Method for preparing optical pure 1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine by separation
An ethylamine and optical technology, which is applied in the field of preparing optically pure 1-ethylamine, can solve the problems of high cost and difficulty in large-scale production, and achieve good results, high-efficiency preparation methods, and simple separation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
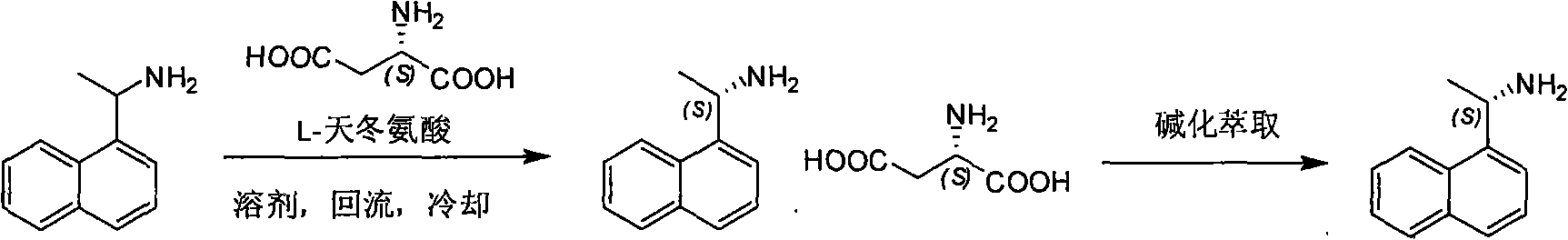
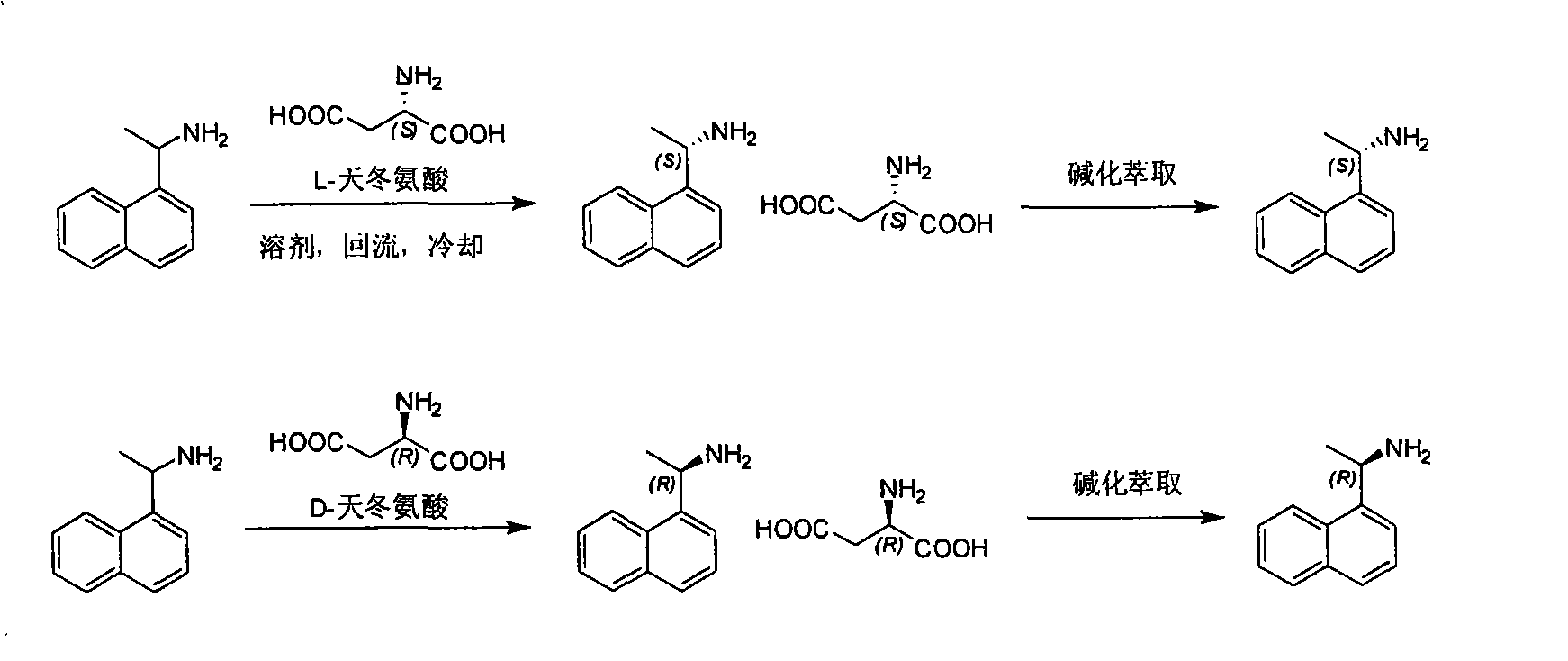
[0012] 1, the preparation of (S)-1-(1-naphthalene) ethylamine
[0013] Method A:
[0014] 1-(1-naphthalene) ethylamine (5g, 2.9mmol) and L-aspartic acid (3.9g, 2.9mmol) join in the mixed solution of dioxane (10ml) and water (100ml), heat to The reaction solution was clarified, cooled overnight, and filtered to obtain the aspartic acid salt of (S)-1-(1-naphthalene)ethylamine. Recrystallized with dioxane (1ml) and water (10ml), the obtained solid was added to water (50ml), and washed with K 2 CO 3 Adjust the pH to 9-10, extract three times with dichloromethane (60ml, 30ml, 20ml), combine the dichloromethane layers, wash with water (30ml), saturated brine (30ml) once each, and wash with anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 Dry, filter, and concentrate the filtrate to dryness to obtain light yellow oil (0.6g, yield: 24%)
[0015] Method B:
[0016] 1-(1-naphthalene) ethylamine (5g, 2.9mmol) and L-aspartic acid (3.9g, 2.9mmol) join in the mixed solution of dioxane (100ml) and water (10m...
Embodiment 2
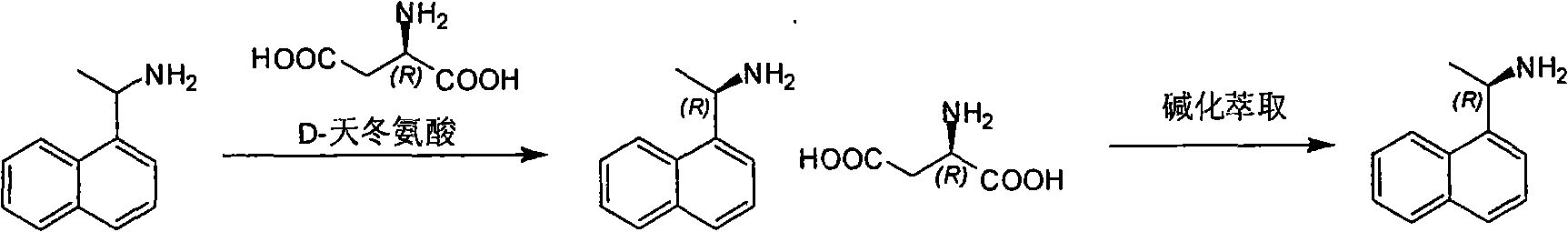
[0022] 1, the preparation of (R)-1-(1-naphthalene) ethylamine
[0023] 1-(1-naphthalene) ethylamine (500g, 2.9mol) and D-aspartic acid (389g, 2.9mol) are added in the mixed solution of dioxane (1000ml) and water (1500ml), heated to reaction The liquid was clarified, cooled overnight, and filtered to obtain (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine aspartic acid salt. Use dioxane (500ml) and water (750ml) to recrystallize, and the solid obtained joins in the water (500ml), with K 2 CO 3 Adjust the pH to 9-10, extract three times with dichloromethane (600ml, 300ml, 200ml), combine the dichloromethane layers, wash with water (300ml), saturated brine (300ml) once each, and wash with anhydrous Na 2 SO4 was dried, filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness to obtain a pale yellow oil (100 g, yield: 40%).
Embodiment 3
[0025] L, D- aspartic acid cross split
[0026] The mother liquor that obtains among the embodiment 1 or 2 is used K 2 CO 3 After alkalization, extract three times with dichloromethane (1000ml, 500ml, 300ml), wash with water (500ml), saturated brine (500ml) once each, and wash with anhydrous Na 2 Dry over SO4, filter, and concentrate the filtrate to dryness to give a pale yellow oil. Then add a mixed solution of dioxane (1000ml) and water (1500ml), D-aspartic acid or L-aspartic acid (276g) is added, heated to the reaction solution clarification, cooled overnight, filtered to obtain ( R)-1-(1-naphthalene)ethylamine aspartic acid salt or (S)-1-(1-naphthalene)ethylamine aspartic acid salt. Use dioxane (500ml) and water (750ml) to recrystallize, and the solid obtained joins in the water (1000ml), with K 2 CO 3 Adjust the pH to 9-10, extract three times with dichloromethane (1000ml, 500ml, 300ml), combine the dichloromethane layers, wash with water (500ml), saturated brine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com