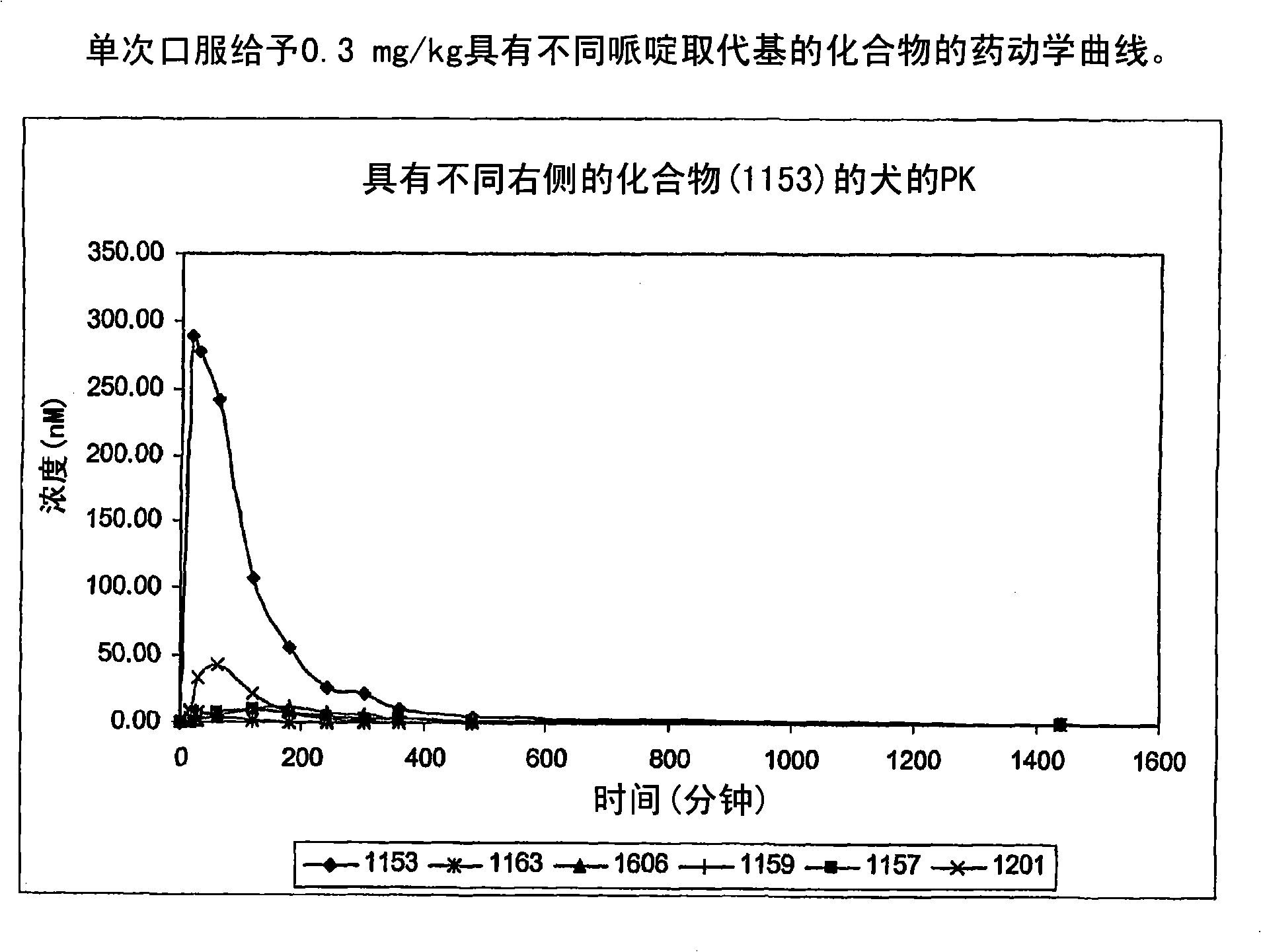
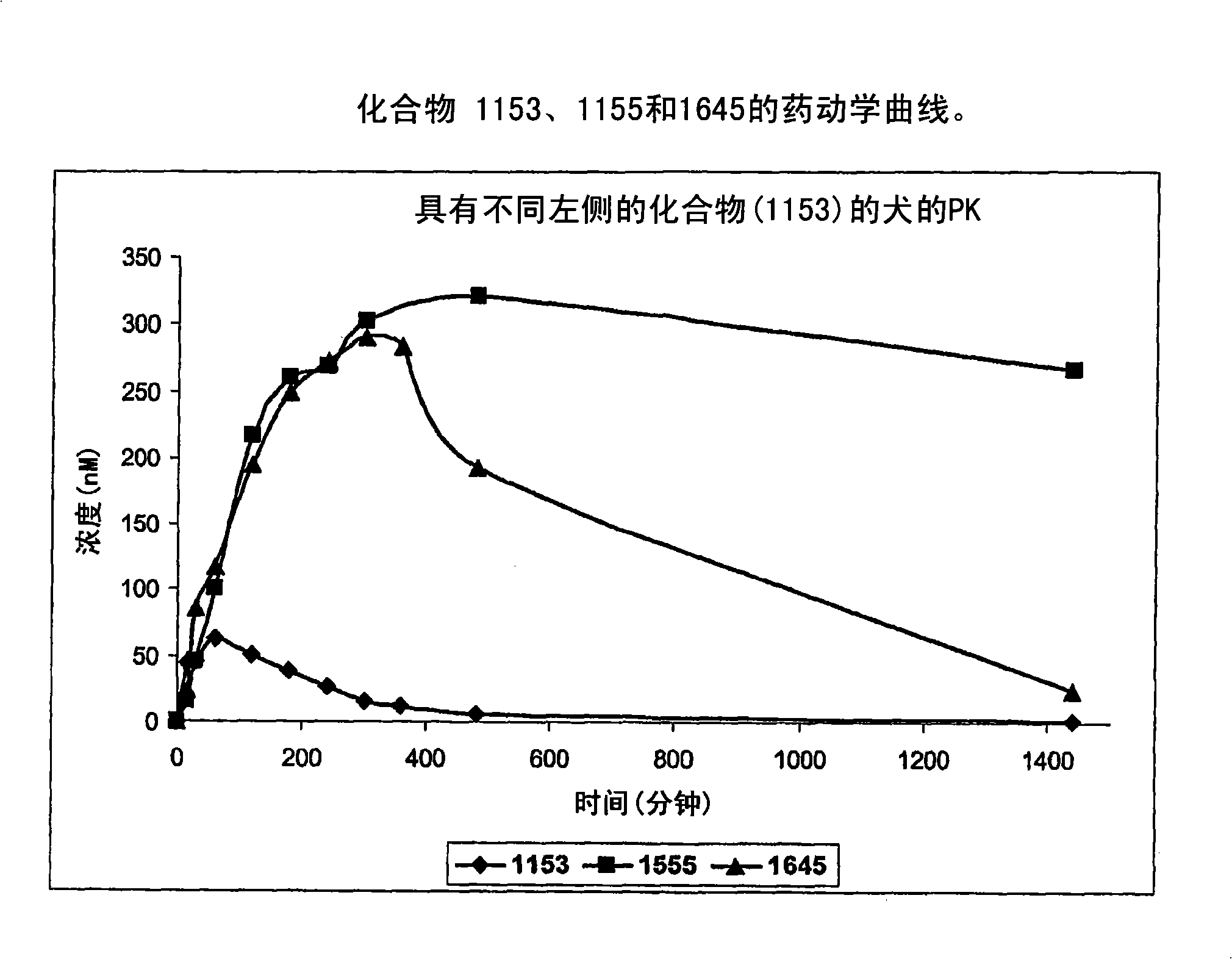
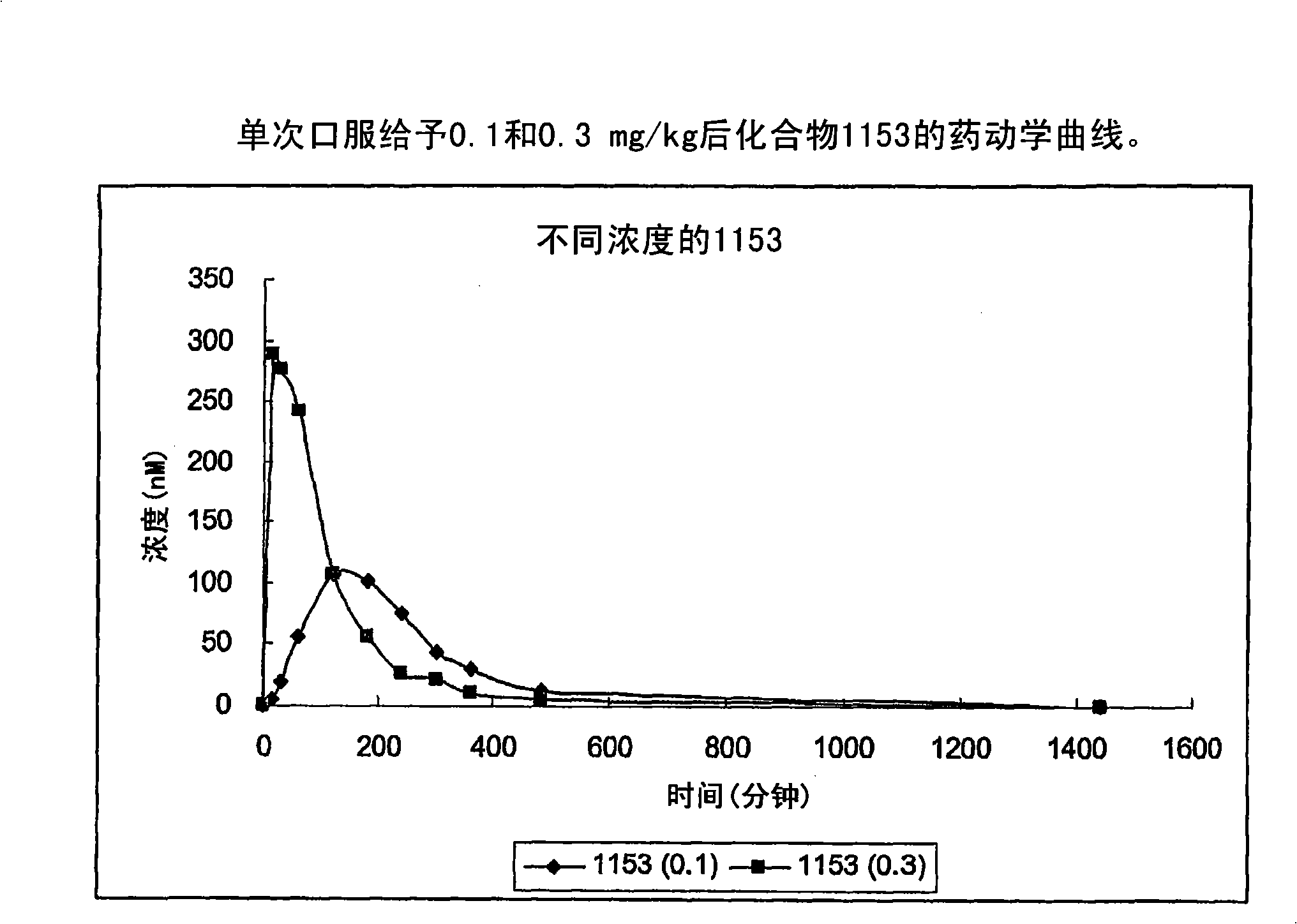
Piperidinyl, indolyl, pirinidyl, morpholinyl and benzimidazolyl urea derivatives as inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase for the treatment of hypertension, inflammations and other diseases
A technology of derivatives, compounds, piperidinyl, indolyl, pyridyl, morpholinyl and benzimidazolyl inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase for the treatment of hypertension, inflammation and other diseases Urea derivatives field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0265] 4-Aminopiperidine (2.125 g, 21.2 mmol) was dissolved in toluene (50 mL). Benzaldehyde (2.16 mL, 21.2 mmol) was added. The reaction was equipped with a Dean-Stark trap and condenser and refluxed for 4 hours under nitrogen atmosphere. At this point, if no more water was formed, the reaction was cooled to 0°C and BOC anhydride (4.63 g, 21.2 mmol) was added via syringe over 10 minutes. The reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature over 1 hour and stirred for an additional 12 hours. The solvent was removed in vacuo and the resulting oil washed with KHSO 4 (aqueous) (1M, 21.2 mL) was treated. Stir for 1.5 hours. Water (25 mL) was added to the reaction, and the aqueous suspension was washed with diethyl ether (3x100 mL). The aqueous layer was then basified with KOH to pH = 10 and extracted with dichloromethane (3 x 100 mL). MgSO for organic layer 4 Drying and evaporation gave 4.76 g of a yellow oil. To this oil (1.0 g) was added THF (25 mL). Stir for 5 minutes ...
Embodiment 2
[0273] Piperidinyl urea: General procedure for the alkylation of N-(1-ethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N'-(adamantan-1-yl)urea (R=Et, 1152):
[0274]
[0275] The appropriate piperidinyl urea (0.319 mmol) was mixed with the appropriate alkyl or benzyl bromide (X=Br) (0.382 mmol) and K 2 CO 3 (132 mg, 0.96 mmol) were mixed in DMF (3.0 mL). The reaction solution was heated at 50° C. for 12 hours. At this point, the reaction was allowed to cool to room temperature and the solvent was removed in vacuo. Residues in DCM and NaHCO 3 Partition between saturated aqueous solutions, remove the organic layer and wash with Na 2 SO 4 dry. The solvent was evaporated and the residue was chromatographed on silica gel using ammonia saturated methanol / DCM as eluent (5:100). Yield = 42%. Mp.: 203-213°C dec. 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 ): 4.15-4.05 (br, 2H), 3.63-3.47 (m, 1H), 2.91-2.81 (br m, 2H), 2.39 (q, J=7.18Hz, 2H), 2.13-1.88 (brm, 13H) , 1.66 (br, 6H), 1.40 (qd, J=8.3, 3.3Hz, 2H), 1.07 (t, J=...
Embodiment 3
[0277]
[0278] N-(1-n-propylpiperidin-4-yl)-N’-(adamantan-1-yl)urea (1155)
[0279] Yield = 60%. Mp.: 195-200°C dec. 1 H (300MHz, CDCl 3 ): 4.10-4.00(br, 2H), 3.60-3.45(m, 1H), 2.90-2.78(m, 2H), 2.32-2.22(m, 2H), 2.10-1.70(m, 13H), 1.70-1.57 (br, 6H), 1.56-1.30 (m, 4H), 0.88 (t, J=7.4Hz, 3H).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com