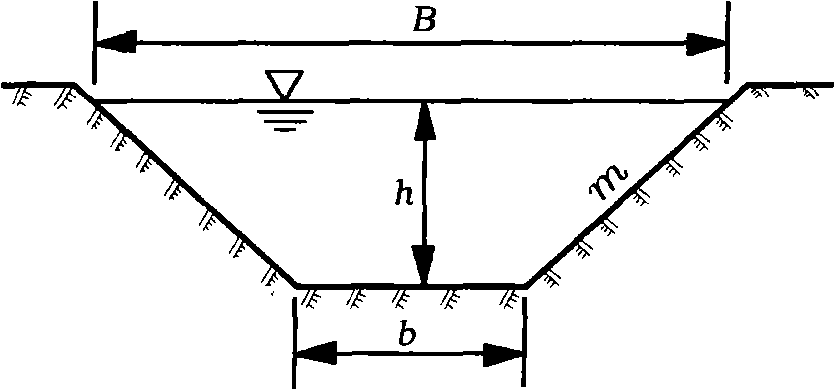
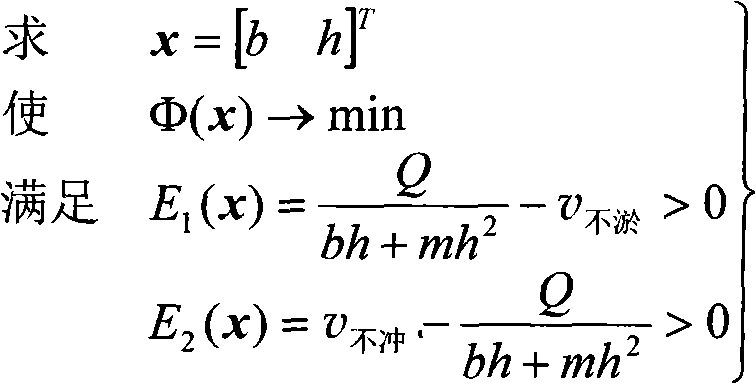Stable water transfer channel
A channel and stable technology, applied in irrigation pipelines, applications, buildings, etc., can solve the problems of large variation in river facies coefficient, channel deformation, and failure to reach a practical level, and achieve the effect of stable geometric section shape and avoid erosion or deposition deformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] Known channel design flow Q=200m 3 / s, annual average sand concentration S=18.35kg / m 3 , the average sinking velocity of suspended sediment ω=0.15cm / s, the roughness n=0.01, the slope coefficient m=1.5, and the cross-section and vertical gradient of the channel are calculated using the mathematical model of the non-scouring and non-silting water delivery channel.
[0089] Firstly, the following two formulas are used to calculate the non-scouring velocity and the non-silting velocity respectively:
[0090] υ 不冲 = υ0 (2.5sR 3 / 2 ω 1 / 2 +1) 1 / 3
[0091] In the formula: υ 不冲 is the non-flushing velocity (m / s); υ 0 When it is clear water, the non-flushing velocity (m / s) under the same hydraulic radius is taken as υ in this embodiment 0 =0.52m / s; S is the sand content (kg / m 3 ); R is the hydraulic radius (m); ω is the average sedimentation velocity (cm / s).
[0092]
[0093] In the formula: υ 不淤 is the non-silting velocity (m / s); S is the sand concentration (kg / m ...
Embodiment 2
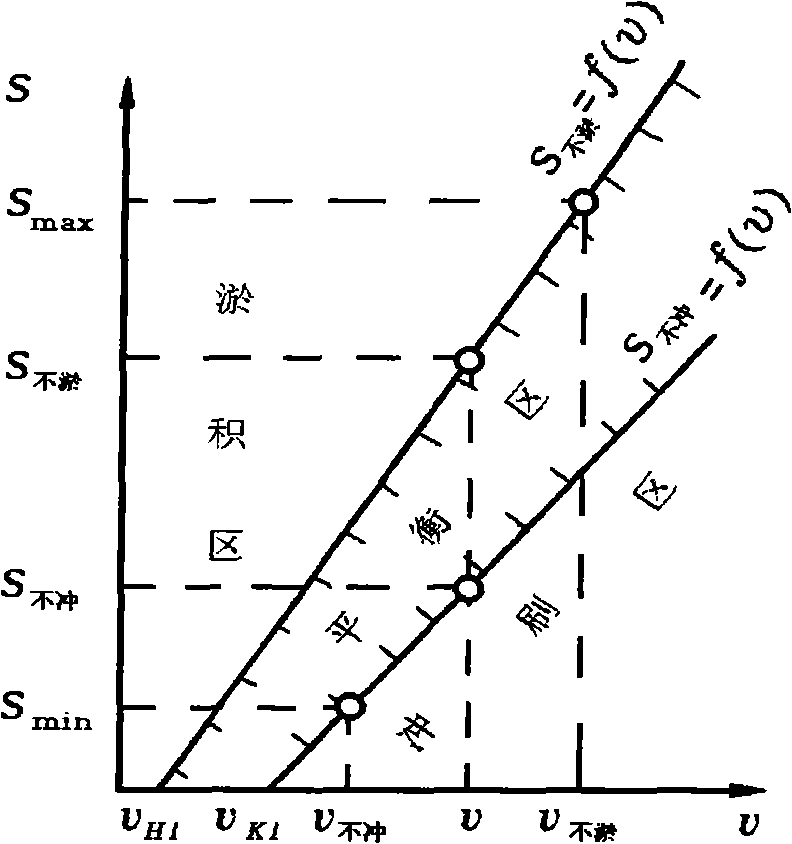
[0098] Known channel design flow Q=10.0m 3 / s, the maximum allowable sand concentration S max =296kg / m 3 , the median diameter of suspended sand d 50 = 0.039mm, roughness n = 0.025, slope coefficient m = 1.0, the cross-section and vertical gradient of the channel are calculated using the mathematical model of the scour-silting balance water delivery channel.
[0099] First, use the following two formulas to calculate the maximum allowable sediment concentration s max non-silting velocity υ 不淤 and the minimum sand concentration s min dead flow υ 不冲 :
[0100]
[0101]
[0102] In the formula: K H 、K K are the non-silting and non-scouring sediment-carrying coefficients, respectively. For loess channels, K H =3200,K K =1100; d 50 is the median particle size of the sediment (mm); R is the hydraulic radius (m); ω is the average sedimentation velocity (mm / s); Stop unit speed (m / s) and start unit speed (m / s) respectively.
[0103] Then the calculation formulas of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com