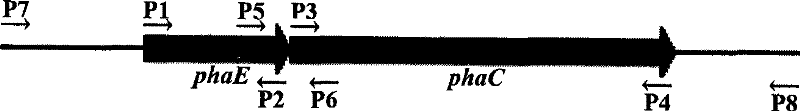Extremely halophilic archaea polyhydroxy fatty acid ester synthases and encoding gene and application
A technology of archaea polyhydroxyalkanoate and extreme halophilic archaea, which is applied to the polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase of extreme halophilic archaea and its encoding gene and application field, and can solve deletion mutants and non-highly expressed strains and other problems, to achieve the effect of increasing the production of PHA and increasing the activity of PHA synthase.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase and its coding gene (the schematic diagram of cloning strategy is as follows figure 1 shown)
[0034] 1. Two subunits of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase (PhaE Hh and PhaC Hh ) and the acquisition of its coding gene
[0035] The extreme halophilic archaea Haloarcula hispanica AS1.2049 has a very close relationship with the extreme halophilic archaea Haloarcula marismortui ATCC 43049 (GenBank number: AY596297) whose complete genome sequence has been published. According to the There is a PHA synthase subunit gene annotated as phaC in the whole genome sequence Hm , this laboratory study proved that the ORF of an unannotated gene function adjacent to its upstream encoded another subunit of PHA synthase, and named it phaE Hm . According to phaC in the extreme halophilic archaea Haloarcula marismortui ATCC 43049 Hm and phaE Hm Two pairs of primers, P1 / P2 and P3 / P4, were designed.
[0036] P1: 5′...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2, PHA synthase gene phaEC Hh and phaEC Hh The gene encoding the two subunits of phaE Hh and phaC Hh functional verification of
[0057] 1. Overexpression of the PHA synthase gene phaEC in the extreme halophilic archaea Haloarcula hispanica AS1.2049Hh , phaE Hh and phaC Hh The construction of recombinant plasmids and the construction of overexpression recombinant engineering bacteria
[0058] The following primers were designed according to the cloned sequence information of the extreme halophilic archaea Haloarcula hispanica AS1.2049:
[0059] PE1: 5′ATT GGATCC CAACTCGAAGAAGTGCAG 3′( BamHI )
[0060] PE2: 5'GGC GGTACC TTACTCTTCCAGGTGTTC 3'( KpnI )
[0061] PE3: 5'CGC CCATGG CAACTCGAAGAAGTGCAG 3′( NCOI )
[0062] PE4: 5′ATA GGATCC AATAGTACCTCGGCGGCG 3′( BamHI )
[0063] PC1: 5′CTA GGATCC ATGTCCAGCAACCCGTTT 3′( BamHI )
[0064] PC2: 5′CGT GGTACC TTACAGTTGGTCGAGCCA 3′( KpnI )
[0065] 1) Using Haloarcula hispanica AS1.2049 gen...
Embodiment 3
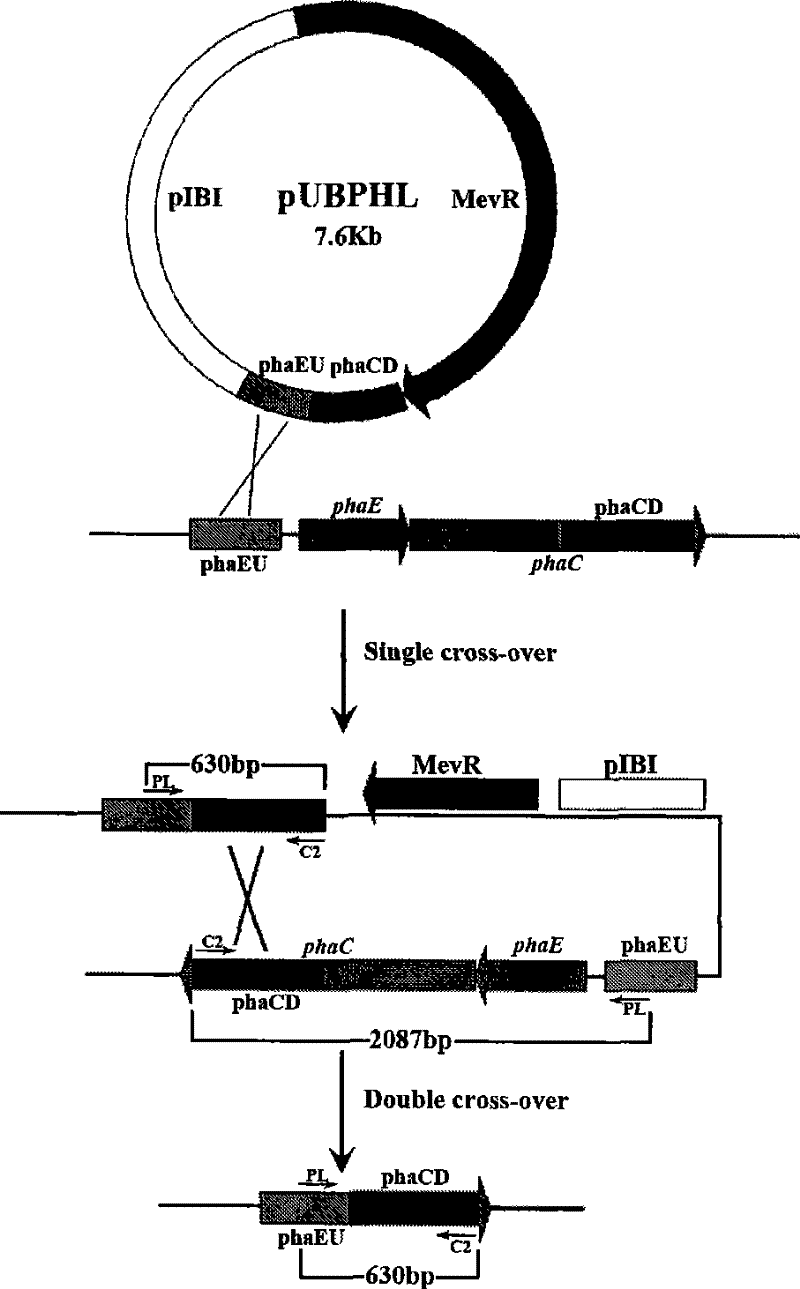
[0072] Example 3, PHA synthase gene deletion mutant strain Haloarcula hispanica PHB - 1 construction and its functional verification
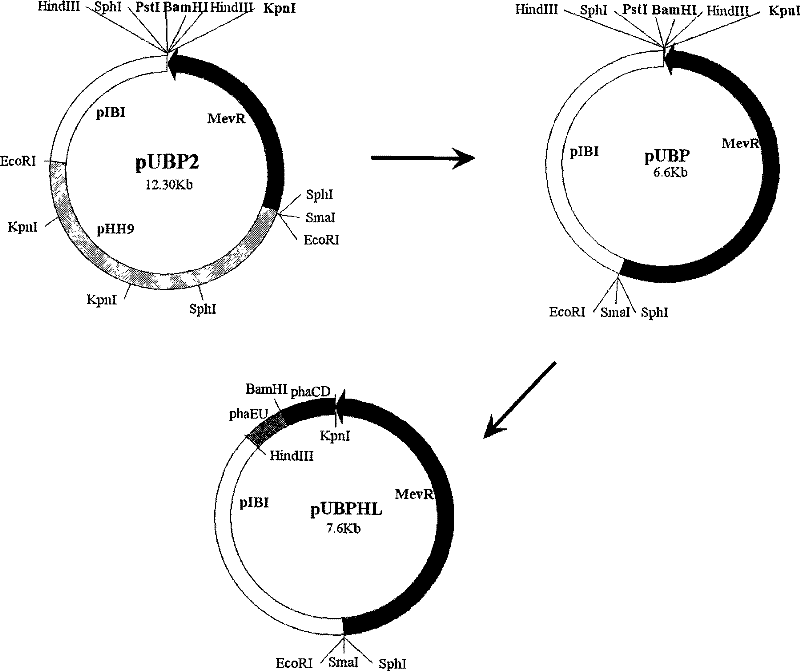
[0073] 1. Destruction of phaEC Hh Construction of the homologous recombination integration plasmid pUBPHL
[0074] The construction process of pUBPHL is as follows figure 2 As shown, the specific implementation is as follows:
[0075] 1) Construction of departure plasmid pUBP
[0076]pUBP2 is a shuttle plasmid for extreme halophilic archaea and Escherichia coli (see the literature Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA87: 6772-6 for pUBP2 sequence information and construction method). First, pUBP2 was digested with EcoRI to remove the replicon pHH9 of the halophilic archaea in pUBP2 to obtain a 6.6 kb linear fragment, and then the 6.6 kb linear fragment was self-ligated to form plasmid pUBP, which was used to construct the integration vector pUBPHL.
[0077] 2) Used to destroy phaEC Hh Amplification of the homologous recombination double crossover a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com