An outside cavity high-power semiconductor laser alternating array power
A semiconductor and laser technology, applied in the field of external cavity high-power semiconductor laser array light sources, can solve the problems of parallel coupling, difficult industrialization, and inconvenient semiconductor laser array assembly.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
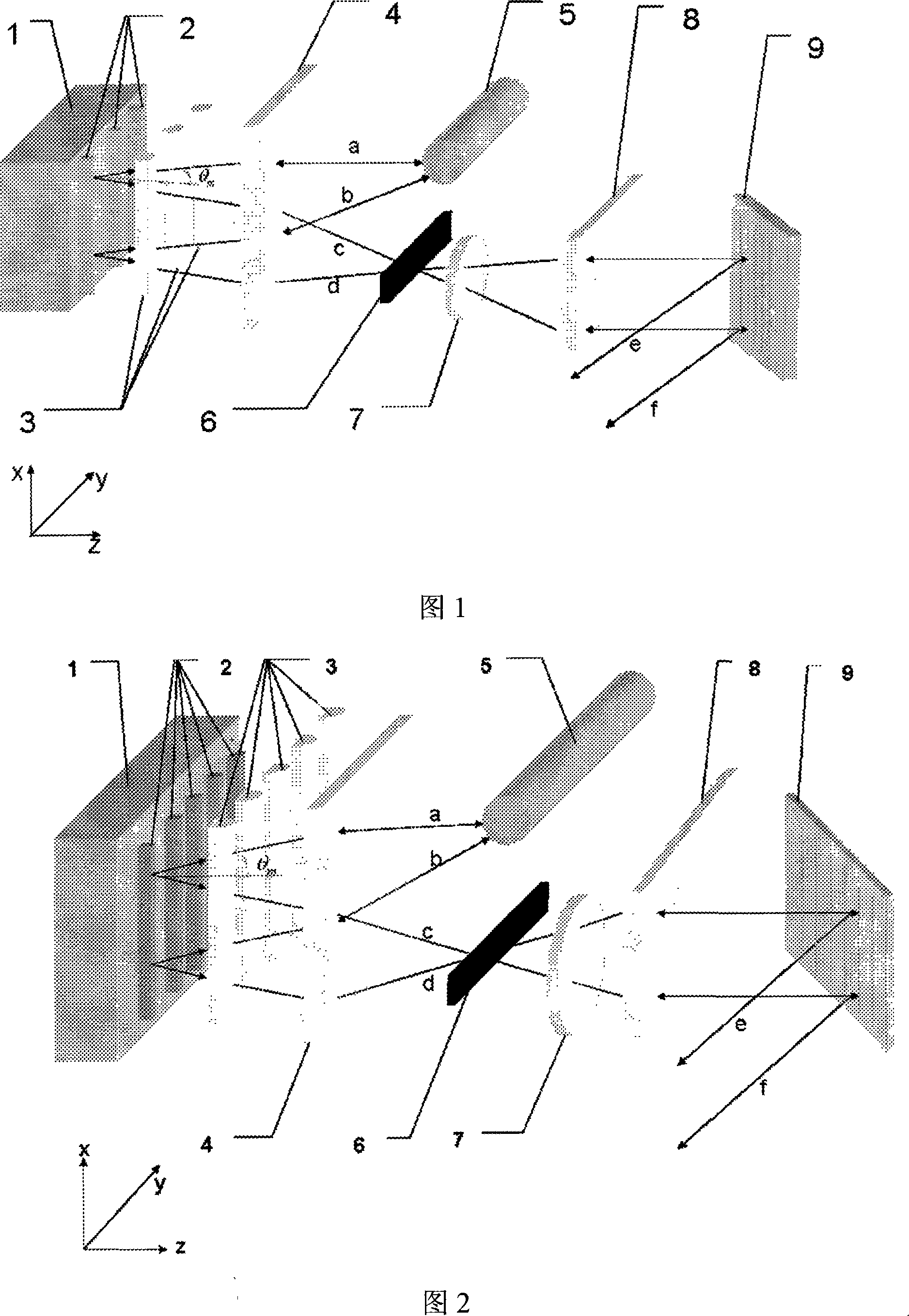
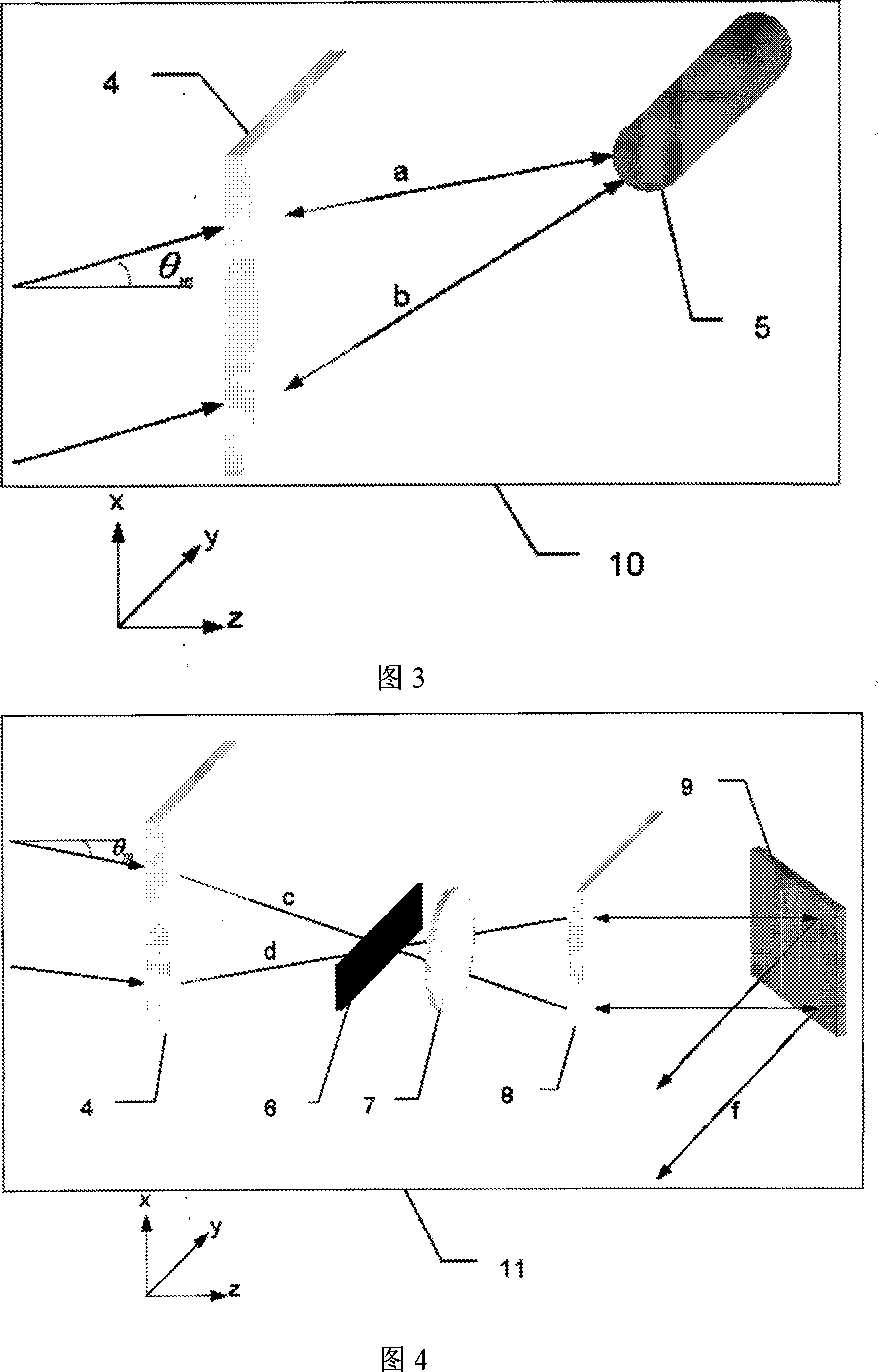
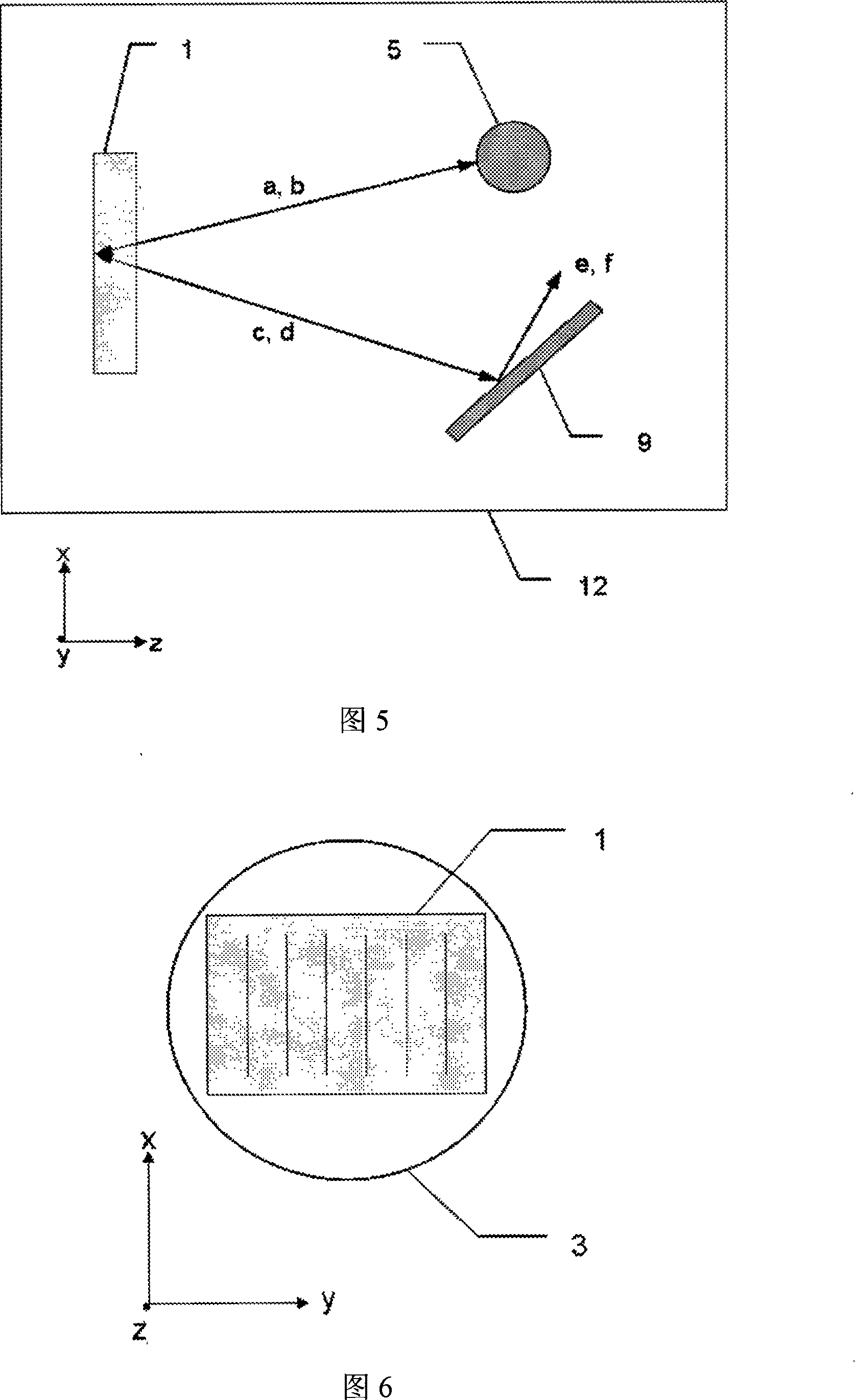
[0029] Referring to accompanying drawing 1, semiconductor laser stacked array 1 is formed by stacking 3 semiconductor laser arrays 2, layer spacing is 5mm, y direction length is 1.2cm, x direction length is 1.2cm, emission wavelength is 808nm, each semiconductor laser The fast axis direction (y direction in FIG. 1 ) of the line array 2 is provided with respective fast axis collimating mirrors 3 to collimate the fast axis. The fast-axis collimating mirror 3 is a microcylindrical lens. The lasers a, b, c, and d after the fast-axis collimation are approximately parallel light in the fast-axis direction, and the slow-axis direction (the x direction in FIG. 1 ) is divided into two paths. A path of light a and b propagating upward forms an upper far-field lobe; a path of light c and d propagating downward forms a lower far-field lobe. The angle between the upper optical path a, b and the lower optical path c, d and the optical axis (z direction in Figure 1) before entering the fast ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Referring to accompanying drawing 2, semiconductor laser stacked array 1 is formed by stacking 5 semiconductor laser arrays 2, layer spacing is 4mm, y direction length is 2.0cm, x direction length is 1.2cm, emission wavelength is 980nm, semiconductor laser array The fast axis direction of 2 (the y direction in FIG. 2 ) is provided with respective fast axis collimating mirrors 3 to collimate the fast axis. The fast-axis collimating mirror 3 is an aspheric lens. The lasers a, b, c, and d after the fast-axis collimation are approximately parallel light in the fast-axis direction, and the slow-axis direction (the x direction in FIG. 2 ) is divided into two paths. A path of light a and b propagating upward forms an upper far-field lobe; a path of light c and d propagating downward forms a lower far-field lobe. The angle between the upper optical path a, b and the lower optical path c, d and the optical axis (z direction in Figure 2) before entering the fast axis collimator i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com