Revascularization of ischemic retinal tissue and screening method therefor
A technique for retinal ischemia and retina, which is applied in the field of treatment of retinal neovascular diseases, can solve problems such as laborious, unquantified tissue, and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1 Quantification of the area of vascular occlusion and the rate of retinal vascular regeneration
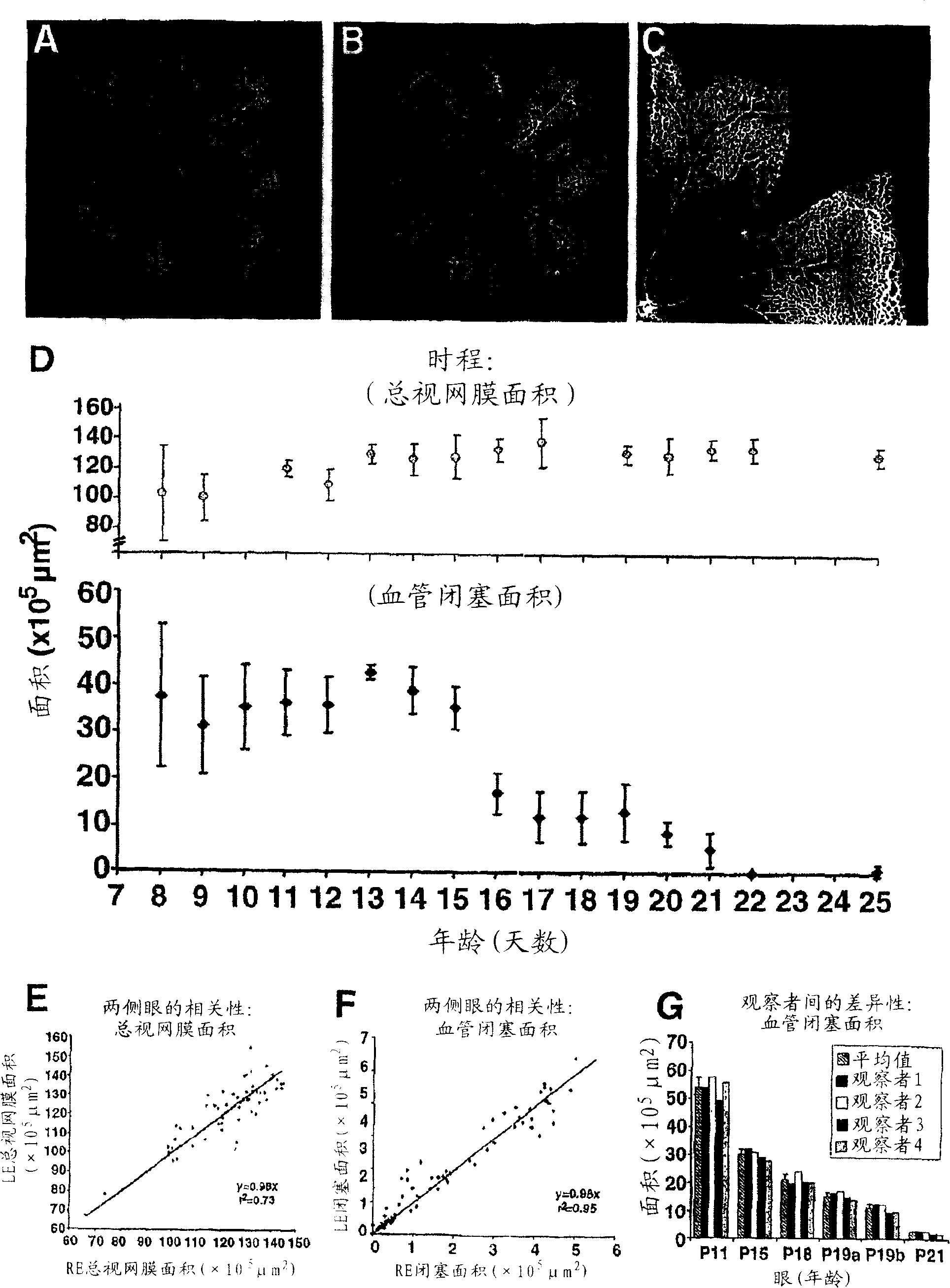
[0068] To quantify the area of vascular occlusion and the rate of retinal vascular regeneration, dextran-injected or isolectin-stained retinal mounts were photographed at low magnification using a fluorescence microscope. 4 overlapping photos were used to construct the retinal stitched photo ( figure 2 , inset A), occlusion area (yellow) and total retinal (blue line) area ( figure 2 , inset B). Since the border between vascular and avascular retina is usually well defined in these preparations, interobserver variability is very small ( figure 2 , inset G). Be careful not to include areas with cutting or fixation artifacts in the analysis area. The change in total retinal area over time is shown in figure 2 The upper inset D. Retinal growth appeared to continue during hyperoxia, with the total retinal area growing approximately 20% between P8 and P13. ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2. Quantification of Extent of Abnormal Neovascularization
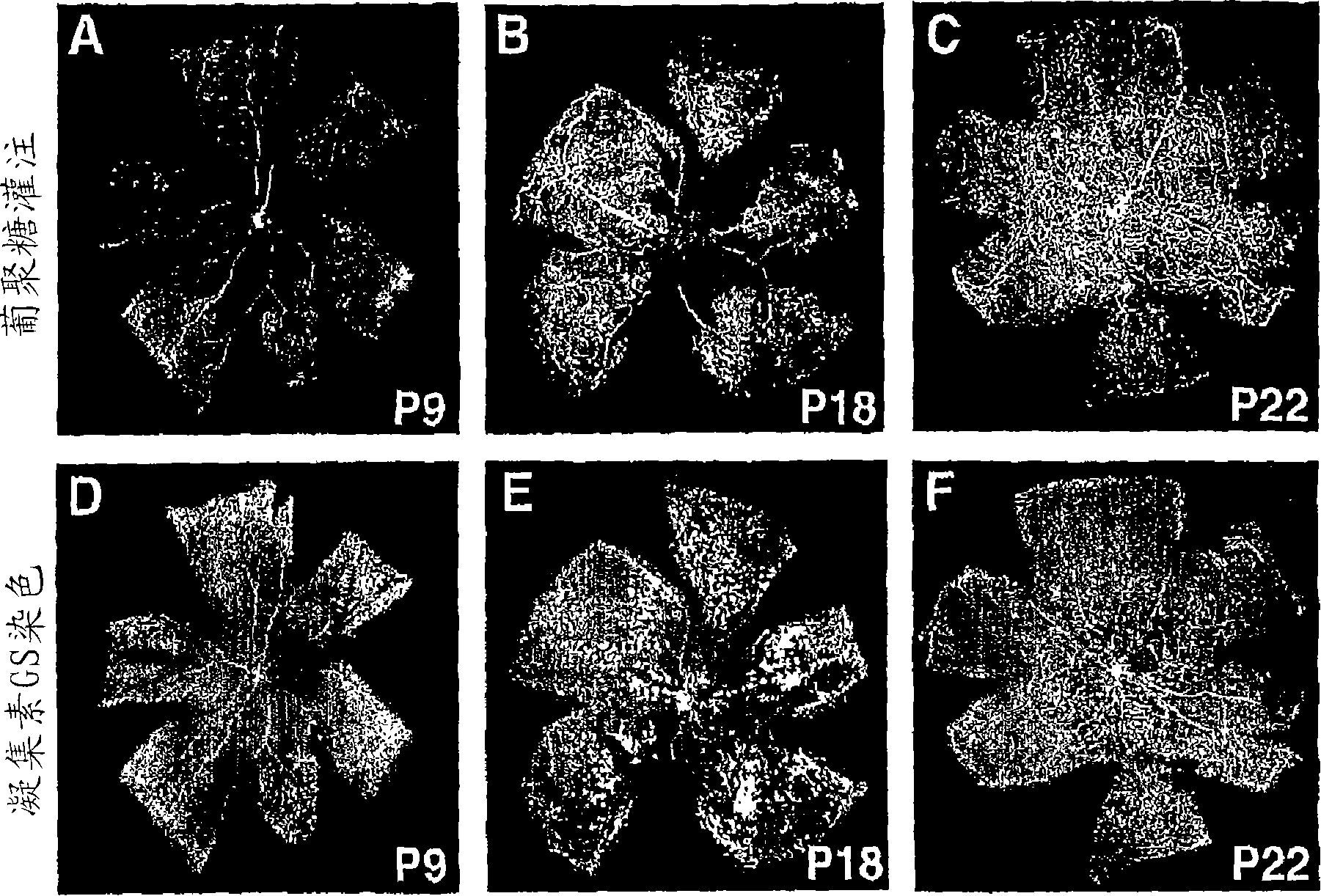
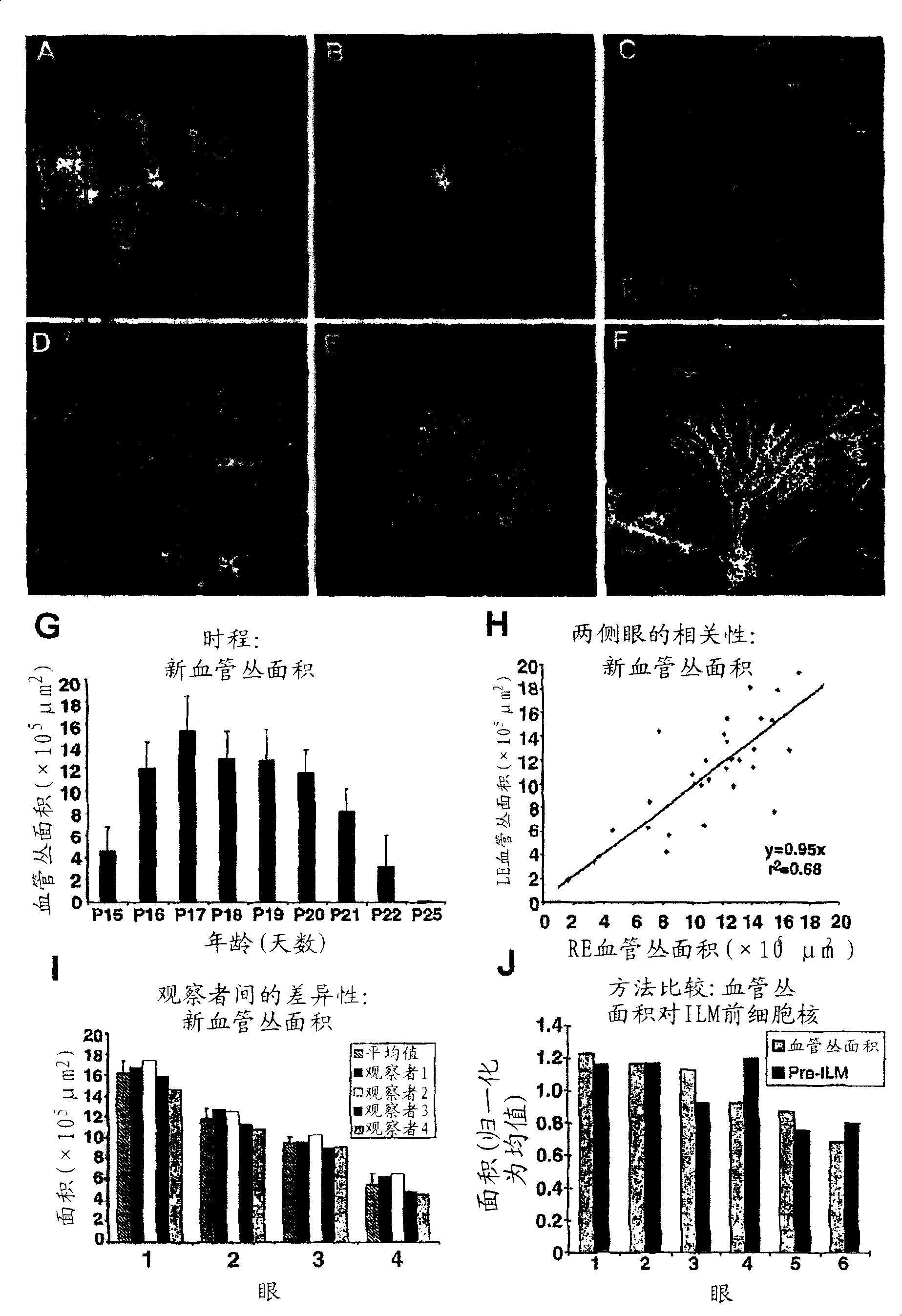
[0070] Between P15 and P22, especially from P17-P19 onwards, abnormal blood vessel growth appeared at the interface of retina and vitreous in mouse OIR model. These preretinal vascular plexuses are particularly prominent at the junction of the vascularized peripheral region and the occluded central region of the retina. These misdirected vascular elements are usually quantified in H&E-stained, paraffin-embedded cross-sections by counting the nuclei of cells projecting toward the vitreous side of the inner limiting membrane (ILM). However, these areas are also clearly visible in isolectin-stained whole-mount mount photographs due to cell populations overlying the superficial vascular network ( figure 1 Inset E, image 3 Illustration A). Using the intensity threshold tool (available in several commercial photo analysis programs), or Adobe PHOTOSHOP The area of preretinal vascular plexus formation ...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3. Angiogenesis Inhibitory Effects of iNOS Inhibitors
[0074] The application of the quantification technique of the present invention was further evaluated by examining the effect of a new angiogenesis inhibitor, the inhibitor iNOS, on retinal vascular regeneration and angiogenesis inhibition, and compared with the prior art pre-ILM nuclei counts. Inhibitors (or control saline) were delivered to mouse eyes between P12-P17 by once daily intraperitoneal injection, eyes were enucleated at P17, and quantified using either of the two techniques described. Figure 4 Inset A shows whole mount and transverse sections of retinas from P17 control mice (upper row) and iNOS inhibitor-treated animals (lower row). The area of vascular occlusion (blue line) is plotted in the left inset, the area of the neovascular plexus (red) is marked on the same whole mount in the middle inset, and an example of the pre-ILM nuclei is shown in the transverse section on the right in (a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com