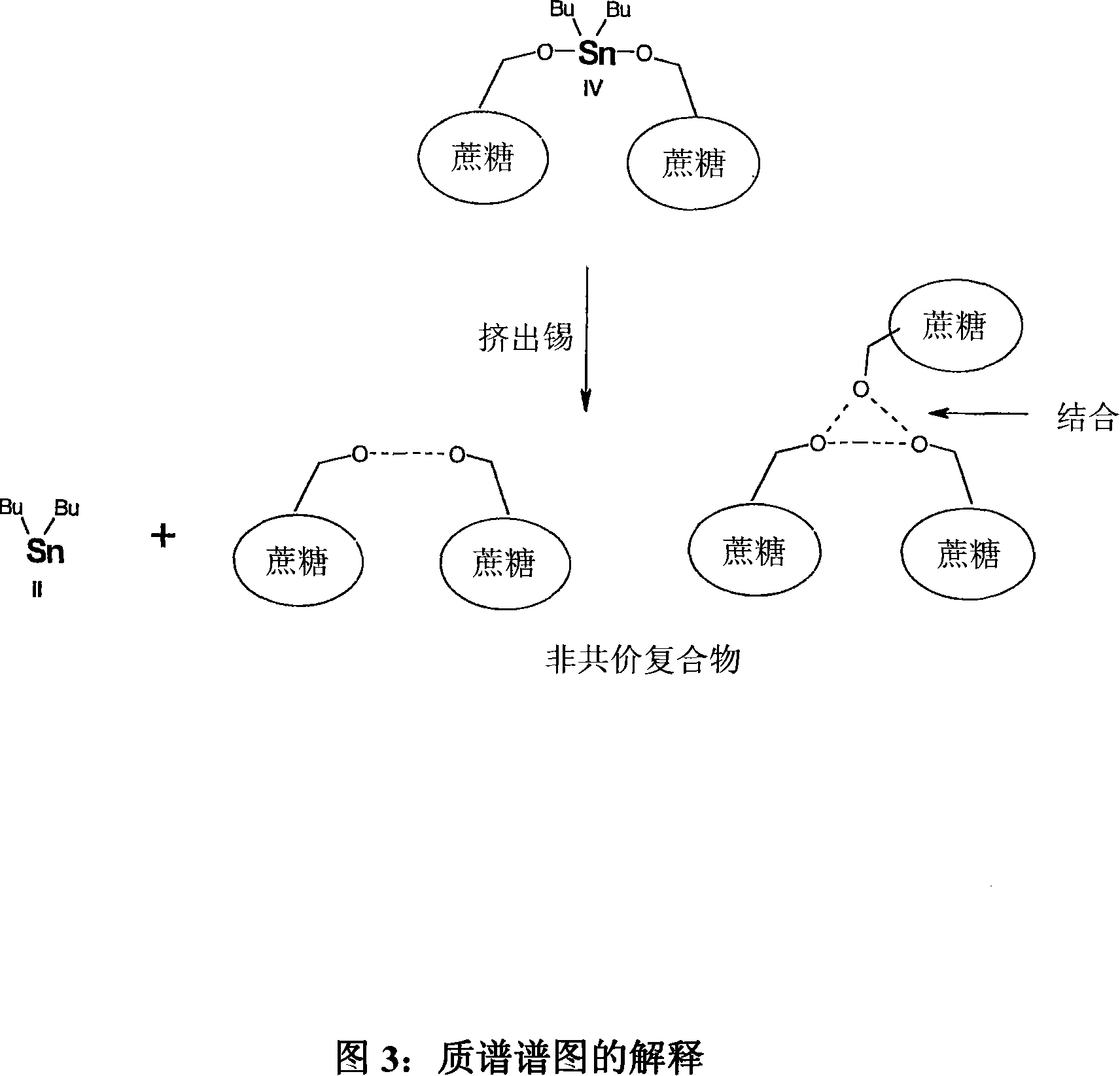
Tin mediated regioselective synthesis of sucrose-6-esters
A technology of sucrose and compounds, applied in the direction of sugar derivatives, sugar derivatives, esterified saccharides, etc., can solve problems such as separation troubles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1 Preparation of 3-(two O-sucrose) dibutylstannylidene
[0030] Sucrose (200 g) was dissolved in 600 ml of DMF, 145.6 g of DBTO was added, and heated to 80-85°C. This heating was maintained for 10-13 hours to remove the water formed during adduct formation. The reaction mass was cooled and DMF was completely removed by azeotropic distillation. The resulting thick material was treated with 1:2 volumes of dichloromethane.
[0031] The solid formed was filtered and washed with excess dichloromethane. The tin content in the obtained yellow powder was analyzed.
[0032] The same experiment was performed again in the same manner with 200 g of sucrose and 72.8 g of DBTO, and the tin content in the resulting yellow powder was analyzed.
[0033] Analyze these products.
[0034] Analytical Methods and Analysis
[0035] Tin Content Analysis: By Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
[0036] Other elemental analysis: by CHN analyzer
[0037] Molecular weight analysis: by ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Synthesis of sucrose-6-acetate
[0047] A) In situ formation of sucrose-6-acetate from 3-(diO-sucrose)dibutylstannylidene during the reaction
[0048] Sucrose (200 g) was dissolved in 600 ml of DMF, 72.8 g of DBTO was added, and heated to 80-85°C. This heating was maintained for 10-13 hours to remove the water formed during adduct formation. The reaction mass was then cooled to room temperature and cooled to 0°C. While stirring, 75 ml of acetic anhydride was added dropwise to the reaction mass. The reaction mass was then gradually warmed to room temperature and the acetylation reaction was monitored by frequent TLC analysis. After about 3-4 hours, acetate formation was complete. Then 50ml of water was added to stop the reaction. DBTO in the acetate formed was extracted twice into 1:2 v / v cyclohexane. The layers were then separated and the reaction mass was dehydrated. When the azeotropic distillation of water was complete, sucrose-6-acetate was analyz...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Conversion of sucrose to sucrose-6-benzoate using dioctyltin oxide
[0053] Sucrose (20g) was dissolved in 100ml of DMF, 10.6g of dioctyltin oxide was added, and heated to 85-90°C. This heating was maintained for 10-15 hours to remove the water formed during adduct formation. The reaction mass was then cooled to room temperature and cooled to 15°C. 19.8 g (90% purity) of benzoic anhydride was dissolved in 20 ml of DMF and added dropwise to the reaction mass with stirring. The reaction mass was then gradually warmed to room temperature and the benzoylation reaction was monitored by frequent TLC analysis. After about 10-15 hours, benzoate formation was complete. 5 ml of water were then added to terminate the reaction. Dioctyltin oxide in the benzoate formed was extracted twice into 1:2 v / v cyclohexane. The layers were then separated and the reaction mass was dehydrated. When the azeotropic distillation of water was complete, sucrose-6-benzoate was analyz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com