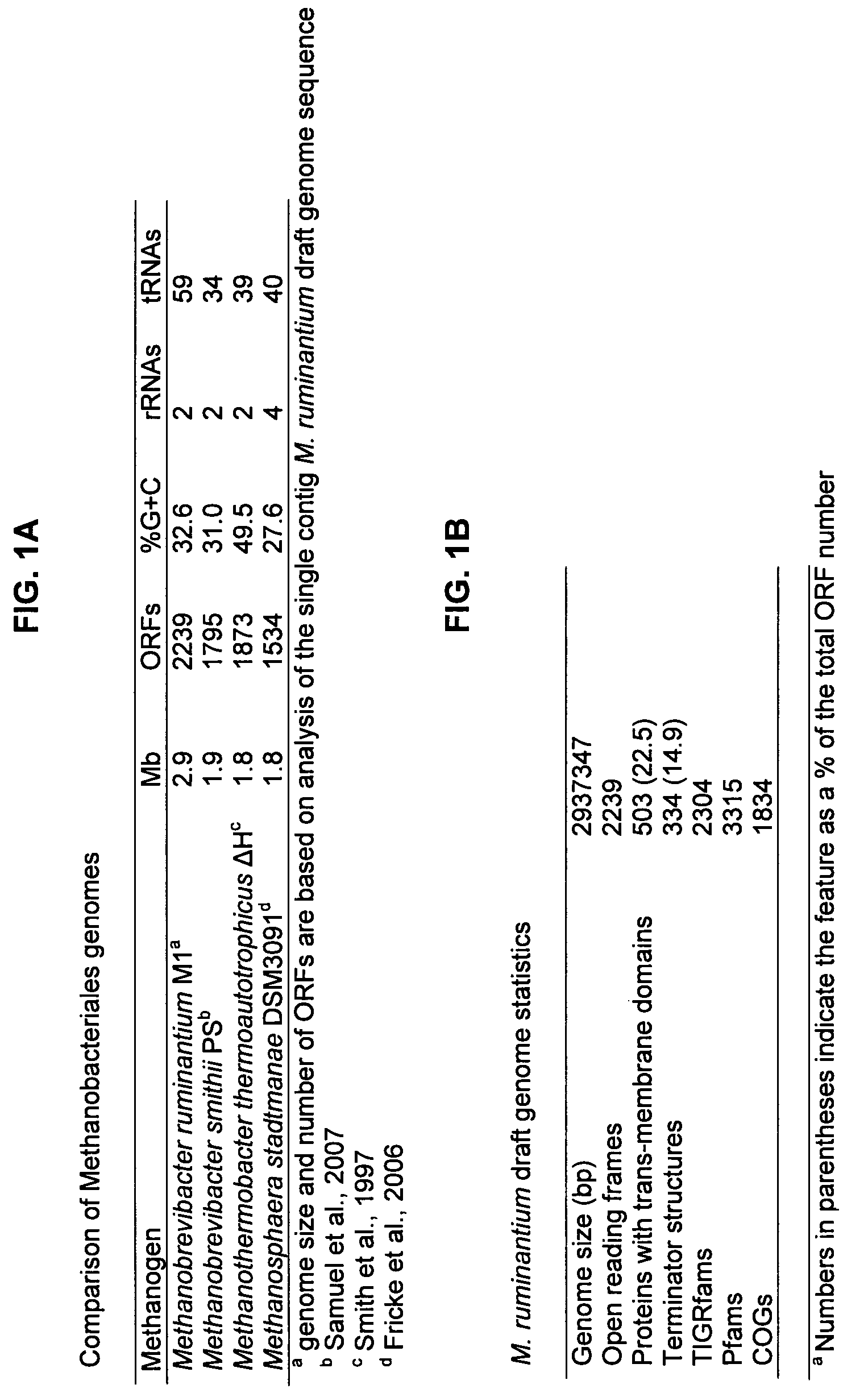
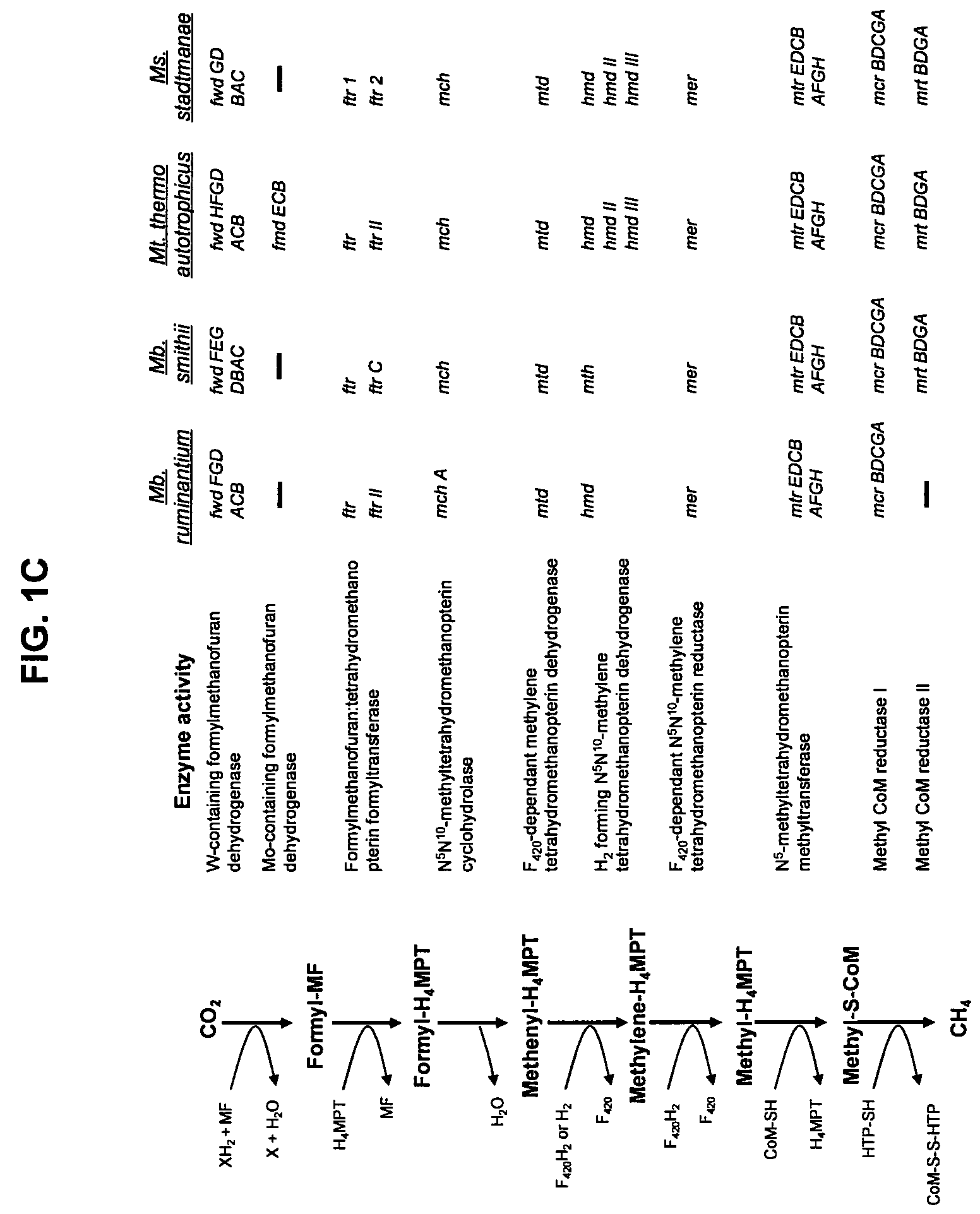
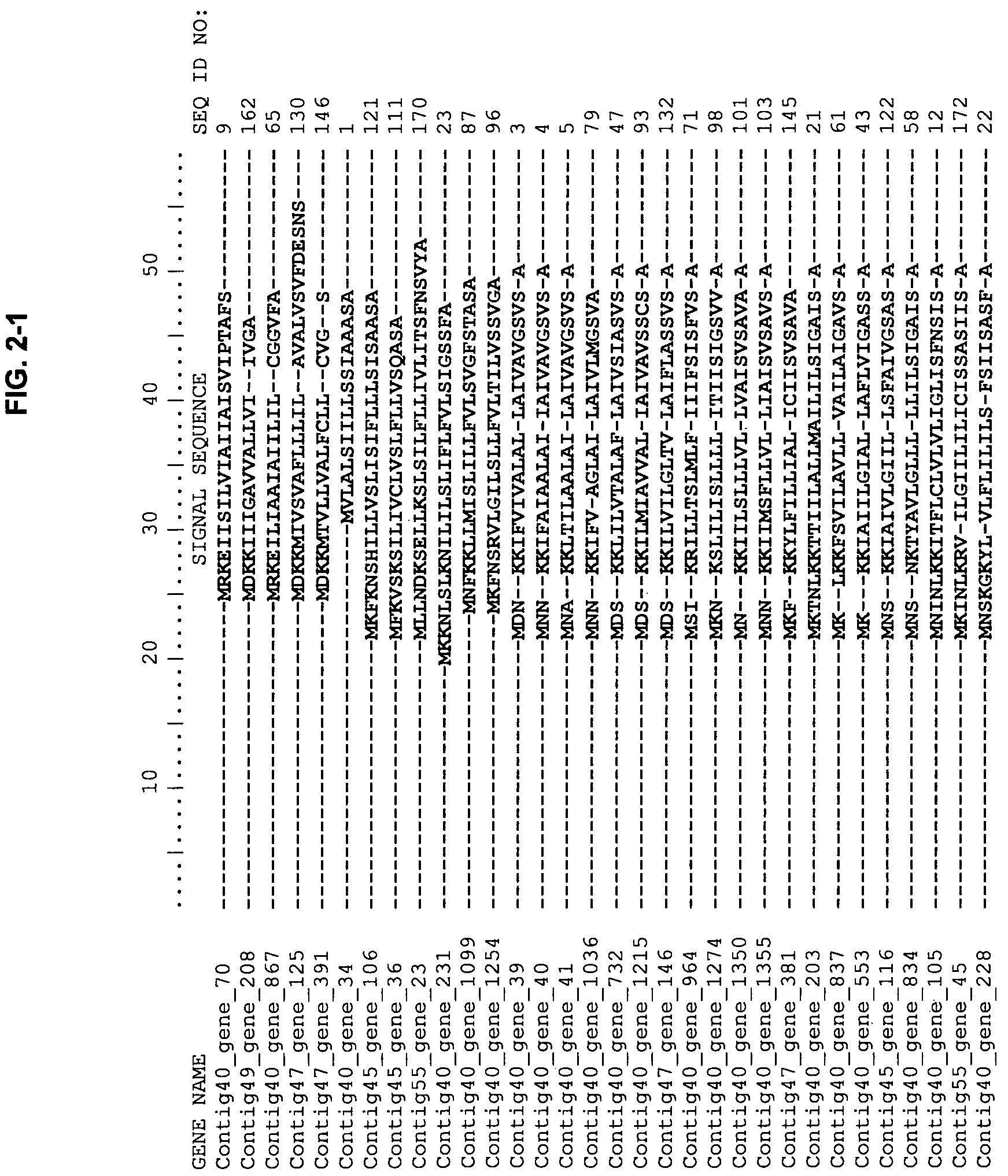
Patents
Literature
80 results about "Archaeal Viruses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Viruses whose hosts are in the domain ARCHAEA.
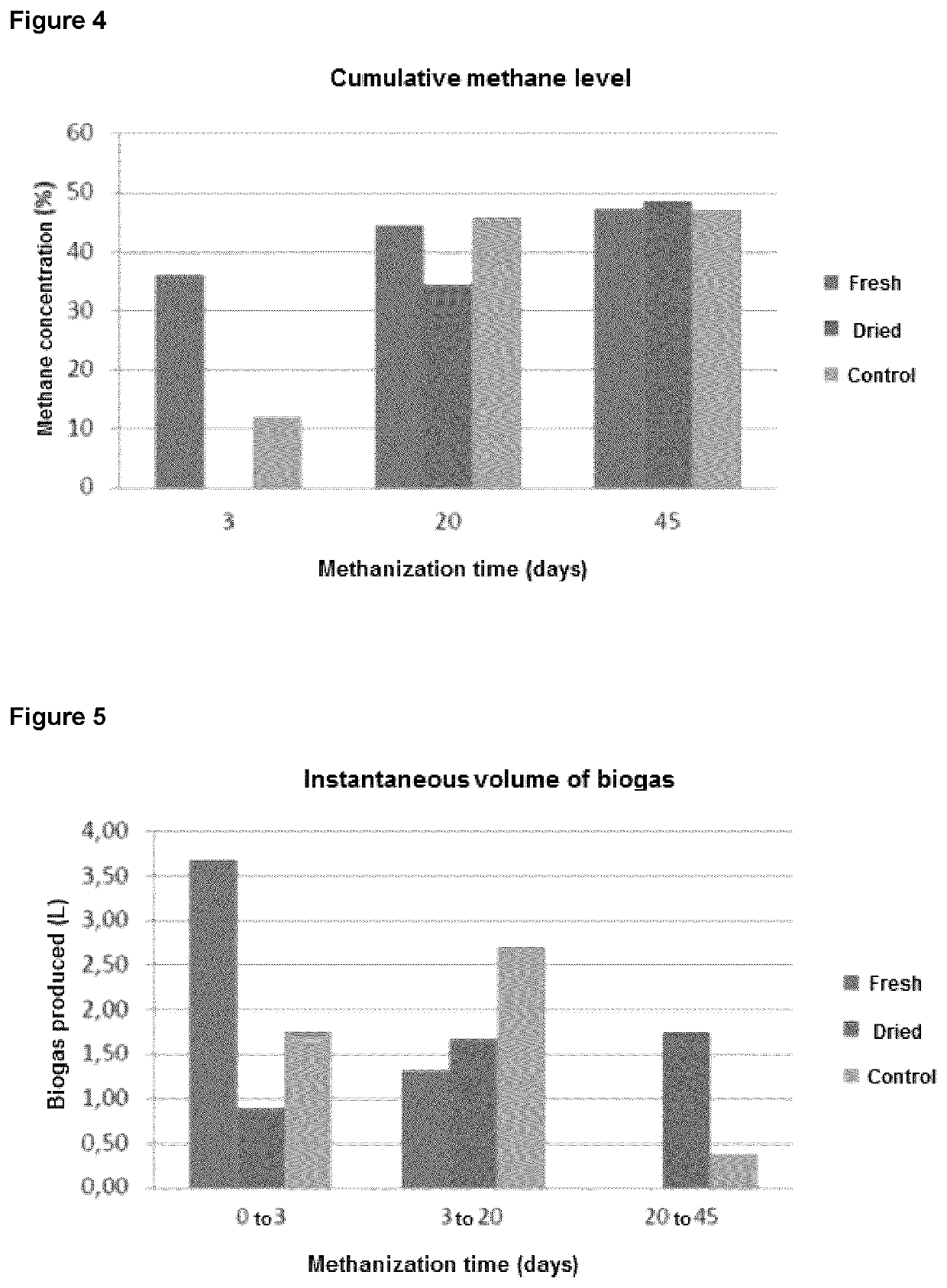
Preparation method of methane dry fermentation compound bacterial preparation
InactiveCN102559499AReduce volumeLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCellulose
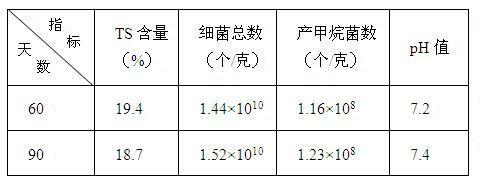
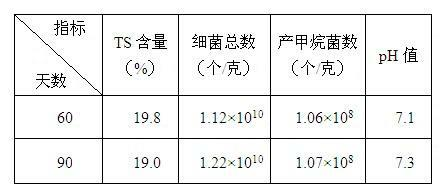
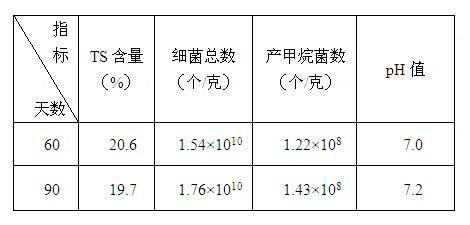
The invention discloses a preparation method of a methane dry fermentation compound bacterial preparation, which comprises the following steps: mixing fermentation substrate with an inoculum which is compound bacteria composed of cellulose decomposing bacteria, proteolytic bacteria, fat decomposing bacteria, hydrogen-producing aceogenic bacteria, sulfate reducing bacteria and methanogenic archaea, adjusting the water content and pH of the mixed materials to 70-80% and 7.0 respectively, performing anaerobic fermentation under the condition of 35 DEG C plus or minus 2 DEG C for 60-90 days to obtain methane dry fermentation compound bacterial preparation. The preparation method of the invention can prepare compound bacterial preparation with a relatively complete methane fermentation function, and the total number of microbial cells and methanogenic archaea cells in the bacterial preparation are at least 10*10<10> / g and 1.0*10<8> / g respectively. Using the compound bacterial preparation as an inoculum of methane dry fermentation can reduce the starting time, and the fermentation process is stable and easy to control.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
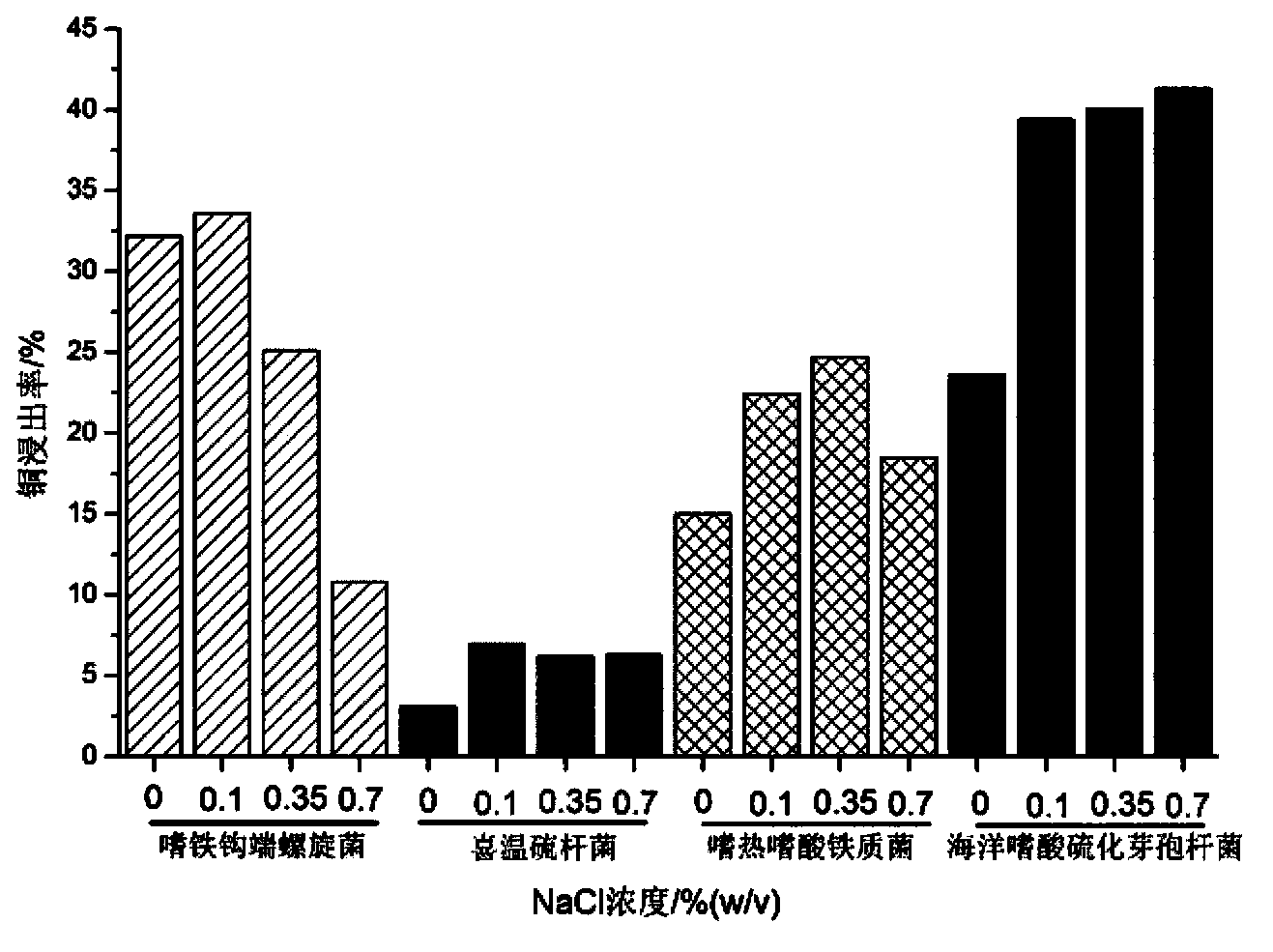
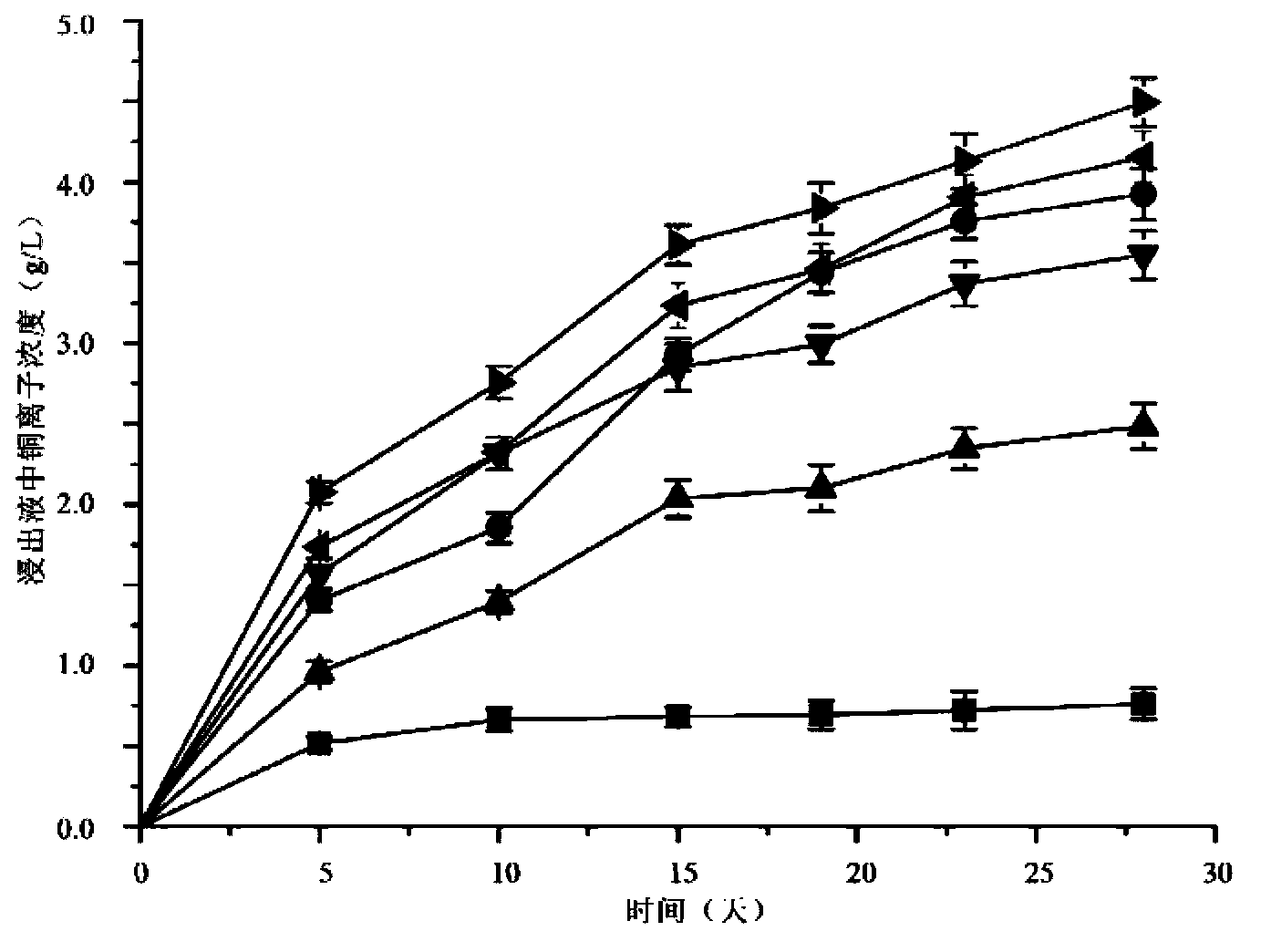
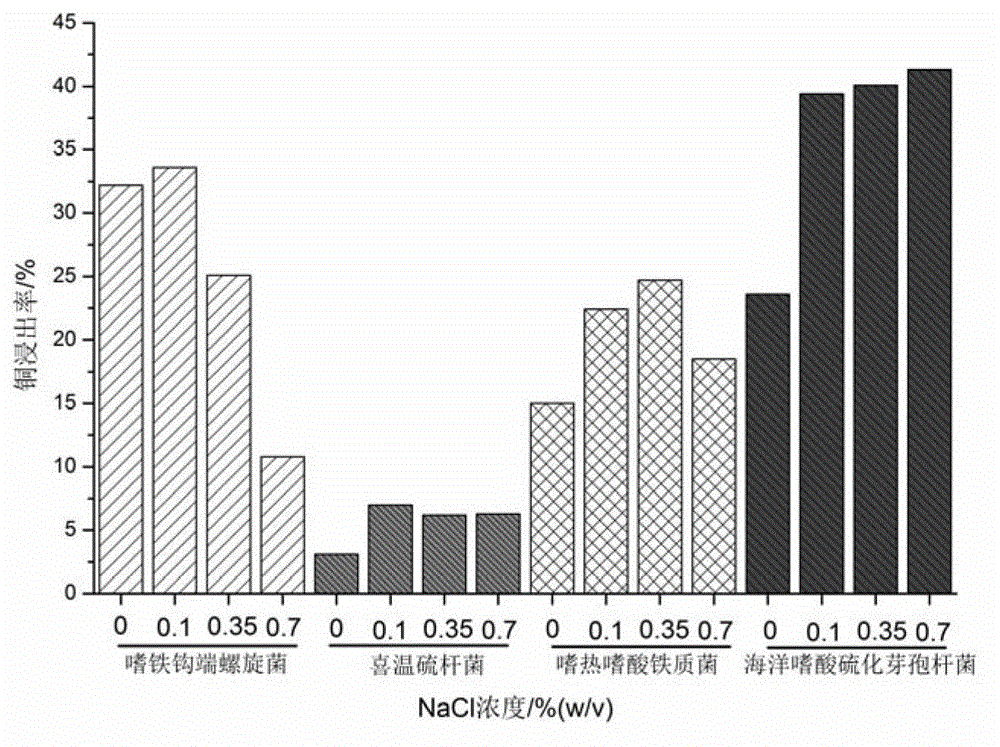
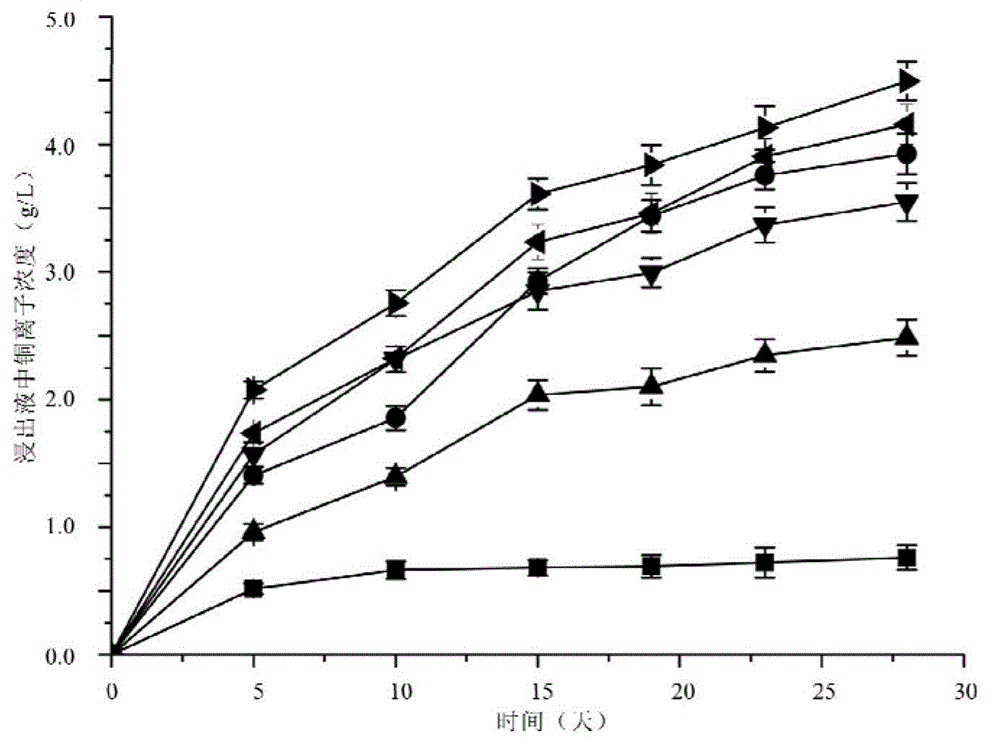
Compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching sulphide ore, and compounding method and application method thereof
ActiveCN103396964AIncrease resistanceImprove leaching efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical reactionEngineering
The invention discloses a compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching a sulphide ore, and a compounding method and an application method thereof, and belongs to the technical filed of wet-process metallurgy. Aiming at a biological leaching mechanism of the sulphide ore and the physiological-biochemical characteristics of microorganisms, a community capable of efficiently leaching the sulphide ore is compounded by a plurality of mineral leaching microorganisms, wherein the mineral leaching microorganisms comprise marine bacteria which come from deep-sea hydrothermal vents and are capable of enduring high concentration sodium chloride, sulfur-oxidized bacteria, iron-oxidized bacteria and archaea which are from a freshwater environment, autotrophic bacteria and facultative heterotrophic bacteria. Not only can the difficult problem that the mineral leaching microorganisms from the freshwater environment are intolerance of sodium chloride be solved, but also microorganisms required by oxidation and dissolution of the sulphide ore and diversity of chemical reactions are guaranteed. The compound bacterium community can obviously increase leaching efficiency and leaching rate of the sulphide ore such as copper pyrites and can be applied in a leaching process and a dump leaching process of a stirring tank. A certain basis for popularization and application of biological metallurgy of the sulphide ore is provided by the invention.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
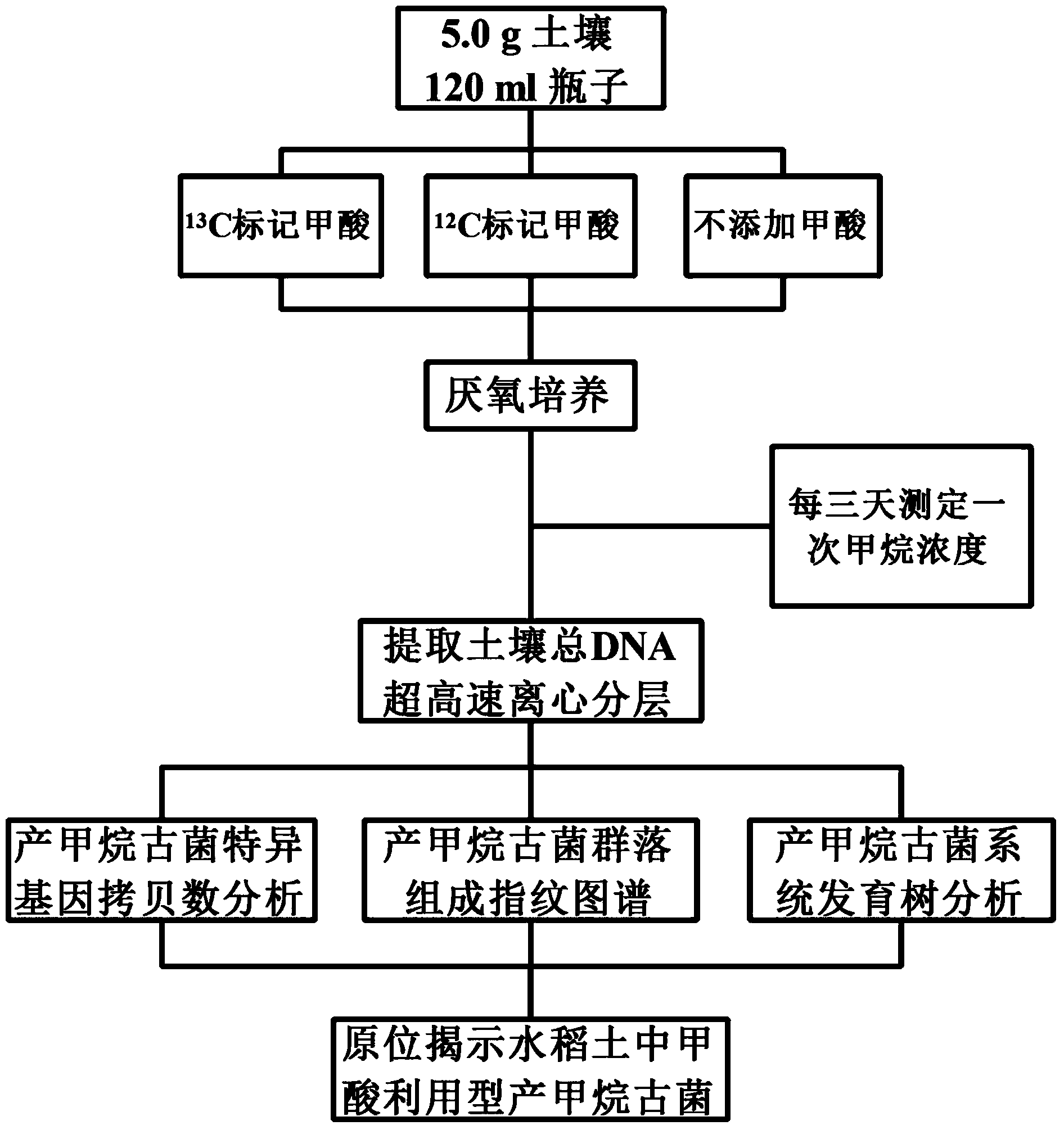
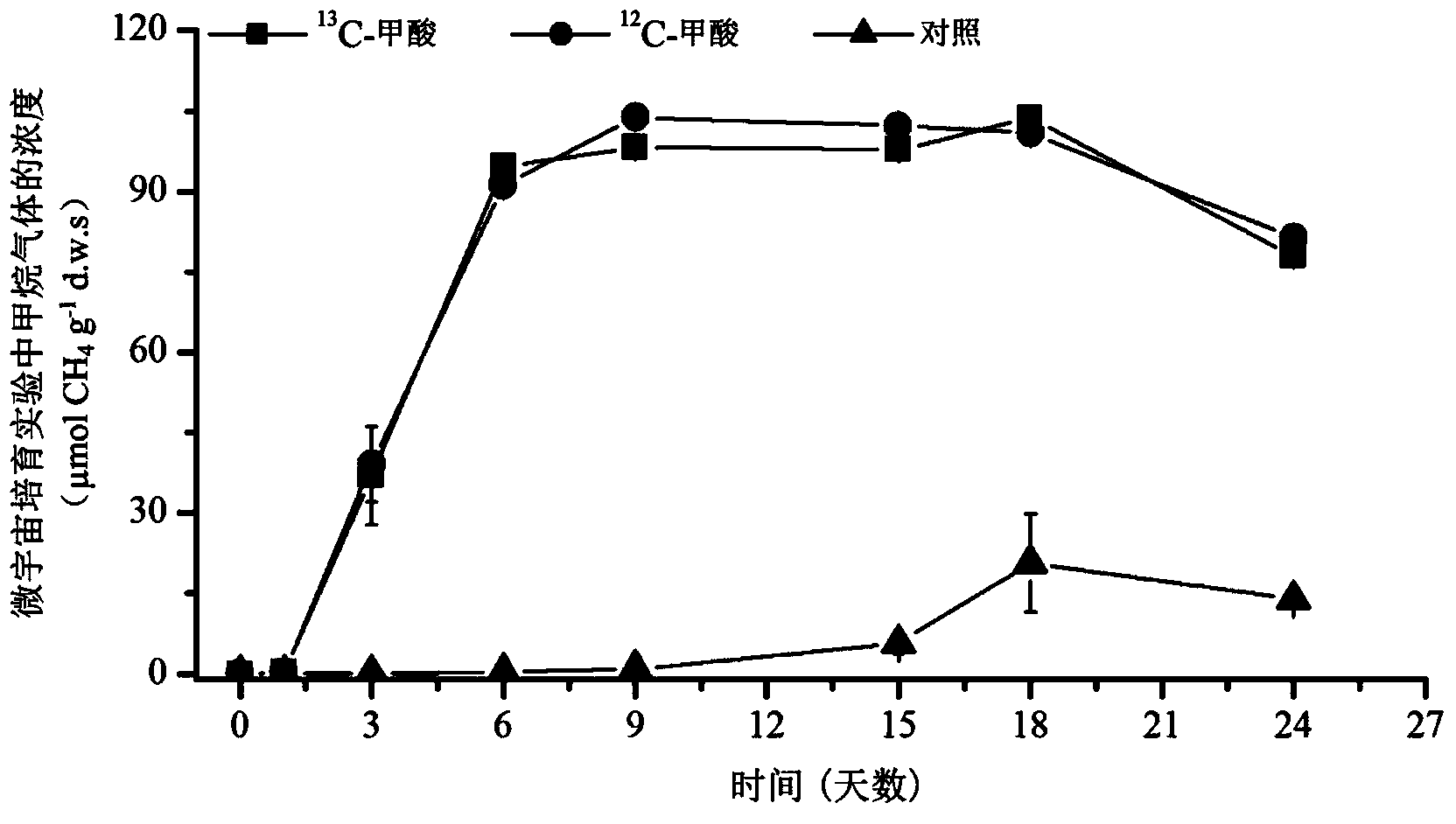
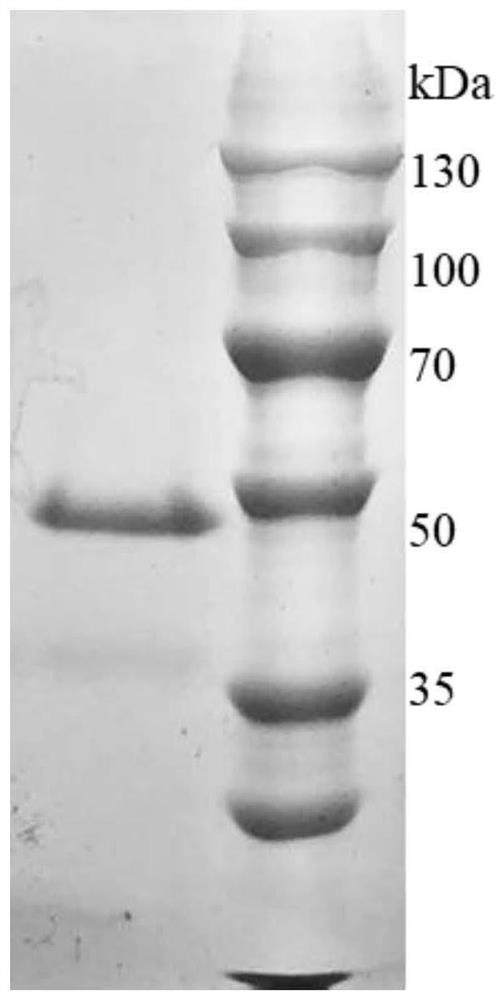
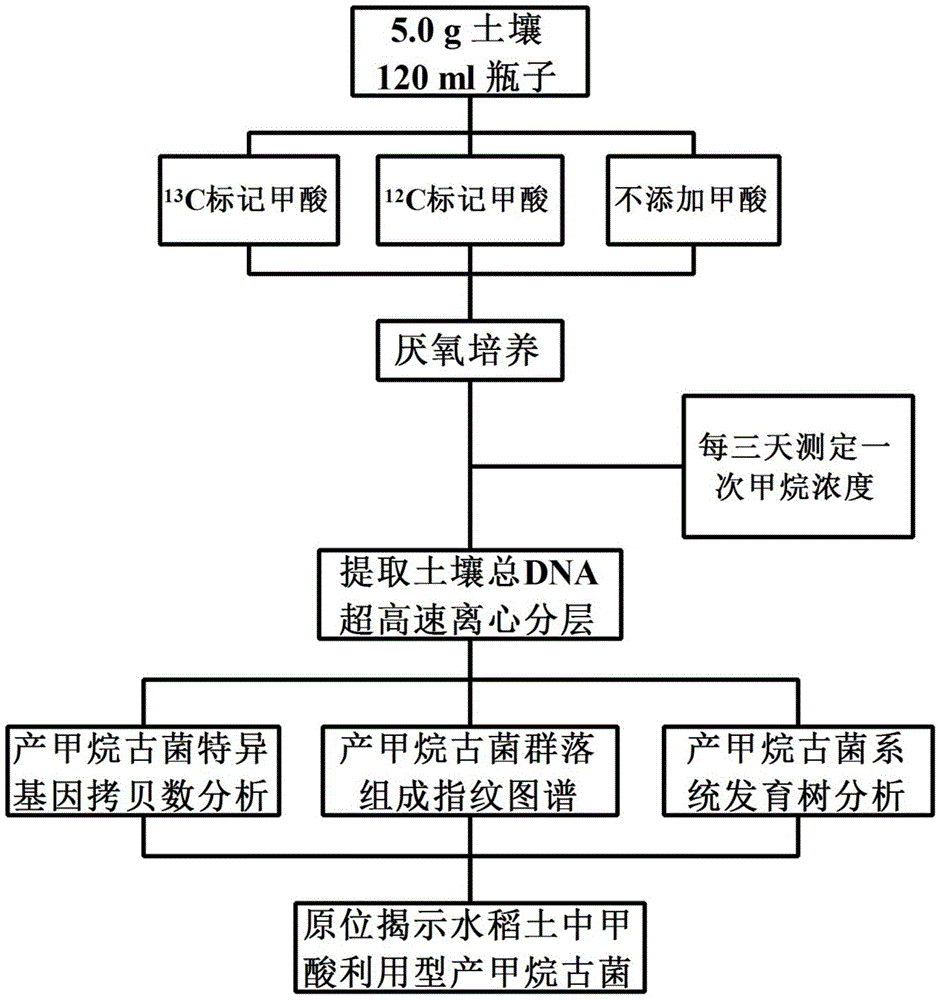
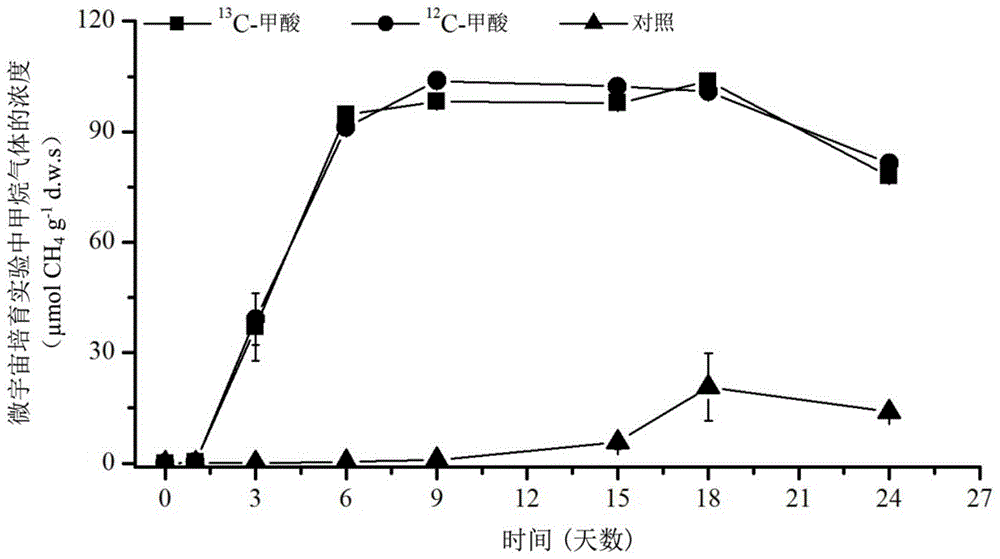
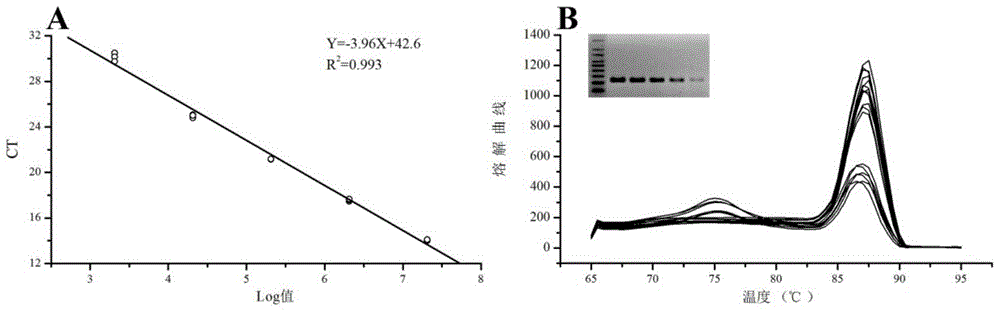
Method for revealing and distinguishing paddy field formic acid utilization type methanogenic archaea in situ by adopting DNA-based stable isotope probing technology
A method for revealing and distinguishing paddy field formic acid utilization type methanogenic archaea in situ by adopting DNA-based stable isotope probing technology comprises the followings steps: (1), collecting a paddy soil sample; (2), performing a micro universe cultivation experiment of <13>C-formic acid; (3), performing centrifugation layering on the microbe total DNA of <13>C-formic acid cultivation soil by using an ultracentrifuge; (4), performing real-time quantitative PCR analysis and finger-print analysis on methanogenic archaea genes in layers of multiple buoyant densities after layering to judge whether the paddy soil contains the formic acid utilization type methanogenic archaea with metabolic activity. Therefore, the method can be used for keenly revealing the paddy field formic acid utilization type methanogenic archaea in situ based on the DNA-based stable isotope probing technology, and has great significance on the understanding of the paddy field nutrient cycling process driven by microbes and the cognition of the ecological functions of paddy field methanogenic archaea functional groups.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound halophilous-microorganism bacterium agent and application thereof
InactiveCN105062936AEfficient and stable degradationStrong resistance to salinity impactFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyHalophilic microorganisms
The invention discloses a compound halophilous-microorganism bacterium agent and an application thereof. Halophilous microorganisms are the microorganisms which are not inhibited or poisoned by high-concentration inorganic salts in the high-salt environment, can carry out normal growth and metabolism and comprise salt-resistant microorganisms and halophilic microorganisms. The compound halophilous-microorganism bacterium agent at least comprises two of halophilic bacteria, halophilic archaea, salt-resistant bacteria, salt-resistant archaea, halophilic fungi and salt-resistant fungi, wherein the types and the quantity of the halophilous microorganisms are at least 10, and the halophilous microorganisms at least comprise one type of uncultured microorganisms. The compound halophilous-microorganism bacterium agent disclosed by the invention has the advantages that high-efficiency and stable degradation can be carried out on organic matters under the condition of 1%-20% salt; by using the compound halophilous-microorganism bacterium agent for biochemical treatment of high-salt waste water and microorganism restoration of saline-alkaline soil, the pollution treatment cost can be reduced.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Extreme halophilic archaea engineering bacteria for producing bioplastics PHBV by effectively utilizing carbon source
ActiveCN103451201AIncrease concentrationSolve stickyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHaloferax mediterraneiProtein C
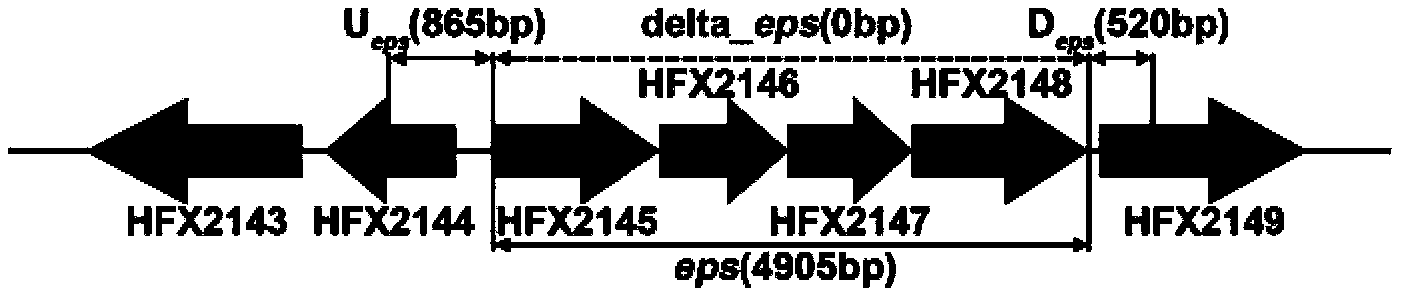
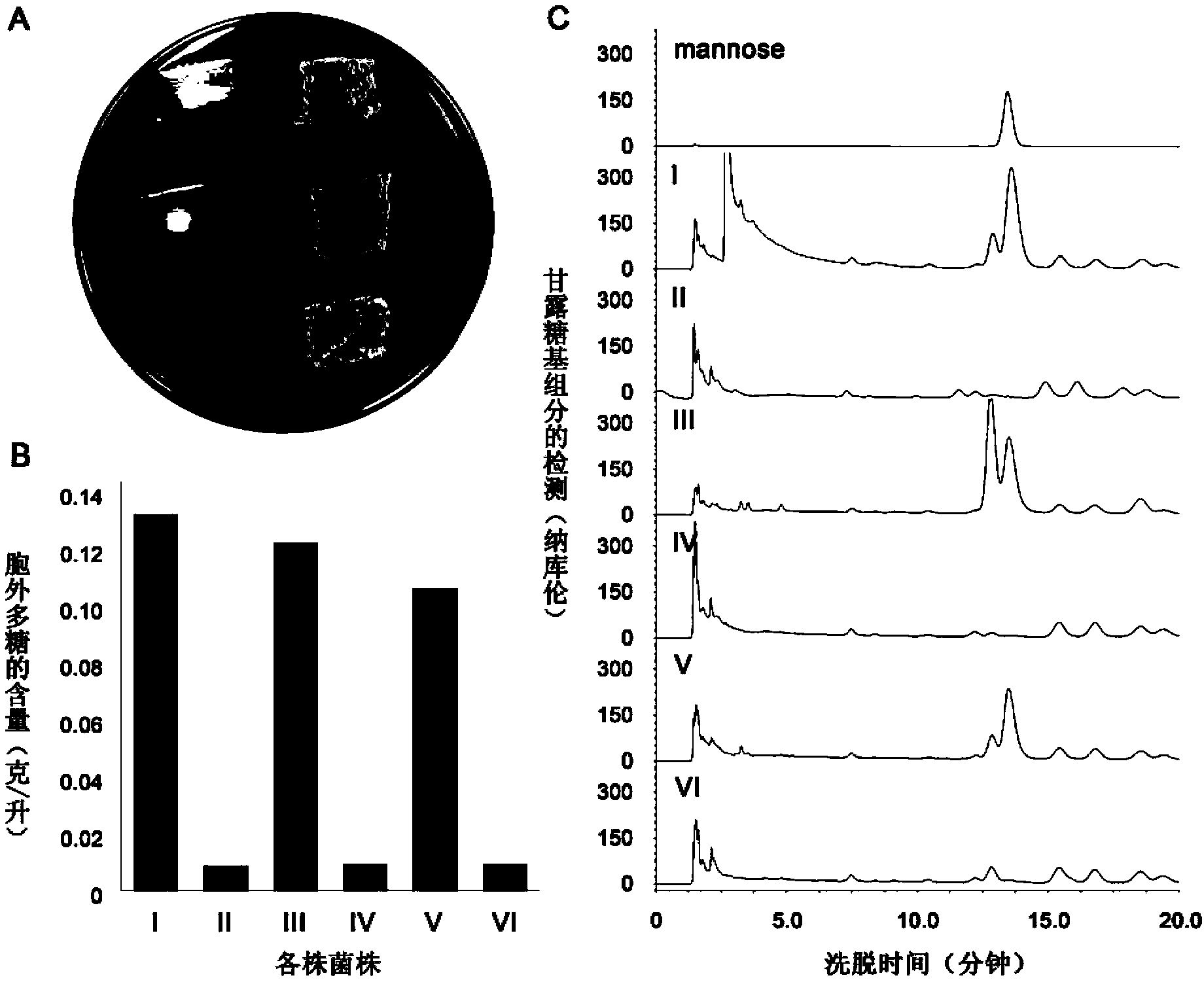
The invention discloses extreme halophilic archaea engineering bacteria for producing bioplastics PHBV (Poly-(HydroxyButyrate-co-Hydroxy Valerate)) by effectively utilizing a carbon source. The recombined extreme halophilic archaea is extracellular polysaccharide synthesis function-deficient engineering bacteria obtained by deleting at least one protein function expressed by an extracellular polysaccharide synthesis cluster in the genome of the extreme halophilic archaea Haloferax mediterranei. The extreme halophilic archaea has the advantages that infectious microbe is not easy to pollute, PHA (Poly Hydroxy Alkanoate) is convenient to extract, the PHBV from a non-correlated carbon source can be synthesized, and the like, and is considered as a highly preponderant PHBV producing strain. The extracellular polysaccharide synthesis function-deficient strain engineering bacteria are characterized in that the polyhydroxyalkanoate can be produced from various carbon sources such as glucose, starch and whey more efficiently in contrast with a wild type strain, the concentration of the PHBV is 20% higher than that of the wild type strain under the same fermentation conditions, and the problems such as sticking, lots of bubbles and dissolved oxygen reduction of a culture solution caused by extracellular polysaccharide accumulation are also solved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ammonia-oxidizing archaea flora cultivating method and application thereof in aerobic composting
InactiveCN103409335AAmmonia nitrogen oxidation rate increasedIncrease the number ofBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyActivated sludge
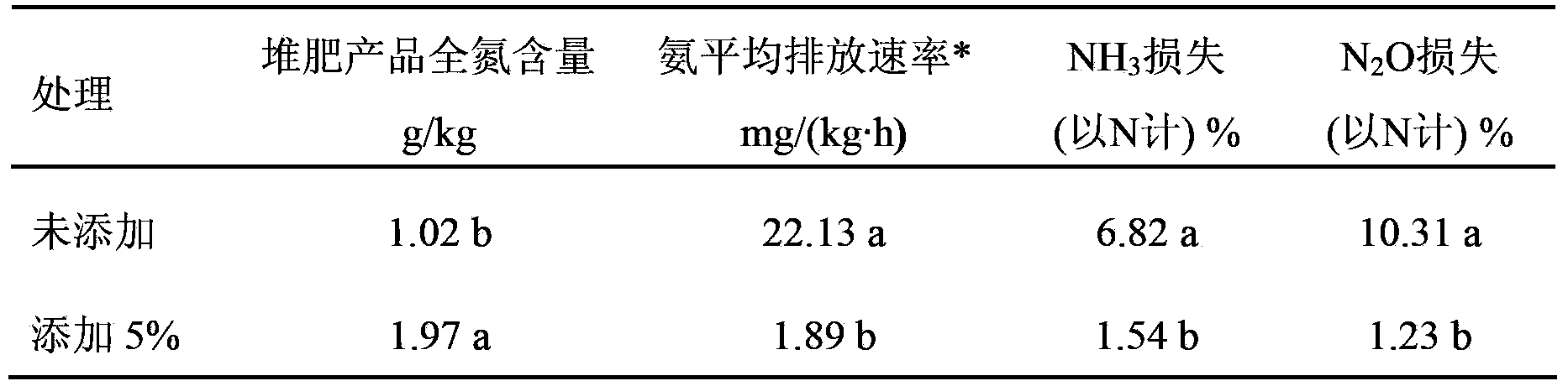
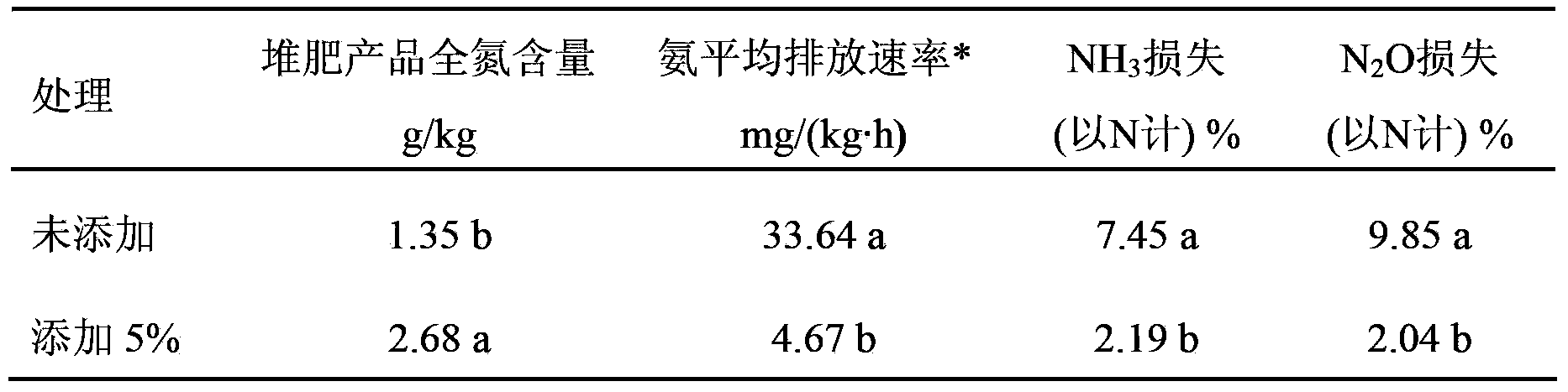
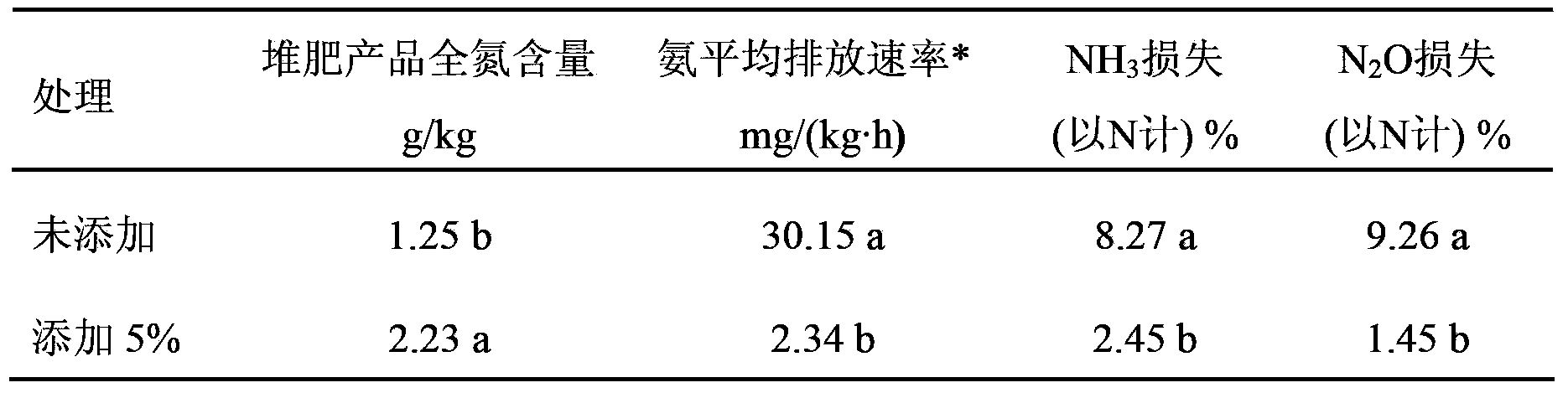
The invention relates to an ammonia-oxidizing archaea flora cultivating method and application thereof in aerobic composting. The cultivating method comprises the following steps of: the first step, collecting sludge containing an ammonia-oxidizing archaea flora and preparing an activated sludge solution; the second step, performing enrichment culture in a substituting culture way, thereby obtaining a first-generation culture solution; the third step, under the conditions that the pH is 6.5, the rotation speed is 140 rpm / min and the constant temperature is 30 DEG C, performing shake cultivation on the first-generation culture solution, finishing the first-generation culture when the quantity is increased by an magnitude order, and then carrying out substitution; the four step, performing enrichment culture on the first-generation culture solution which is subjected to shake cultivation previously, thereby obtaining a second-generation culture solution; the fifth step, continuously repeating the shake cultivation to the fifth to eighth generation, thereby obtaining 800 mL of enriched ammonia-oxidizing archaea flora. The cultivating method is capable of remarkably increasing the quantity of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea, promoting the progress of a digestion reaction, reducing the emission of N2O and reducing the loss of nitrogen.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Rapid and effective cellar mud archaea community analysis method
InactiveCN102912025AEfficient removalQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyA-DNA
The invention relates to an analysis method of a cellar mud archaea community, in particular to an analysis method of a highly flavored type white wine cellar mud archaea community and the characteristic of diversity. The method comprises the following specific steps of: (1) weighing a certain quantity of cellar mud, and adding a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) and an aluminum sulfate solution for pretreatment; (2) adding a DNA extraction buffer solution, lysozyme, achromopeptidase and other multienzyme systems for cell wall disruption; (3) adding chloroform-phenol for extraction and impurity removal; (4) adding isopropanol to precipitate to obtain sample genome DNA; and (5) carrying out nested PCR-DGGE (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) analysis by using the archaea genome DNA as a template. The PBS buffer system is provided for cellar mud microorganisms before DNA extraction, and added aluminum sulfate can efficiently remove humus; achromopeptidase capable of effectively cracking archaea cell walls is pertinently added, and the purposes of increasing the quality and the purity of the genome DNA are achieved; and true and reliable wine cellar archaea community diversity information is obtained by combining the nested PCR-DGGE fingerprint spectrum technology, and an accurate and rapid analysis means for accurately analyzing the transition rule of the highly flavored type white wine cellar mud archaea community along with the age of the cellar.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Cell-permeabilising peptides and polypeptides for microbial cells
Owner:PASTORAL GREENHOUSE GAS RES LTD
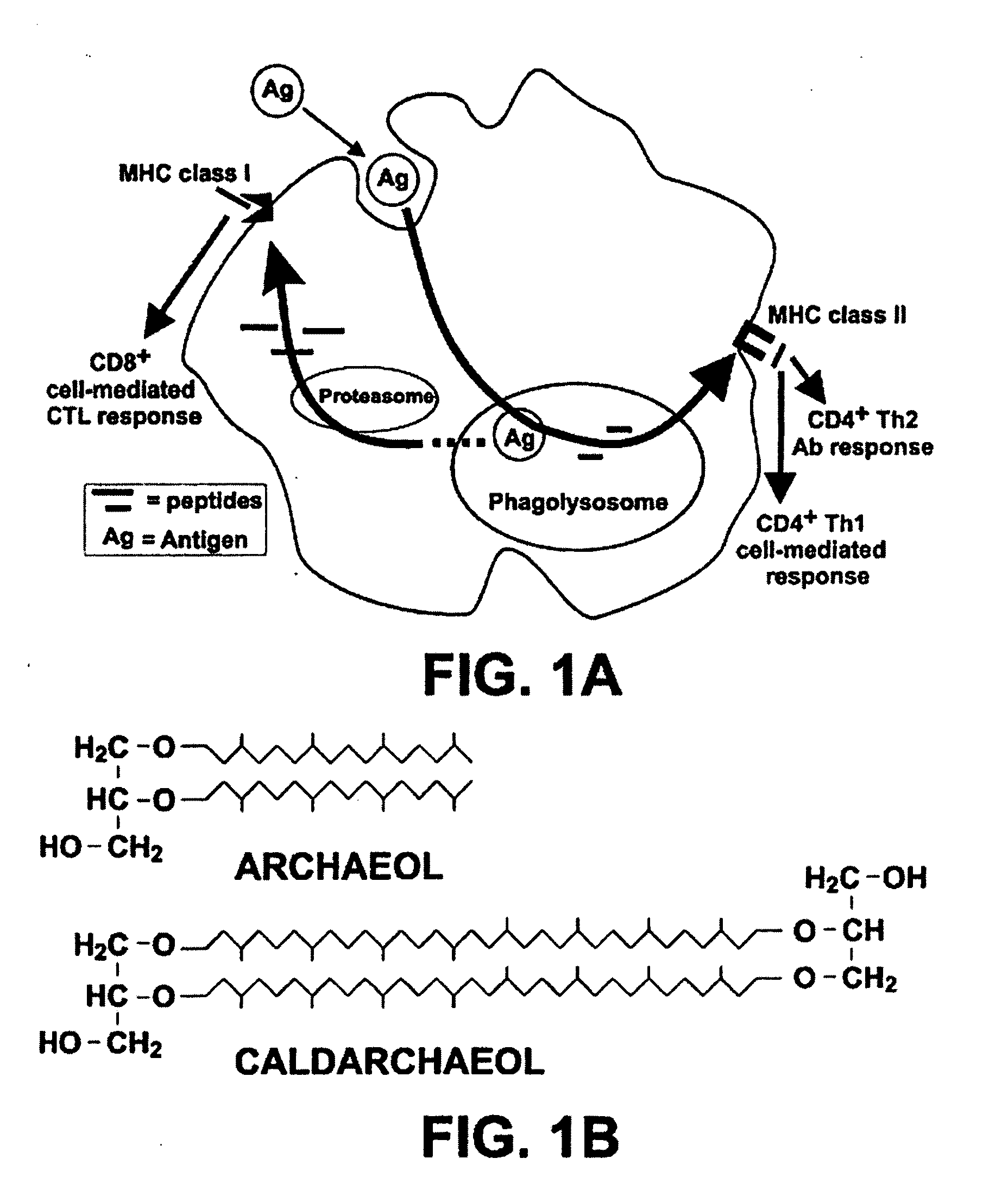
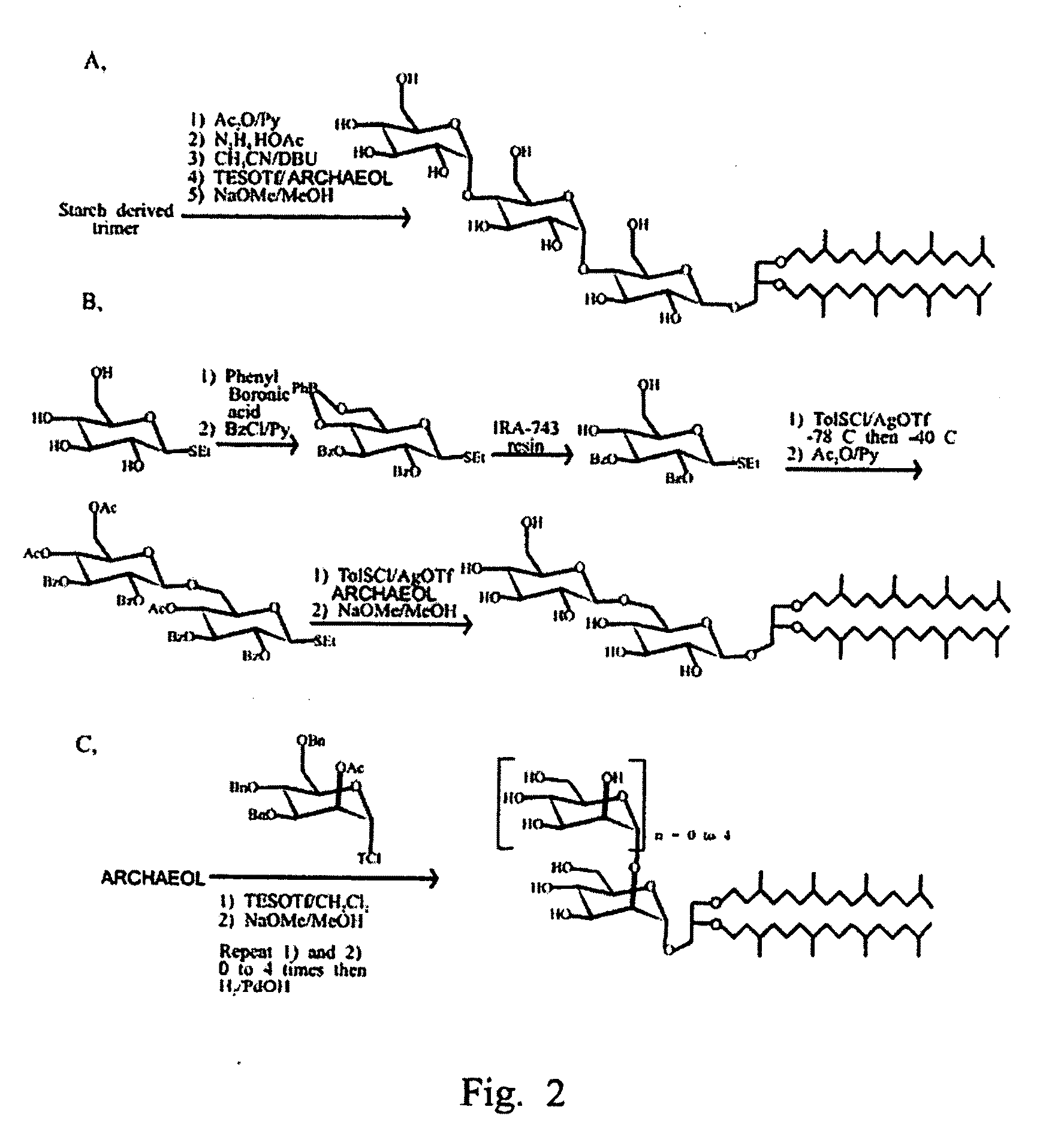
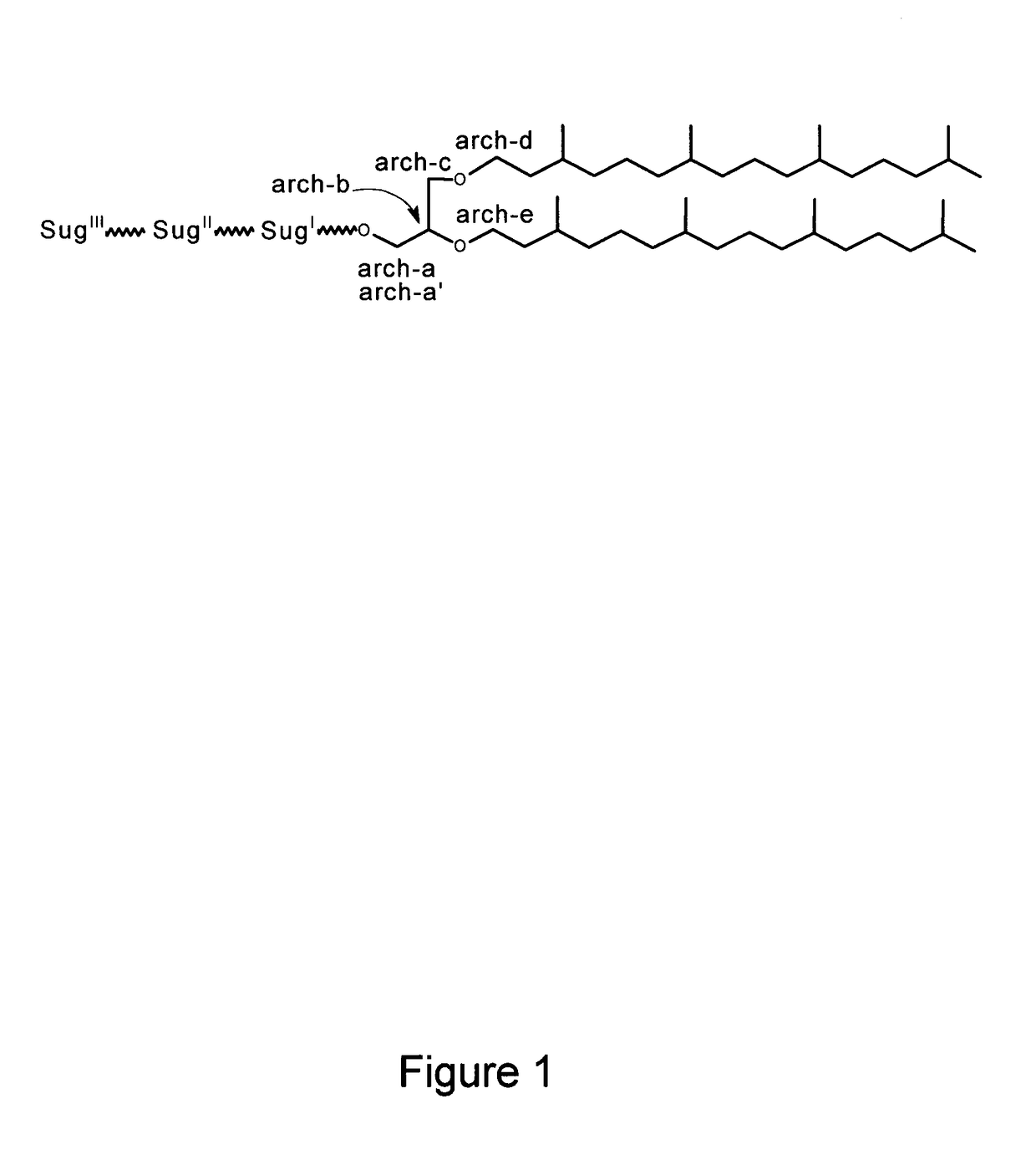
Synthetic Archaeal Glycolipid Adjuvants
Archaeal lipid adjuvants are synthesized by chemically coupling various carbohydrates or anionic polar groups to the free hydroxyl(s) of archaeal lipid cores. Chemically stable lipid cores such as saturated archaeol and caldarchaeol are obtained from appropriate Archaea. Archaeosome lipid vesicles are formulated from the synthetic lipids selected to serve as antigen carriers that target antigen-presenting cells and promote an appropriate immune response to the antigen.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
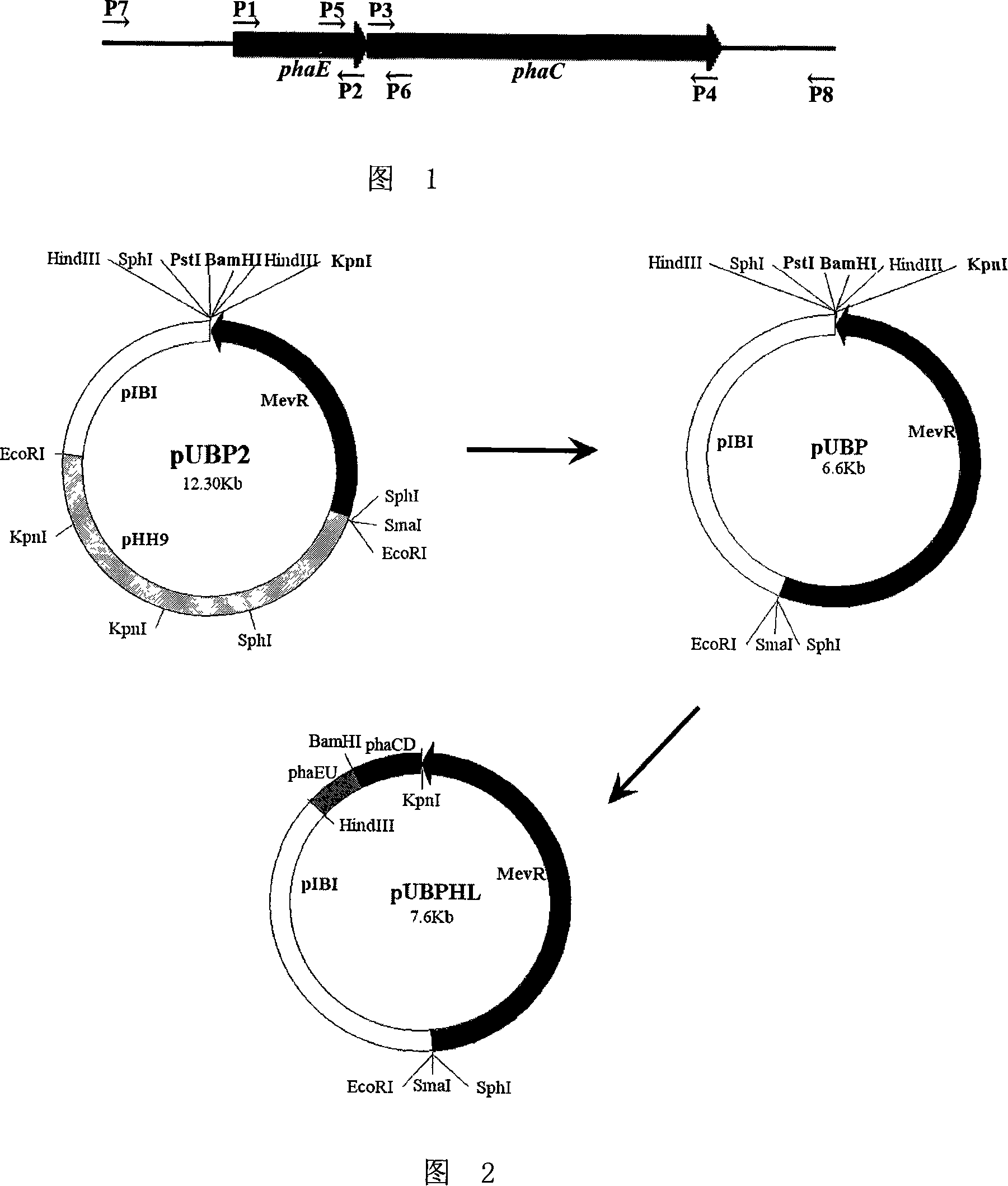
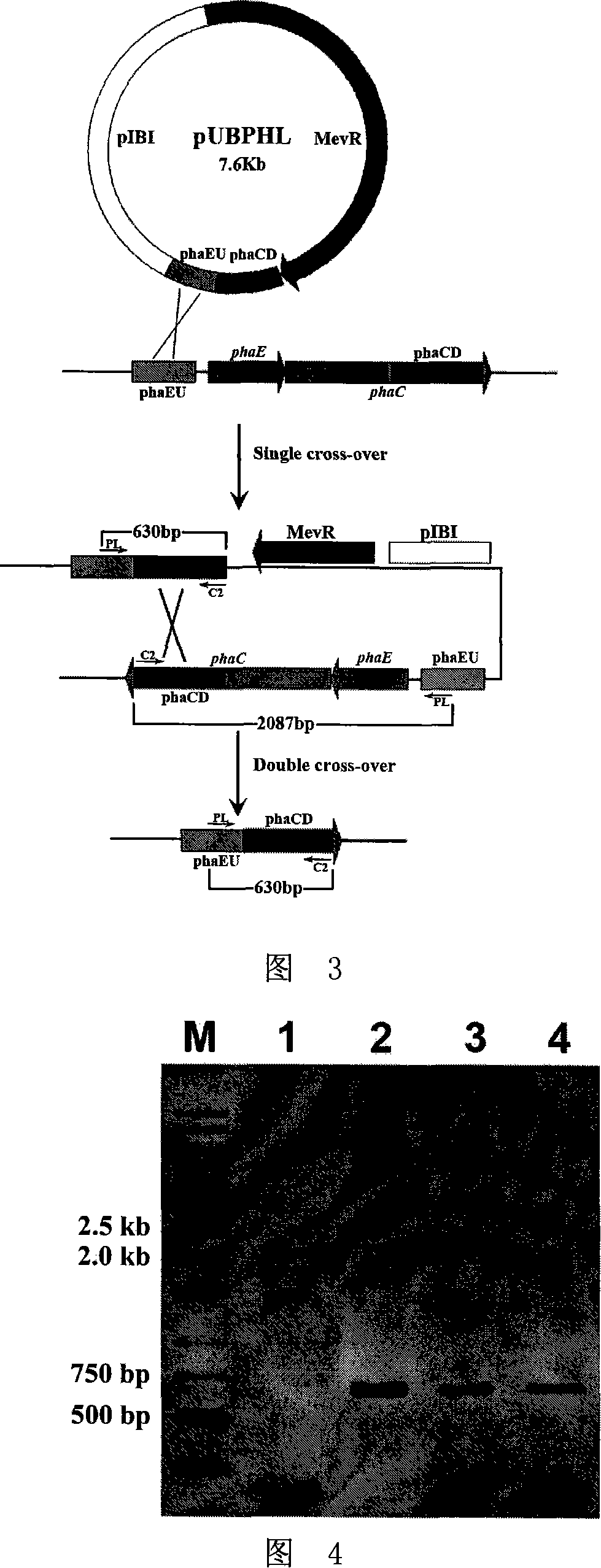
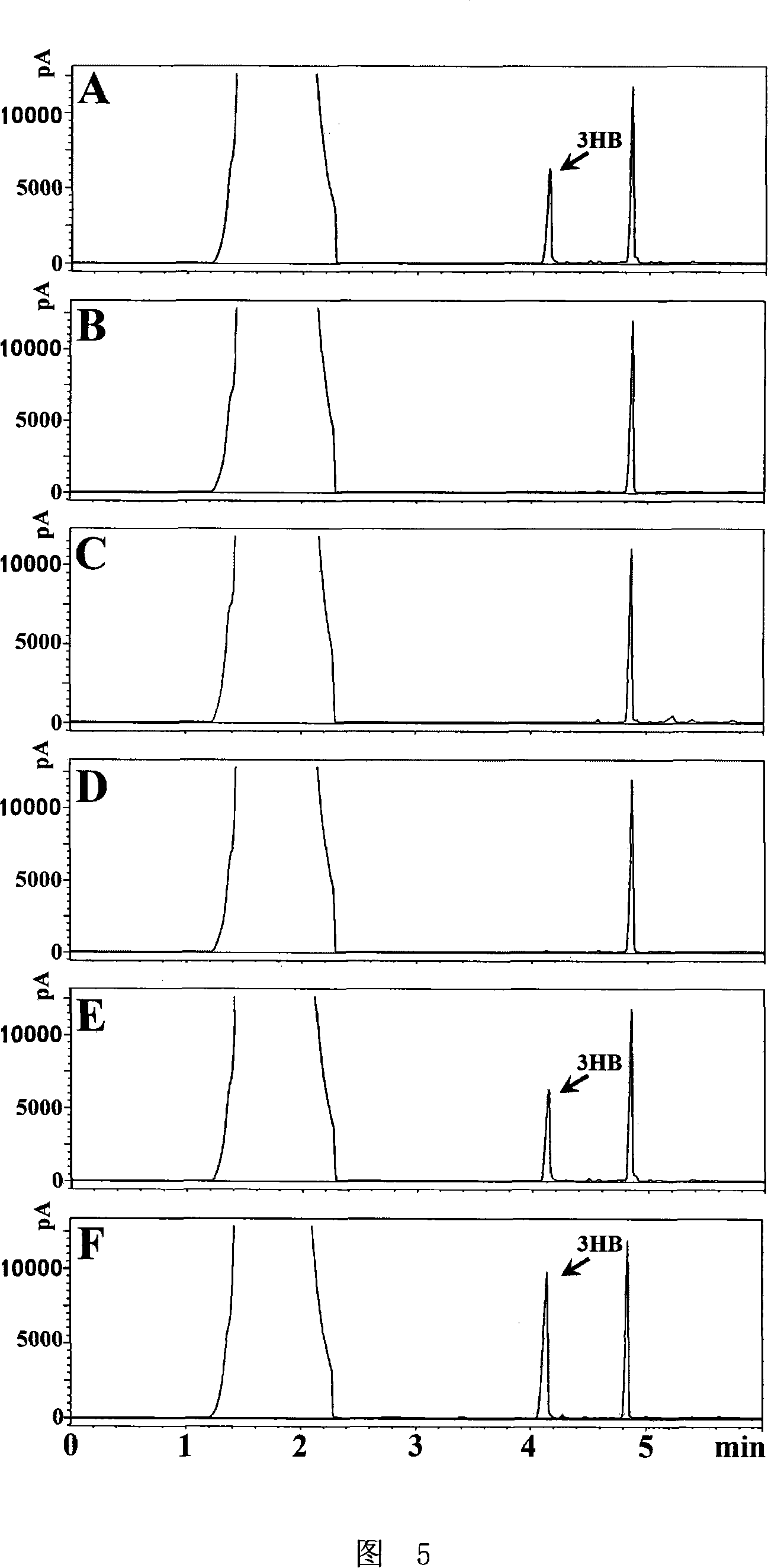
Extremely halophilic archaea polyhydroxy fatty acid ester synthases and encoding gene and application
InactiveCN101139575AHigh PHA synthase activityIncreased PHA synthase activityBacteriaEnzymesEnzyme GenePHA synthase
The invention discloses an extremely halophilic archaea polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme and the code gene and application of the enzyme. The polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme comprises PhaEHh subunit and PhaCHh subunit; the PhaEHh subunit has amino acid residue sequence in sequence 1 in the sequence table or amino acid residue sequence got by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residue for the amino acid residue sequence in sequence 1 in the sequence table; the PhaCHh subunit has amino acid residue sequence in sequence 2 in the sequence table or amino acid residue sequence got by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residue for the amino acid residue sequence in sequence 2 in the sequence table. The polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme is of very high PHA enzyme activity; introducing the polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme gene phaECHh into a host bacterial strain will make possible high-efficient expression of PHA enzyme, and can improve the activity of the extremely halophilic archaea polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme and PHA output.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
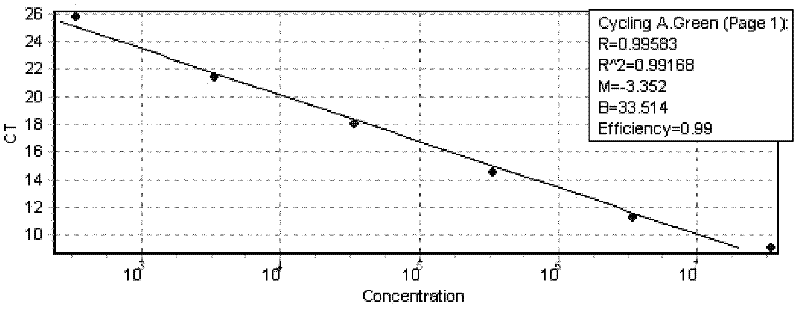
Method for quantifying ammonia oxidizing archaea in lacustrine deposit
InactiveCN102230009ARapid research methodSimple research methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNitrogen cycleLacustrine deposits
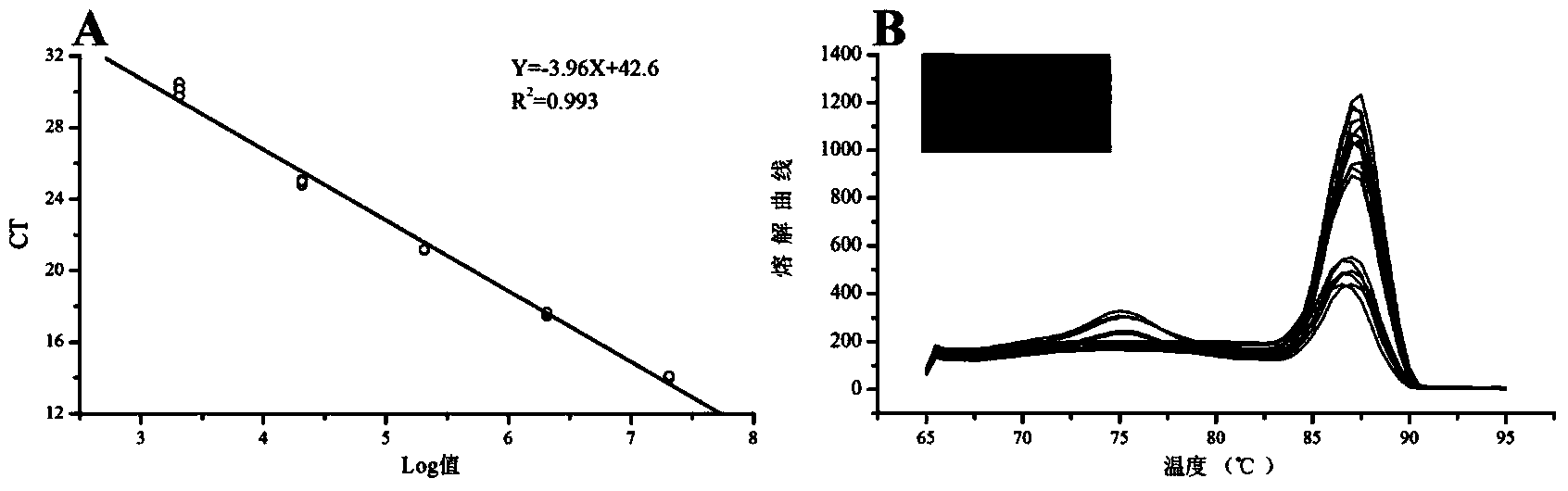
A method for quantifying ammonia oxidizing archaea in lacustrine deposit. The method comprises the following steps of (1) extracting DNA, and (2) constructing an ammonia oxidizing archaea plasmid standard substance and analyzing a sample, wherein the copy number of Ammonia oxidizing archaea in an unknown sample is obtained through processes of a detection of a Ct value of the unknown sample and a contrast of an amplification standard curve and the Ct value after the amplification standard curve is obtained. In the invention, ammonia oxidizing archaea in lacustrine deposit is detected quantificationally through a real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology. The method is a rapid, simple and accurate method for researching a nitrogen cycle mechanism of lacustrine deposit.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
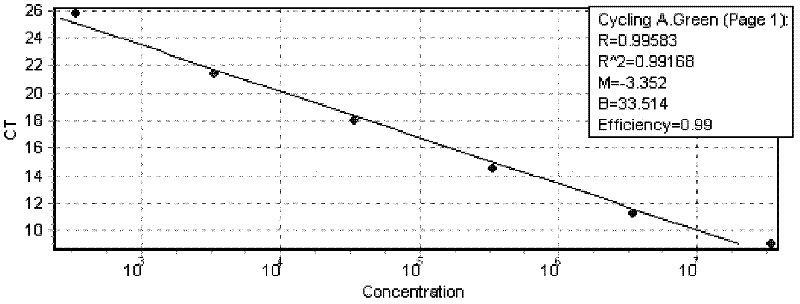
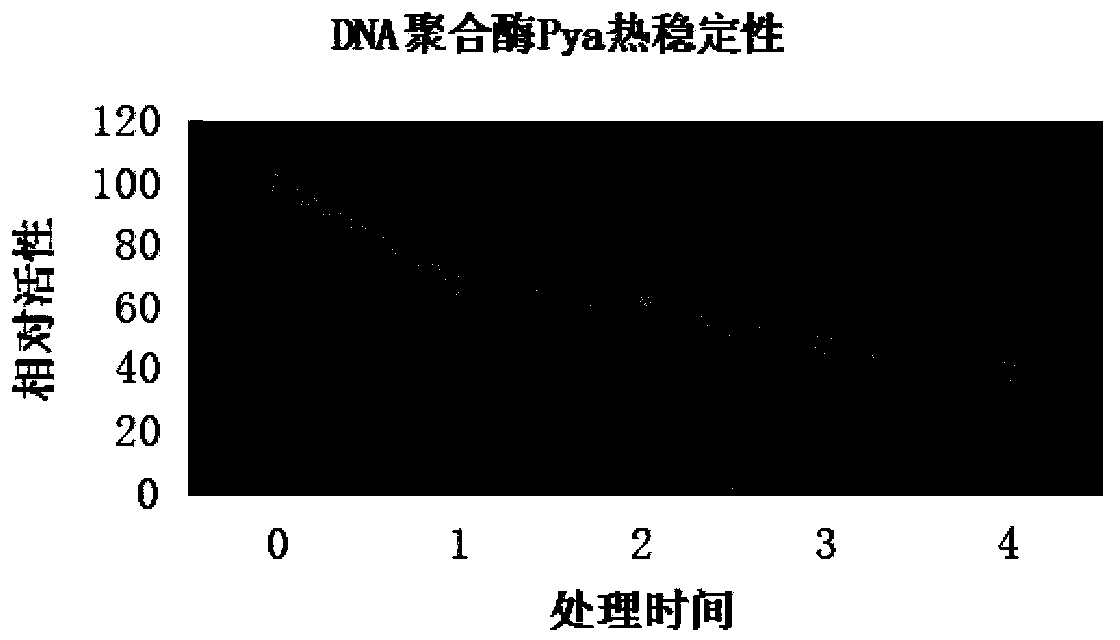
DNA polymerase coding DNA, enzyme coded thereby, and application and preparation method of DNA polymerase
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and relates to a DNA polymerase gene separated from Hyperthermophilic Archaeon, a plasmid thereof, a DNA polymerase coded thereby, a preparation method of the DNA polymerase, and an application of the DNA polymerase, and concretely relates to DNA polymerase coding DNA separated from Pyrococcus yayanosii, and an application and a preparation method thereof. The sequence of the DNA polymerase coding DNA is one of a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1in a sequence table, and a nucleotide sequence obtained by deleting, inserting and substituting one or more nucleotides into the sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1. The encoded DNA polymerase has the advantages of super strong high-temperature resistance, high fidelity performance, excellent anti-inhibitor ability, and realization of a direct PCR reaction by using crude samples.
Owner:SNOVA BIOTECH
A kind of β-ketothiolase related to the 3-hv monomer synthesis of phbv, its coding gene and application
The invention provides a research and an application of beta-ketothiolase in extreme halophilic archaeon, wherein beta-ketothiolase is related to 3-HV monomer synthesis of a biodegradable material PHBV. The protein provided by the invention is a protein showed by the following description (1) or (2): (1) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence represented by a sequence 1 in the sequence table; (2) a protein formed after the amino acid sequence represented by the sequence 1 is processed after substitutions and / or deletions and / or additions of one or more amino acid residues, wherein the obtained protein is derived from the protein represented by (1), and is PHBV and / or 3-HV related. As a result of experiments, when the coding gene of the poly(3-hydrobutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and / or 3-hydroxyalkanoate synthesis related protein is introduced into host bacteria, the molar ratio of generated 3-HV monomer for synthesizing PHBV is greater than 3-HV generated from the host bacteria.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Archaeal polar lipid aggregates for administration to animals
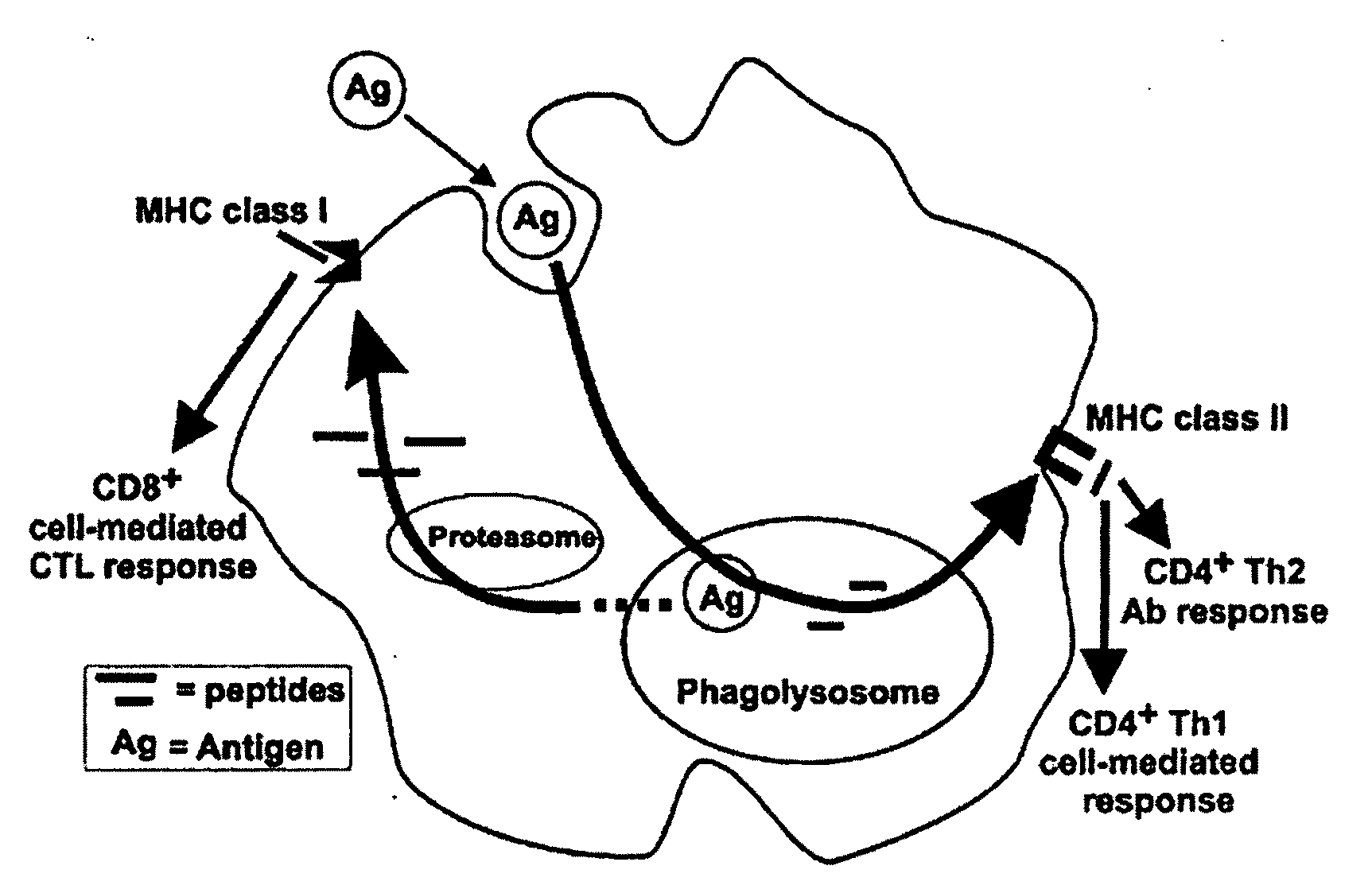
InactiveUS20080220028A1Strong responseLower immune responseBacterial antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAdjuvantBiochemistry
The invention provides non-replicating compositions, and methods for the delivery of these compositions containing pharmaceuticals, biologically relevant molecules, and / or antigens to the host, by administration via a mucosal route such as the intranasal. This invention provides non-replicating vaccine compositions and methods for the delivery of antigens in these vaccine compositions comprising an antigen and a self-adjuvanting carrier, useful for inducing antigen-specific mucosal and systemic immune responses in the host upon immunization via a mucosal route such as intranasal. The vaccine compositions comprise multivalent cations in association with a plurality of spherical archaeal polar lipid aggregates containing aqueous compartments, the AMVAD structure, formed by the interaction of archaeosomes and antigen(s) with multivalent cations such as Ca2+, wherein the AMVAD structure acts as a self-adjuvanting carrier for the antigen(s) in the vaccine composition. Certain advantageous immune responses can also be elicited with the subject compositions.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Kit and method for rapidly detecting archaea
PendingCN112646902AReduce experiment costSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicroorganismExperimental laboratory
The invention belongs to the field of microbial molecular ecology detection, and particularly relates to a kit and a method for rapidly detecting archaea. According to the kit and the method for rapidly detecting archaea, the problems existing in abundance, diversity, composition and structure of archaea communities under different environments in real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR and high-throughput sequencing at present are solved, and the kit for quickly detecting archaea comprises a primer group, a DNA fragment, a PCR buffer solution and an STE buffer solution; in addition, the DGGE technology is used for rapidly detecting the archaea, the experiment cost is low, operation is easy and convenient, and meanwhile the method has the advantages of being high in specificity, easy to popularize in a laboratory, independent of large experiment equipment and the like; and the method is an efficient, rapid, economical and convenient detecting method.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Method for producing high-temperature alpha-amylase by thermococcaceae aeropyrum pernix and product thereof
InactiveCN101070527AImprove thermal stabilityEasy processing conditionsBacteriaEnzymesFiberBiotechnology
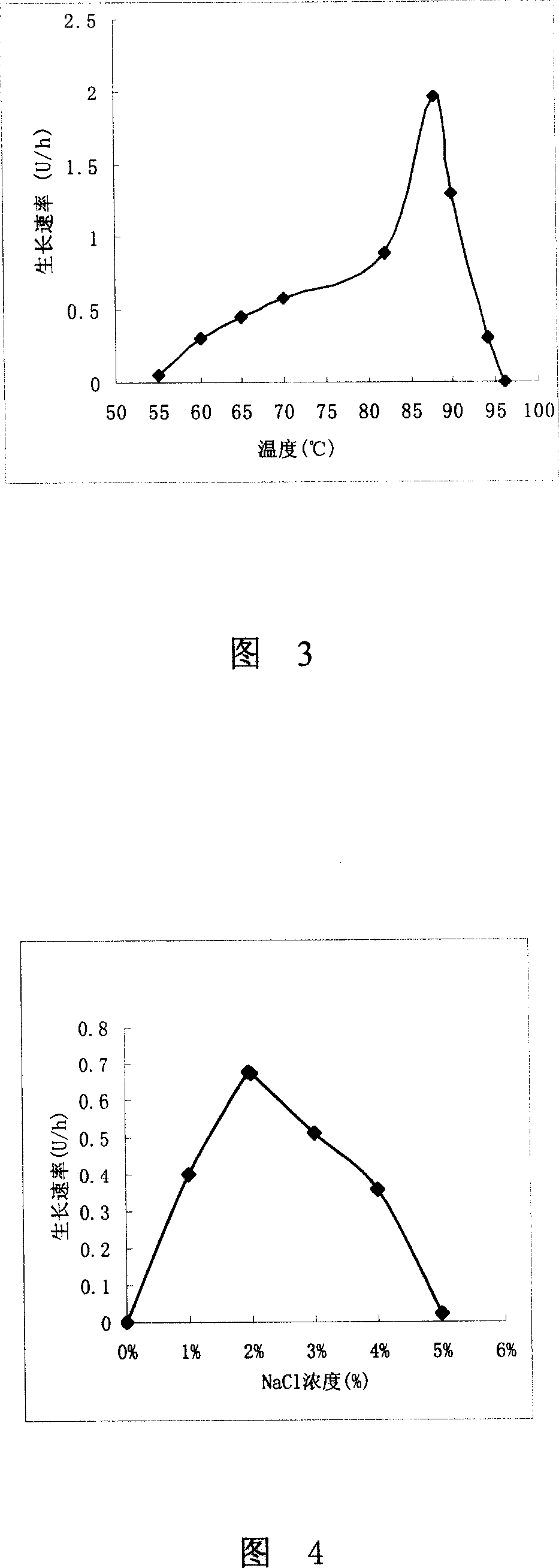
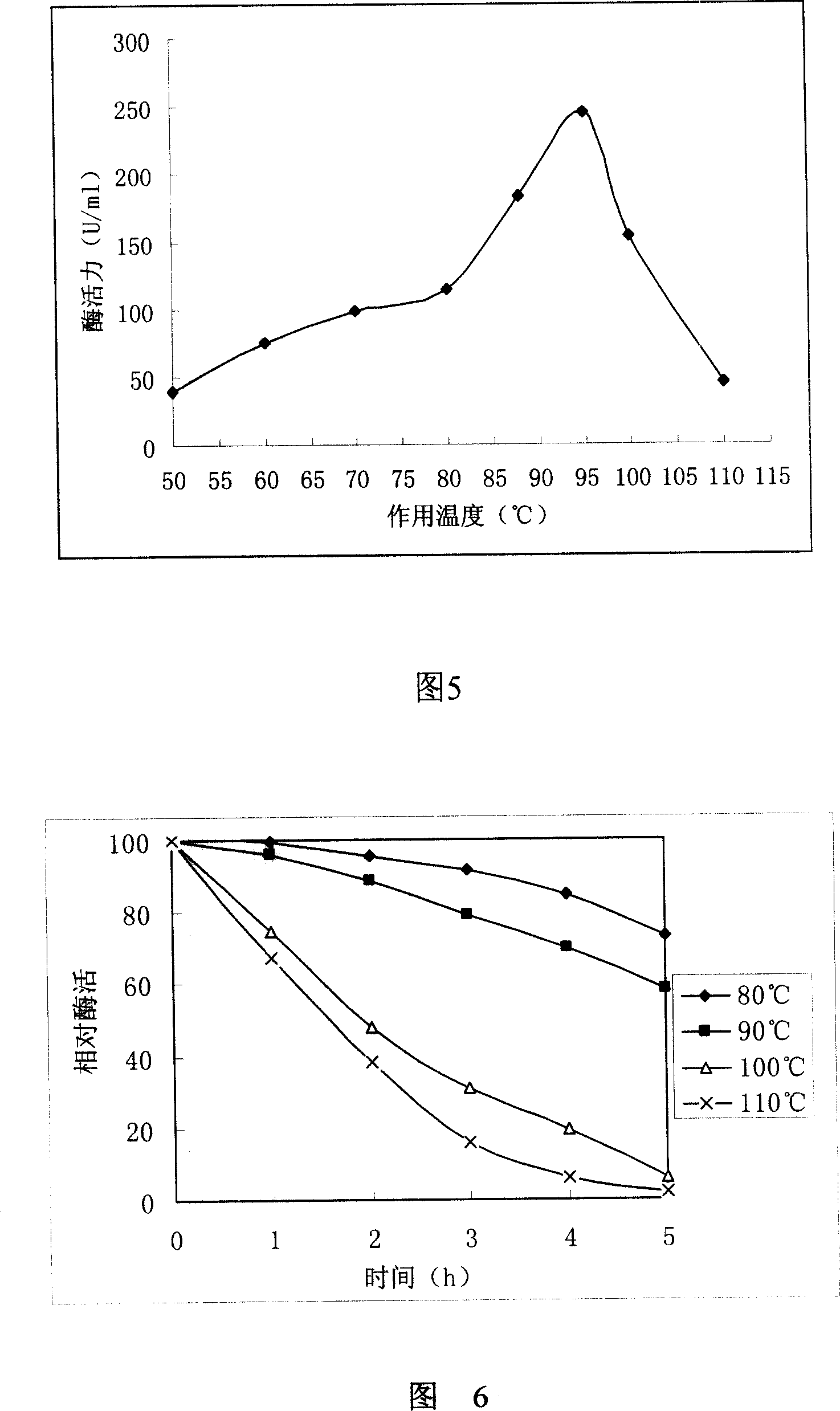
This invention is a heat of thermophiles are cocci bacteria HJ21 (Thermococcus siculi HJ21) CCTCC N0: M 207010. The strain is the strict anaerobic coccus , the diameter is 0.5-1 mum ; Strain growth temperature range for 55-94degree C, Its most suitable growth temperature for 88degree C; Grows the pH scope is 6.5-7.0 suitably , It will not growth if lower than 4.5 or is higher than 9.0; Suits the growth the NaCl density scope is 1-5%, 2% NaCl concentration for the most appropriate ,no NaCl or higher than 5% will not grow ; Bacterial strain has good growth in the basal manure with rich protein; Starch, maltose, glucose, sucrose, 2 fiber sugars, milk sugar and sugar original , gelatin promotes the growth of bacterial strain. This invention still publicizes a is using hot coccus to be addict to hot ancient bacterium HJ21CCTCC N0: M207010 produces high temperature resistant acidity alpha the method of - starch enzyme and the high temperature resistant acidity produced alpha - starch enzyme.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Preparation method of recombinant halophilic archaea protease
ActiveCN110862978AHigh purityVersatileHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliZymogen
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a preparation method of recombinant halophilic archaea protease. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a recombinant plasmid by taking a genome of Halostella sp. DL-M4 as a template and taking a pET28a plasmid as an expression vector; transforming escherichia coli cell by recombinant plasmid, inducing expression, centrifugally collecting thalli for cell resuspension and crushing, centrifuging again, taking a supernatant, adding beta-mercaptoethanol to obtain a mixed solution, enabling the mixed solution to pass through a nickel column, combining zymogen with a nickel medium for renaturation, and finally performing secondary impurity protein removal and target protein elution, performing ultrafiltration centrifugal concentration and performing gel filtration chromatography to obtain the recombinant halophilic archaea protease. The method provided by the invention has good universality, simpler purification steps and shorter production cycle, the obtained protease has high purity, and finally the halophilic archaea protease with specific enzyme activity of 1159.15 U / mg is obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Compound microorganism bacterium agent for purifying duck slaughter house sewage and using method and application of compound microorganism bacterium agent
The invention discloses a compound microorganism bacterium agent for purifying duck slaughter house sewage and a using method and application of the compound microorganism bacterium agent, and belongs to the technical application field of sewage treatment. The compound microorganism bacterium agent capable of decreasing the content of ammonia nitrogen and COD in the duck slaughter house sewage is prepared from lactic acid bacteria, aspergillus oryzae and halophilic archaea. The invention further discloses a compound preparation capable of decreasing the content of ammonia nitrogen and COD in the duck slaughter house sewage. The compound preparation is prepared from a first component and a second component, wherein the first component comprises oil bran, flax cakes, trash fishes and the compound microorganism bacterium agent, and the second component comprises mountain flour, clay and the compound microorganism bacterium agent. The actual purification effect on the duck slaughter house sewage is observed, and results show that the compound microorganism bacterium agent can effectively decrease the content of COD and ammonia nitrogen in the duck slaughter house sewage, has the advantages of being low in cost, high in efficiency, good in effect and the like and can be effectively applied to duck slaughtering sewage treatment.
Owner:菏泽益舟食品有限公司
Sulfated-glycolipids as adjuvants for vaccines
ActiveUS20170158728A1Improve stabilitySuitable efficacySugar derivativesCancer antigen ingredientsBacteroidesLipid formation
A synthetic charged glycolipid is described comprising a sulfated saccharide group covalently linked to the tree sn-1 hydroxyl group of the glycerol backbone of an archaeal core lipid via a beta linkage. The synthetic charged glycolipids include compounds of formula I wherein n is 0 or 1; R is hydrogen or hydroxyl; and Y is hydrogen or a sulfate group, at least one Y being a sulfate group; and including pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The sulfated glycolipid produces stable archaeosomes at a mol % ratio of from 100:0 to 30:70 (sulfated glycolipid: uncharged glycolipid) and which induce a protective immune response, including CD8+ and CD4+ T cell responses. Archaeosomes comprising the sulfated glycolipids described have desirable adjuvant properties, particularly when mixed with uncharged glycolipid at a mol % ratio of about 50:50.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
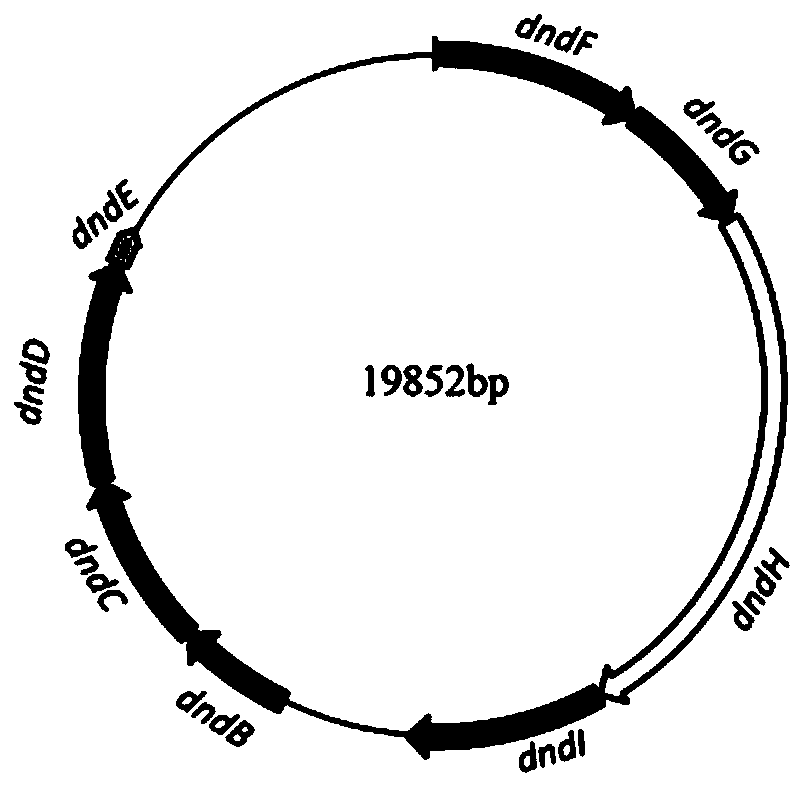
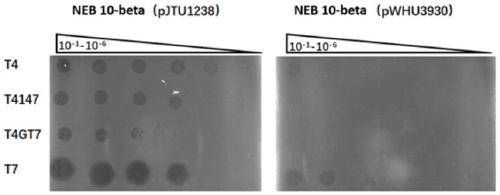
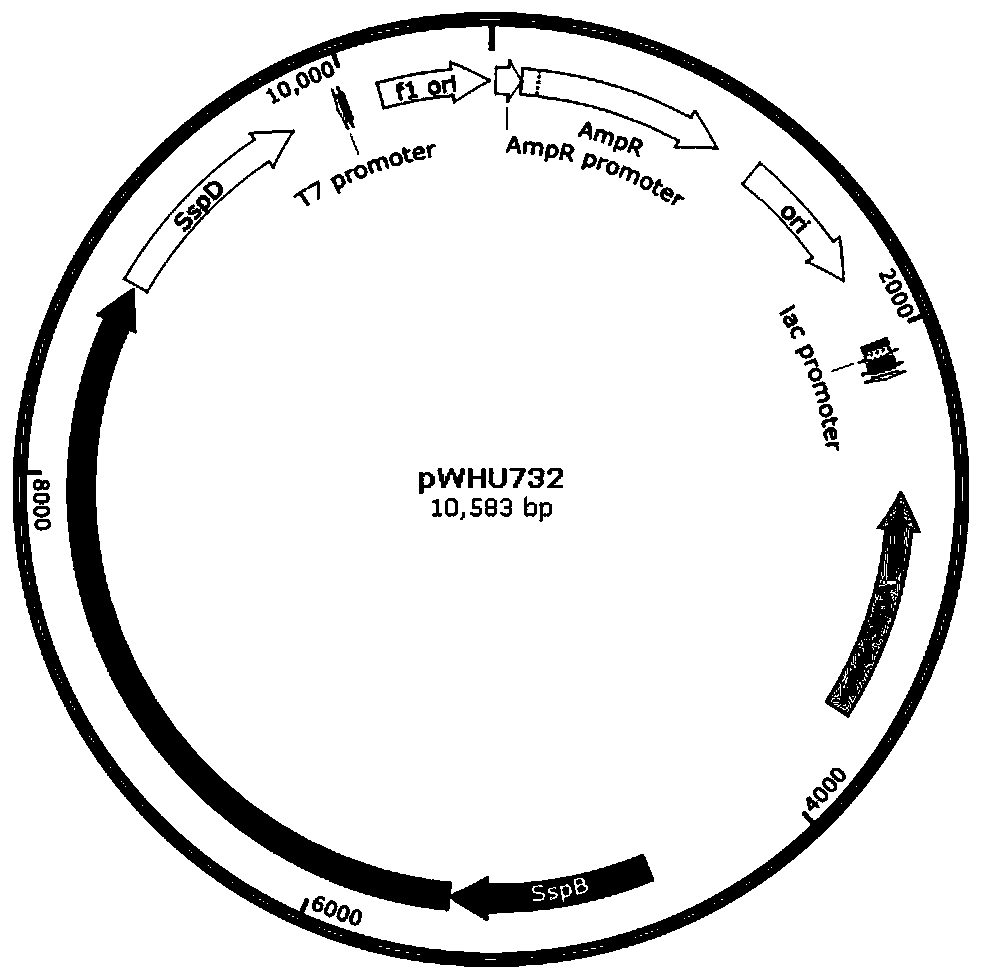
Antiphagin and artiviral system based on DNA sulfur phosphorus acylation modification
The invention discloses an antiphagin and artiviral system based on DNA sulfur phosphorus acylation modification, and relates to antiphagin systems in bacteria and antiviral systems in archaea. On onehand, in bacteria, type-I sulfur phosphorus acylation modification gene clusters dndABCDE and dndFHGI gene clusters can protect hosts to resist infection of phages, and the antiviral system in archaea is composed of dndCDEA-pbeABCD gene clusters; on the other hand, the invention further discloses type-II antiphage systems composed of sspBCD-sspE, and infection of the phages of the bacteria can also be resisted. The antiphagin and artiviral system can be applied to development of biotechnologies and industrial fermentation technologies.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV +1
Compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching sulphide ore, and compounding method and application method thereof
The invention discloses a compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching a sulphide ore, and a compounding method and an application method thereof, and belongs to the technical filed of wet-process metallurgy. Aiming at a biological leaching mechanism of the sulphide ore and the physiological-biochemical characteristics of microorganisms, a community capable of efficiently leaching the sulphide ore is compounded by a plurality of mineral leaching microorganisms, wherein the mineral leaching microorganisms comprise marine bacteria which come from deep-sea hydrothermal vents and are capable of enduring high concentration sodium chloride, sulfur-oxidized bacteria, iron-oxidized bacteria and archaea which are from a freshwater environment, autotrophic bacteria and facultative heterotrophic bacteria. Not only can the difficult problem that the mineral leaching microorganisms from the freshwater environment are intolerance of sodium chloride be solved, but also microorganisms required by oxidation and dissolution of the sulphide ore and diversity of chemical reactions are guaranteed. The compound bacterium community can obviously increase leaching efficiency and leaching rate of the sulphide ore such as copper pyrites and can be applied in a leaching process and a dump leaching process of a stirring tank. A certain basis for popularization and application of biological metallurgy of the sulphide ore is provided by the invention.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Archaeal polar lipid aggregates for administration to animals
InactiveUS20130195932A1Strong responseLower immune responseBacterial antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAdjuvantBiochemistry
The invention provides non-replicating compositions, and methods for the delivery of these compositions containing pharmaceuticals, biologically relevant molecules, and / or antigens to the host, by administration via a mucosal route such as the intranasal. This invention provides non-replicating vaccine compositions and methods for the delivery of antigens in these vaccine compositions comprising an antigen and a self-adjuvanting carrier, useful for inducing antigen-specific mucosal and systemic immune responses in the host upon immunization via a mucosal route such as intranasal. The vaccine compositions comprise multivalent cations in association with a plurality of spherical archaeal polar lipid aggregates containing aqueous compartments, the AMVAD structure, formed by the interaction of archaeosomes and antigen(s) with multivalent cations such as Ca2+, wherein the AMVAD structure acts as a self-adjuvanting carrier for the antigen(s) in the vaccine composition. Certain advantageous immune responses can also be elicited with the subject compositions.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
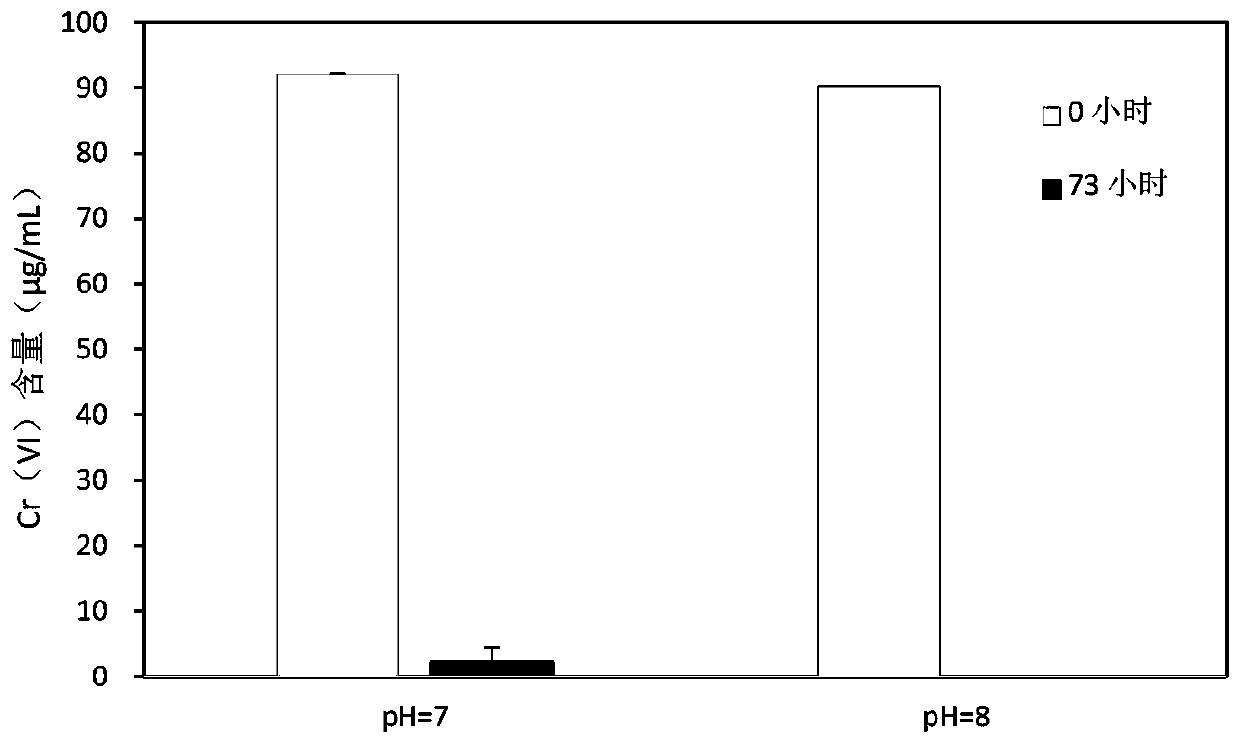
microbial flora and application thereof in treating Cr heavy metal pollution
InactiveCN109628352AEffective recoveryMaintain resilienceBacteriaWater contaminantsBacteroidesMethanosarcinales
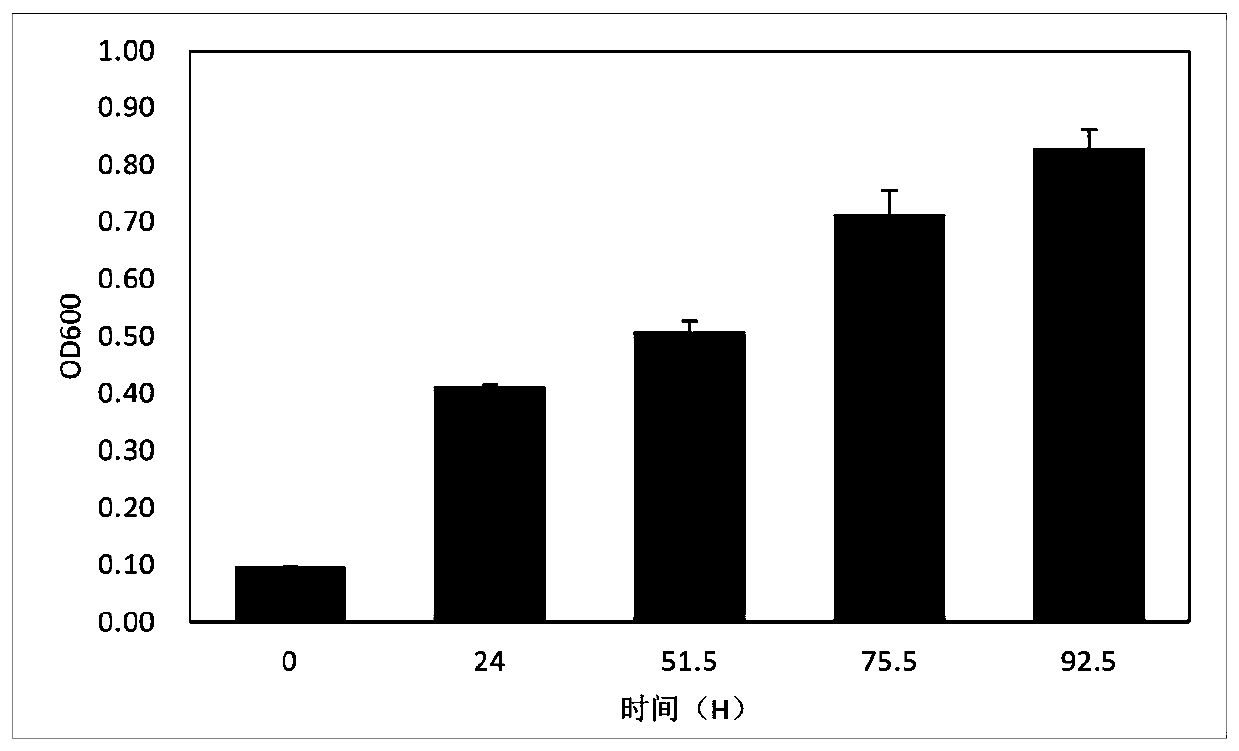
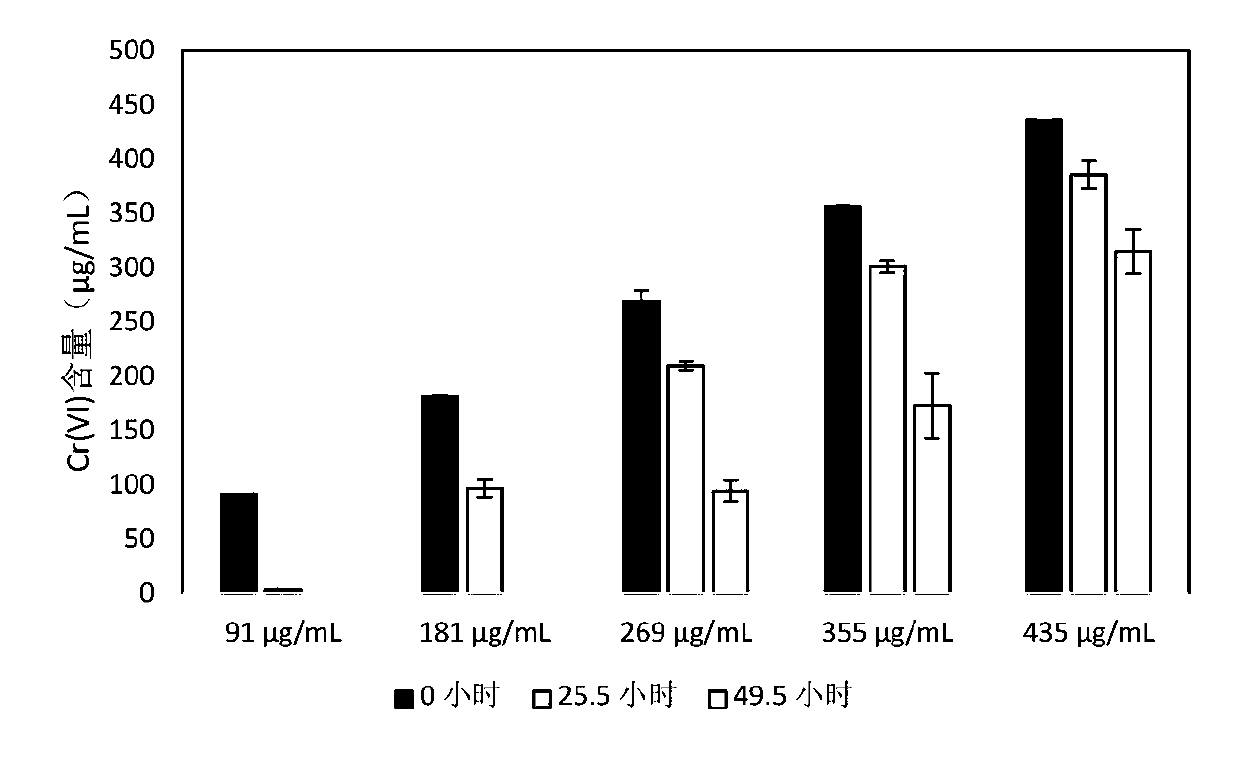
The invention provides microbial florawhich is composed of bacteria and archaea. The bacteria (manipulation taxon, recorded as OTUs) include Burkholderiales, Clostridiales and other strains. The archaea (OTUs) include Methanobacteriales, Methanomicrobiales, Methanosarcinales and other strains. The microbial flora can effectively reduce Cr (VI) and can completely reduce 91 microgram / mL of Cr (VI) within 49.5 h. The microbial flora can tolerate the environmental Cr(VI) concentration of 435 microgram / mL and maintain the reduction capacity. The microbial flora has the capacity of reducing Cr (VI)at 15-45 DEG C, and the efficiency of reducing Cr(VI) at 30 DEG C and 35 DEG C is the best.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Dried microbial sludge granule as additive for wastewater treatment
PendingUS20200031698A1Improve effectivenessImprove system stabilityBacteriaWater/sewage treatmentPhosphateSludge
The present invention provides compositions as additives for wastewater treatment. A first composition comprising archaea microorganism granules for bioaugmentation for treatment of COD in wastewater, and a second composition of activated silicate beads that allow removal of phosphate, nitrogen and suspended solids. The mixture of both compositions act synergistically by promoting organic matter degradation and allowing the removal of phosphate without consuming alkalinity of the treated solution.
Owner:PROBIOSPHERE INC
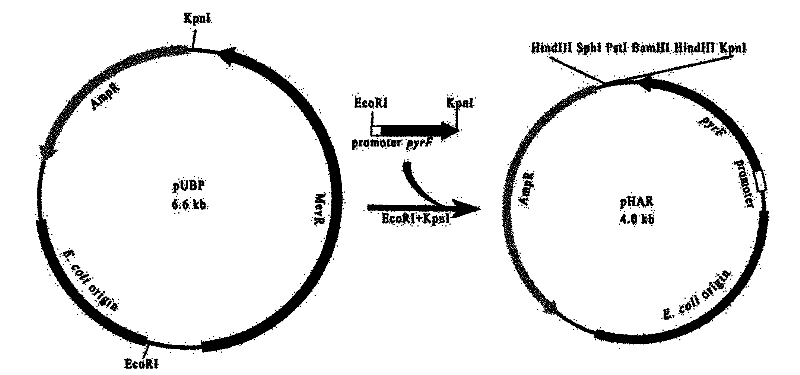
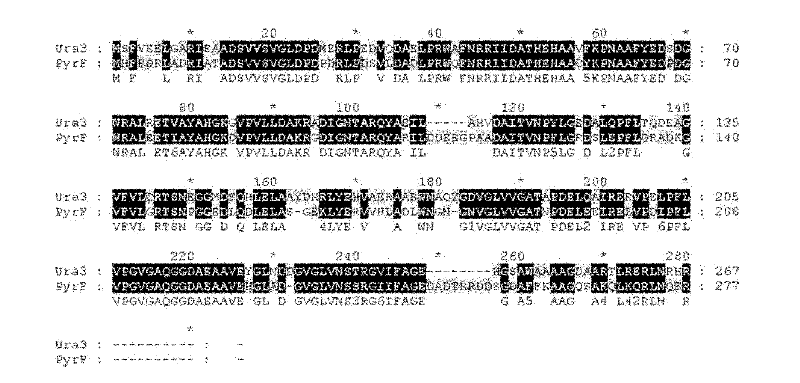
Genetic manipulation system based on Haloarcula hispanica and pyrF gene and its application
ActiveCN102676414AEnriched selectable marker geneScreenedFungiBacteriaMultiple cloning siteMetabolic pathway
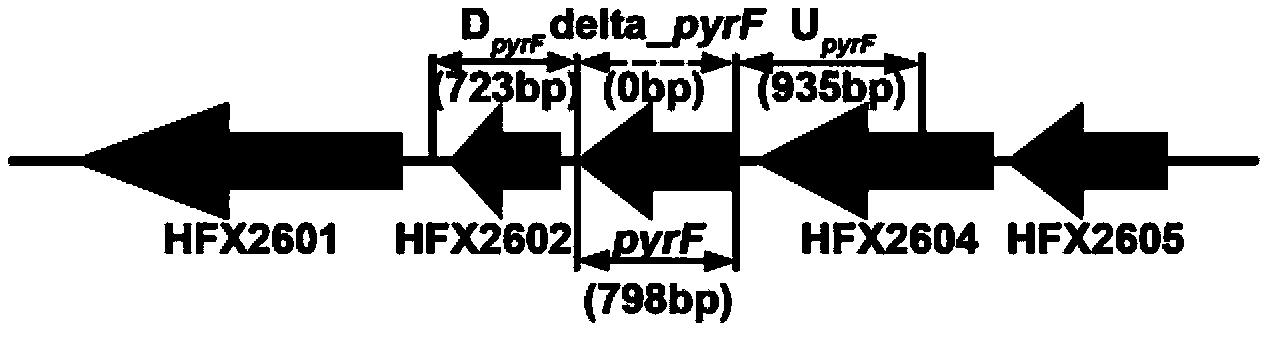
The invention discloses a genetic manipulation system based on Haloarcula hispanica and pyrF genes and its application. The genetic manipulation system comprises recombinant halophilic archaea and a recombinant plasmid carrier. The recombinant halophilic archaea is prepared by defunctionalizing an encoding gene of a protein sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 in initial halophilic archaea. The recombinant plasmid carrier at least contains a replication origin required by replication of Escherichia coli, an expression cassette for screening resistance selectable marker genes of Escherichia coli transformants, an expression cassette of the encoding gene of the protein sequence of SEQ ID NO:1, and polycloning sites for allowing exogenous genes to insert. The genetic manipulation system can be used as a high-efficiency gene knockout system, and can carry out extensive genetic function research and metabolic pathway illumination on Haloarcula hispanica. According to the experiment, the frequency of positive recombinants obtained from genetic transformation by using the inventive system is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
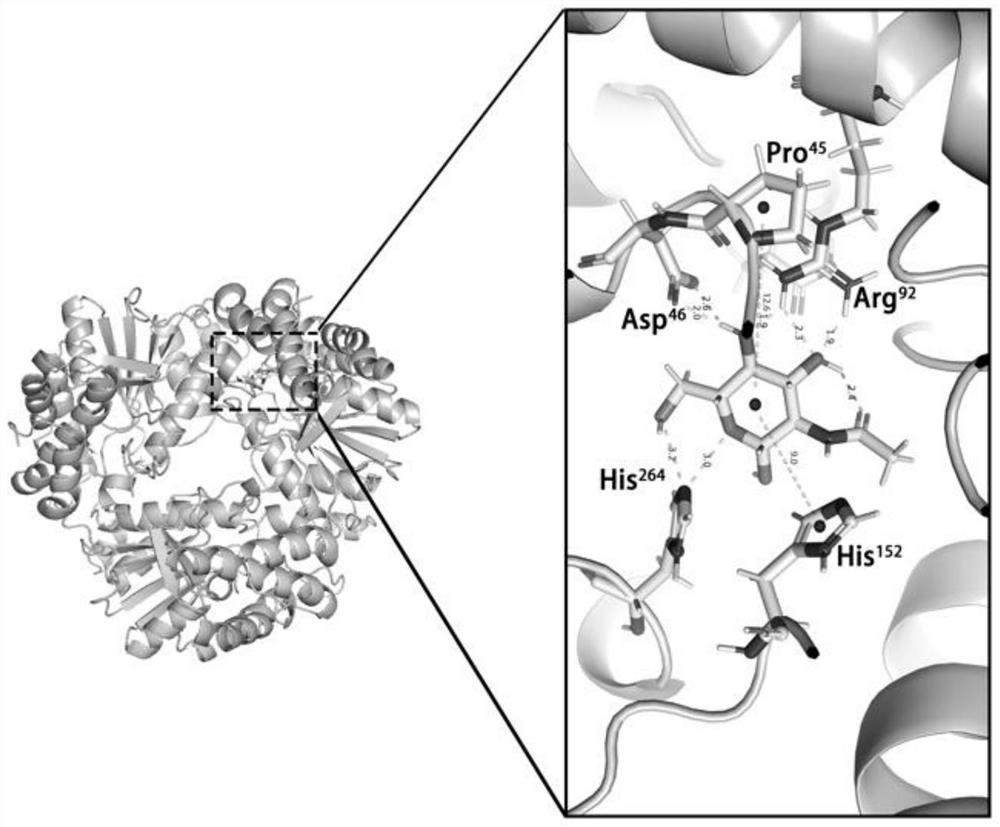
Chitobiose deacetylase mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN113293155AHigh expressionHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesGlycinePyrococcus horikoshii
The invention relates to a chitosan disaccharide deacetylase mutant, which is obtained by mutating glycine G at the 74th site of chitosan disaccharide deacetylase of extreme thermophilic archaea Pyrococcus horikoshii into alanine A. According to the invention, the enzyme activity, the expression quantity and the catalytic efficiency of the chitobiose deacetylase Dac are improved, and the problem that the efficiency of converting the chitobiose deacetylase Dac into glucosyl GlcN is not high is solved.
Owner:SHANDONG RUNDE BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Preparation method and application of novel halophilic archaea extracellular protease
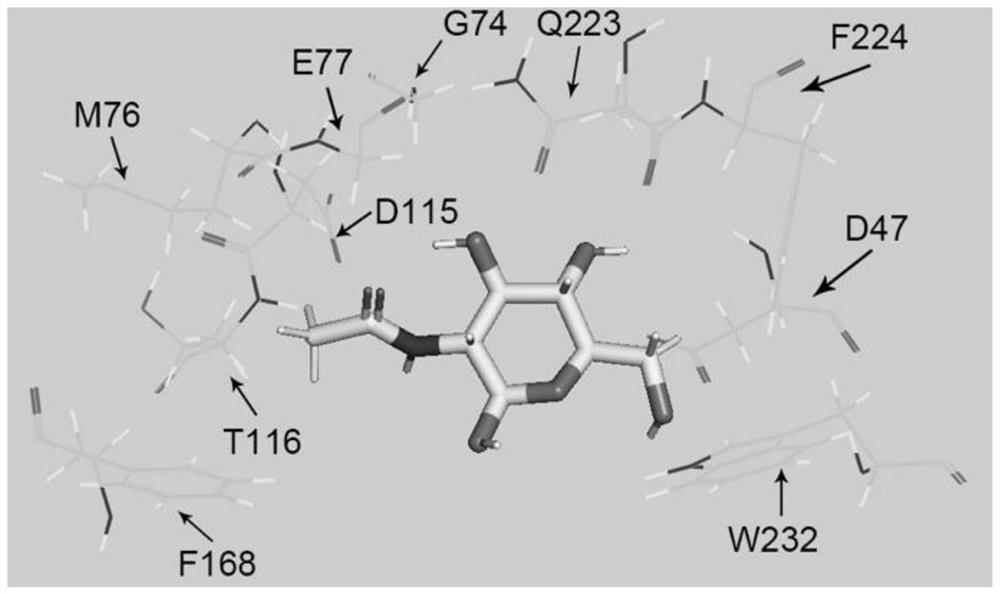
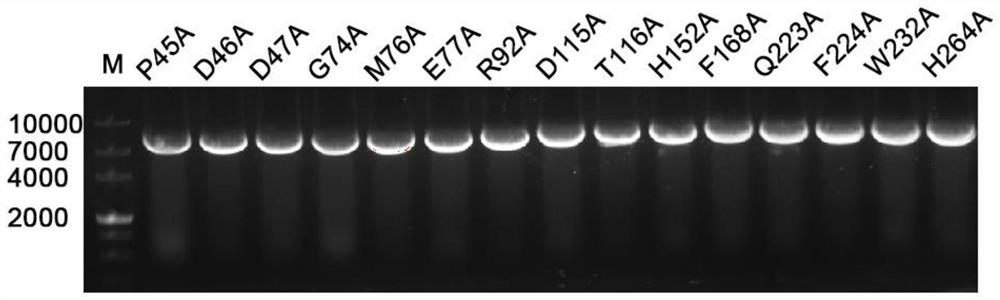
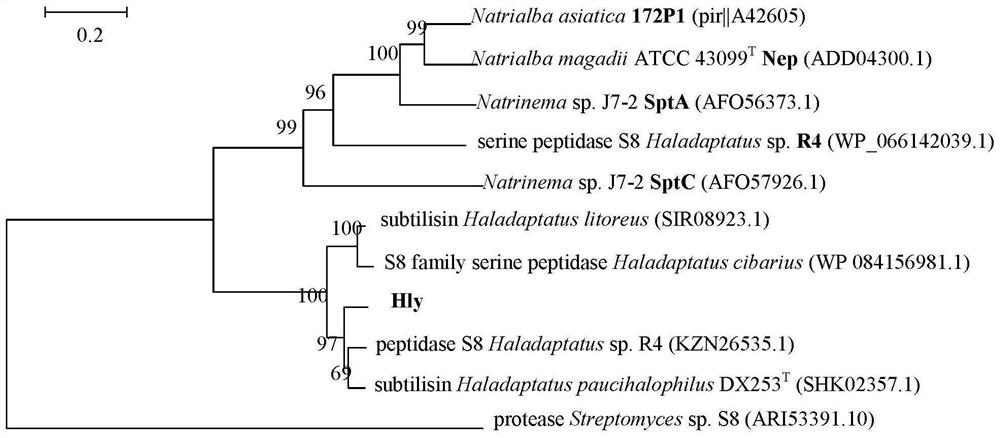
ActiveCN111705050AHigh research valueExcellent enzymatic propertiesHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionKanamycinGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a preparation method and application of novel halophilic archaea extracellular protease. The preparation method comprises thefollowing steps: firstly, obtaining a coding gene hly based on a genome of halophilic archaea DYF 46; connecting the hly to a vector by a molecular cloning technology to construct a recombinant plasmid; transforming the recombinant plasmid into a prokaryotic host, culturing the transformed recombinant host cells in an LB liquid culture medium containing kanamycin, centrifugally collecting thalli at low temperature after culture and inducible expression, resuspending in a cell lysis solution, ultrasonically crushing, centrifugally collecting supernatant for recombinant protein purification; andpurifying protein by nickel affinity chromatography, obtaining mature enzyme by a column renaturation method, and purifying by gel filtration chromatography to obtain high-purity Hly. The Hly obtained by the preparation method has excellent enzymatic characteristics, and can be applied to production and processing processes of complex and salt-containing degraded proteins such as detergents, wastewater treatment, pharmacy and environmental remediation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
A method for in situ revealing of formic acid-utilizing methanogenic archaea in paddy fields using DNA stable isotope probes
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of method for producing propionic acid by fermentation with mixed bacteria system
ActiveCN106244661BDoes not affect activityPromote proliferationMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes, and discloses a method for producing propionic acid by mixed bacteria system fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out sequencing batch anaerobic fermentation on a fermentation system composed of Methanogenic archaea / propionic-acid-producing bacteria-containing anaerobic sludge and an anaerobic fermentation culture medium, wherein in the fermentation process, the ammonium ion concentration in the fermentation system is enhanced to 1-2 g / L and kept constant, and methane is collected; and after the fermentation finishes, collecting the fermentation liquid, extracting the propionic acid, and adding the residual flora-containing solid into the anaerobic fermentation culture medium for the next fermentation round. The ammonium ion concentration is regulated to control the flora distribution of the Methanogenic archaea / propionic-acid-producing bacteria-containing anaerobic sludge, so that the fermentation environment is beneficial to the proliferation of the propionic-acid-producing bacteria; and the method can obtain a large amount of methane in the process of producing high-concentration high-purity propionic acid, has the advantages of unrestricted material sources and lower input-output ratio, and is beneficial to industrialized implementation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com