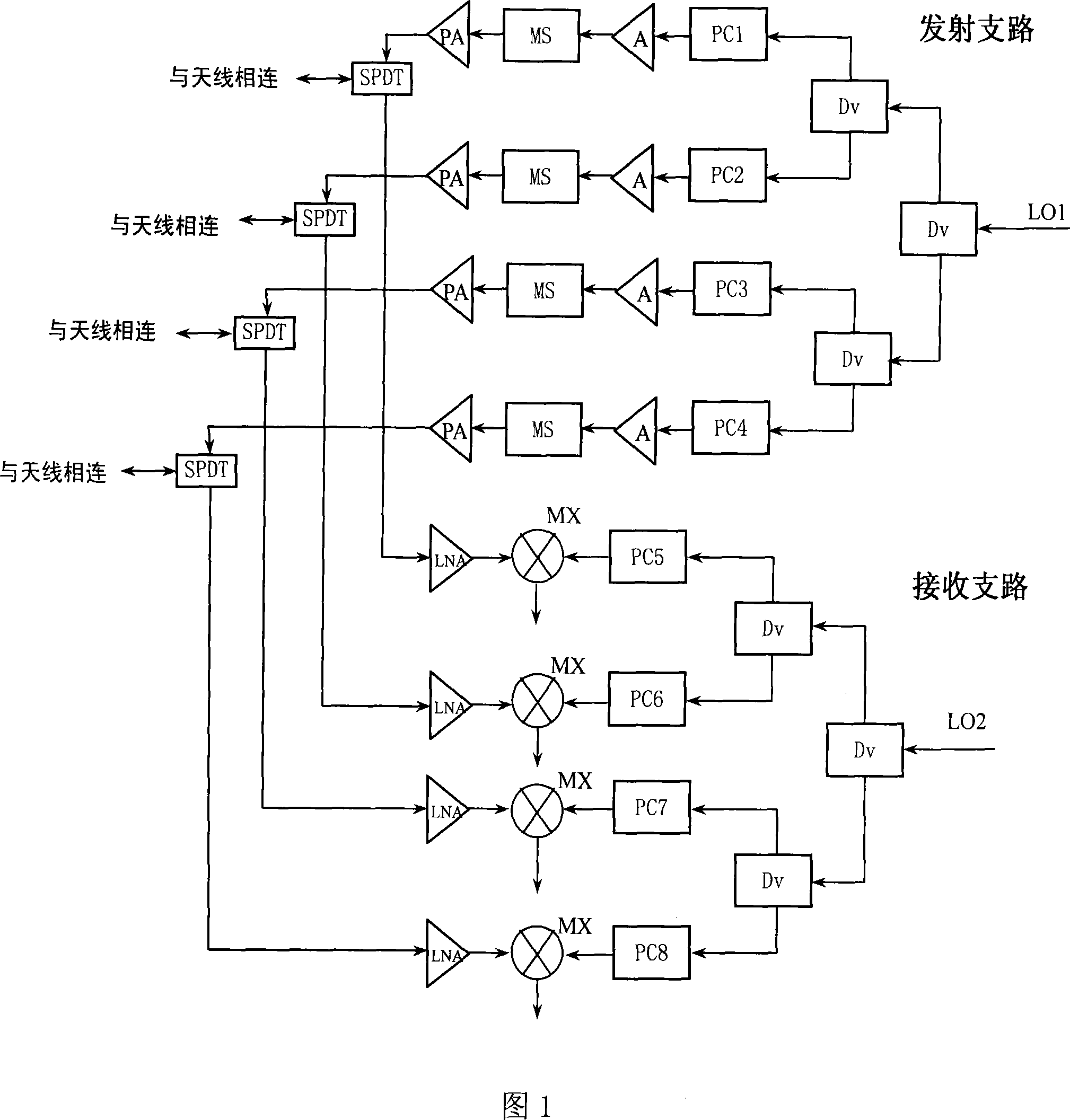
Millimeter wave miniaturized multichannel transmitting-receiving subassembly and its phase compensation process
A transceiver component and phase compensation technology, applied in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unguaranteed phase consistency, no implementation method, poor phase modulation accuracy, etc., to achieve simple and easy operation of phase compensation method, and improve power Combination efficiency, the effect of increasing the effective radiation gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
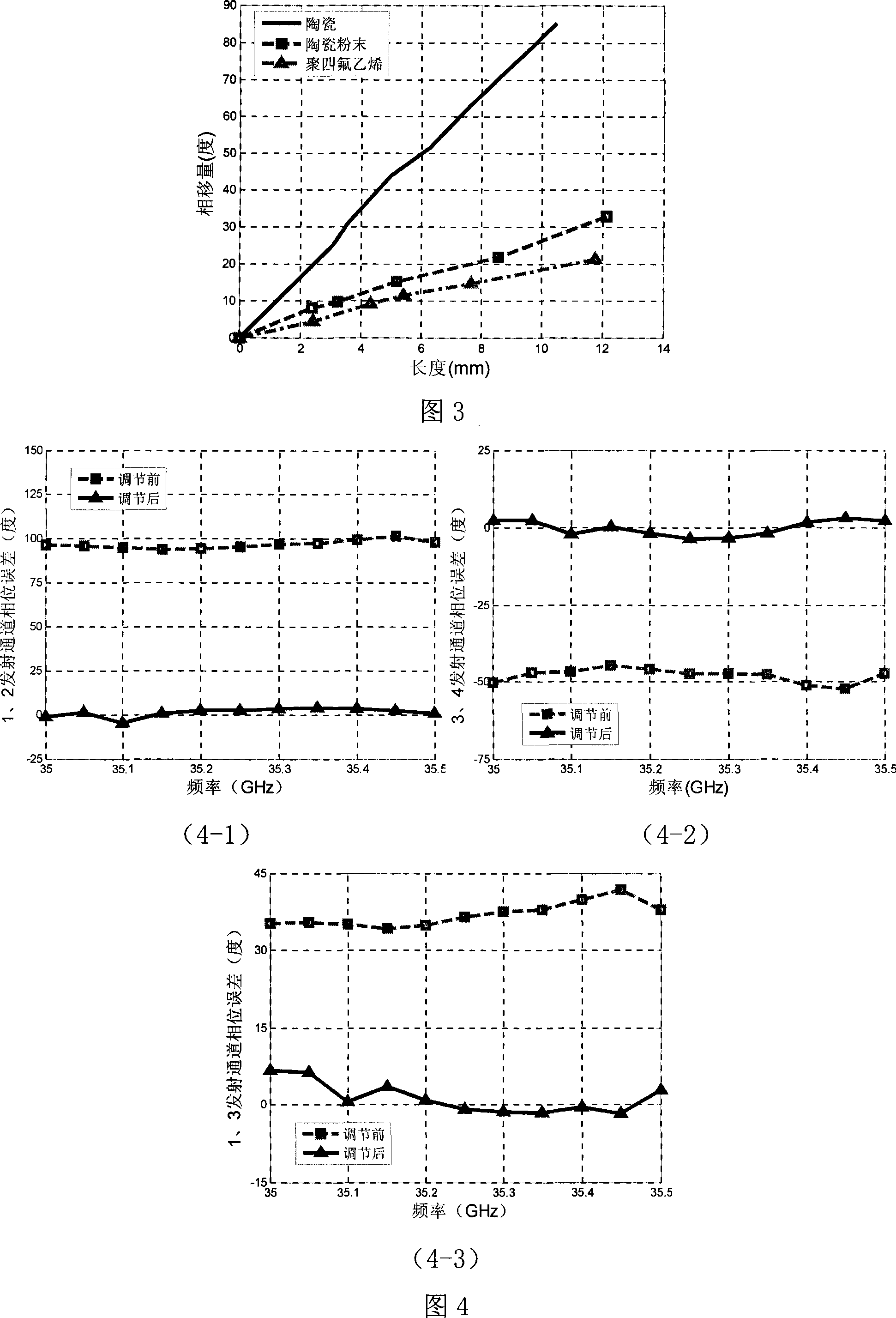
[0047] Taking the phase error of the transmission channel as an example of 95 degrees to introduce the operation steps of the phase error compensation of the transceiver component proposed by the present invention:
[0048] 1. According to the requirements of the radar device, it is estimated that the phase relationship between the transmission channels is zero degrees;
[0049] 2. Use a vector network analyzer to measure the phase error of the transmit channel, and obtain the phase error θ between the two transmit channels of the transceiver component when the operating frequency is 33GHz 1 is 95 degrees.
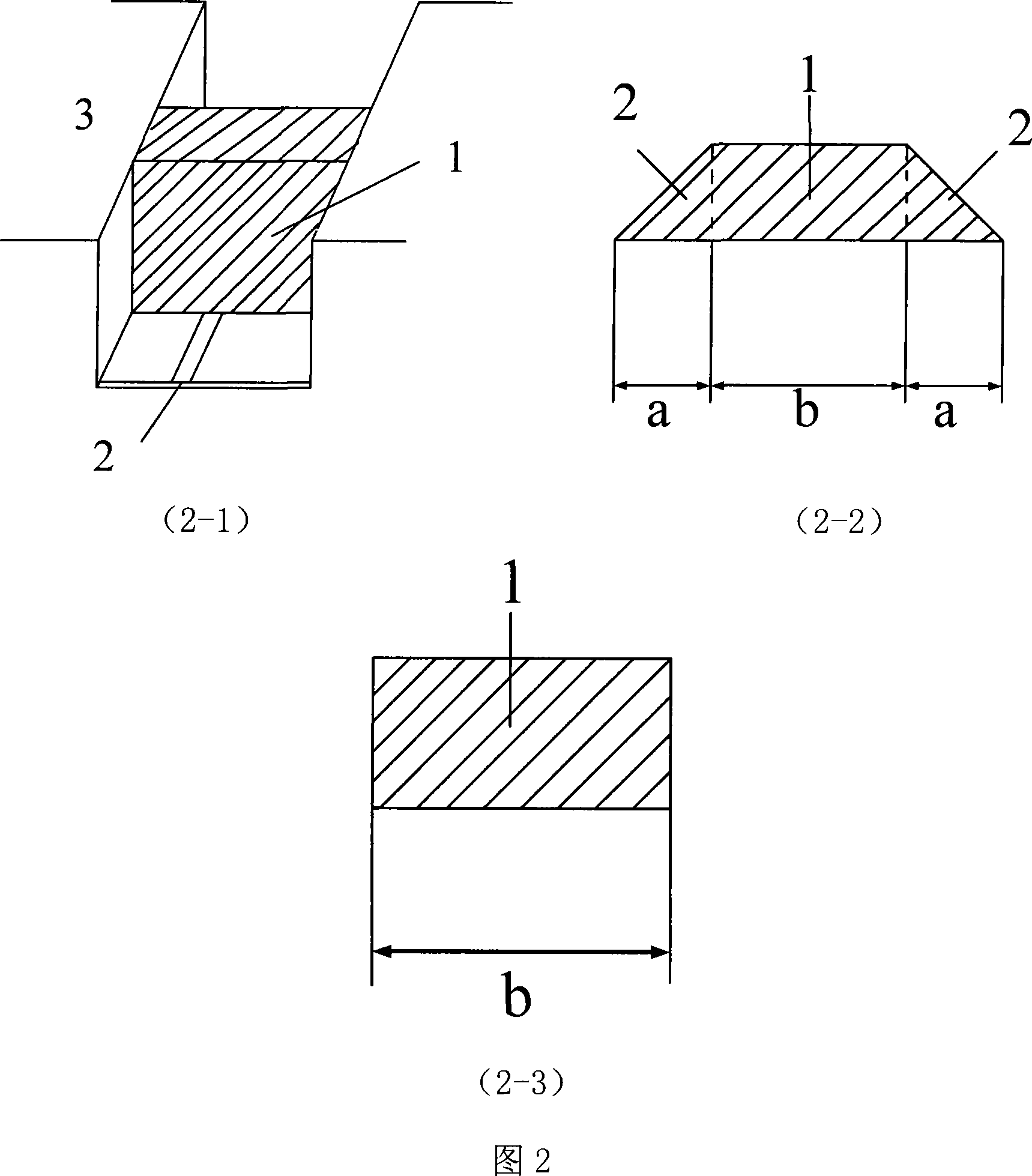
[0050] 3. Choose a regular cuboid ceramic medium to load, the thickness is 0.5mm, the width is equal to the shielding cavity and the side wall is in full contact with the metal side wall of the shielding cavity. The height of the air shielding cavity is 3 mm, which is convenient for calculation and selection of a cuboid structure without transition section . At this time...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Taking the phase error of the transmission channel as 50 degrees as an example to introduce the phase error compensation operation steps of the transceiver component proposed by the present invention, the specific operation steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1, except that the length of the compensation section is different. Suppose the phase error θ 2 λ is 50 degrees and the operating frequency is 33GHz 0 9.09 mm, equivalent dielectric constant ε re is 1.583, and these known parameters are substituted into formula (1) to get
[0058] (4)
[0059] Perform phase compensation according to the operation steps in Example 1. Figure 4-2 shows the measured results of the phase error before and after compensation using the medium-loaded microstrip line method proposed by the present invention when the channel phase error is 50 degrees. After compensation, the operating frequency is 33GHz. The channel phase error is 2.21 degrees.
Embodiment 3
[0061] Taking the phase error of the transmission channel as 35 degrees as an example to introduce the phase error compensation operation steps of the transceiver component proposed by the present invention, the specific operation steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1, except that the length of the compensation section is different. Suppose the phase error θ 3 is 35 degrees, when the operating frequency is 33GHz λ 0 is 8.57 mm, the equivalent dielectric constant ε re is 1.583, and these known parameters are substituted into formula (1) to get
[0062] (5)
[0063] Perform phase compensation according to the operation steps in Example 1. Figure 4-3 shows the measured results of the phase error before and after compensation using the medium-loaded microstrip line method proposed by the present invention when the channel phase error is 35 degrees. After compensation, the working frequency is 33GHz. The channel phase error is 4.57 degrees.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com