Probe-fixing and example-oscillating non-micro rod scanning force microscope lens
An oscillating, microscope technology, applied in the field of scanning probe microscopy, can solve the problems of difficulty in the manufacture of scanning force microscopy probes, inability to use microrodless probes, etc., to improve atomic resolution, reduce probe costs, and improve measurement. The effect of sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: The basic probe is fixed and the sample is oscillating without a microrod scanning force microscope lens body.
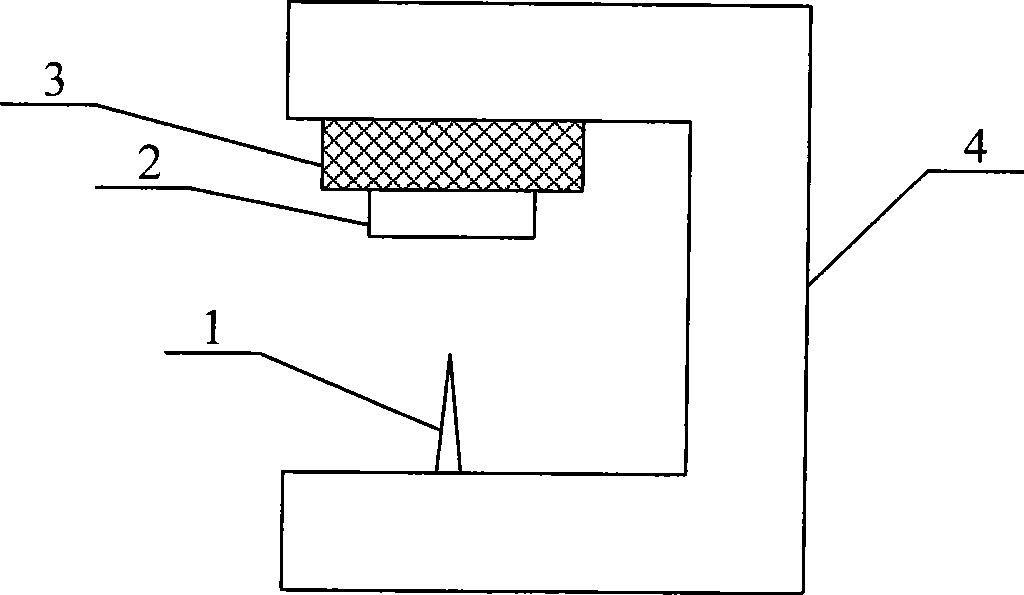
[0030] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the basic probe-fixed and sample-oscillating microrodless scanning force microscope mirror body. The positioner 4 is arranged between the probe 1 and the vibrator 3 , and the probe 1 points to the sample 2 fixed on the vibrator 3 .
[0031] During operation, the positioner 4 is used for positioning, scanning, and probe-sample gap adjustment between the probe 1 and the sample 2 . The variation of the force between probe 1 and sample 2 is given by the variation of the dynamic eigenfrequency of the vibrator.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Using the XYZ positioning piezoelectric tube with the probe fixed and the sample oscillating without a microrod scanning force microscope mirror body.
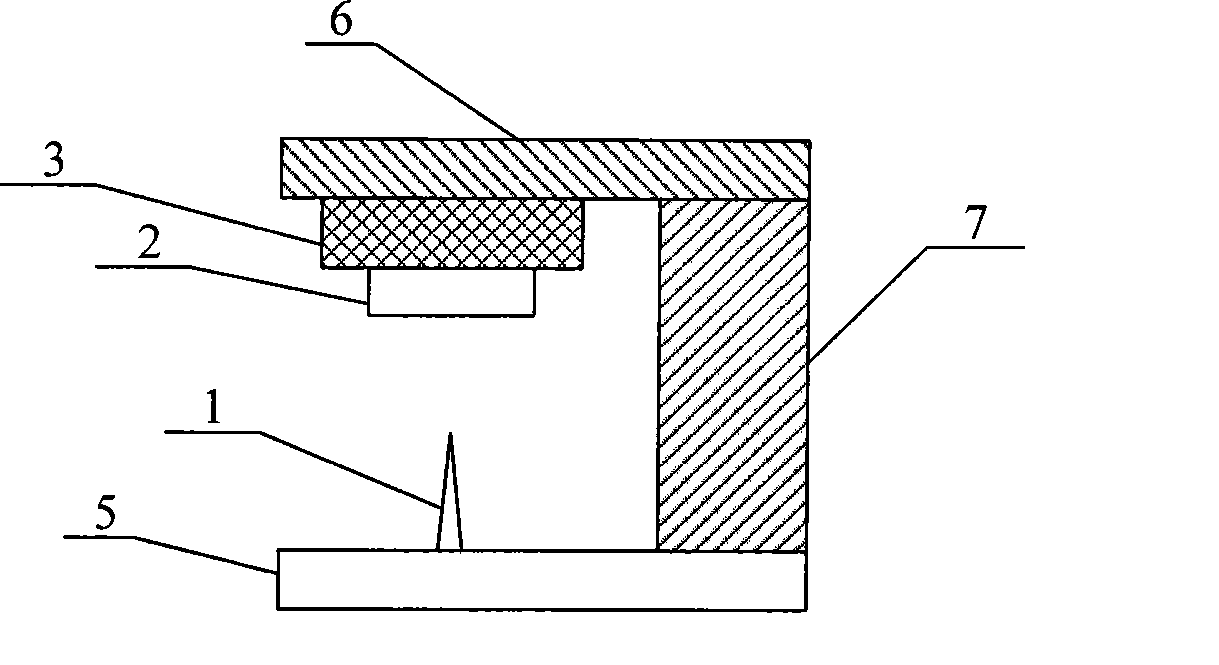
[0033] The positioner 4 in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is composed of an XYZ positioning piezoelectric tube 7 and a probe seat 5 and a vibrator seat 6 respectively arranged at both ends thereof, as figure 2 , the vibrator 3 is fixed on the vibrator base 6, the probe 1 is fixed on the probe base 5 and points to the sample 2 fixed on the vibrator 3, so that the XYZ positioning piezoelectric tube 7 can complete the connection between the probe 1 and the sample 2 Positioning, scanning, and probe-sample gap adjustment. The variation of the force between probe 1 and sample 2 is given by the variation of the dynamic eigenfrequency of the vibrator.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: Using a quartz micro-fork vibrator to fix the probe and oscillate the sample without a micro-rod scanning force microscope mirror body.
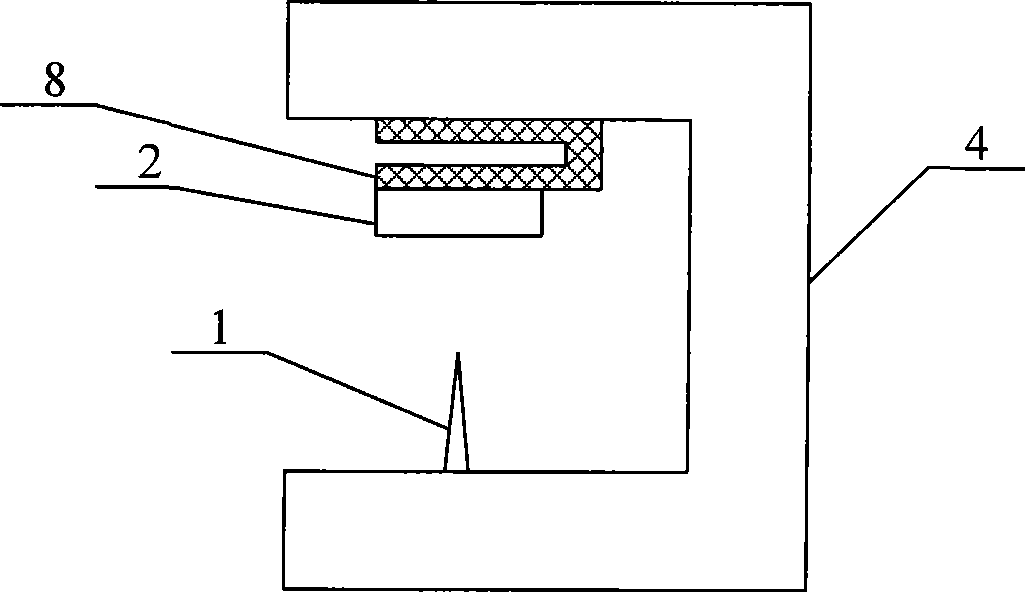
[0035] The vibrator 3 in the above embodiment may be a piezoelectric vibrator, preferably a crystal vibrator, especially a quartz vibrator. The quartz vibrator can also be in the shape of a plate or a tuning fork. image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the scanning force microscope mirror body of the microrod-free scanning force microscope using the quartz micro-fork vibrator 8 with the probe fixed and the sample oscillating.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com