Mammary cancer diversion and prognosis molecule parting gene group, gene chip producing and using method
A gene chip and molecular typing technology, which is applied in the fields of hybridization and analysis, functional genomics and gene chip preparation, can solve the problems of inability to predict patients with high metastatic potential, shortened metastasis-free survival and overall survival, and patients who lose comprehensive treatment Opportunity and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
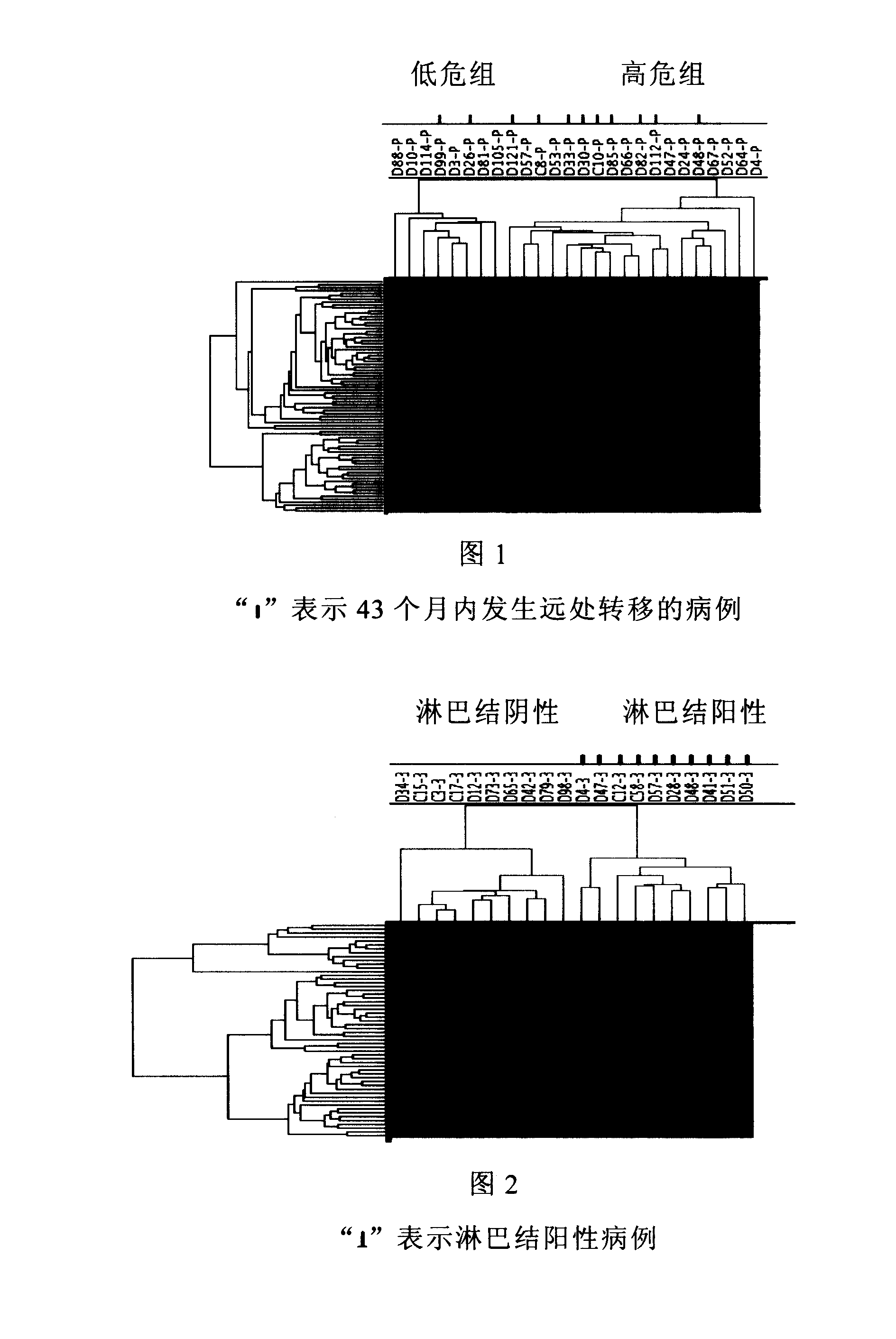
[0019] Example 1. Screening and Application of Lymph Node Positive Breast Cancer Prognosis Prediction Gene Group
[0020] material method
[0021] 1. Case selection and specimen processing
[0022] All specimens were collected from breast cancer patients with positive lymph node metastasis who received radical mastectomy from January 2002 to December 2003 in the Cancer Hospital Affiliated to Tianjin Medical University. lymph nodes. Samples of primary breast cancer and lymph node metastases were taken from each case. HE staining of histological sections confirmed that cancer cells accounted for more than 75% of lymph node metastases. The tissue samples were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C. 26 cases of lymph node positive breast cancer were used as training cases (training cases), with an average follow-up of 43 months, 11 of which developed distant metastasis; the other 9 cases of lymph node positive breast cancer were used as verification cases (test ca...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2, Breast cancer lymph node metastasis diagnosis gene group screening and application
[0053] Materials and methods
[0054] 1. Case selection and specimen processing
[0055] The primary cancer tissues of 49 cases of breast cancer in this group were all obtained from breast cancer patients who underwent radical mastectomy from January 2002 to December 2003 in the Department of Breast Cancer Hospital Affiliated to Tianjin Medical University. Invasive ductal carcinoma (WHO classification), the average follow-up time was 43 months. 10 lymph node-negative breast cancer patients and 10 lymph node-positive breast cancer patients were randomly selected as training cases, and 19 lymph node-negative patients and 10 lymph node-positive breast cancer patients were selected as verification cases. The case data are shown in Table 5. In addition, 32 normal mammary gland tissues of patients with breast tumors were extracted and mixed in equal amounts as control samples. A...
Embodiment 3
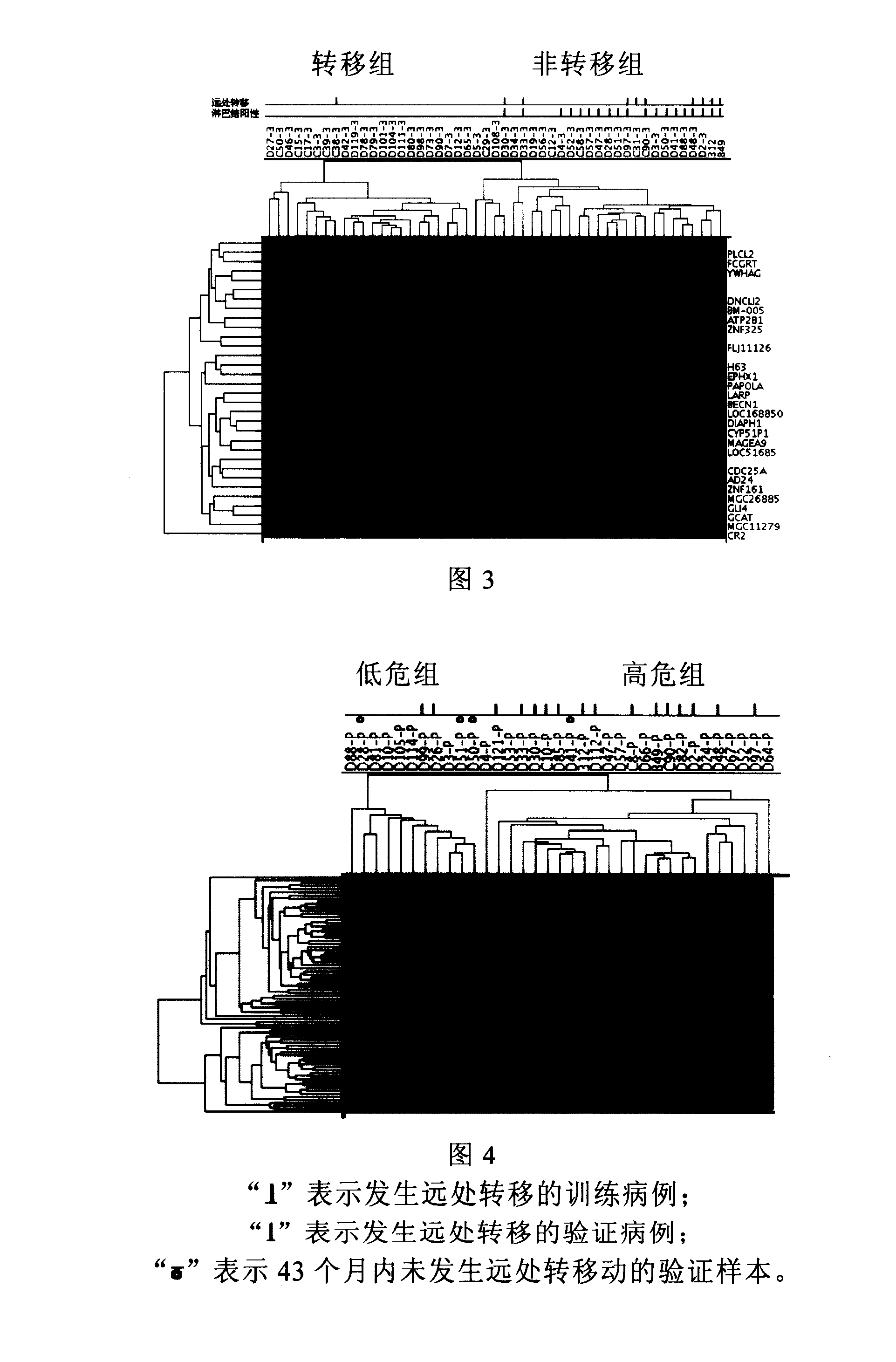
[0076] Example 3. Screening and Application of Lymph Node Negative Breast Cancer Metastasis Prediction Gene Group
[0077] Breast cancer has the biological characteristics of tissue cell heterogeneity. During the process of tumor cell occurrence, progression and metastasis, there are not only quantitative accumulation of clonal growth at the primary site, but also the acquisition of cells with high metastatic potential that are accompanied by selective growth at any time. Without the ability to escape and disseminate, secondary metastases develop in the axillary lymph nodes and distant organs. Therefore, some metastatic cancers are the so-called "heterogeneous metastasis" that occurs in the late stage of tumor progression, but it may also be the so-called "homogeneous metastasis" that occurs in the early stage of tumor development. In the first part of this study, 79 genes were screened to have a common difference trend between multiple cases of primary breast cancer and paire...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com