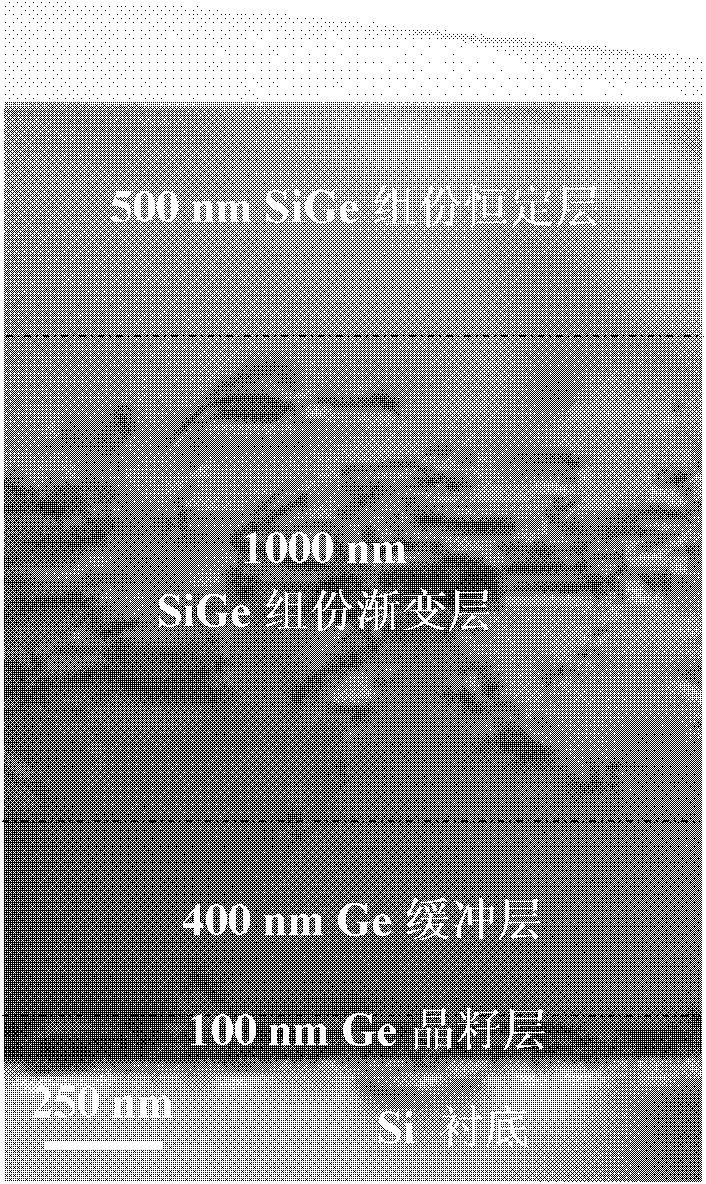Patents
Literature
65 results about "Strain engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Strain engineering refers to a general strategy employed in semiconductor manufacturing to enhance device performance. Performance benefits are achieved by modulating strain in the transistor channel, which enhances electron mobility (or hole mobility) and thereby conductivity through the channel.
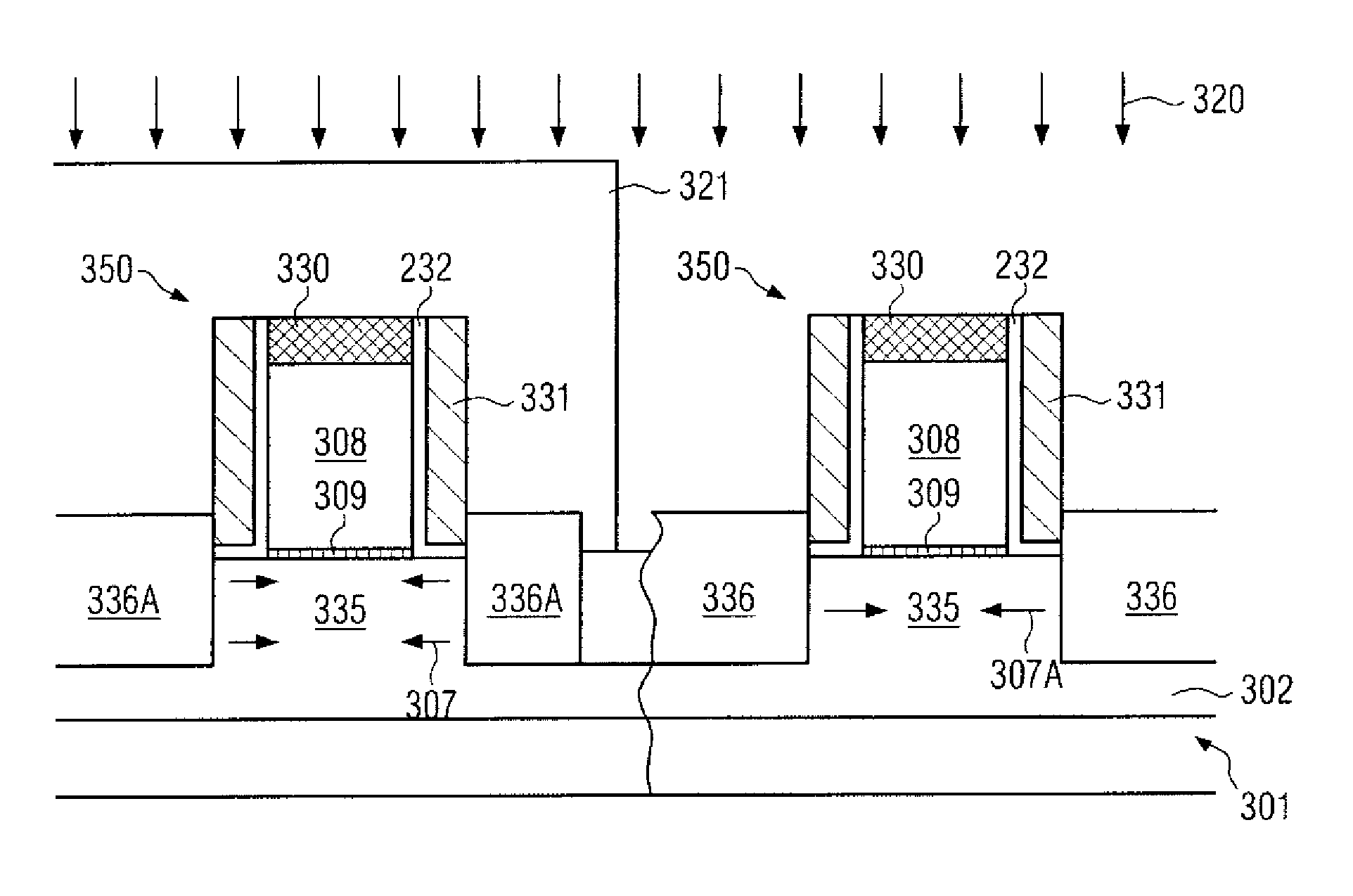
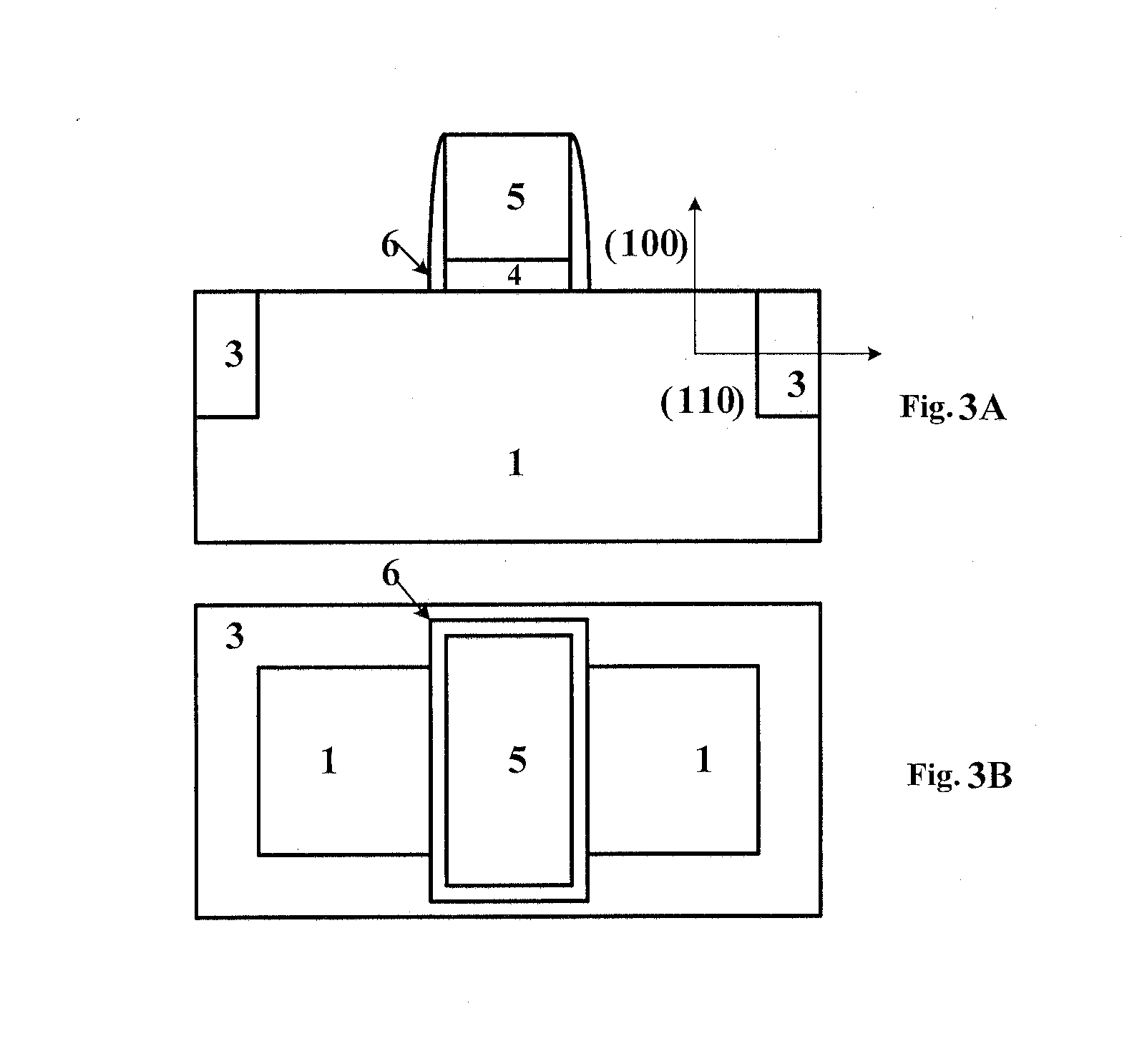
Technique for strain engineering in si-based transistors by using embedded semiconductor layers including atoms with high covalent radius
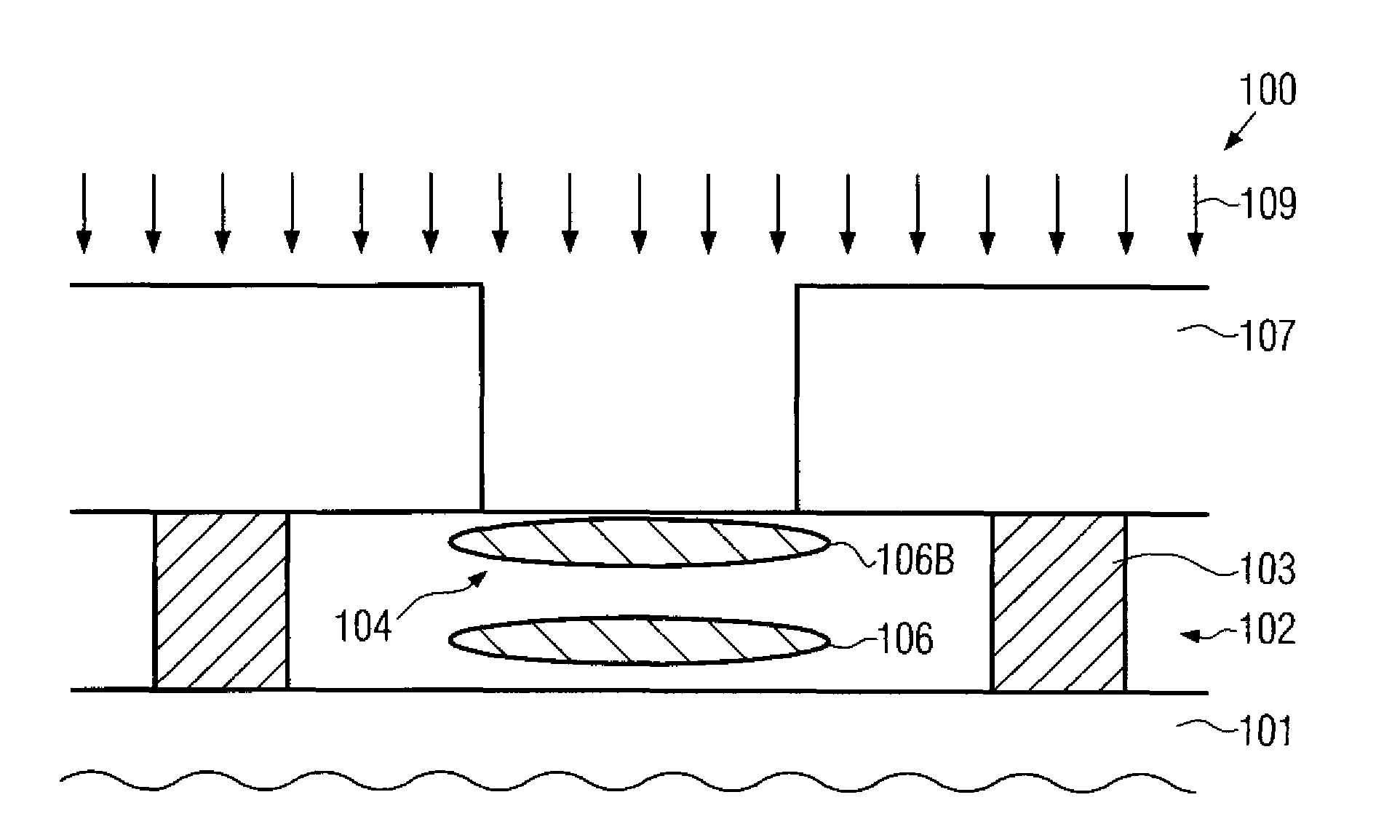
By incorporating an atomic species of increased covalent radius, which may at least partially substitute germanium, a highly efficient strain mechanism may be provided, in which the risk of stress relief due to germanium conglomeration and lattice defects may be reduced. The atomic species of increased radius, such as tin, may be readily incorporated by epitaxial growth techniques on the basis of tin hydride.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
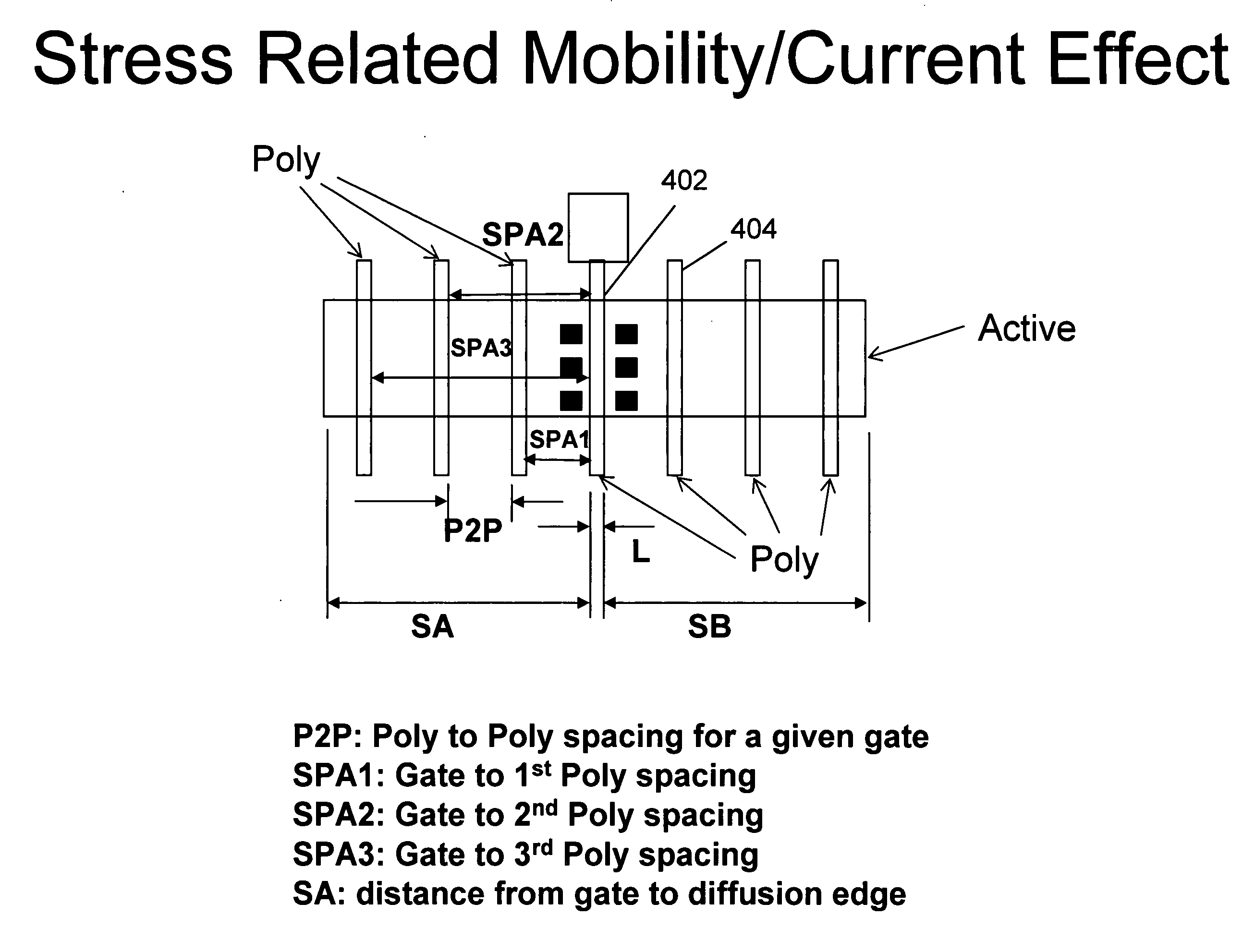
Automated optimization of an integrated circuit layout using cost functions associated with circuit performance characteristics
InactiveUS20100100856A1Low variabilityImprove performanceCAD circuit designMulti-objective optimisationLocal patternIntegrated circuit layout
An integrated circuit (IC) design system and method provide an optimization of a layout of an integrated circuit wherein an assessment is taken into account of the circuit performance characteristics and the layout of the IC design. The system and method assess associated circuit performance characteristics, each as a cost function of a local pattern of shapes in an initial circuit layout, aggregate cost functions of the associated circuit performance characteristics to derive an integral performance number associated to the initial global circuit layout, perturb the integral performance number by varying the global circuit layout, and select perturbations that optimize the performance number, so as to optimize the global circuit layout. Assessment is taken into account of the circuit performance characteristics based on the layout and the interdependence of the circuit performance characteristics for the IC design. The physical process related effects such as well proximity effect and stress / strain engineering and / or performance parameters such as the P-N transistor size ratio are taken into account to achieve optimization.
Owner:MITTAL ANURAG
Assembly of nanoscaled field effect transistors
InactiveUS8063450B2Improve critical high-frequency performanceReduce resistanceTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireWork function
Owner:QUNANO
Assembly of nanoscaled field effect transistors
InactiveUS20100176459A1Improve critical high-frequency performanceReduce resistanceTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireWork function
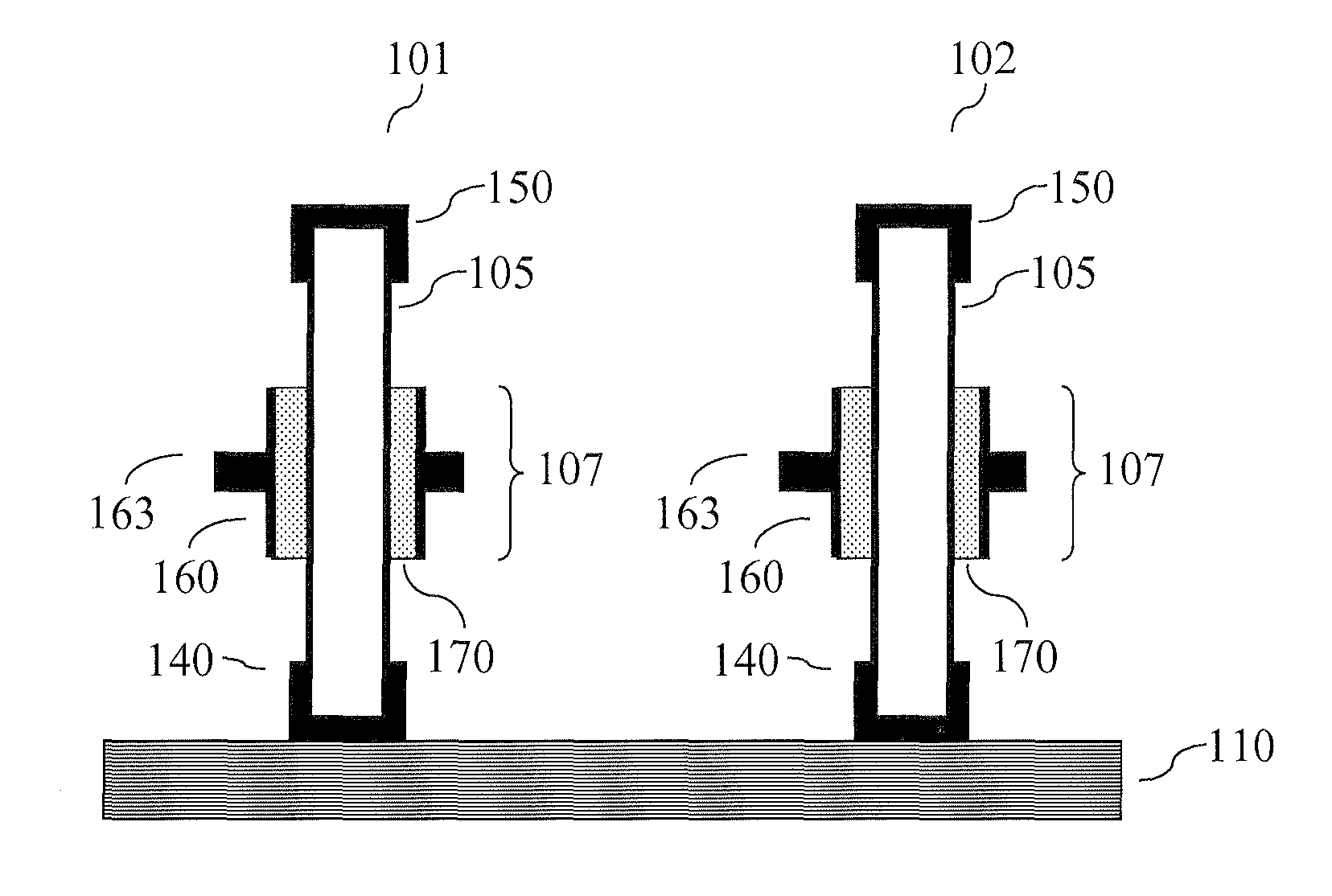
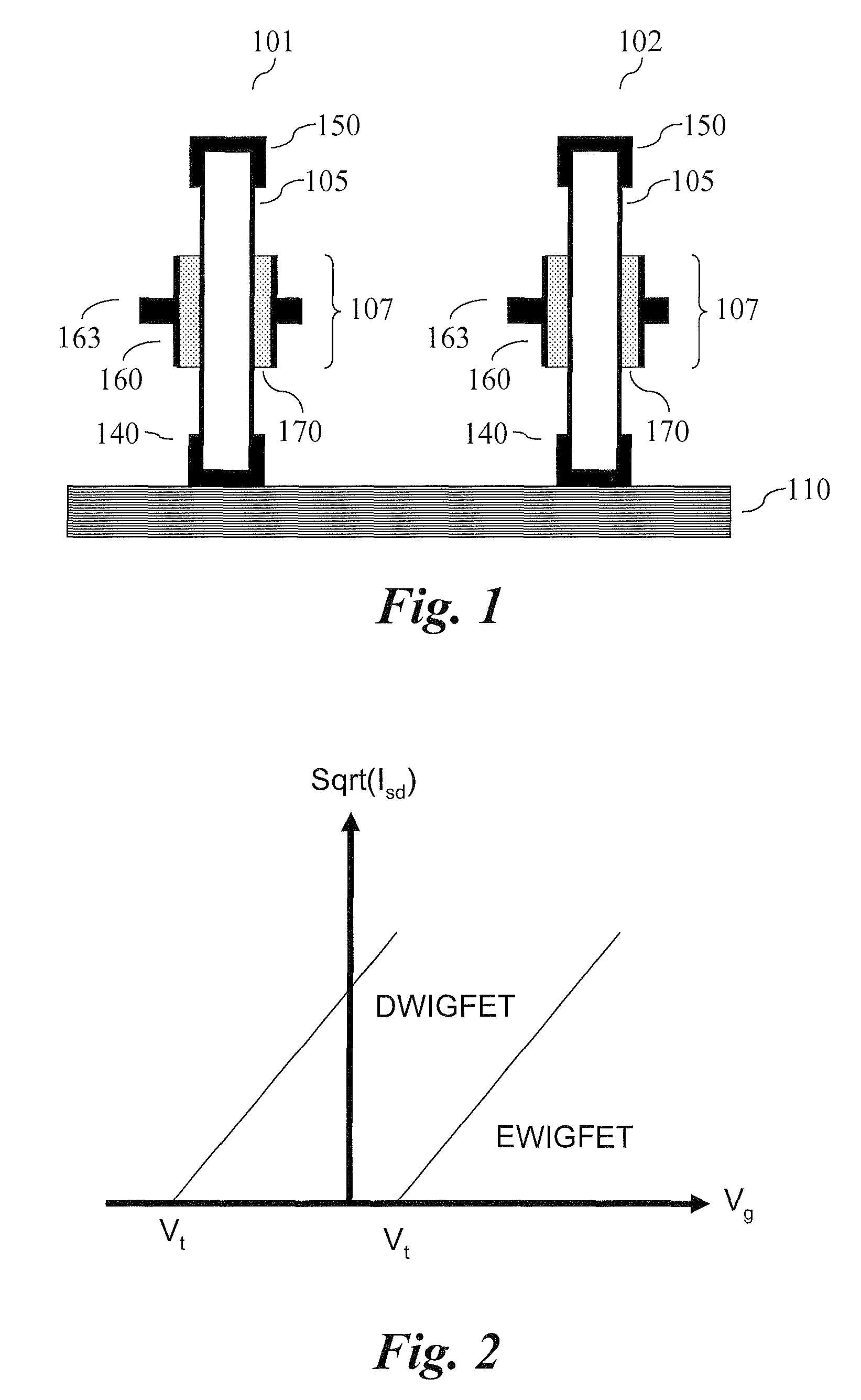
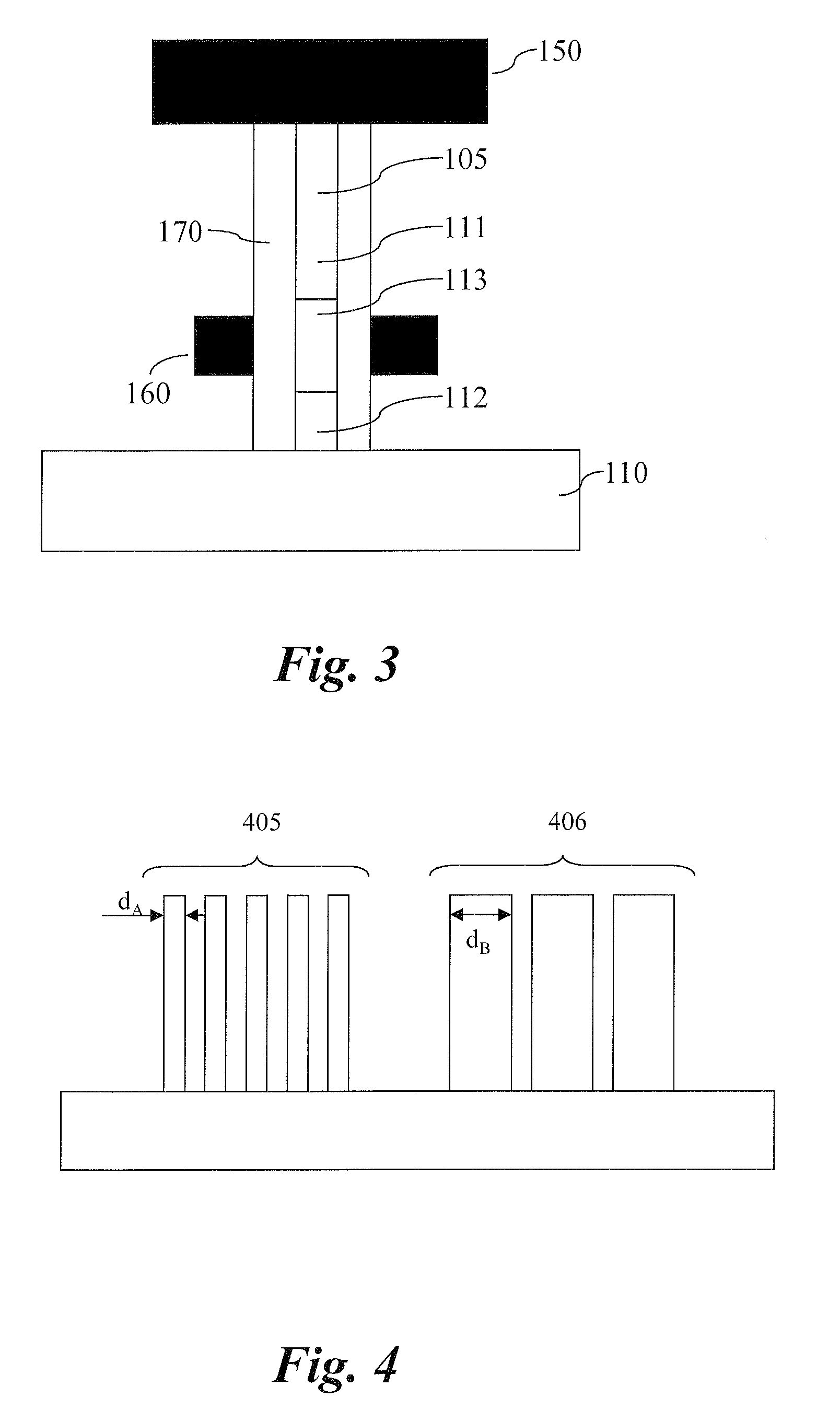
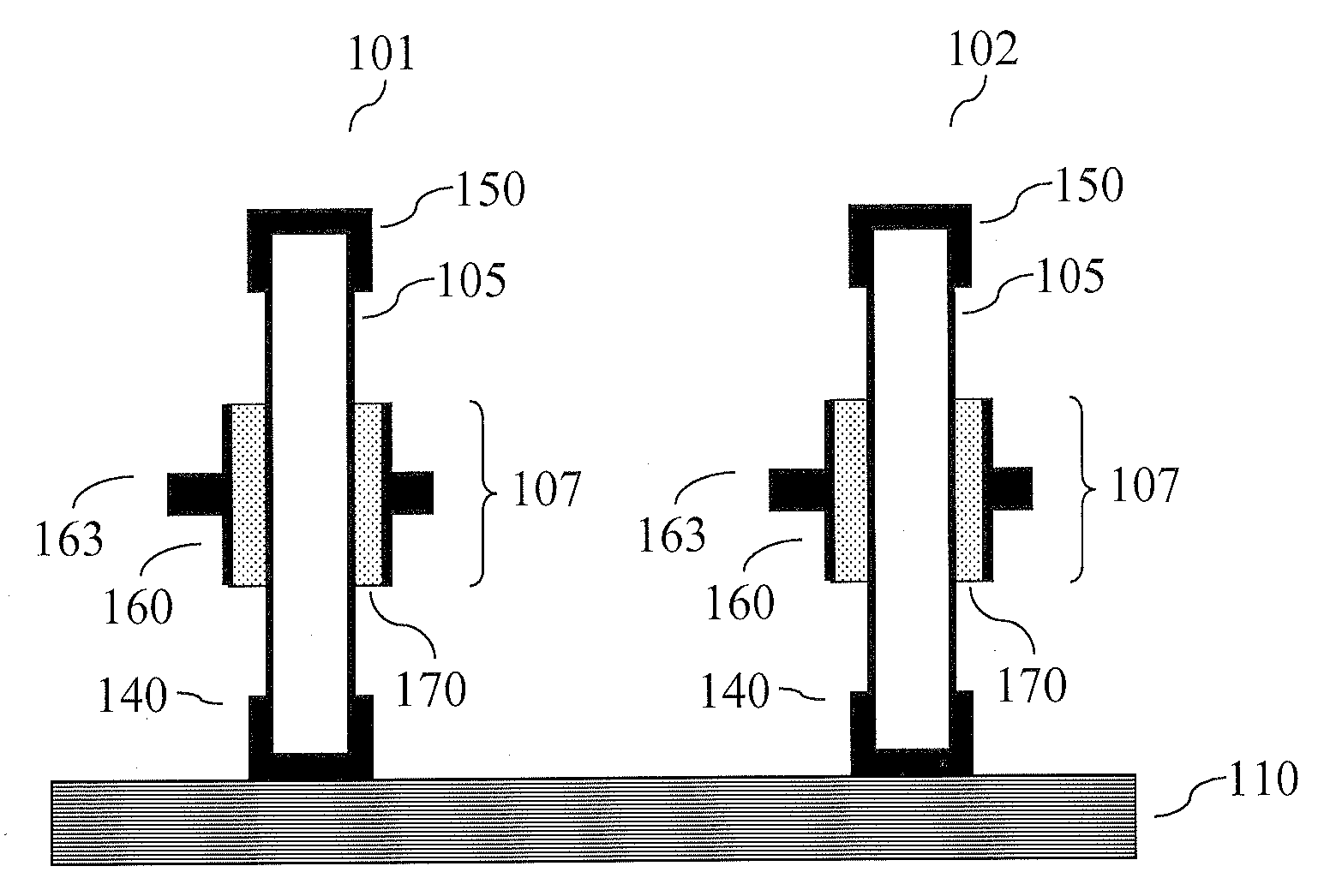
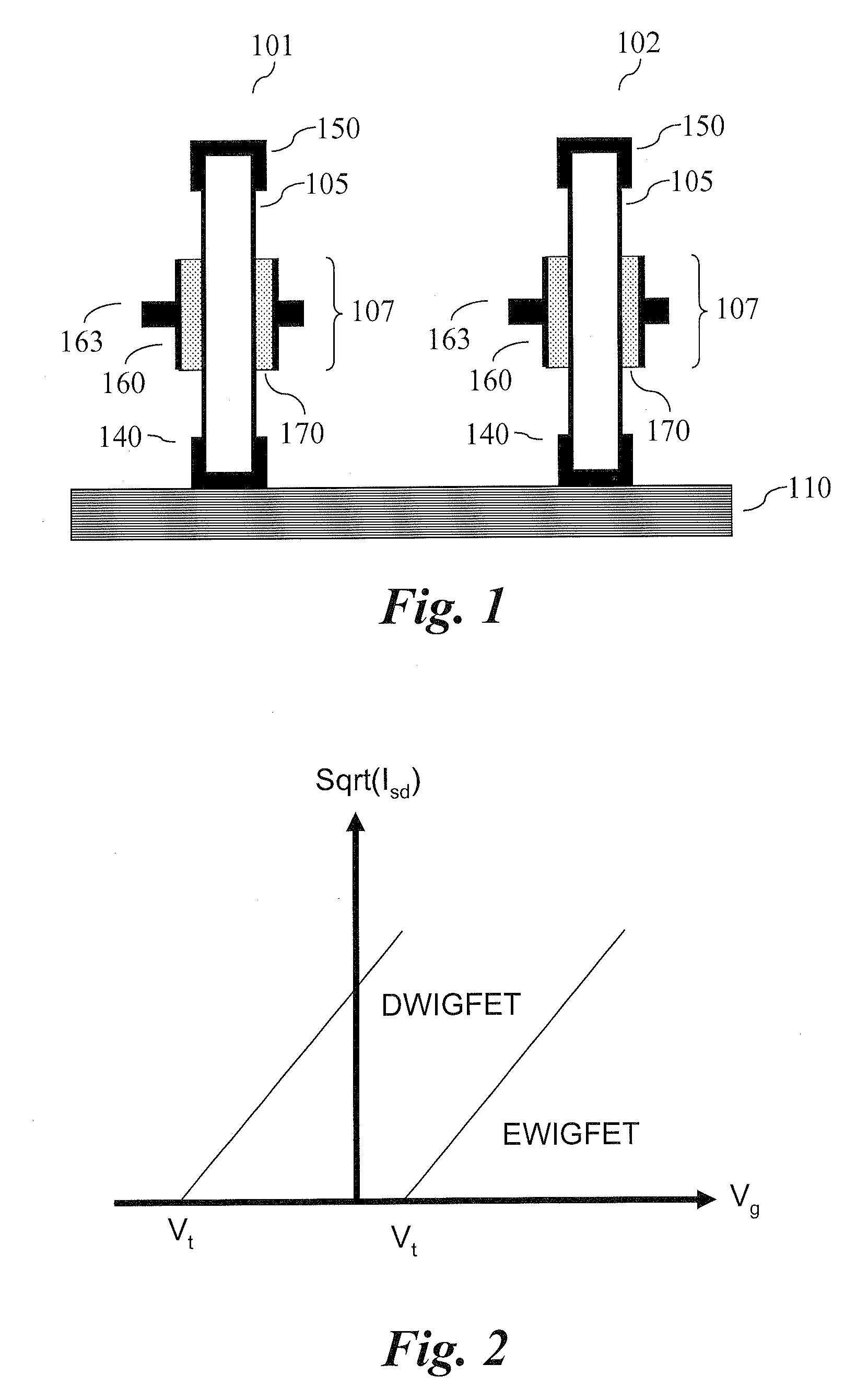
The present invention relates to vertical nanowire transistors with a wrap-gated geometry. The threshold voltage of the vertical nanowire transistors is controlled by the diameter of the nanowire, the doping of the nanowire, the introduction of segments of heterostructures in the nanowire, the doping in shell-structures surrounding the nanowire, tailoring the work function of the gate stack, by strain engineering, by control of the dielectrica or the choice of nanowire material. Transistors with varying threshold voltages are provided on the same substrate, which enables the design of advanced circuits utilizing the shifts in the threshold voltages, similar to the directly coupled field logic.
Owner:QUNANO
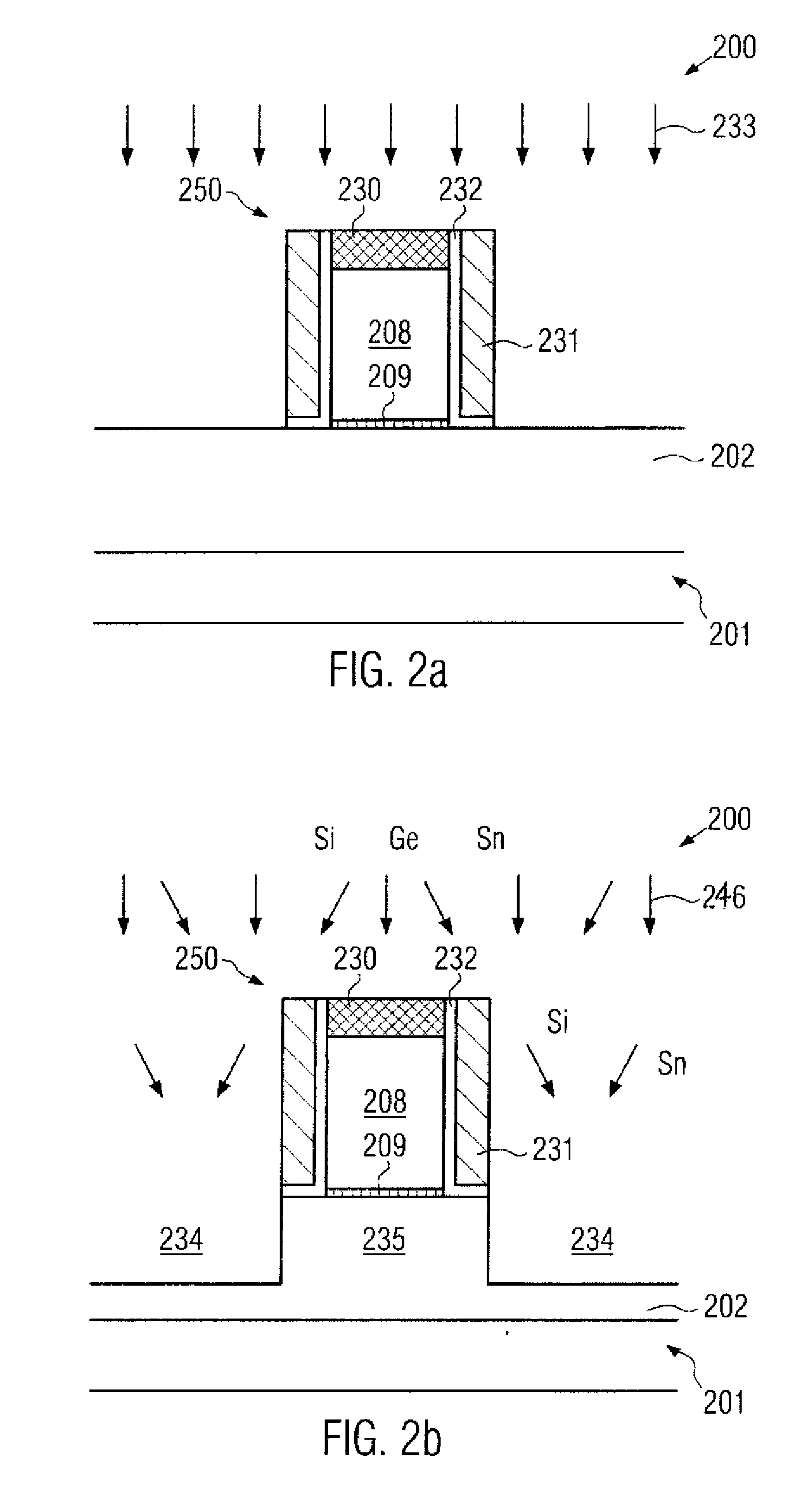
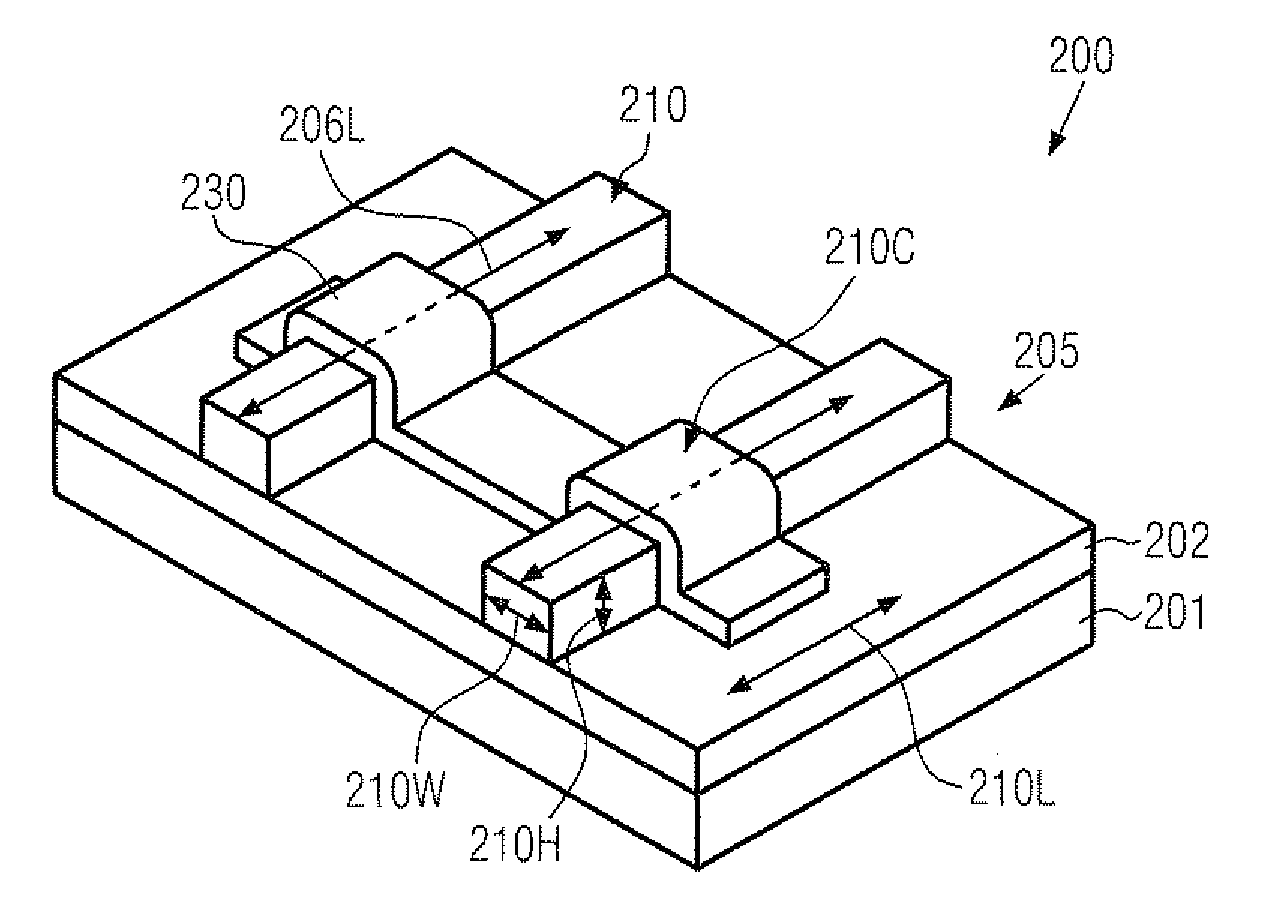
Strain Engineering in Three-Dimensional Transistors Based on a Strained Channel Semiconductor Material
InactiveUS20120025312A1Efficiently formedEfficient growth processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower flowSemiconductor materials
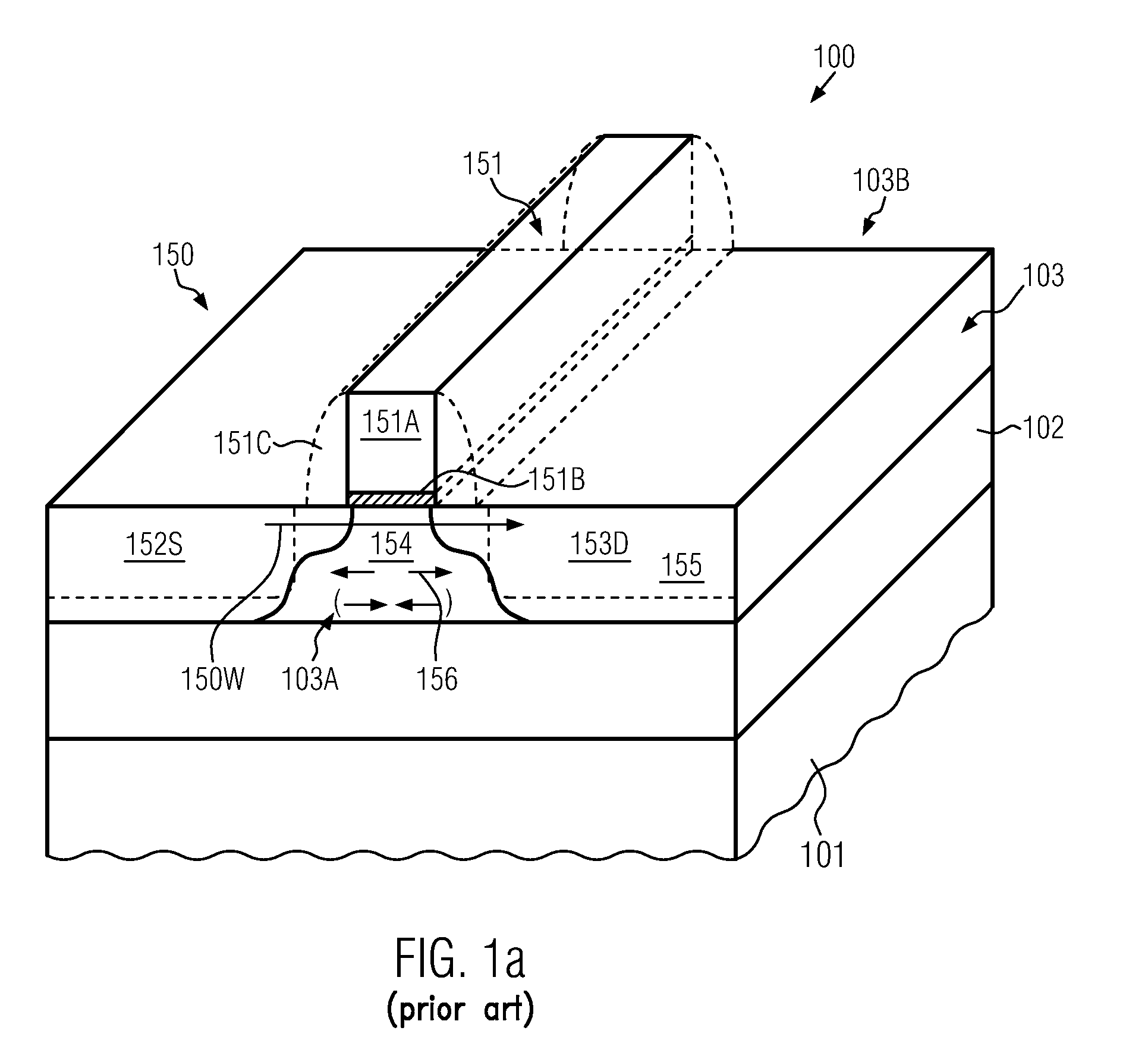
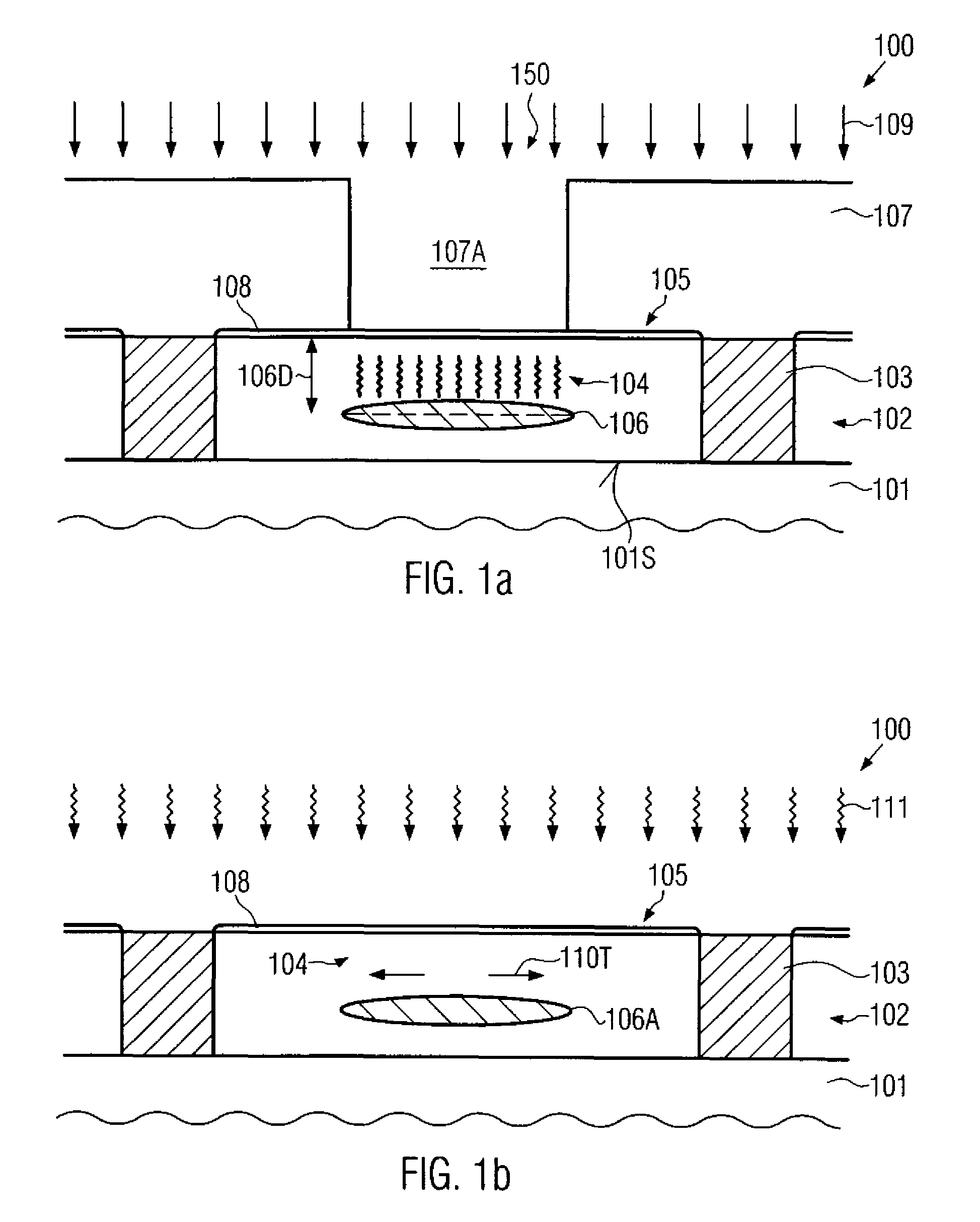
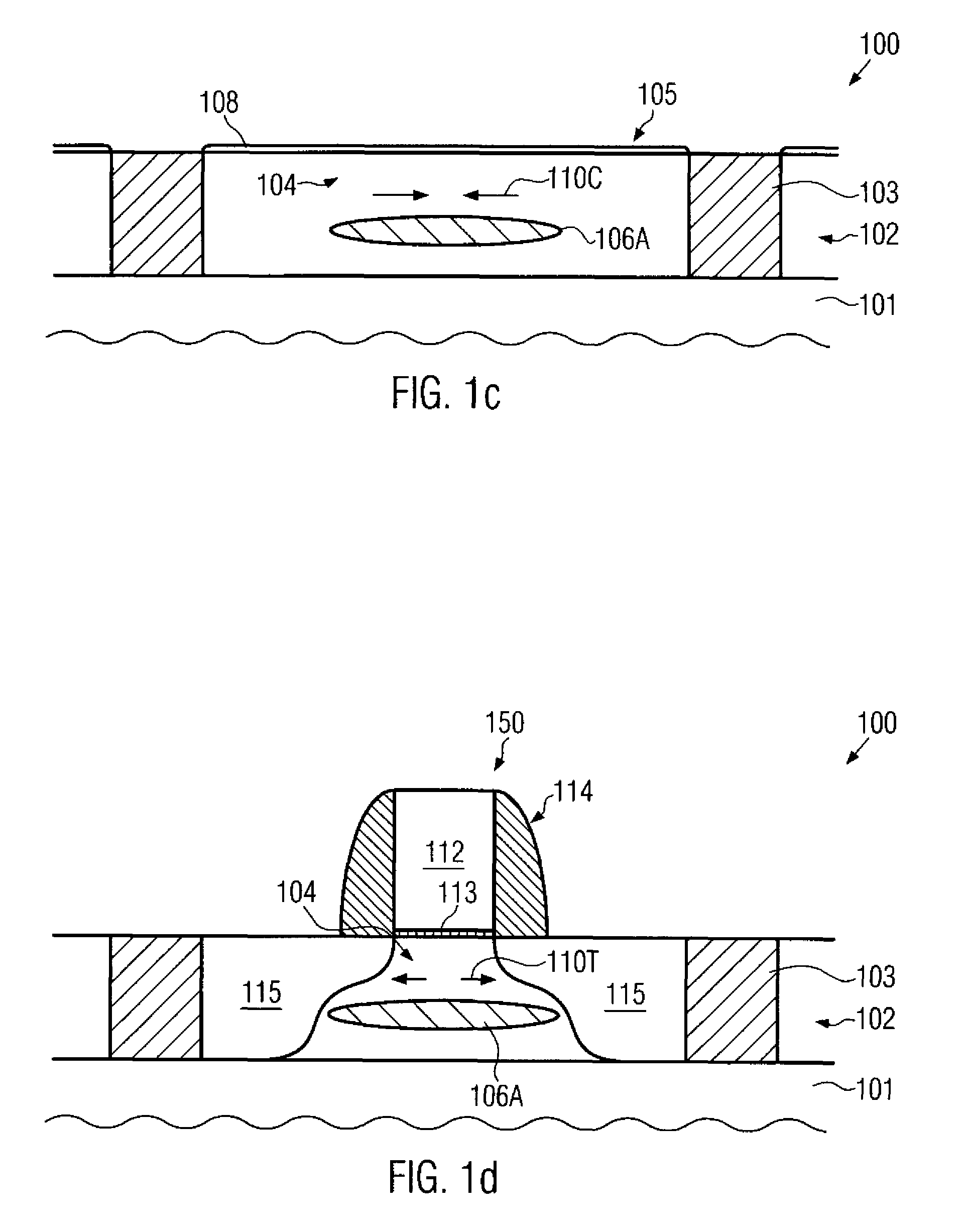
In three-dimensional transistor configurations, such as finFETs, at least one surface of the semiconductor fin may be provided with a strained semiconductor material, which may thus have a pronounced uniaxial strain component along the current flow direction. The strained semiconductor material may be provided at any appropriate manufacturing stage, for instance, prior to actually patterning the semiconductor fins and / or after the patterning the semiconductor fins, thereby providing superior performance and flexibility in adjusting the overall characteristics of three-dimensional transistors.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
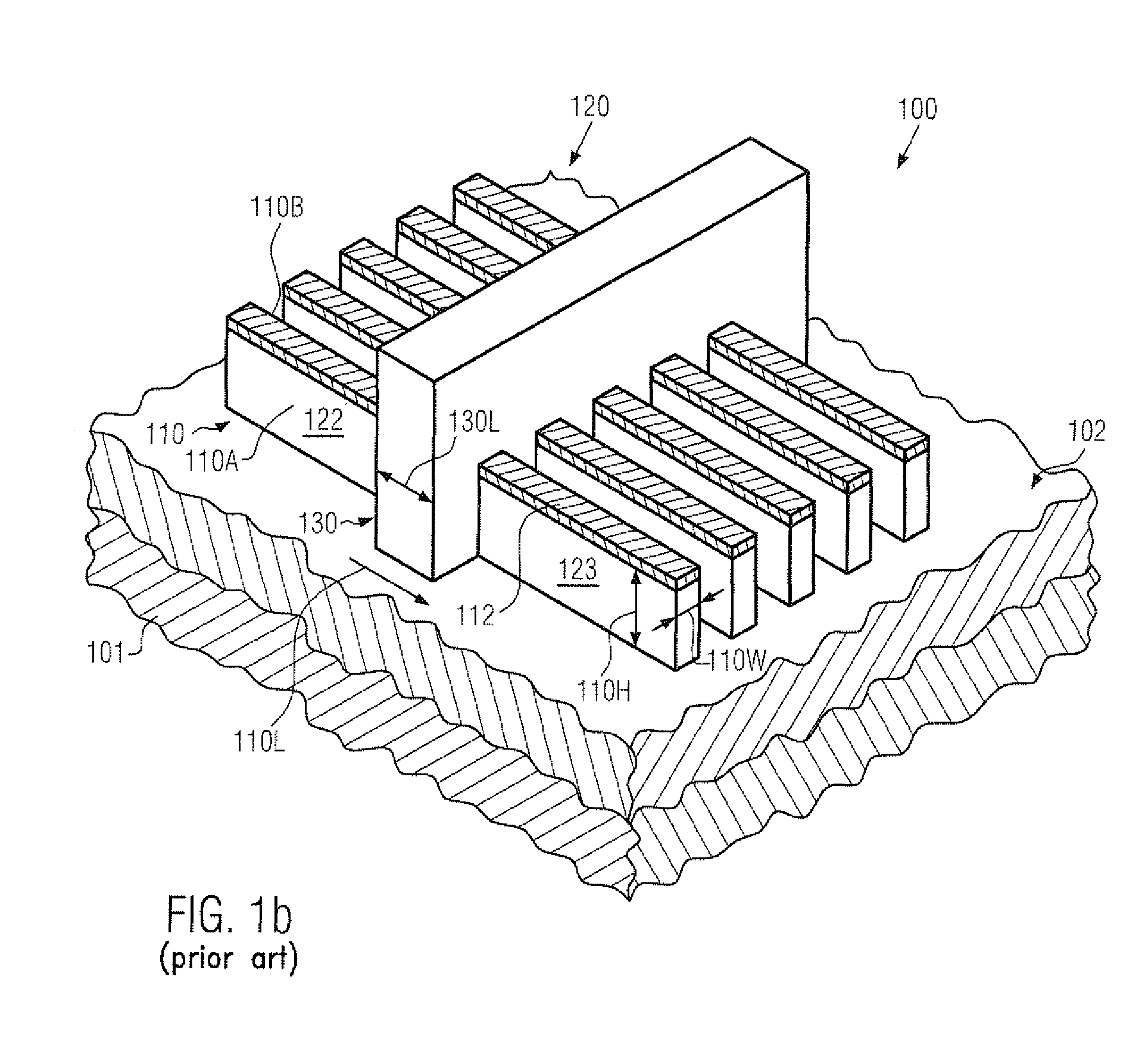
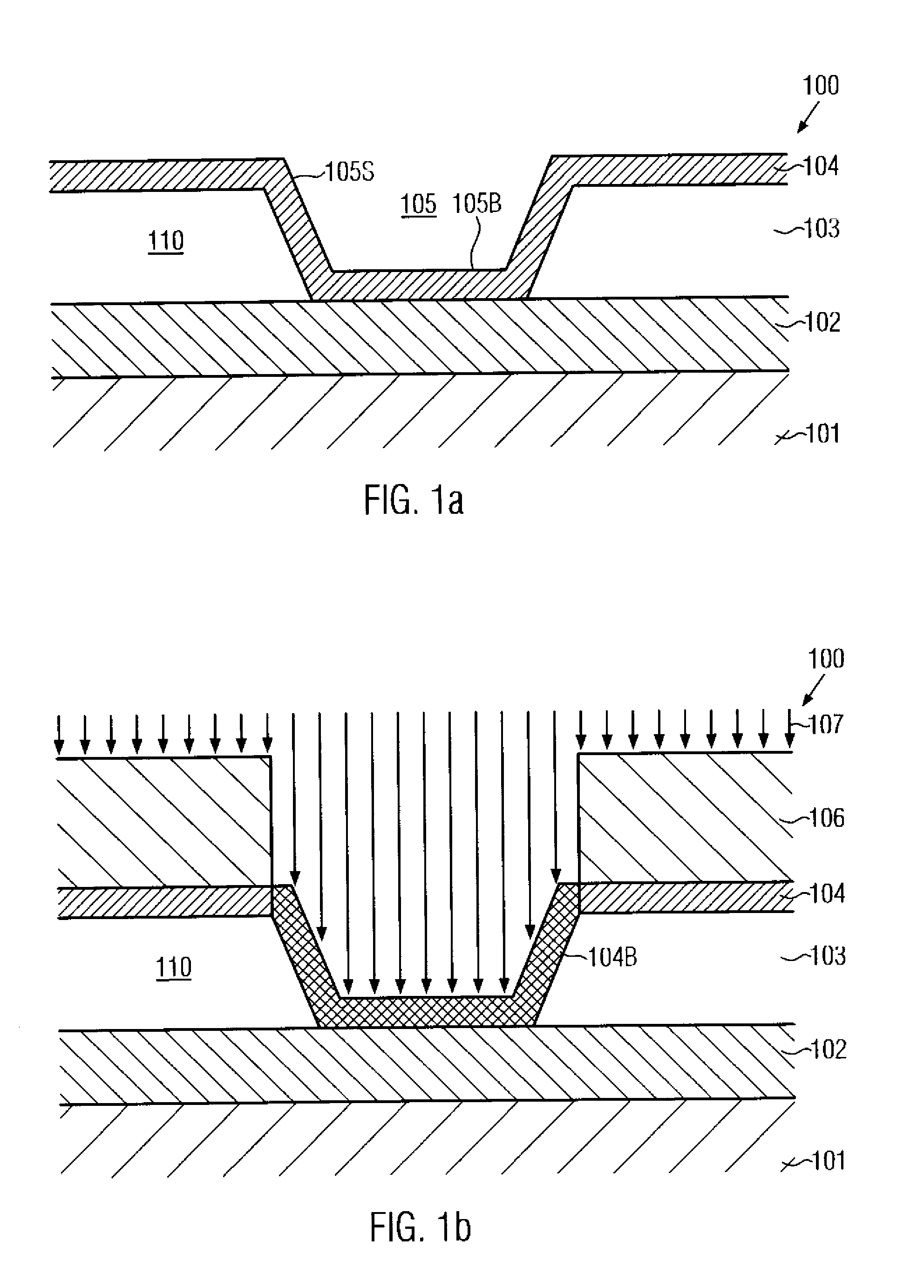
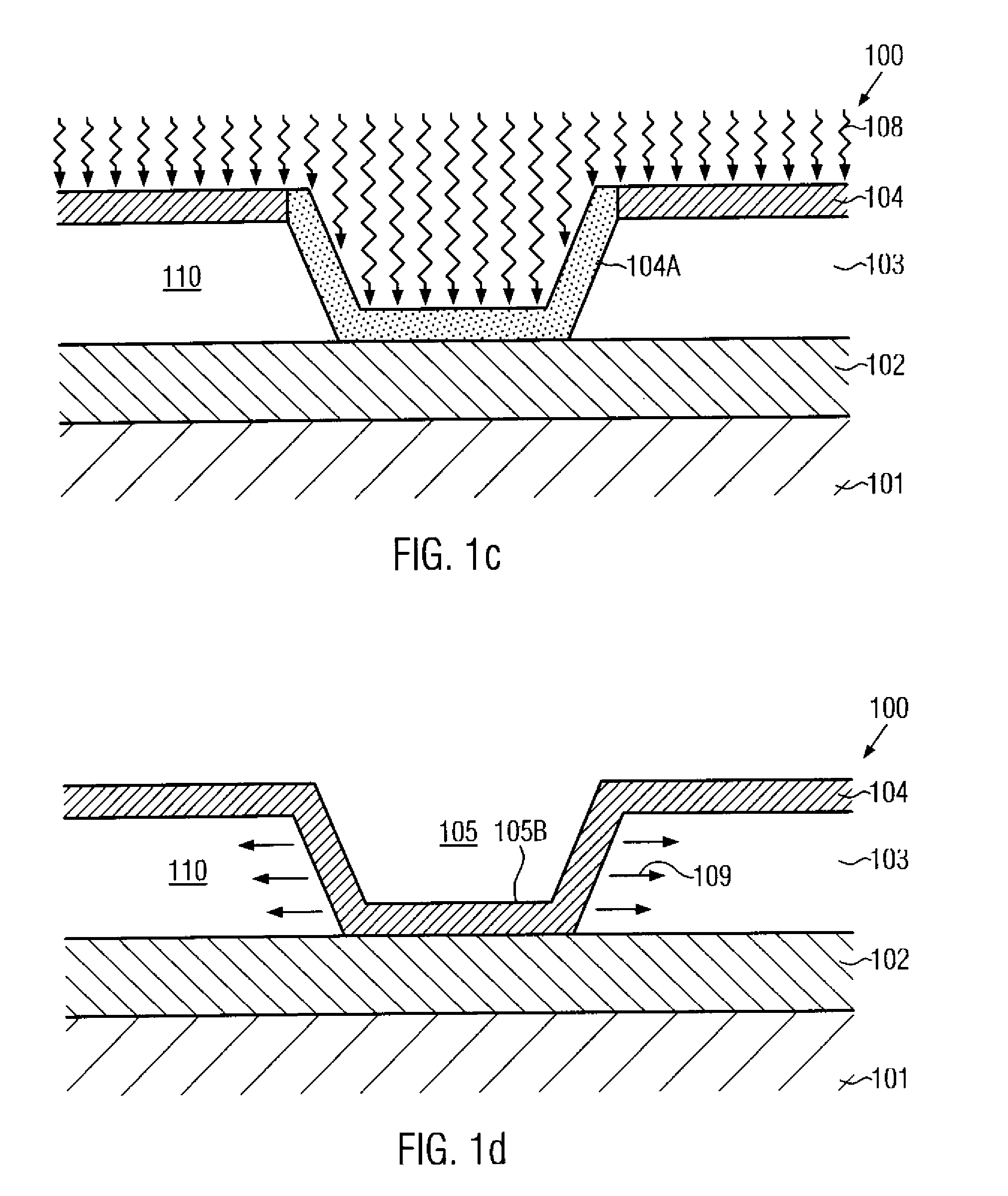
Silicon strain engineering accomplished via use of specific shallow trench isolation fill materials
InactiveUS7081395B2Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETThermal expansion
A method of forming a strained silicon layer created via a material mis-match with adjacent trench isolation (TI), regions filled with a dielectric layer comprised with either a higher, or lower thermal expansion coefficient than that of silicon, has been developed. Filling of trenches with a dielectric layer comprised with a higher thermal expansion coefficient than that of silicon results in a tensile strain in planar direction and compressive strain in vertical direction, in an adjacent silicon region. Enhanced electron mobility in channel regions of an N channel MOSFET device, and enhanced hole mobility and transit time in an N type base region of a vertical PNP bipolar device, is realized when these elements are formed in the silicon layer under tensile strain. Filling of trenches with a dielectric layer comprised with a lower thermal expansion coefficient than the thermal expansion coefficient of silicon results in a compressive strain in planar directions and tensile strain in vertical directions, in an adjacent silicon region. Enhanced hole mobility in channel regions of an P channel MOSFET device, and enhanced electron mobility and transit time in a P type base region of a vertical NPN bipolar device, is realized when these elements are formed in the silicon layer under compressive strain.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Strain engineering in three-dimensional transistors based on globally strained semiconductor base layers
ActiveUS20110101456A1Modification of charge carrier mobilityIncrease flexibilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPerformance enhancementSemiconductor materials
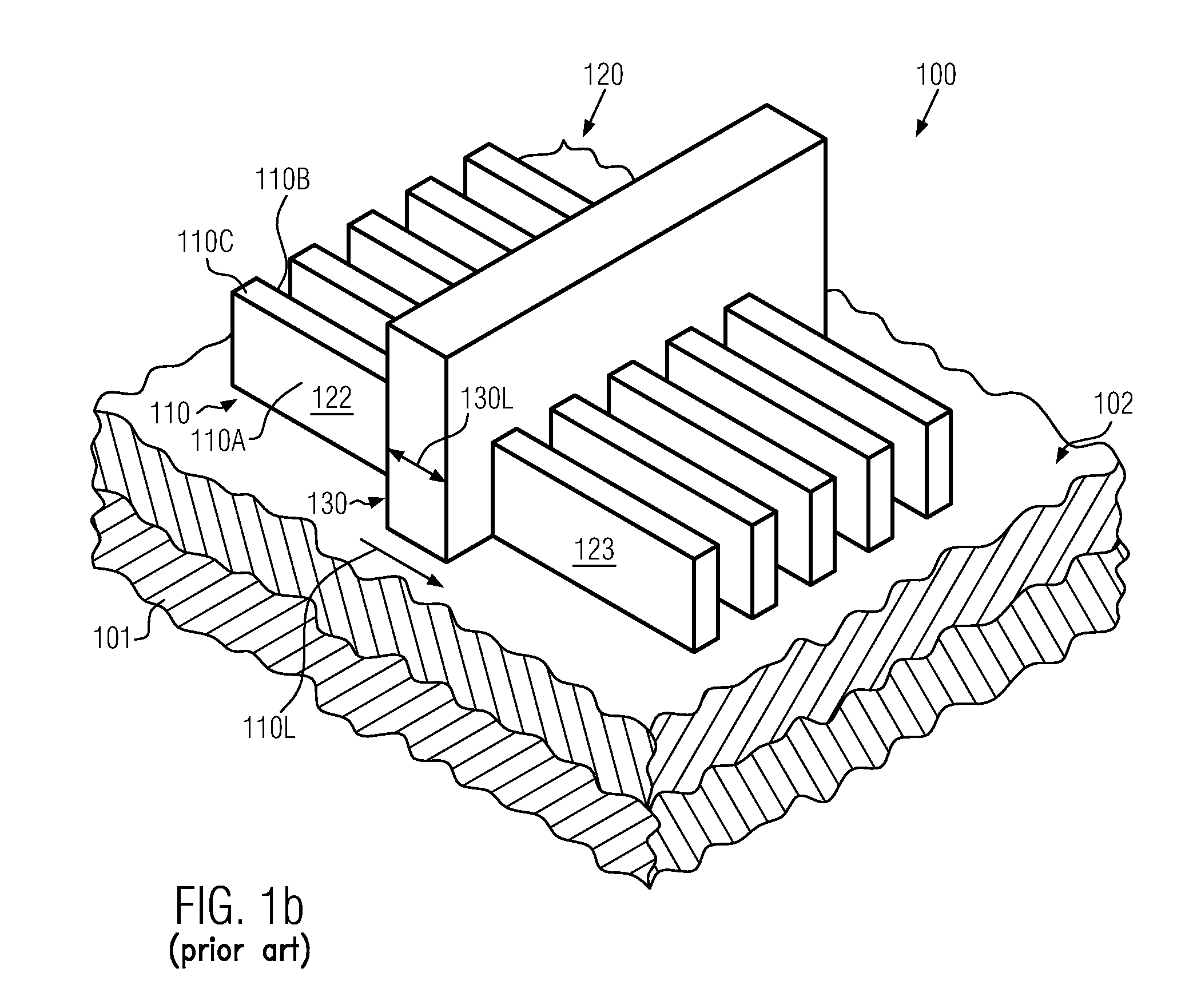
Non-planar transistors, such as FINFETs, may be formed on the basis of a globally strained semiconductor material, thereby preserving a high uniaxial strain component in the resulting semiconductor fins. In this manner, a significant performance enhancement may be achieved without adding process complexity when implementing FINFET transistors.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Strain Engineering in Three-Dimensional Transistors Based on Strained Isolation Material
InactiveUS20130181299A1Well formedSuperior strain conditionTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSource area
In a three-dimensional transistor configuration, a strain-inducing isolation material is provided, at least in the drain and source areas, thereby inducing a strain, in particular at and in the vicinity of the PN junctions of the three-dimensional transistor. In this case, superior transistor performance may be achieved, while in some illustrative embodiments even the same type of internally stressed isolation material may result in superior transistor performance of P-channel transistors and N-channel transistors.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
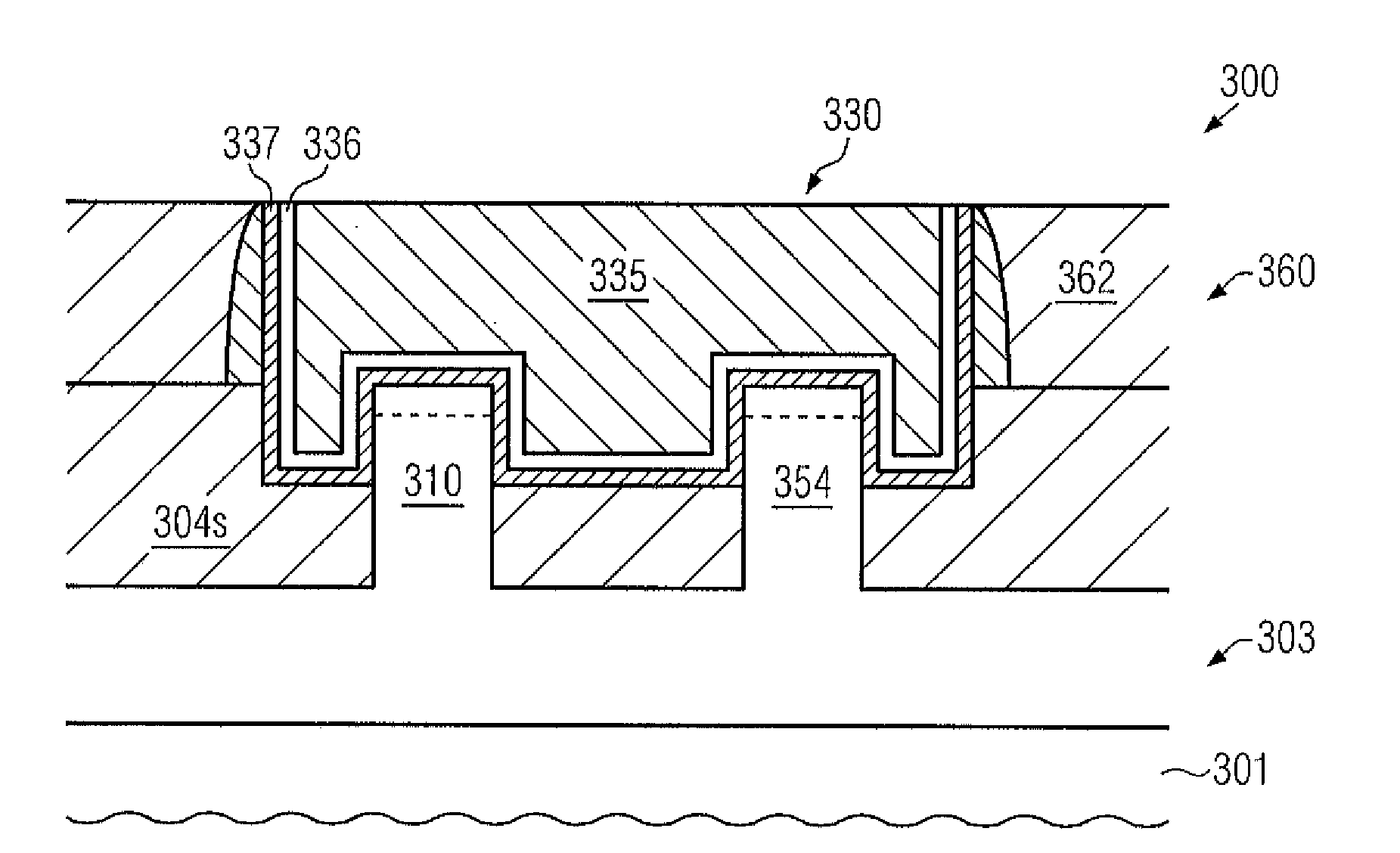
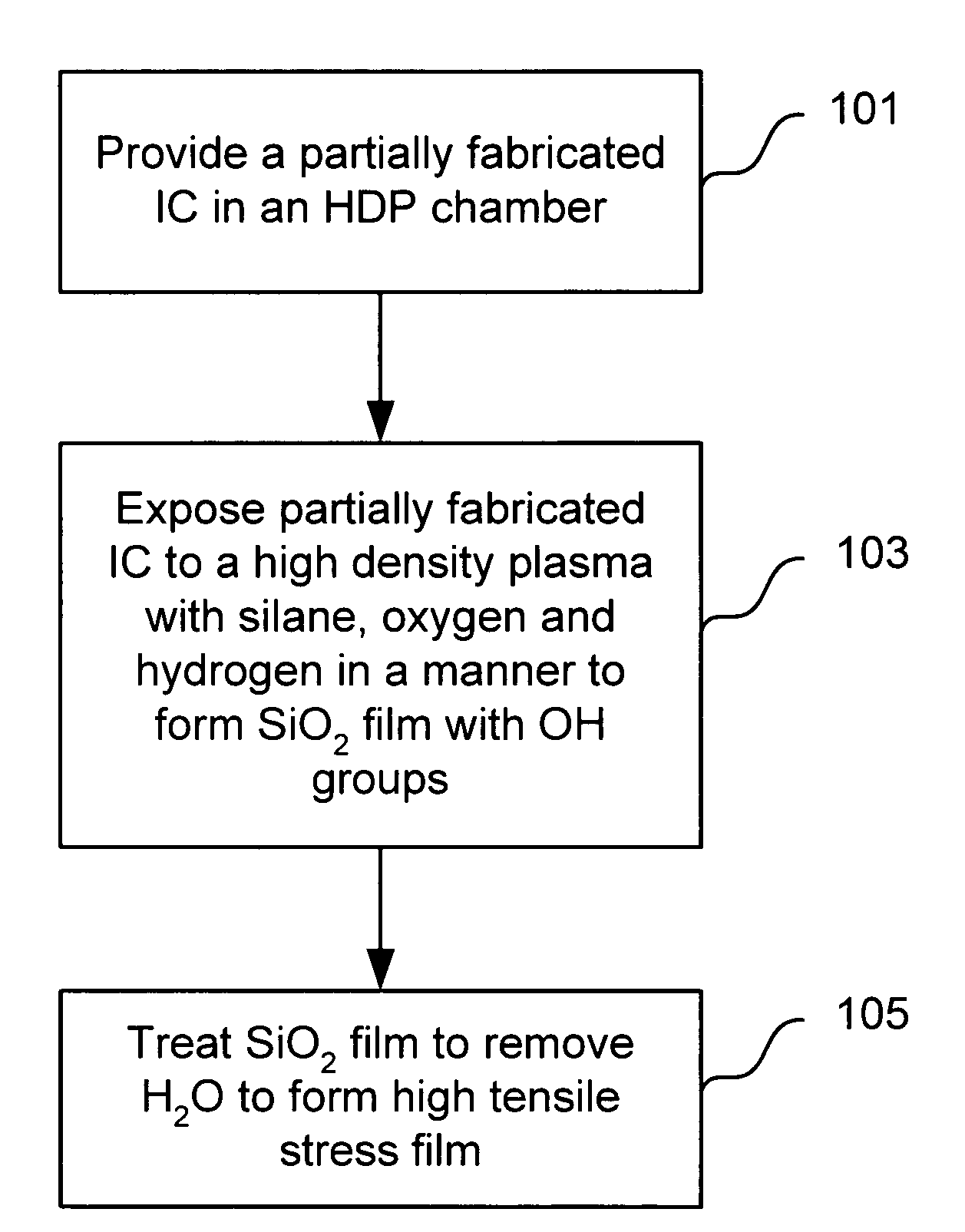
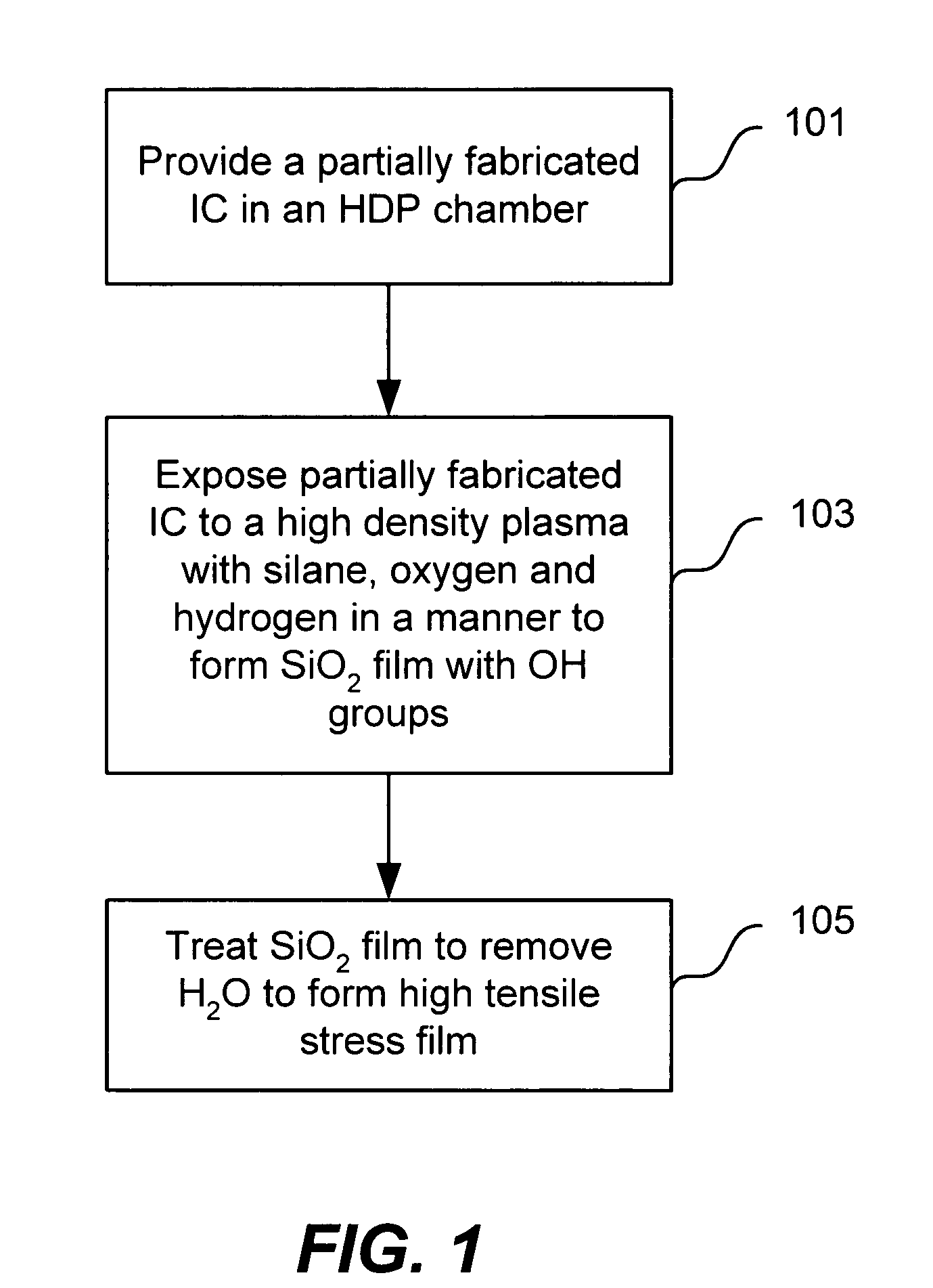
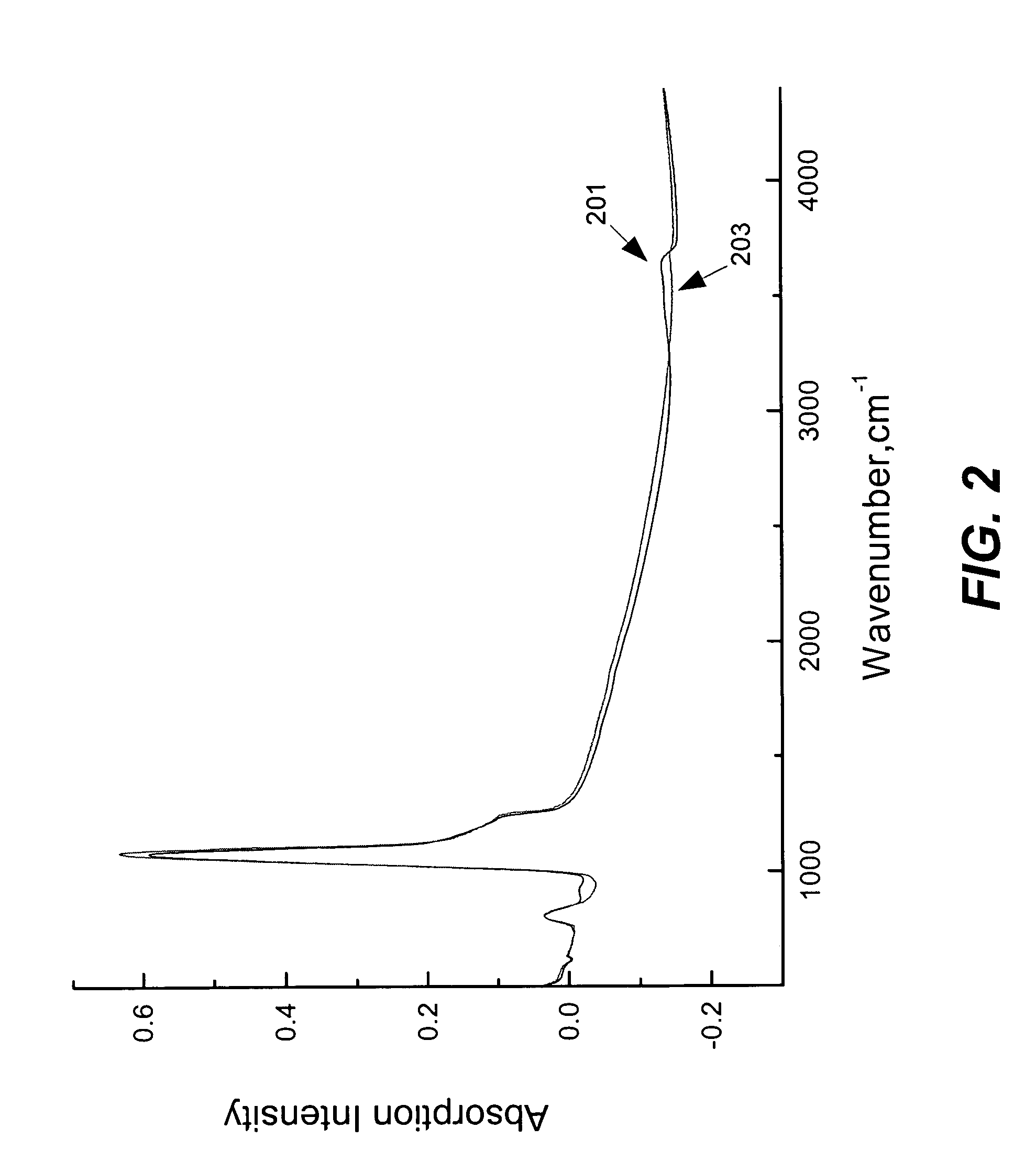
Strain engineering-HDP thin film with tensile stress for FEOL and other applications
High density plasma (HDP) techniques form high tensile stress silicon oxide films. The HDP techniques use low enough temperatures to deposit high tensile stress silicon oxide films in transistor architectures and fabrication processes effective for generating channel strain without adversely impacting transistor integrity. Methods involve a two phase process: a HDP deposition phase, wherein silanol groups are formed in the silicon oxide film, and a bond reconstruction phase, wherein water is removed and tensile stress is induced in the silicon oxide film. Transistor strain can be generated in NMOS or PMOS devices using strategic placement of the high tensile stress silicon oxide. Example applications include high tensile stress silicon oxides for use in shallow trench isolation structures, pre-metal dielectric layer and silicon on insulator substrates.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Strain engineering in three-dimensional transistors based on globally strained semiconductor base layers
ActiveUS8247275B2Efficient “patterningModification of the charge carrier mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPerformance enhancementSemiconductor materials
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
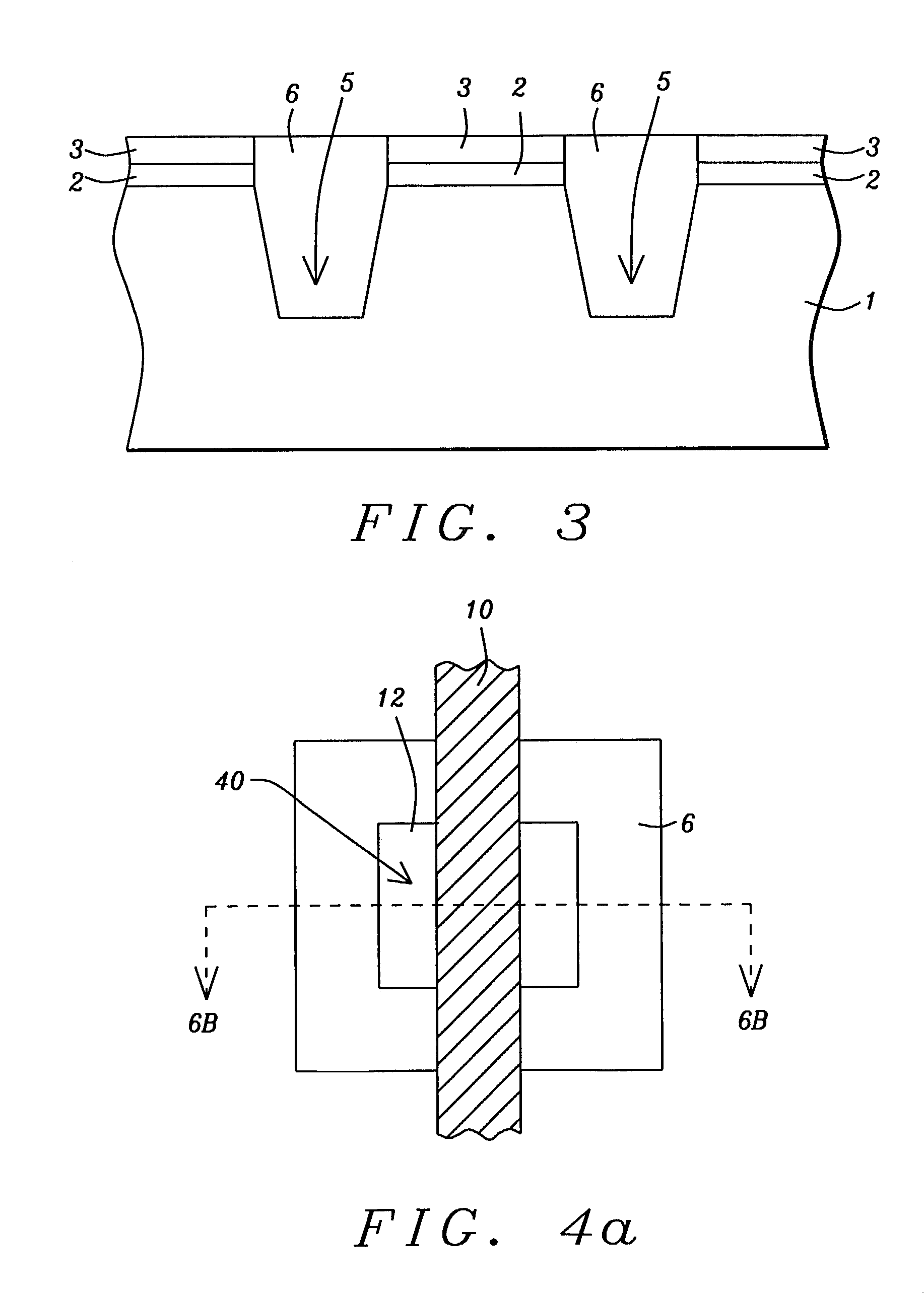
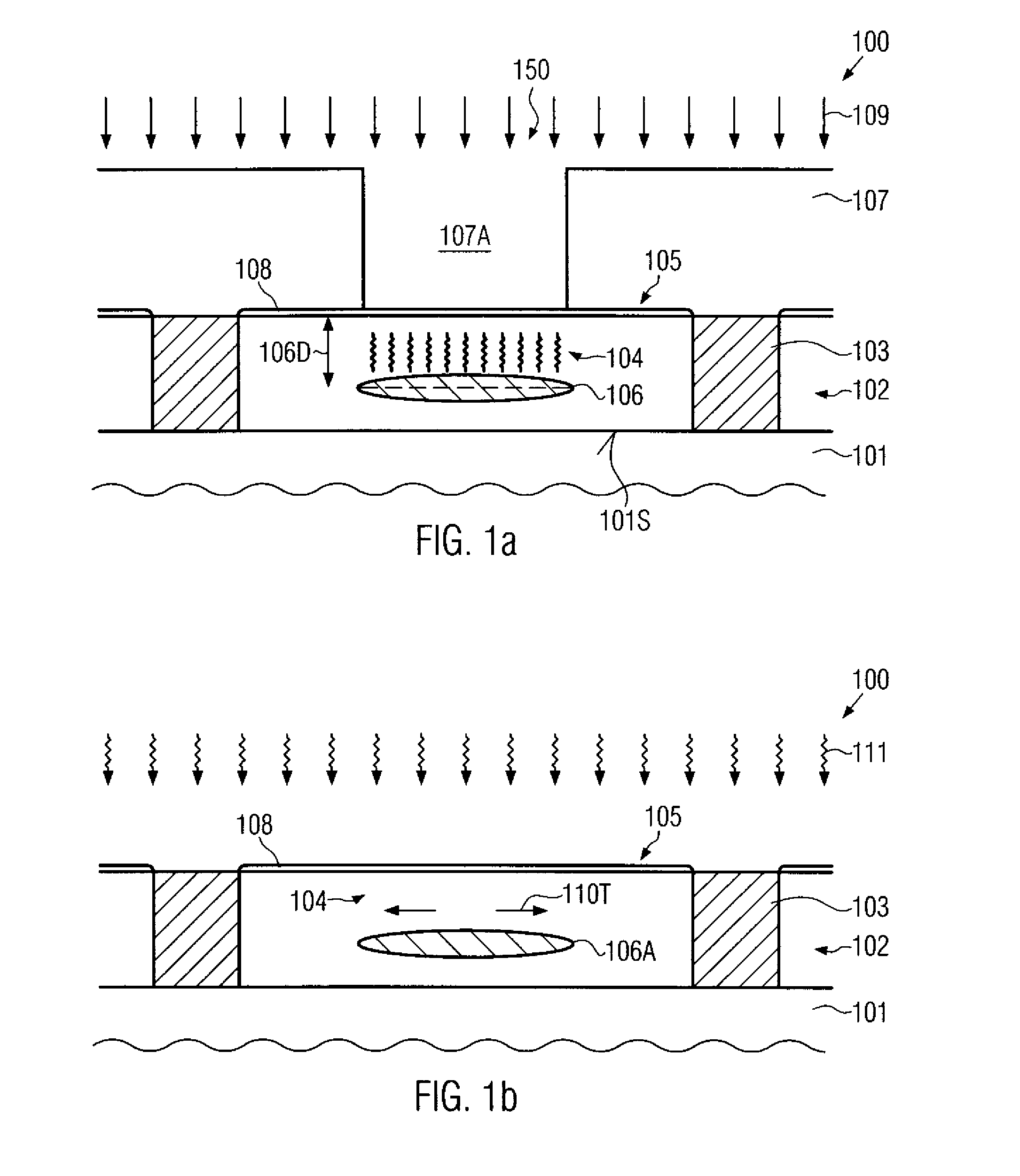
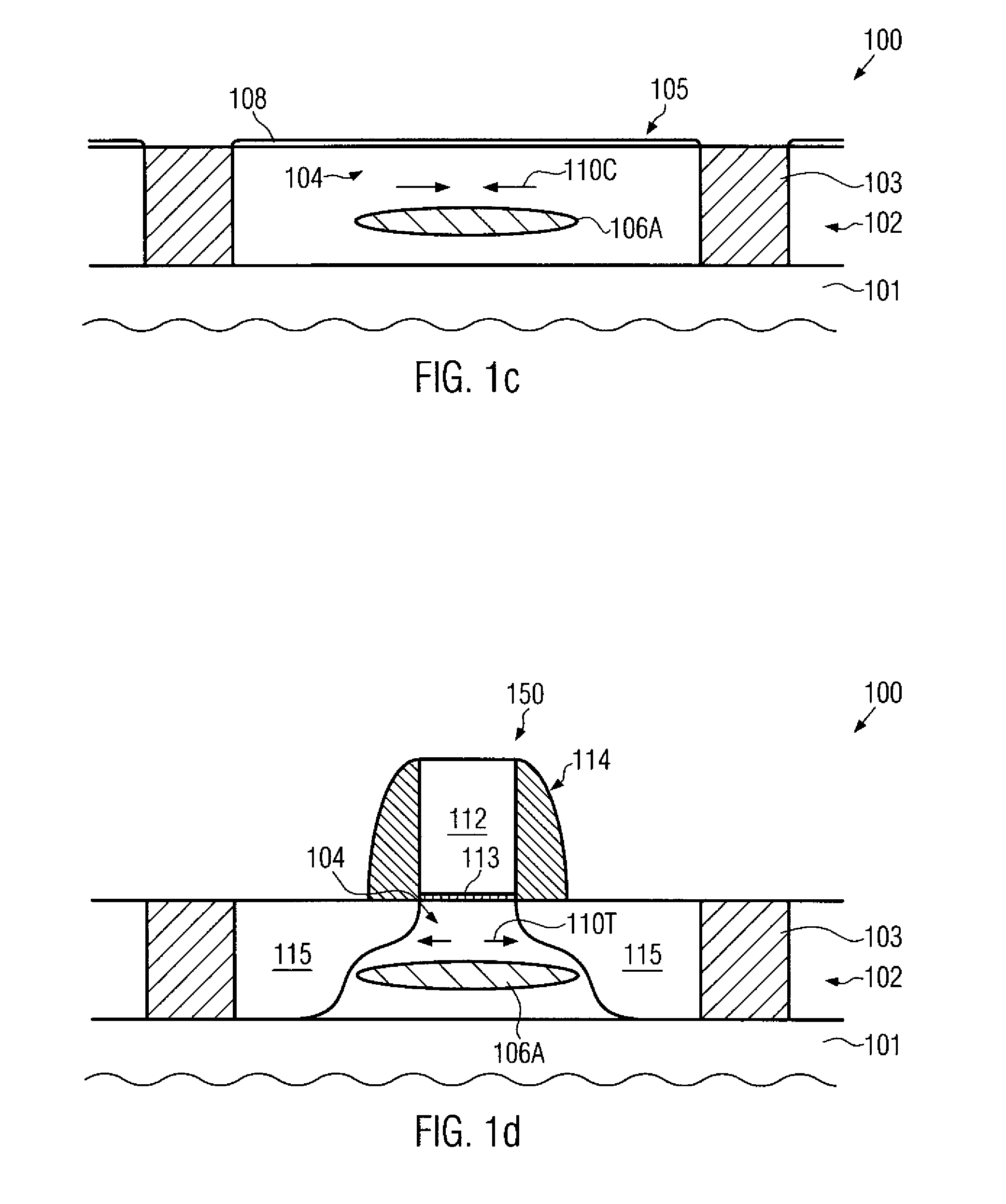
Technique for forming an isolation trench as a stress source for strain engineering
InactiveUS20070155121A1Increase compressive stressEfficient stress engineeringSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIon bombardmentEngineering
By forming a non-oxidizable liner in an isolation trench and selectively modifying the liner within the isolation trench, the stress characteristics of the isolation trench may be adjusted. In one embodiment, a high compressive stress may be obtained by treating the liner with an ion bombardment and subsequently exposing the device to an oxidizing ambient at elevated temperatures, thereby incorporating silicon dioxide into the non-oxidizable material. Hence, an increased compressive stress may be generated within the non-oxidizable layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Process for improved protein expression by strain engineering
ActiveUS20140162279A1Increasing recombinant protein productionReduce energy consumptionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyFusion Protein Expression
This invention is a process for improving the production levels of recombinant proteins or peptides or improving the level of active recombinant proteins or peptides expressed in host cells. The invention is a process of comparing two genetic profiles of a cell that expresses a recombinant protein and modifying the cell to change the expression of a gene product that is upregulated in response to the recombinant protein expression. The process can improve protein production or can improve protein quality, for example, by increasing solubility of a recombinant protein.
Owner:PFENEX
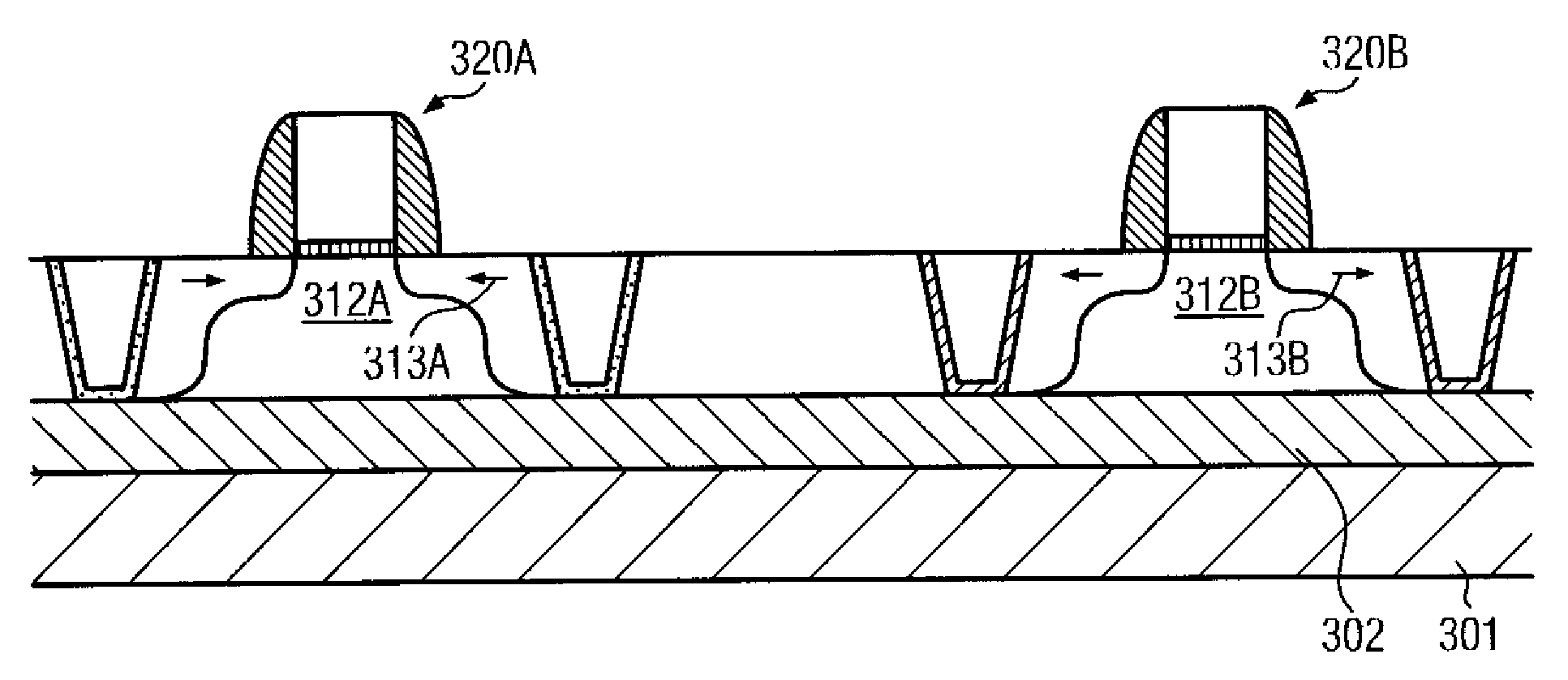
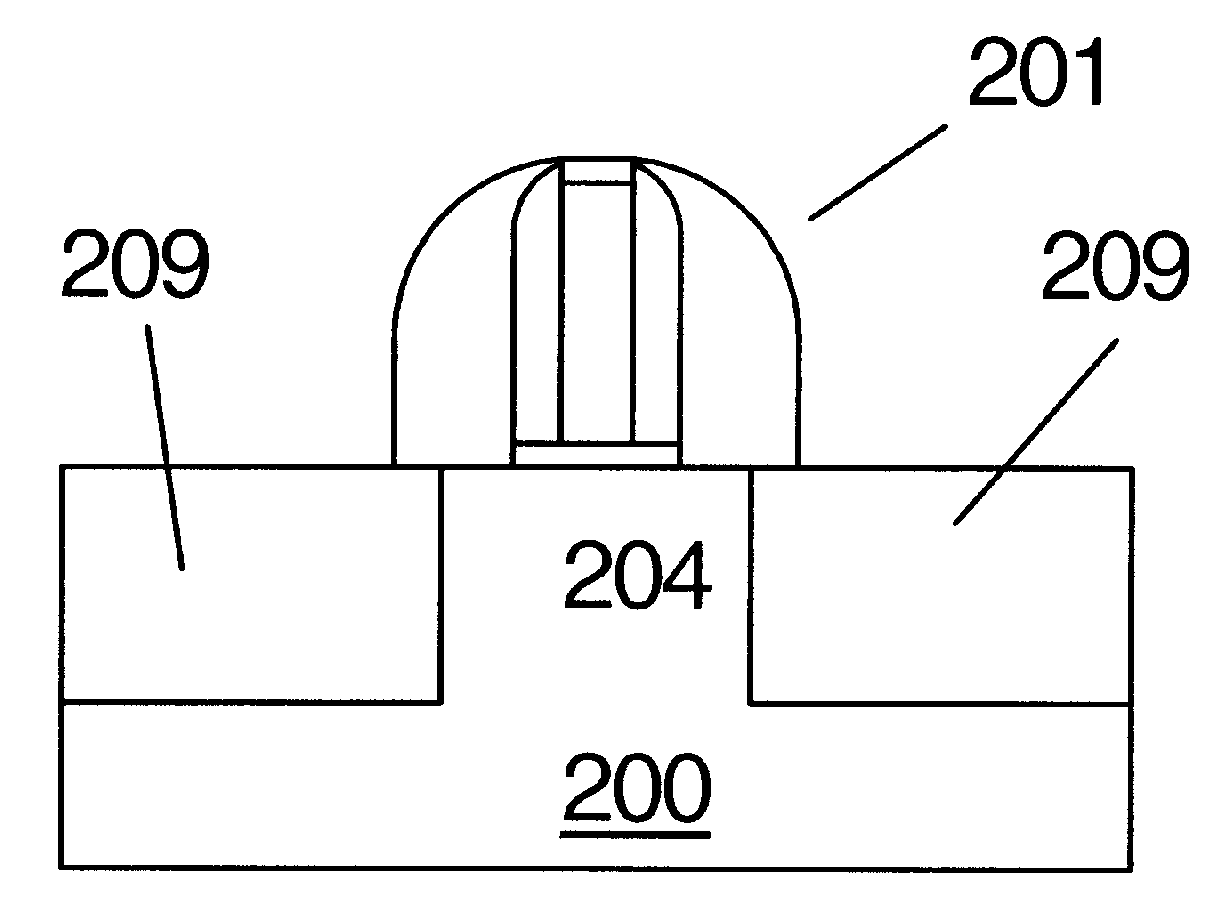
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102623487AEliminate voidsHigh carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricEdge effects
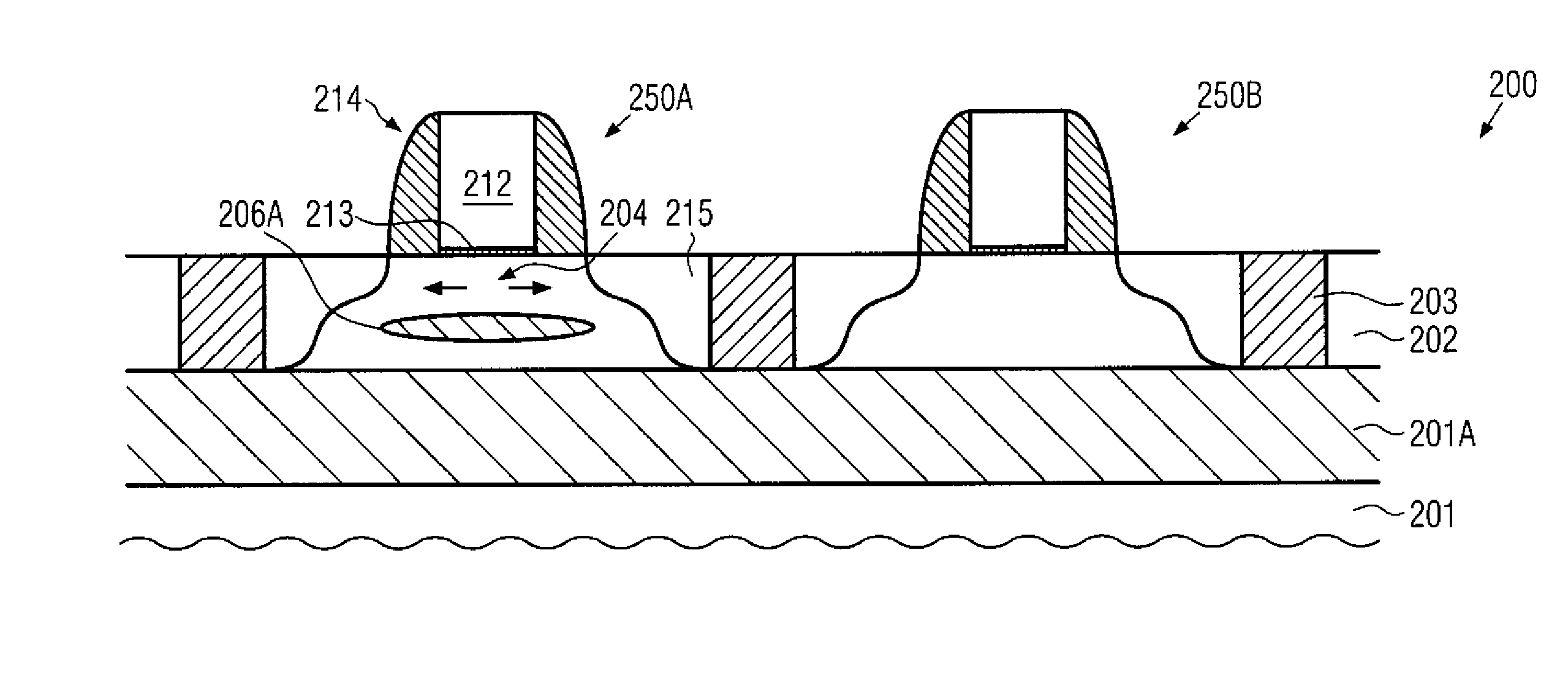
The invention provides a semiconductor device, comprising: a substrate; a shallow trench isolation means embedded in the substrate, and forming at least one open area; a channel region positioned in the open area; a gate stack, positioned on top of the channel region, comprising a gate dielectric layer and a gate electrode layer; a source-drain area, positioned on the two sides of the channel region, comprising a stress layer for providing a strain to the channel region. There is a liner between the shallow trench isolation means and the stress layer. By inserting a liner of a material same or similar to that of the stress layer of the source-drain area between the STI and the stress layer of the source-drain area, wherein the liner acts asa crystal seed layer or a nucleating layer for epitaxial growth an edge effect of STI during the source-drain area process is eliminated, that is a gap between the STI and the stress layer of the source-drain area is eliminated, the reduction of the channel stress caused by the source-drain area is prevented, and a mobility of the current carriers of the metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) device is improved, thus improving a driving capability of the device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
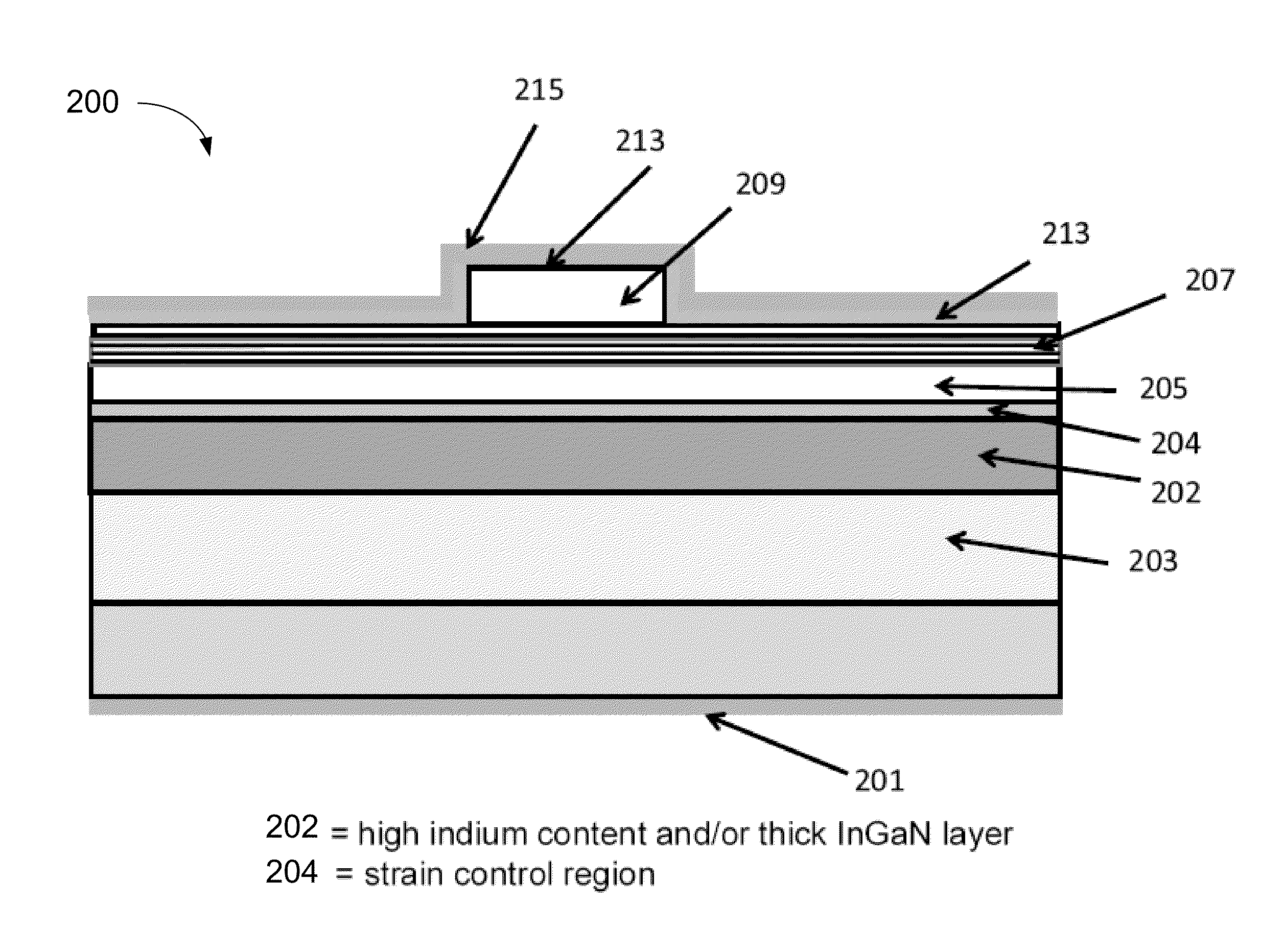
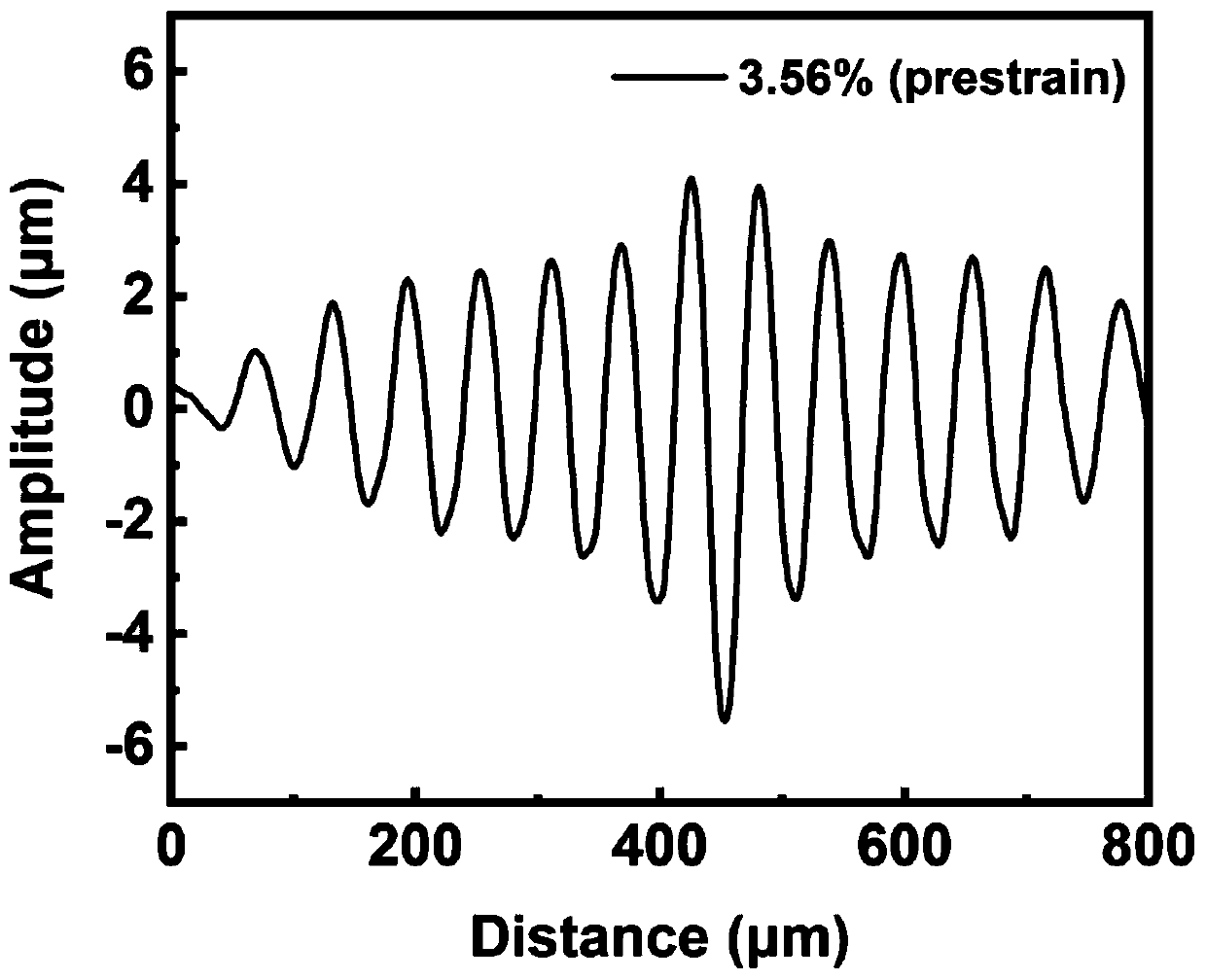
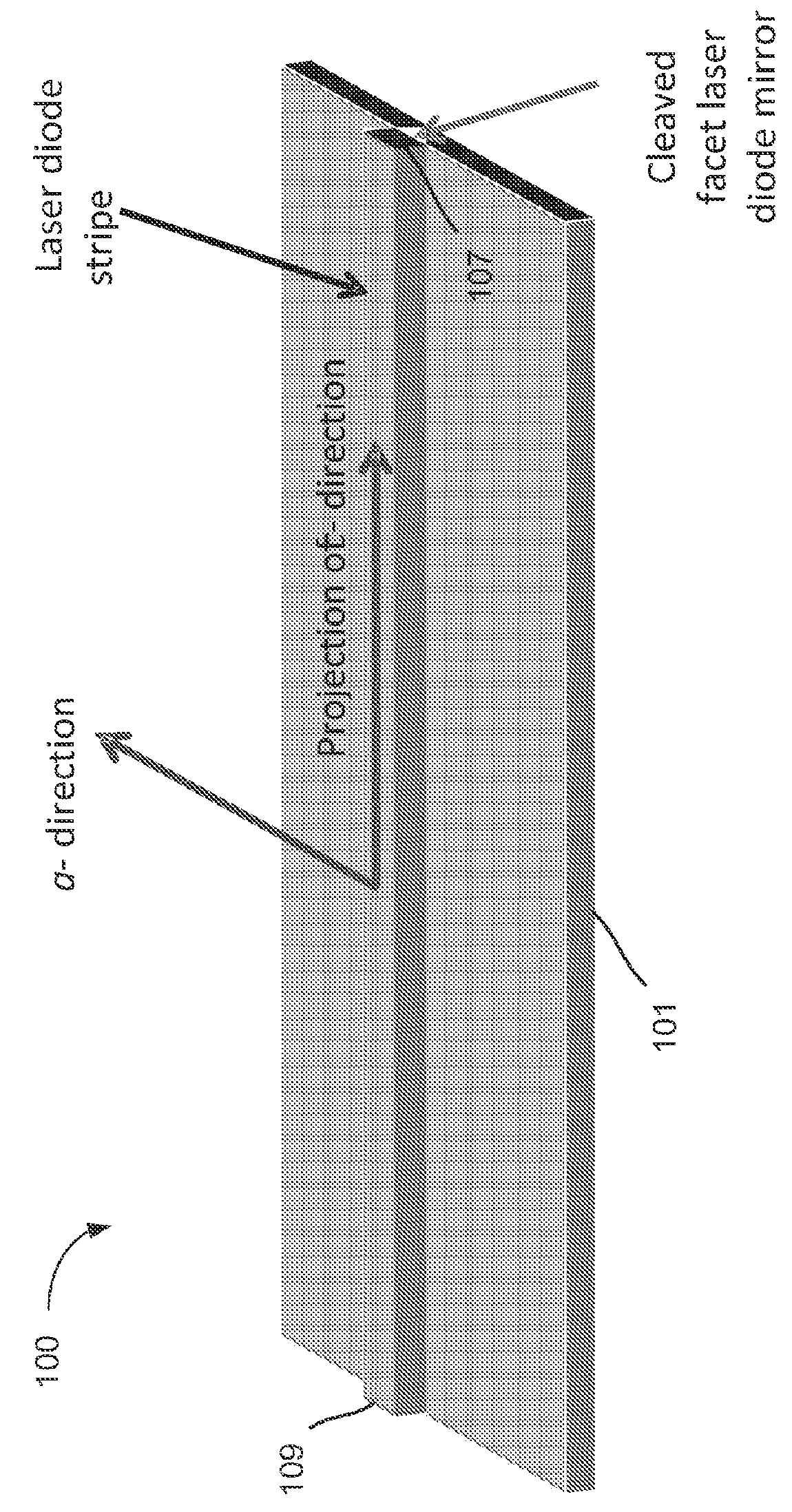
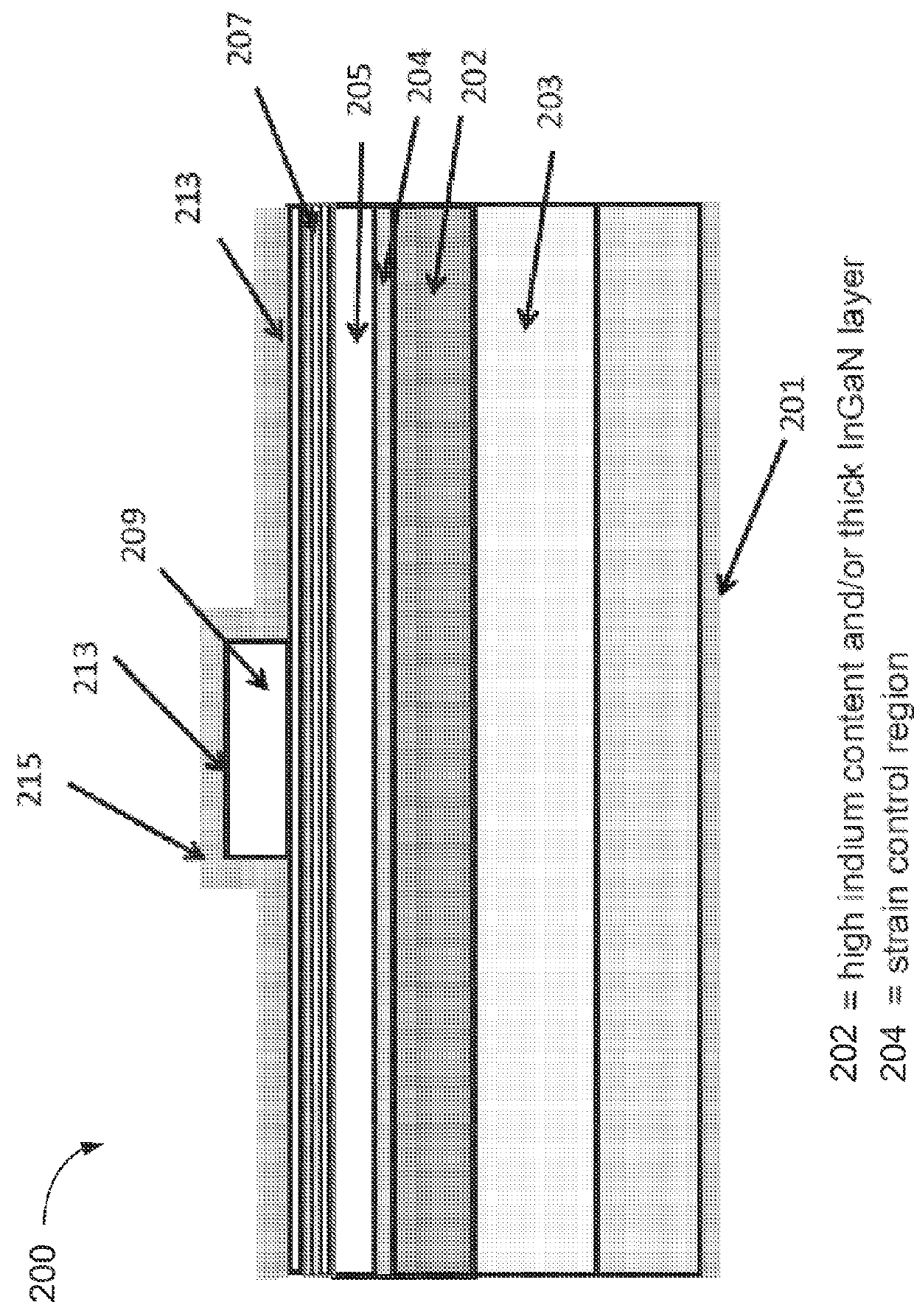
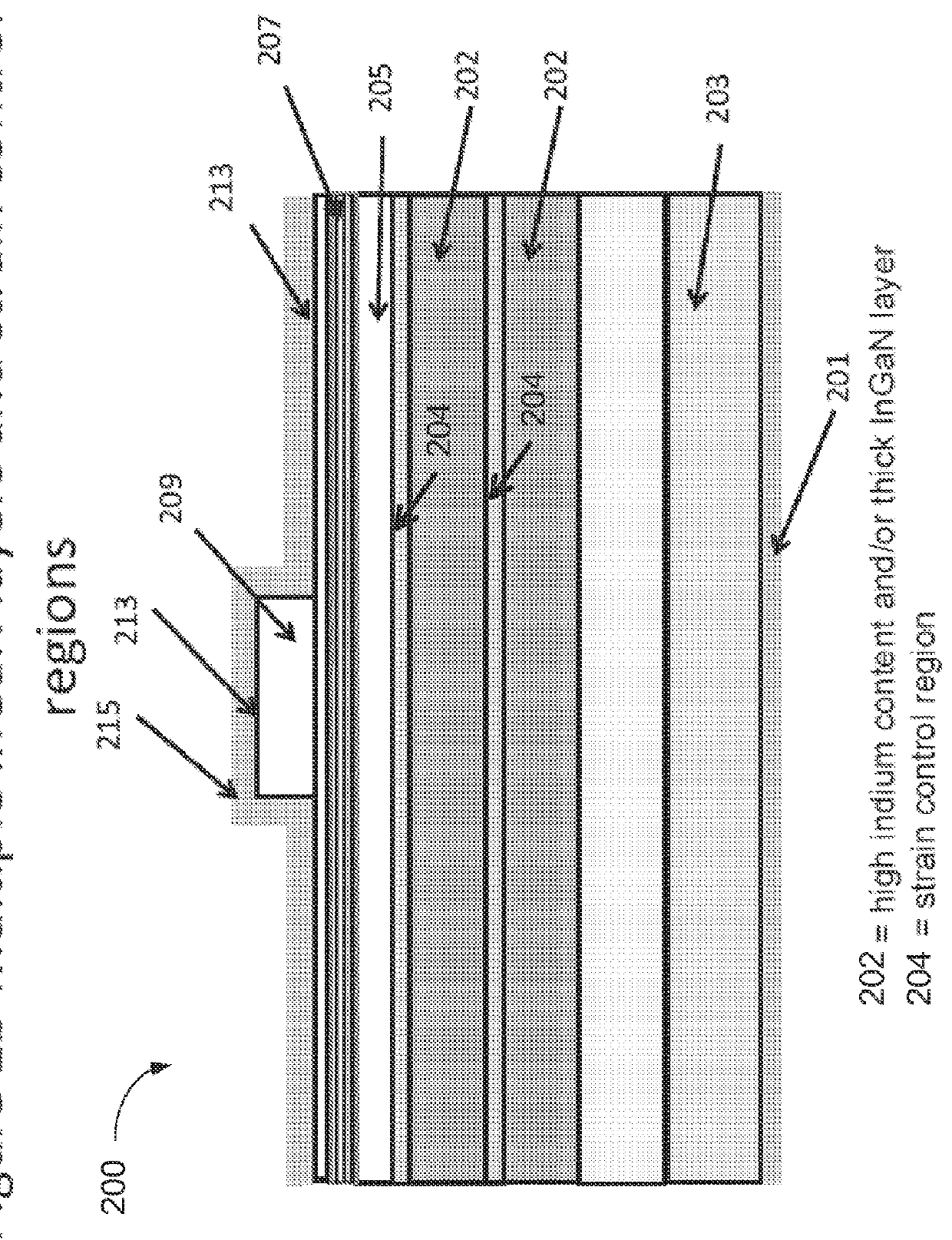
Method of strain engineering and related optical device using a gallium and nitrogen containing active region
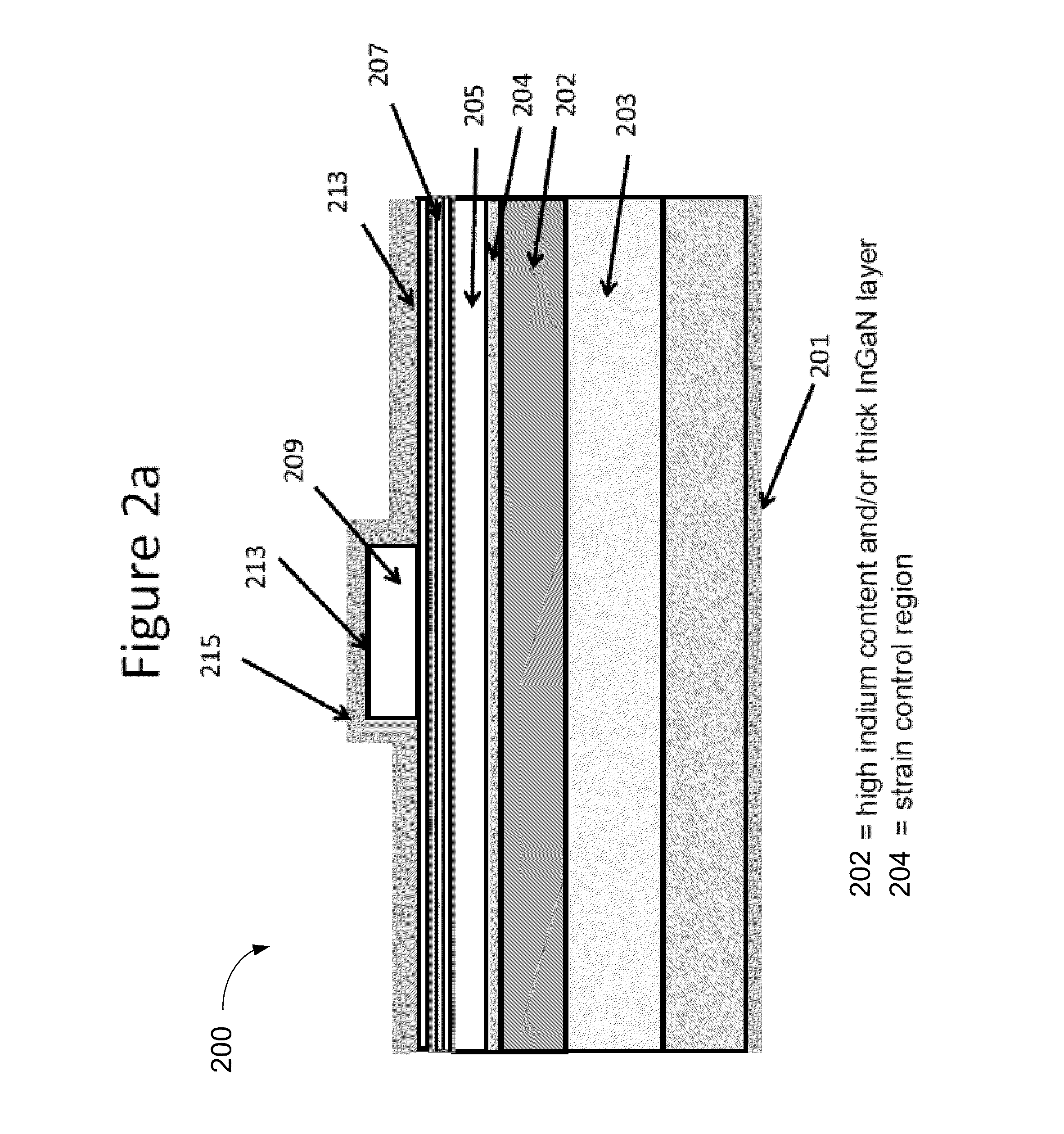
ActiveUS8816319B1Easy to operateEfficient and reliableSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMasersQuantum wellNitrogen
An optical device has a gallium and nitrogen containing substrate including a surface region and a strain control region, the strain control region being configured to maintain a quantum well region within a predetermined strain state. The device also has a plurality of quantum well regions overlying the strain control region.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Superior fill conditions in a replacement gate approach by using a tensile stressed overlayer
ActiveUS20110049640A1Easy to shapeReliable filTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStrain engineeringSemiconductor
In a replacement gate approach for forming high-k metal gate electrodes in semiconductor devices, a tapered configuration of the gate openings may be accomplished by using a tensile stressed dielectric material provided laterally adjacent to the gate electrode structure. Consequently, superior deposition conditions may be achieved while the tensile stress component may be efficiently used for the strain engineering in one type of transistor. Furthermore, an additional compressively stressed dielectric material may be applied after providing the replacement gate electrode structures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
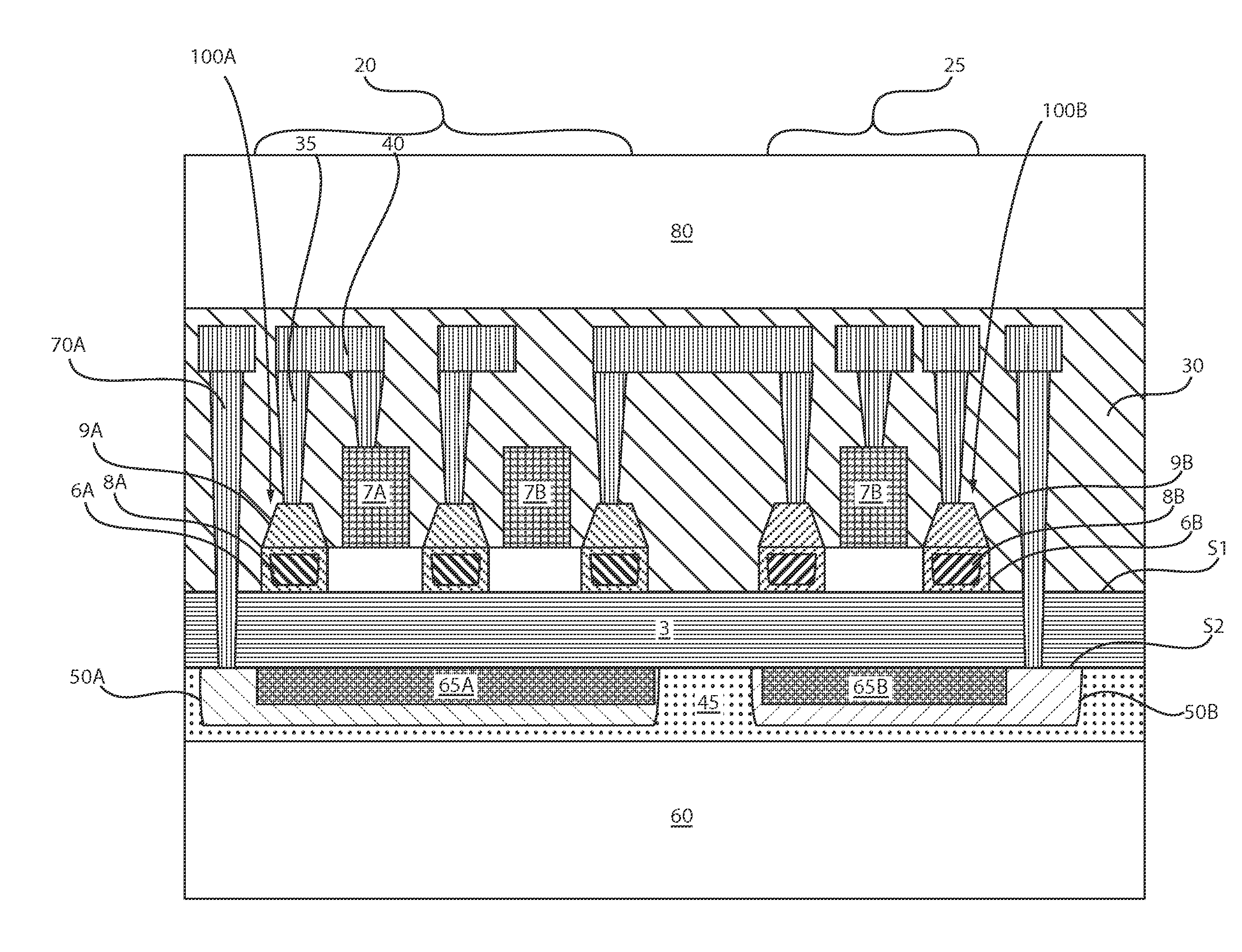
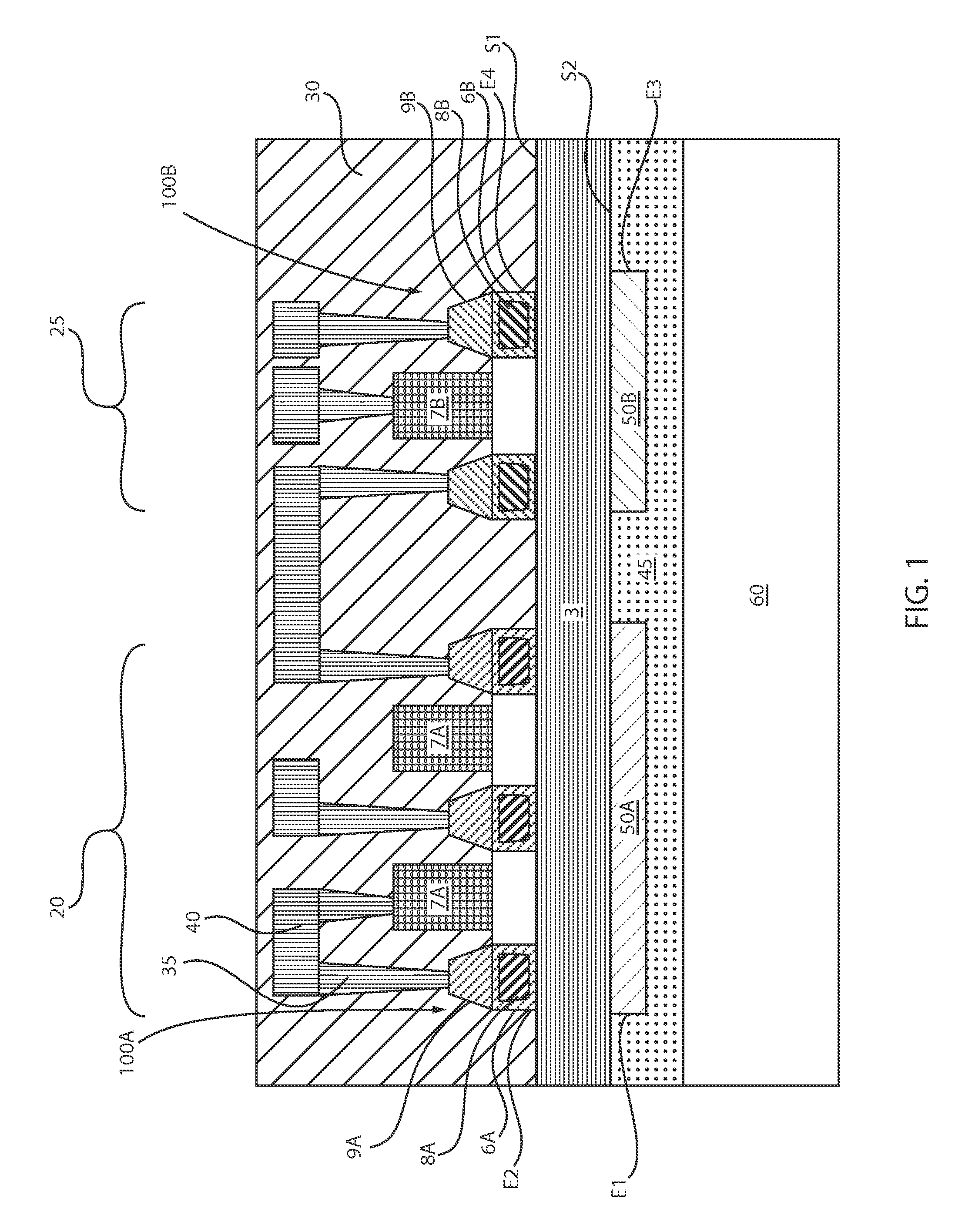
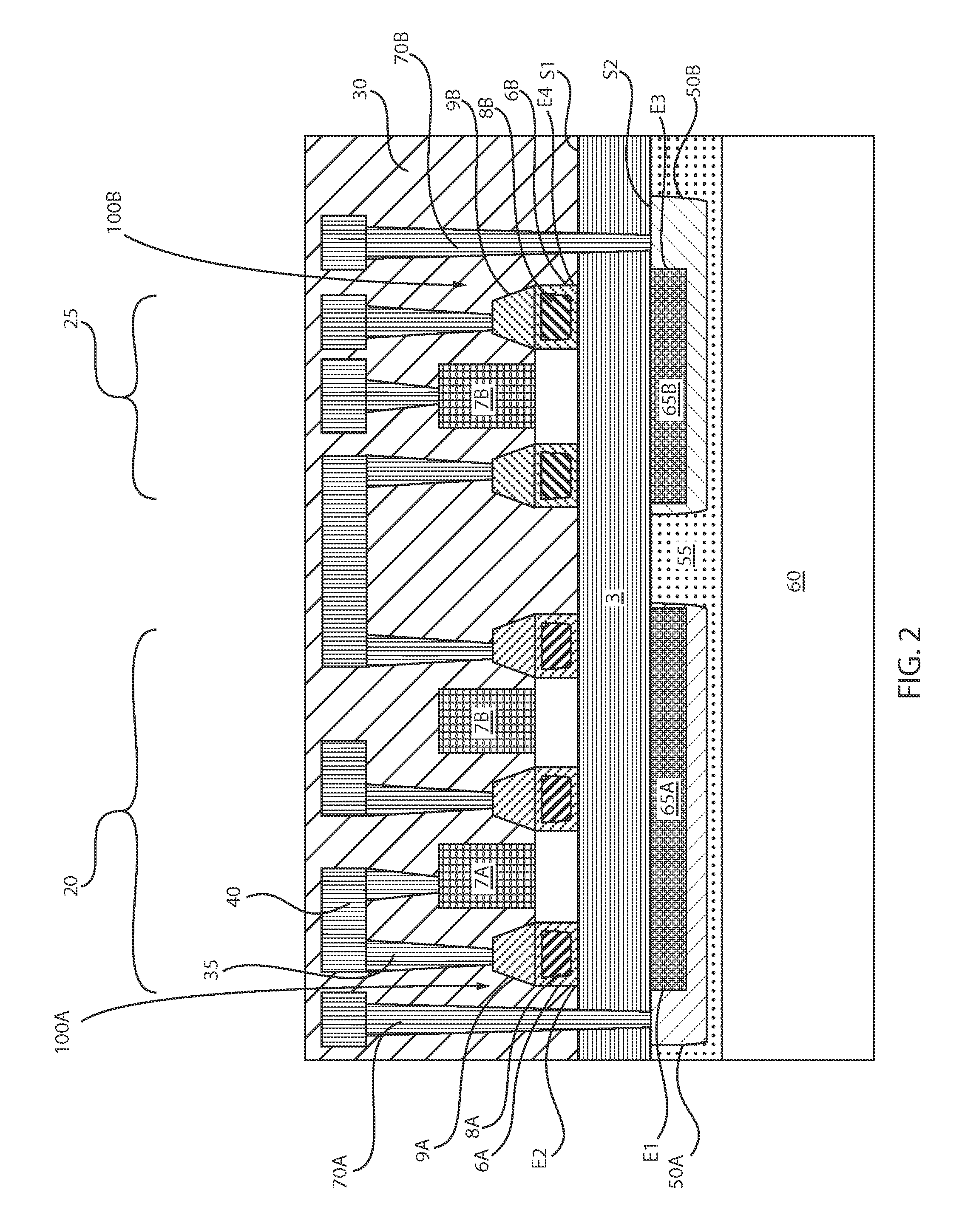
Strain engineering in back end of the line
A semiconductor device including at least one semiconductor device on a first surface of a dielectric layer, and at least one stressor structure having an intrinsic stress on a second surface of the dielectric layer. The at least one semiconductor device and the at least one stressor structure are present on opposing sides of the dielectric layer. The at least one stressor structure induces a stress on the at least one semiconductor device opposite the intrinsic stress.
Owner:IBM CORP
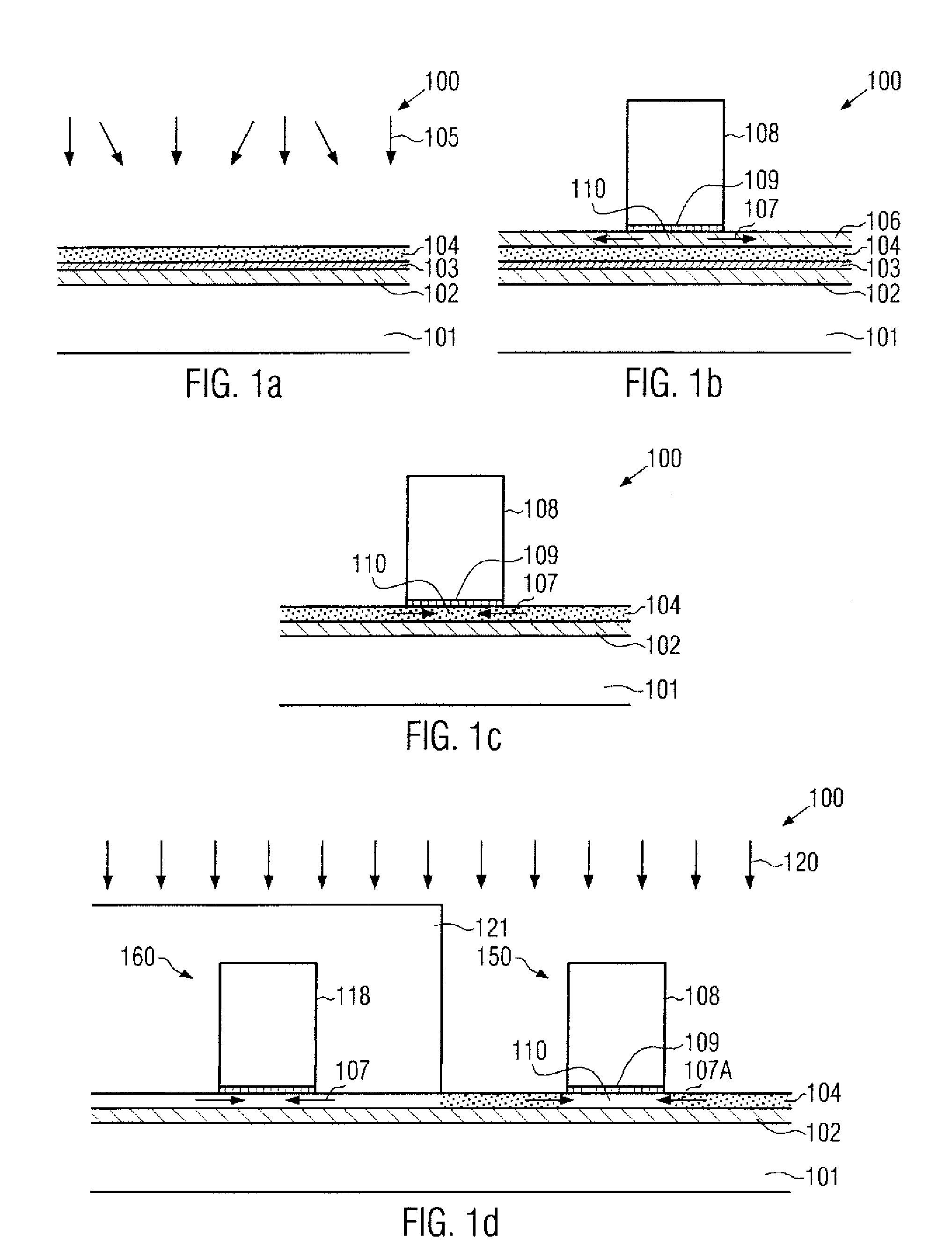
Technique for strain engineering in silicon-based transistors by using implantation techniques for forming a strain-inducing layer under the channel region
InactiveUS20080296692A1Improve compatibilityReduce process complexityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsDevice material
By incorporating a semiconductor species having the same valence and a different covalent radius compared to the base semiconductor material on the basis of an ion implantation process, a strain-inducing material may be positioned locally within a transistor at an appropriate manufacturing stage, thereby substantially not contributing to overall process complexity and also not affecting the further processing of the semiconductor device. Hence, a high degree of flexibility may be provided with respect to enhancing transistor performance in a highly local manner.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Epitaxy of Silicon-Carbon Substitutional Solid Solutions by Ultra-Fast Annealing of Amorphous Material
InactiveUS20070238267A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectronCmos process
Expitaxial substitutional solid solutions of silicon carbon can be obtained by an ultrafast anneal of an amorphous carbon-containing silicon material. The anneal is performed at a temperature above the recrystallization point, but below the melting point of the material and preferably lasts for less than 100 milliseconds in this temperature regime. The anneal is preferably a flash anneal or laser anneal. This approach is able to produce epitaxial silicon and carbon-containing materials with a substantial portion of the carbon atoms at substitutional lattice positions. The approach is especially useful in CMOS processes and other electronic device manufacture where the presence of epitaxial Si1−yCy, y<0.1 is desired for strain engineering or bandgap engineering.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
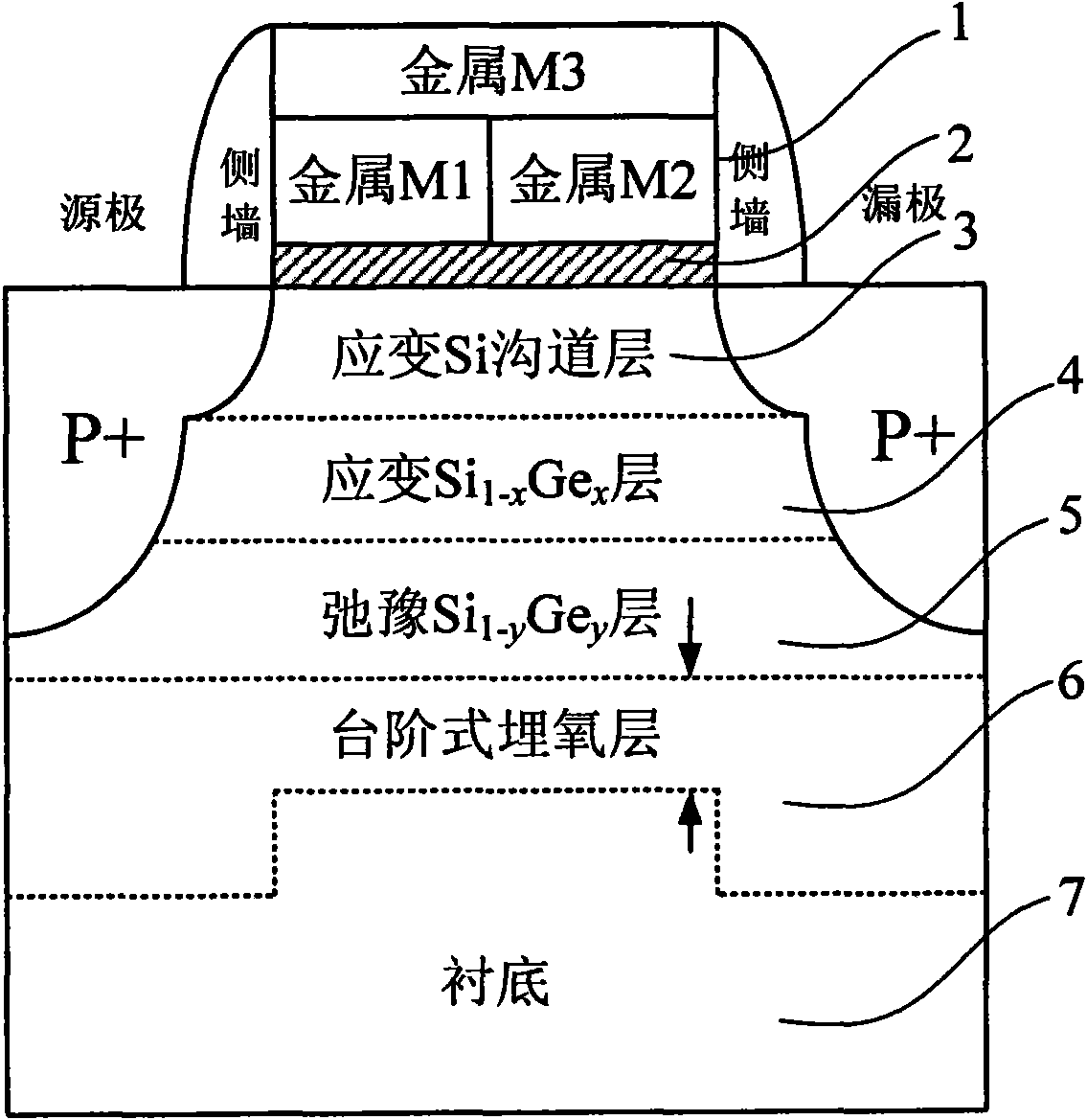
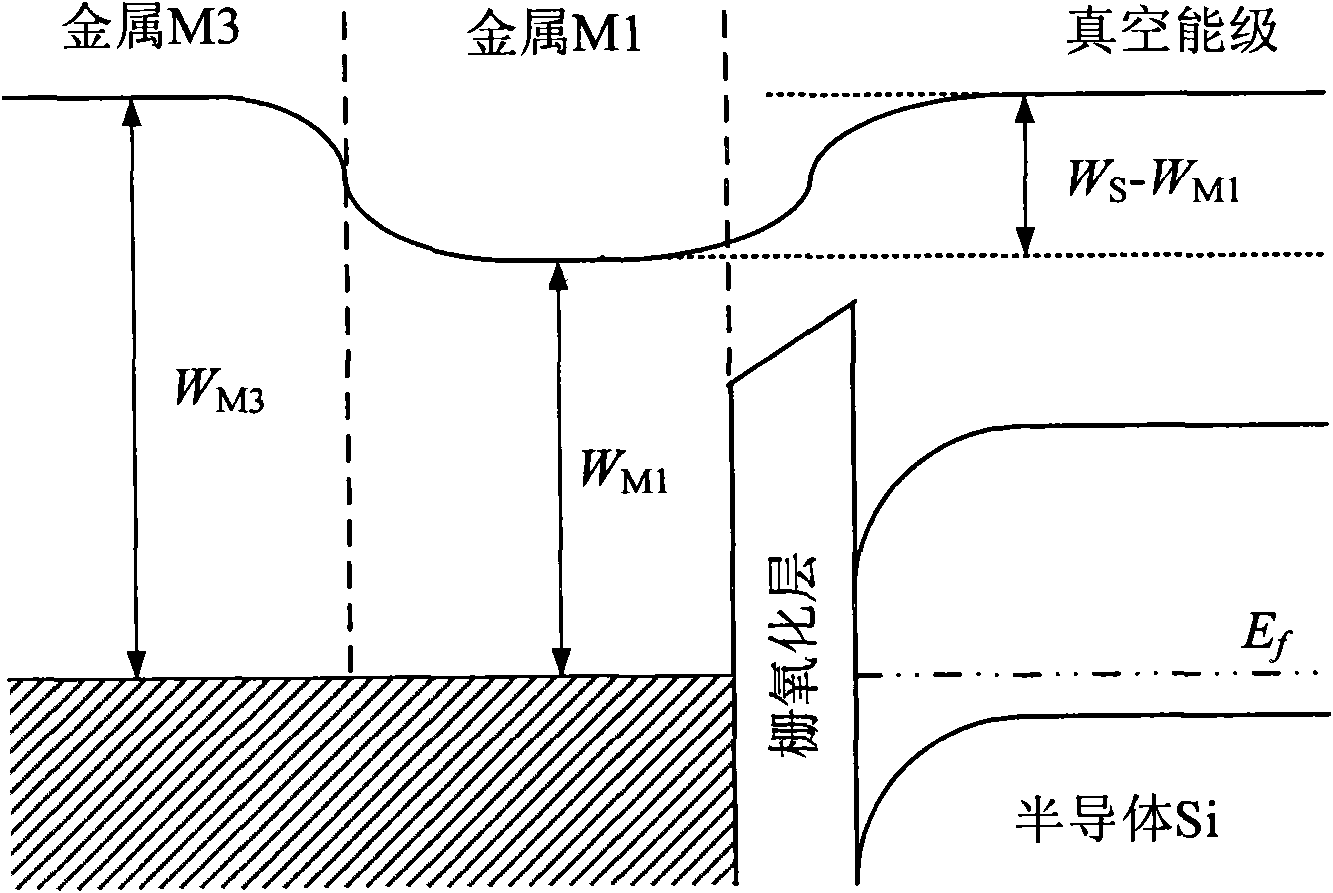
Heterogeneous metal stacked grid strained silicon-germanium on insulator p-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect tube (SSGOI pMOSFET) device structure
InactiveCN102214694AImprove shipping speedImprove transmission efficiencySemiconductor devicesInsulation layerOxygen
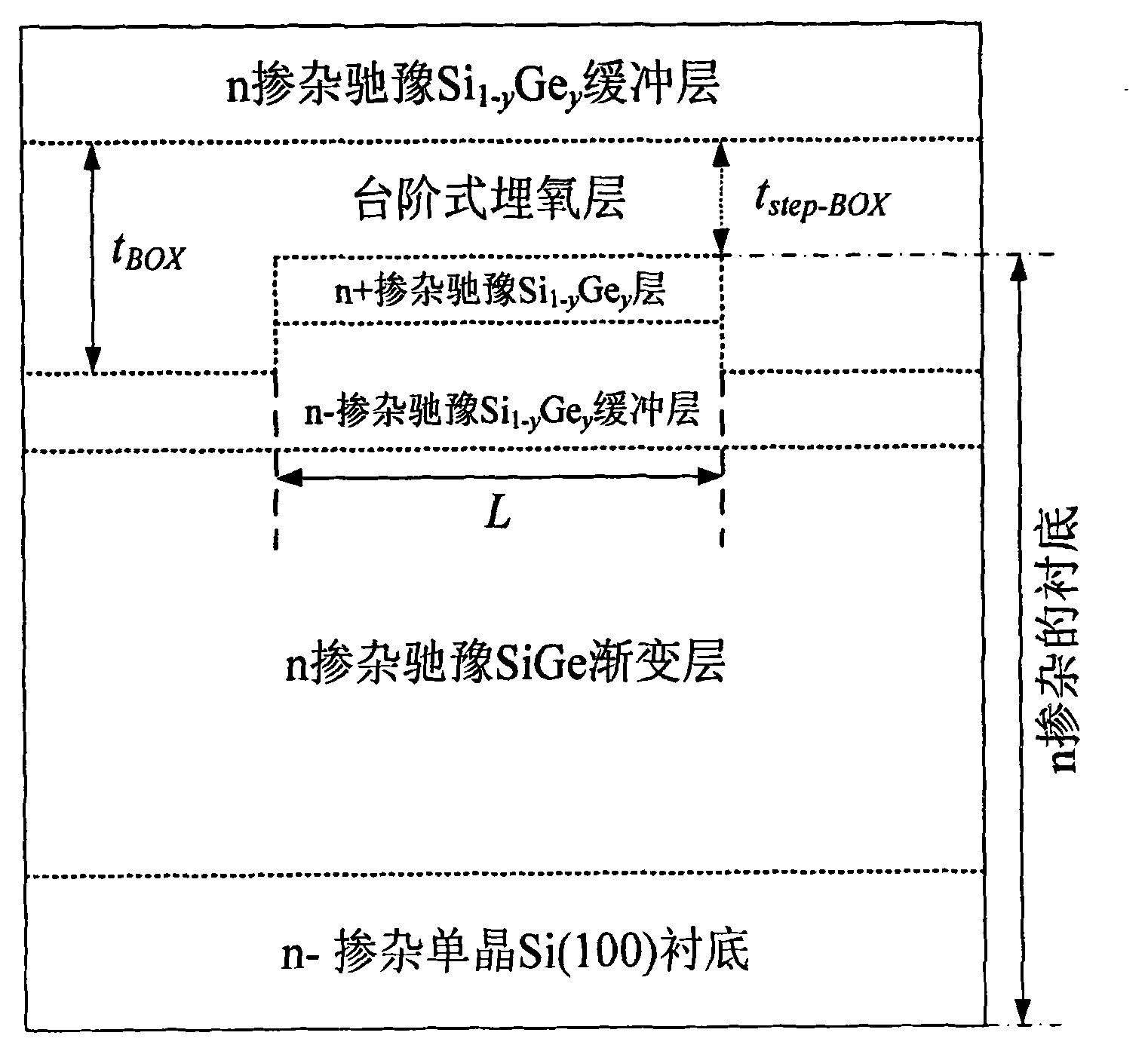
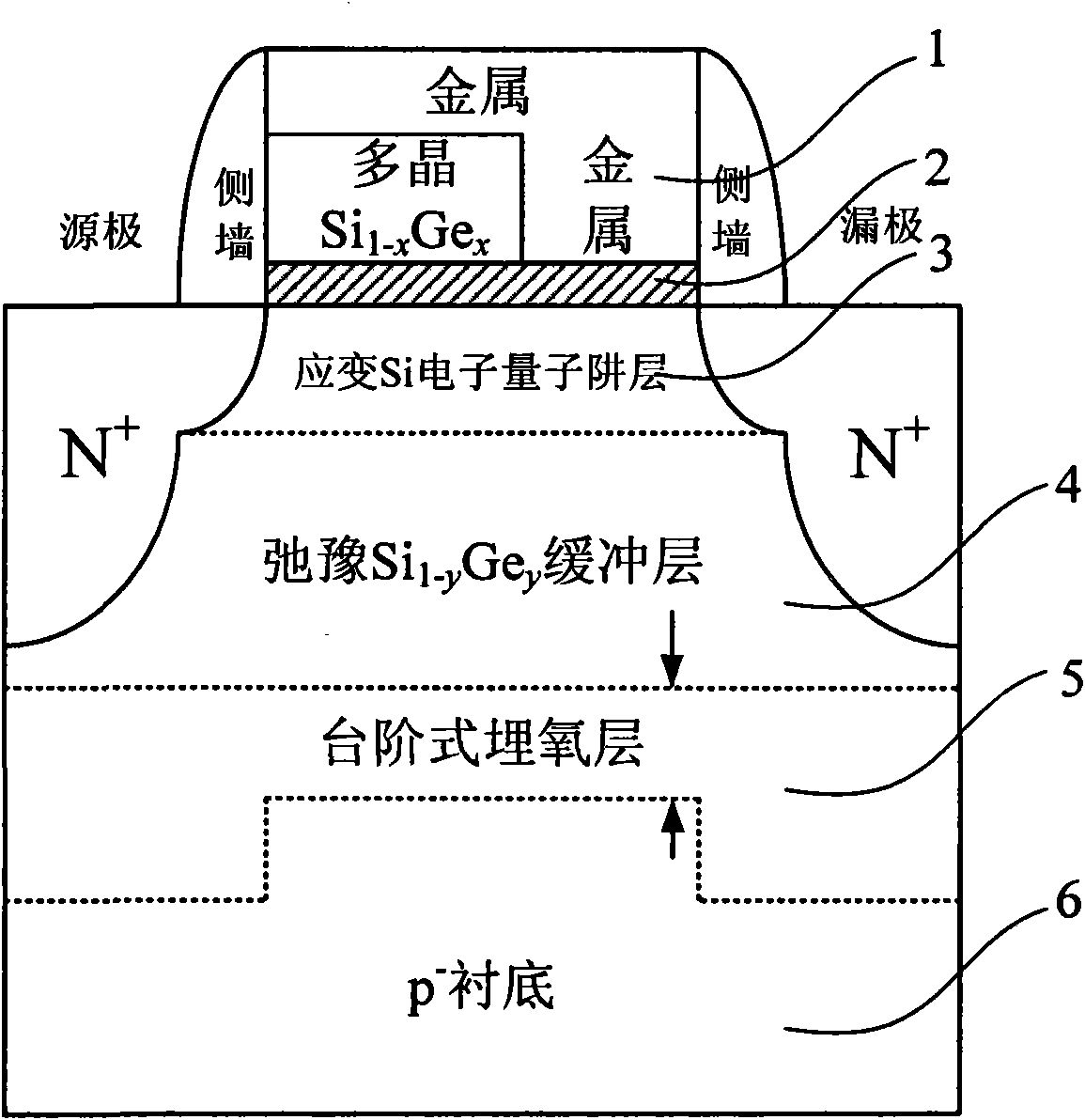
The invention discloses a heterogeneous metal stacked grid strained silicon-germanium on insulator p-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect tube (SSGOI pMOSFET) device structure, which comprises a heterogeneous metal stacked grid structure, a grid insulation layer, an intrinsic or n-doped strained Si channel layer, a strained Si1-xGex layer of which an intrinsic or n-doped component is changed gradually, an n-doped relaxation Si1-yGey layer, a stepped oxygen buried layer and an n-doped substrate part sequentially from top to bottom, wherein the n-doped substrate part consists of four parts, namely an n<+>-doped relaxation Si1-yGey layer, an n<->-doped relaxation Si1-yGey buffer layer, an n-doped relaxation SiGe gradient layer and an n<->-doped monocrystal Si(100) substrate. The device has a simple structure, can be totally compatible with the conventional Si silicon on insulator (SOI) process, is integrated with the advantages of grid engineering, strain engineering and substrate engineering, and makes a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor structure process simply integrated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Field effect transistors with reduced parasitic resistances and method
ActiveUS10062692B1Reduce inactivationOptimal strain engineeringTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceDielectric
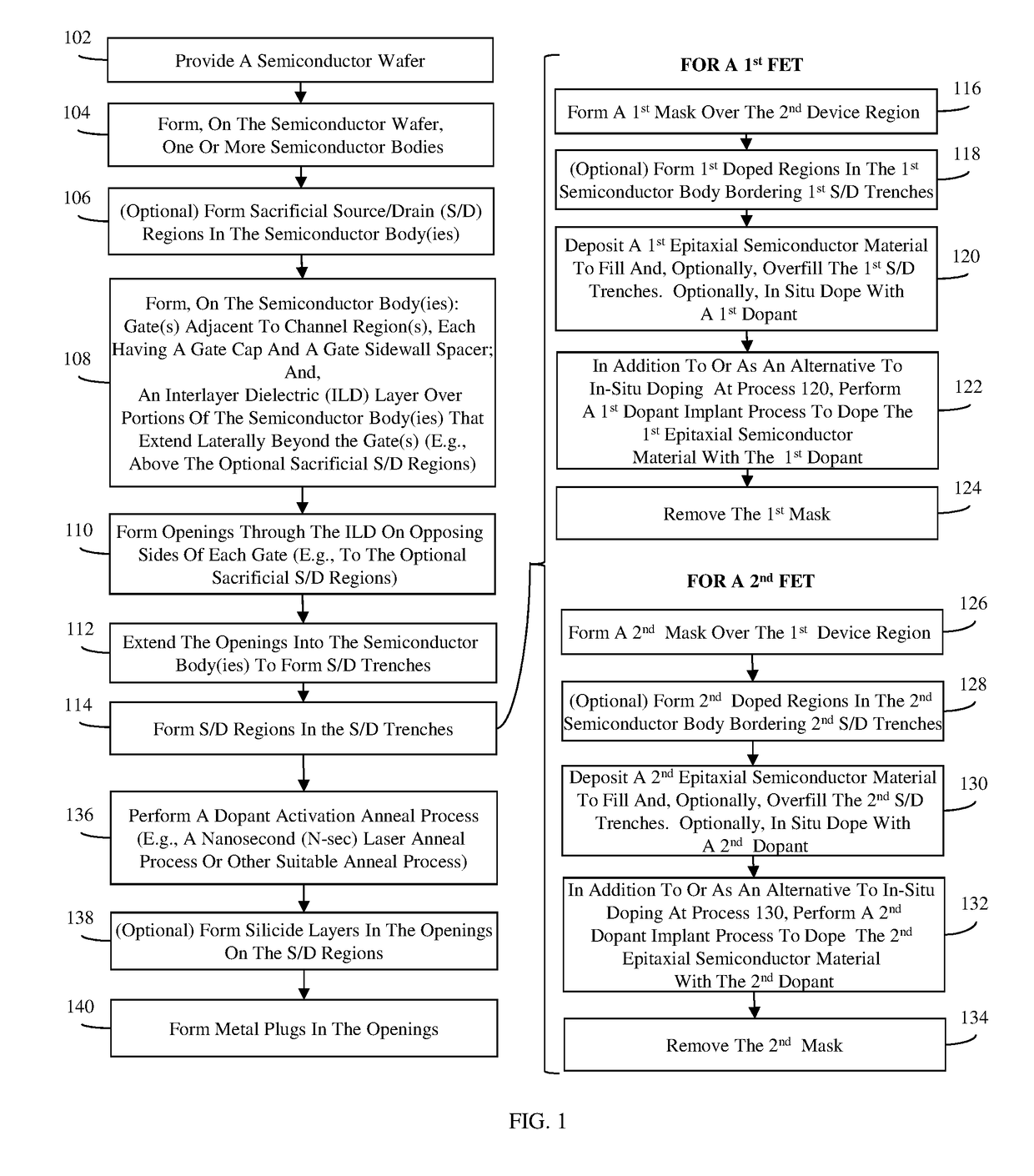
Disclosed are methods of forming field effect transistor(s) (FET) and the resulting structures. Instead of forming the FET source / drain (S / D) regions during front end of the line (FEOL) processing, they are formed during middle of the line (MOL) processing through metal plug openings in an interlayer dielectric (ILD) layer. Processes used to form the S / D regions through the metal plug openings include S / D trench formation, epitaxial semiconductor material deposition, S / D dopant implantation and S / D dopant activation, followed by silicide and metal plug formation. Since the post-MOL processing thermal budget is low, the methods ensure reduced S / D dopant deactivation, reduced S / D strain reduction, and reduced S / D dopant diffusion and, thus, enable reduced S / D resistance, optimal strain engineering, and flexible junction control, respectively. Since the S / D regions are formed through the metal plug openings, the methods eliminate overlay errors that can lead to uncontacted or partially contacted S / D regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
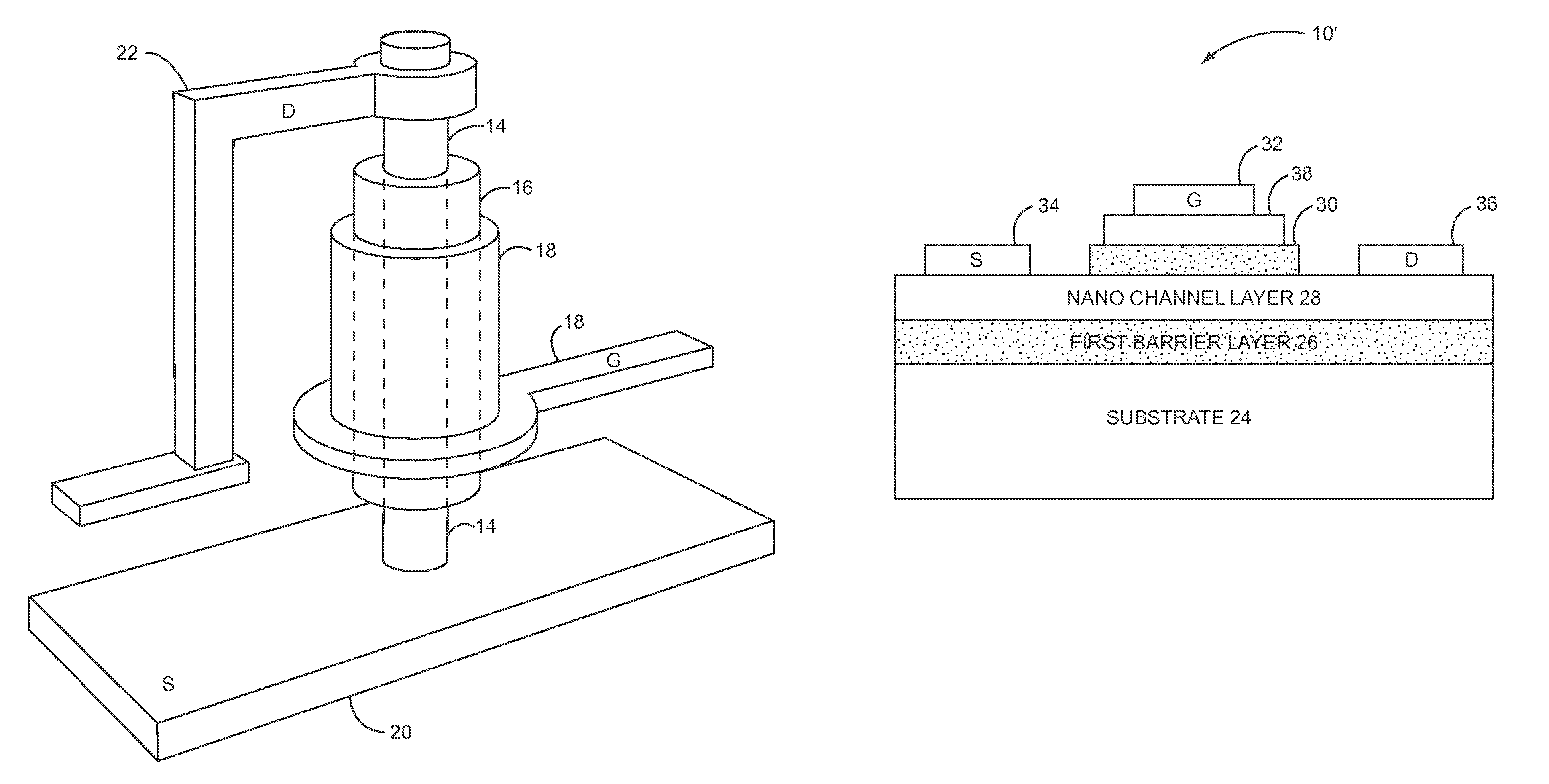
Nanometer-scale transistor architecture providing enhanced carrier mobility
ActiveUS8097922B1High carrier mobilityReduce dispersionTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge carrier mobilityEngineering
The present invention provides a nanometer-scale transistor architecture providing enhanced carrier mobility. In particular, a portion of a channel of a transistor is substantially surrounded with an acoustically hard material to form a barrier shell about the channel. The barrier shell functions to confine phonons in the channel. Confining the phonons in the channel reduces the extent to which atoms in the crystal lattice structure of the channel move as they vibrate. Restricting the extent that the atoms vibrate in the crystal lattice of the channel significantly reduces the scattering of electrons or holes traveling through the channel. In one embodiment of the invention, the thickness of the channel is in the order of the thermal phonon wavelength of the material forming the channel, and the barrier shell is acoustically harder than the channel. The benefits of the present invention may be provided without requiring strain engineering.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130313655A1High carrier mobilityDrive capability can be improvedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricDevice material
A semiconductor device comprises a substrate; a shallow trench isolation embedded in the substrate and forms at least one opening region; a channel region located in the opening region; a gate stack including a gate dielectric layer and a gate electrode layer, located above said channel region; a source / drain region located on both sides of the channel region, including a stress layer which provides strain for the channel region. A liner layer is provided between the shallow trench isolation and the stress layer, which serves as a crystal seed layer of the stress layer. A liner layer and a pad oxide layer are provided between the substrate and the shallow trench isolation. The liner layer is inserted between the STI and the stress layer of the source / drain region as a crystal seed layer or nucleating layer for epitaxial growth, thereby eliminating the STI edge effect during the source / drain strain engineering.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
MBE epitaxial method for positioning and growing low-intensity InAs quantum dot by strain engineering theory and pattern-underlay combining technology
InactiveCN101533770AAvoid randomnessLow densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingQuantum dotStrain engineering
Single photon is realized by the luminescence of a single quantum dot under ideal condition, so that the effective insulation of the single quantum dot becomes very important. At present, InAs / GaAs quantum dots which are used for manufacturing and realizing a quantum dot single photon emission apparatus are obtained by a self-organized growth method, the InAs / GaAs quantum dots are distributed on a growth surface at random and have very high dot density, and several to hundreds of quantum dots are distributed on every square micron, so that the effective insulation of the single quantum dot is comparatively difficult. Due to the randomicity of the distribution of the quantum dots on the growth surface, the positions of the quantum dots in an optical microcavity become very hard to be controlled reliably. The invention prepares low-intensity InAs quantum dots by means of combining a strain engineering theory with a pattern underlay. The strain engineering theory is as follows: during the process of growing multilayer quantum dots, stress field action is produced due to the existence of underlayer quantum dots, and upper layer dots in the multilayer quantum dots tend to keep growing on the same position with the underlayer quantum dots in the vertical direction to form vertical matching. In addition, the optical quality for growing the quantum dots on the pattern underlay can be improved effectively just by a lamina GaAs cushion layer with the thickness of tens of nanometers. The invention provides an MBE epitaxial method for positioning and growing a low-intensity InAs quanta dot by a strain engineering theory and a pattern-underlay combining technology, thus overcoming the randomicity for growing the quanta dot by the self-organized growth method and controlling the position and the density reliably. The method provides a reference measure for a method for preparing a quanta dot single photon emission source.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Extreme halophilic archaea engineering bacteria for producing bioplastics PHBV by effectively utilizing carbon source
ActiveCN103451201AIncrease concentrationSolve stickyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHaloferax mediterraneiProtein C
The invention discloses extreme halophilic archaea engineering bacteria for producing bioplastics PHBV (Poly-(HydroxyButyrate-co-Hydroxy Valerate)) by effectively utilizing a carbon source. The recombined extreme halophilic archaea is extracellular polysaccharide synthesis function-deficient engineering bacteria obtained by deleting at least one protein function expressed by an extracellular polysaccharide synthesis cluster in the genome of the extreme halophilic archaea Haloferax mediterranei. The extreme halophilic archaea has the advantages that infectious microbe is not easy to pollute, PHA (Poly Hydroxy Alkanoate) is convenient to extract, the PHBV from a non-correlated carbon source can be synthesized, and the like, and is considered as a highly preponderant PHBV producing strain. The extracellular polysaccharide synthesis function-deficient strain engineering bacteria are characterized in that the polyhydroxyalkanoate can be produced from various carbon sources such as glucose, starch and whey more efficiently in contrast with a wild type strain, the concentration of the PHBV is 20% higher than that of the wild type strain under the same fermentation conditions, and the problems such as sticking, lots of bubbles and dissolved oxygen reduction of a culture solution caused by extracellular polysaccharide accumulation are also solved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
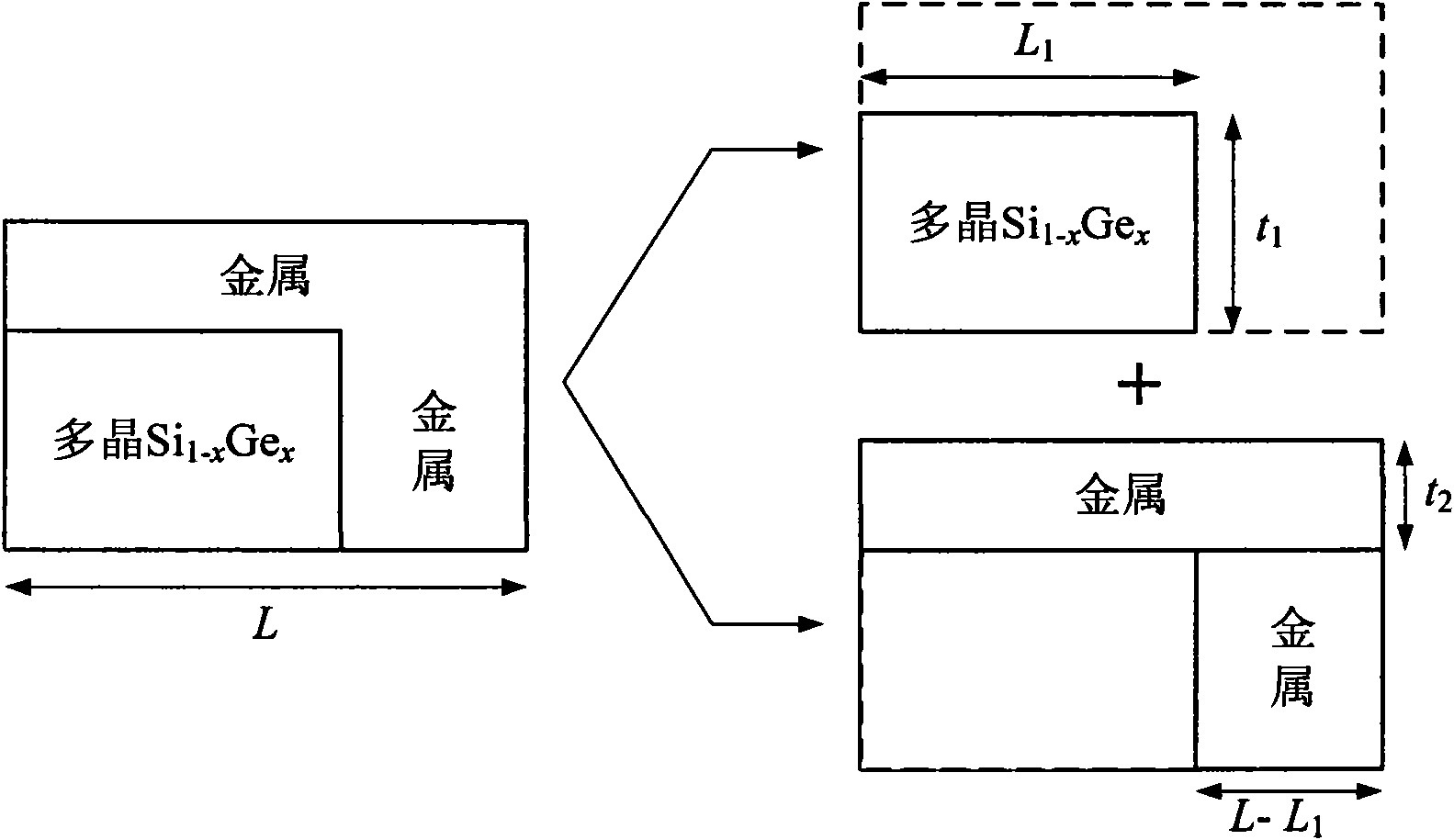
Polycrystalline Si1-xGex/metal parallel covering double-gate strained SiGe-on-insulator (SSGOI) n metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) device structure
The invention discloses a polycrystalline Si1-xGex / metal parallel covering double-gate stepped buried oxide strained SiGe-on-insulator (SSGOI) n metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) device structure. In the technical scheme, the device structure consists of a polycrystalline Si1-xGex / metal parallel covering double-gate structure, a gate insulating layer, an intrinsic or p-doped strain Si electronic quantum well layer, a p-doped relaxation Si1-yGey buffer layer, a stepped buried oxide layer and a p-doped substrate from top to bottom, wherein the p-doped monocrystalline Si(100) substrate consists of three parts, namely a p-relaxation Si1-yGey buffer layer, a p-relaxation SiGe gradient layer and monocrystalline Si. The device structure is simple and completely compatible with the conventional Si silicon-on-insulator (SOI) process, and integrates the advantages of grid engineering, strain engineering and substrate engineering.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103426907AEliminate voidsHigh carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrier mobilityEngineering
The invention provides a semiconductor device which comprises a substrate, a shallow trench isolation, a channel region, a gate stack and source-drain regions. The STI is embedded into the substrate and provided with at least one open region; the channel region is arranged in the open region; the gate stack comprises a gate medium layer and a gate electrode layer, and is located above the channel region; the source-drain regions are arranged on two sides of the channel region, and each source-drain region comprises a stress layer used for providing strain for the channel region. A packing layer is arranged between the STI and each stress layer and serves as a crystal seed layer of the stress layer; a packing layer and a cushion oxidation layer are arranged between the substrate and the STI. According to the semiconductor device, due to the fact that the packing layer is inserted between the STI and the stress layer of each source-drain region and serves as the crystal seed layer or a nucleating layer for epitaxial growth, the STI fringe effect in source-drain strain engineering is eliminated, a gap between the STI and the stress layer of each source-drain region is also eliminated, reduction of stress of the source-drain strain on channels is prevented, the carrier mobility of MOS devices is improved, and therefore the drive capability of the devices is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Technique for strain engineering in silicon-based transistors by using implantation techniques for forming a strain-inducing layer under the channel region
InactiveUS7871877B2Improve compatibilityIncrease flexibilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsEngineering
By incorporating a semiconductor species having the same valence and a different covalent radius compared to the base semiconductor material on the basis of an ion implantation process, a strain-inducing material may be positioned locally within a transistor at an appropriate manufacturing stage, thereby substantially not contributing to overall process complexity and also not affecting the further processing of the semiconductor device. Hence, a high degree of flexibility may be provided with respect to enhancing transistor performance in a highly local manner.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
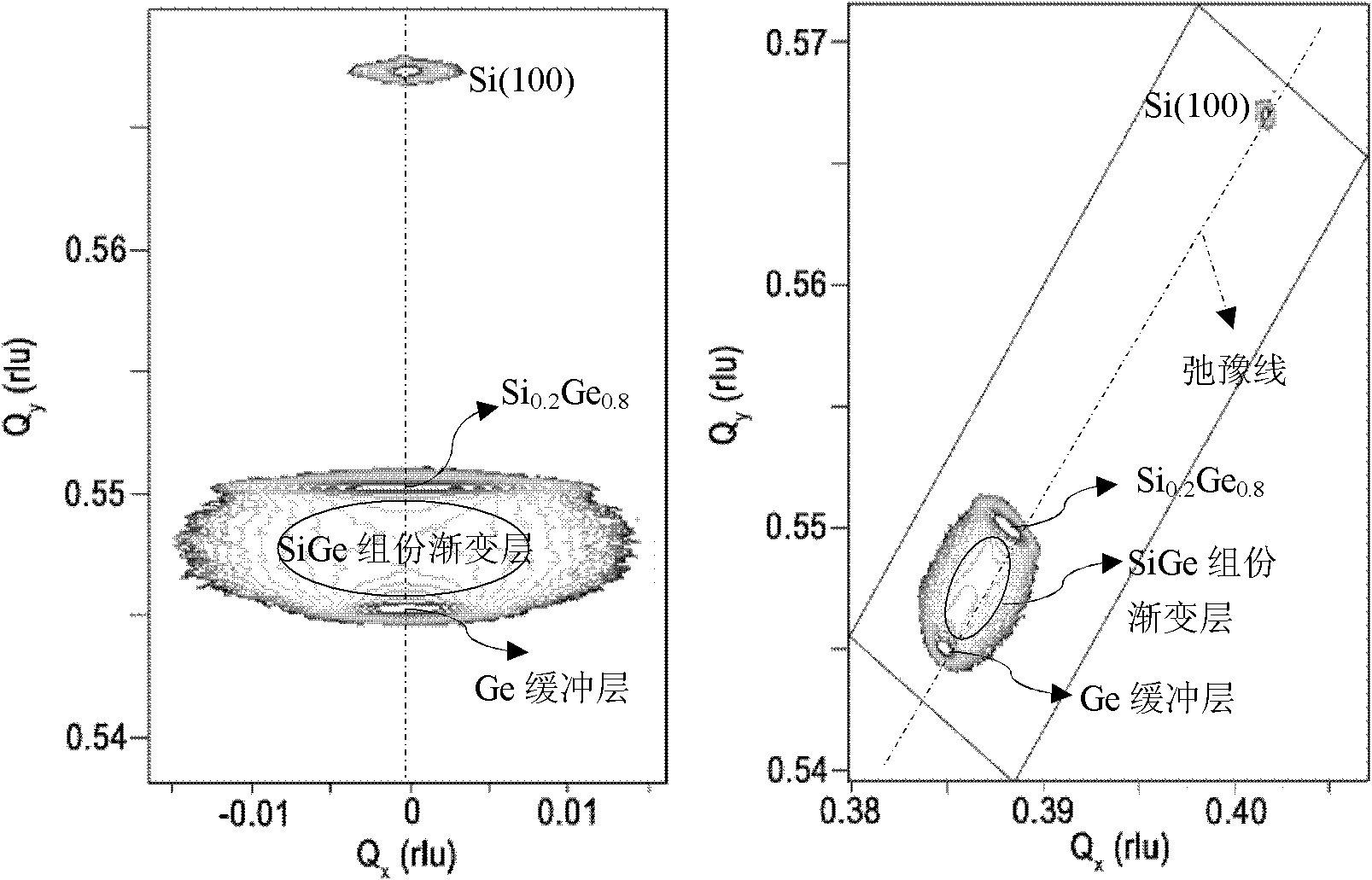
Relaxation SiGe virtual substrate and preparation method thereof
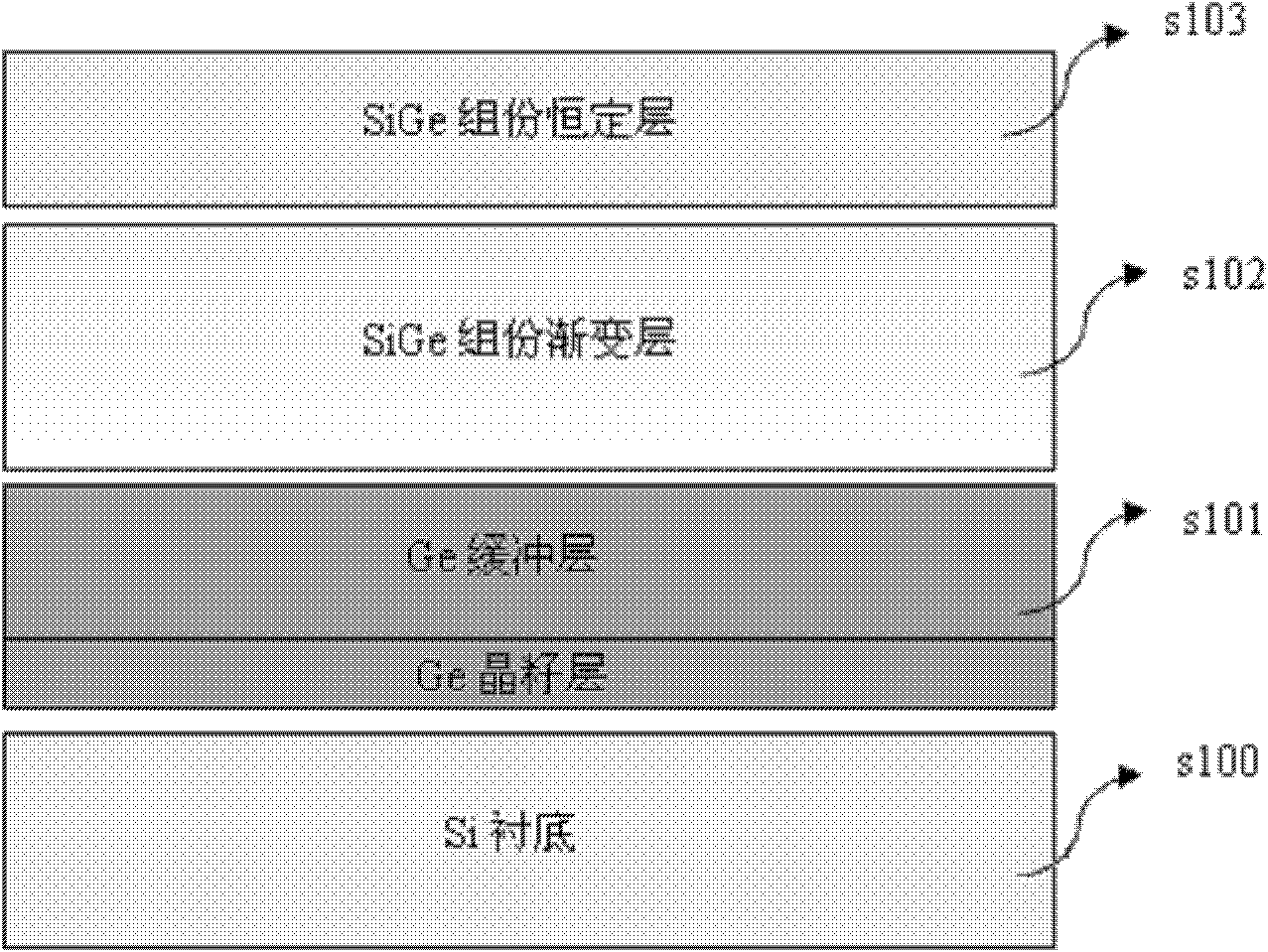
InactiveCN102315246AIncrease germanium contentIncreasing the thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsReduced pressure chemical vapor deposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor materials, and relates to a relaxation SiGe virtual substrate with high Ge content and a preparation method thereof. The SiGe virtual substrate comprises a Si substrate, a Ge crystal seed layer, a Ge buffer layer, a SiGe buffer layer with variable components and a SiGe layer with constant components, wherein the Ge crystal seed layer, the Ge buffer layer, the SiGe buffer layer and the SiGe layer epitaxially grow on the Si substrate from inside to outside in sequence; and the Ge crystal seed layer and the Ge buffer layer form a Ge relaxation buffer layer. The SiGe virtual substrate has the characteristics of high Ge contents, complete relaxation, low dislocation density, thin thickness, smooth surface and the like. The preparation method of the SiGe virtual substrate is characterized in that the epitaxial layers grow on the Si substrate by adopting a decompression chemical vapor deposition method. The relaxation SiGe virtualsubstrate with high Ge content provided by the invention can be widely applied to Ge channel strain engineering and the preparation of high-mobility channel materials in a CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) technology, and the performances of a CMOS device are improved further.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flexible gradient strain film, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110620140ASave resourcesSimple preparation processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIsosceles trapezoidResource saving
The invention provides a preparation method of a flexible gradient strain film and application of the flexible gradient strain film and belongs to the technical field of nano film preparation. According to the preparation method of the invention, the surface of a silicon film is etched, so that symmetrical isosceles trapezoid structures with a common bottom edge is formed; the silicon film with the pattern is transferred to a preloaded PDMS substrate; and preloading is released, so that a periodic ripple structure with gradient strain can be prepared. The prepared flexible film with the ripplestructure can generate gradient strain; and strain values of different magnitudes can be obtained in the absence of stretching and repeated sample preparation. The flexible film is suitable for strain engineering research in various environments and under various conditions. The flexible film has the advantages of resource-saving performance, simple preparation process and convenient use; and gradient ripples, the same as uniform ripples, have certain tensile resistance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method of strain engineering and related optical device using a gallium and nitrogen containing active region
ActiveUS9379522B1Easy to operateEfficient and reliableLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionQuantum wellNitrogen
An optical device has a gallium and nitrogen containing substrate including a surface region and a strain control region, the strain control region being configured to maintain a quantum well region within a predetermined strain state. The device also has a plurality of quantum well regions overlying the strain control region.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com