Semiconductor non-volatile memory
一种非易失性、半导体的技术,应用在静态存储器、只读存储器、信息存储等方向,能够解决增加升压电路、消耗电流增加、妨碍系统高速化等问题,达到高速化访问、减少功耗的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
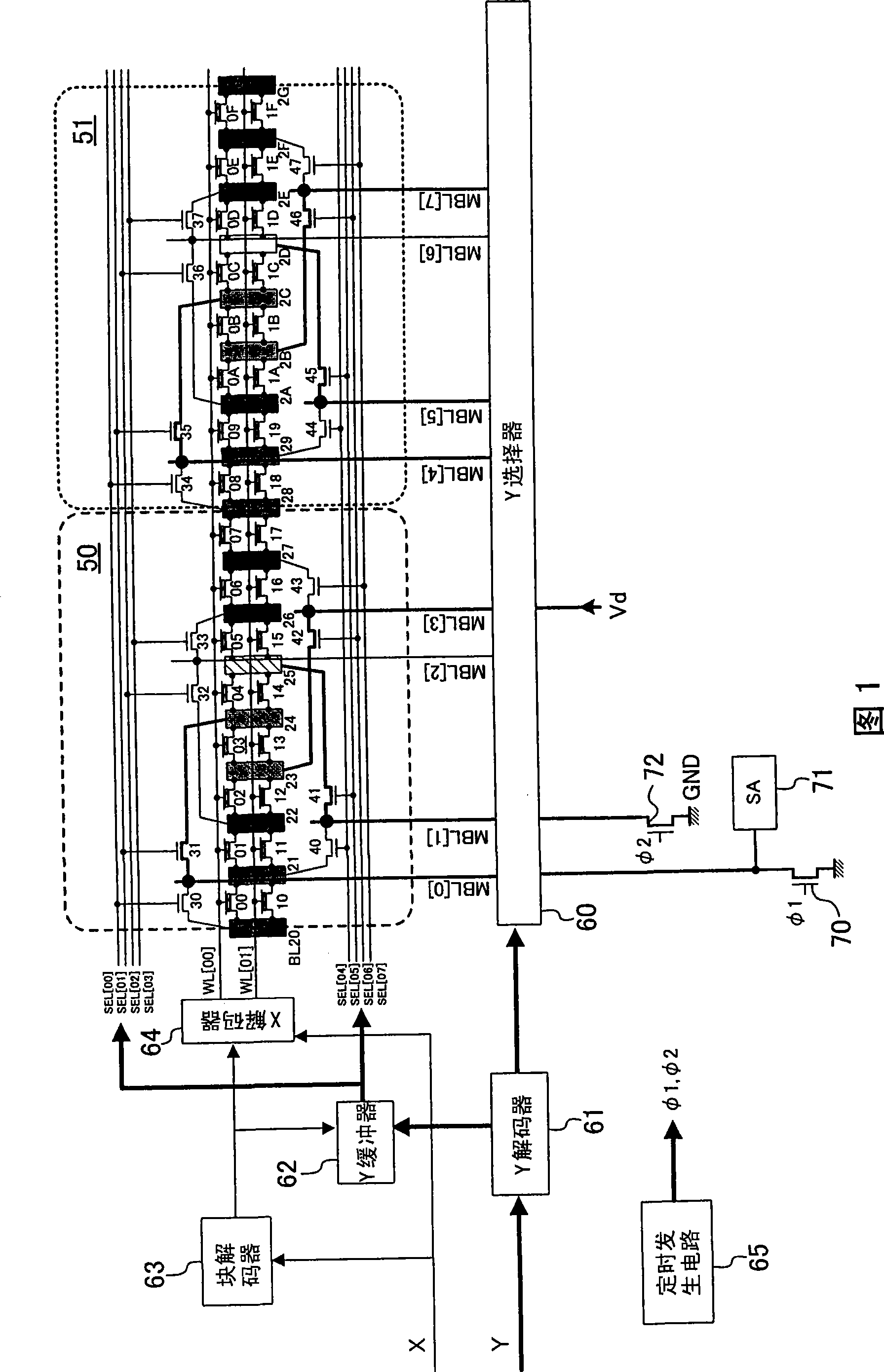
[0056] FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the configuration of a semiconductor nonvolatile memory according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0057] The semiconductor nonvolatile memory shown in FIG. 1 is a VGA (Virtual Ground Architecture) type, in which memory cells are arranged continuously between bit lines, and adjacent memory cells share bit lines. 00 to 0F and 10 to 1F are memory cells, BL20 to 2G are bit lines, and these constitute a memory cell array. For example, bit line BL24 is connected to both the source of memory cell 03 and the drain of memory cell 04 .
[0058] Moreover, in FIG. 1, WL[00]~[01] are word lines, MBL[0]~[7] are main bit lines, 30~37, 40~47 are selected according to the selection gate signal SEL[00]~ [07] The selection gates of the bit lines BL20-2G and the main bit lines MBL[0]-[7] are selectively connected. Also, 63 is a block decoder that accepts an X address and activates a sector, 64 is an X decoder that receives an X address and activate...
Embodiment approach 2
[0076] 4 is a diagram showing the structure of a semiconductor nonvolatile memory according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In FIG. 4 , the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 1 are assigned to components common to those in FIG. 1 , and detailed description thereof will be omitted here.
[0077] The semiconductor nonvolatile memory of FIG. 4 includes, in addition to the configuration of FIG. 1 , a proximity effect compensator unit NEC as a circuit element used for reading. The proximity effect compensator unit NEC includes a proximity bit line reset transistor 73 and a current source 74 that flows a current smaller than the ON current of the memory cell. The current of the power source 74 is adjusted to be equal to the reference current, that is, approximately half of the current when the memory cell is "1". The same control signal Φ1 as that of the read input reset transistor 70 is given to the adjacent bit line reset transistor 73 . Y selector 60 a is config...
Embodiment approach 3
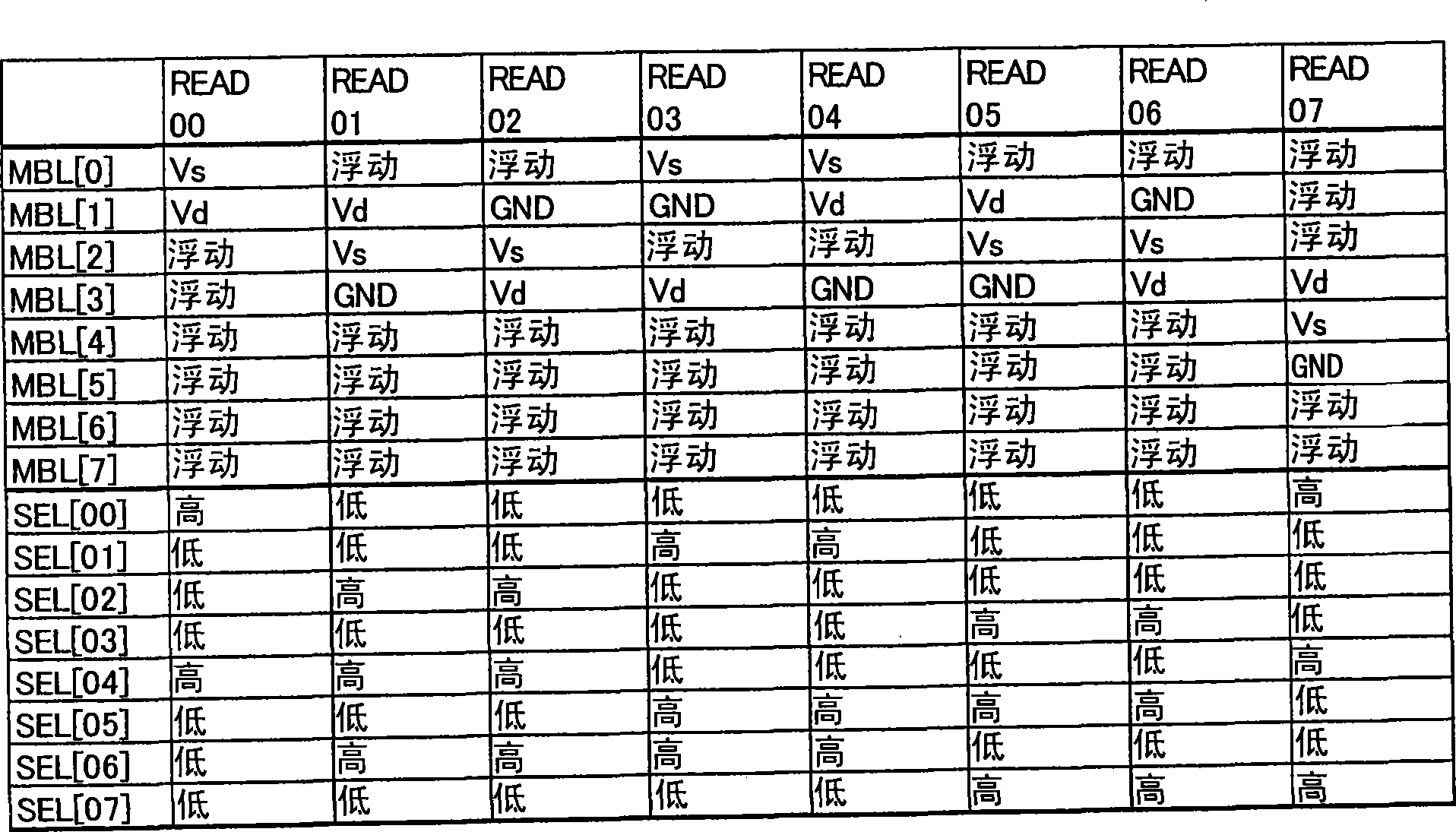
[0093] The configuration of the semiconductor nonvolatile memory according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention is the same as that of FIG. 1 . In this embodiment, the bit line adjacent to the drain bit line on the side opposite to the source bit line is forced to be at the ground potential also during reading of the memory cell. For example, when reading the memory cell 03, the bit line BL22 connected to the drain of the memory cell 02, which is the third memory cell having the drain bit line BL23 connected to the source, is also connected to the ground power supply GND. . Other operations are the same as in Embodiment 1.
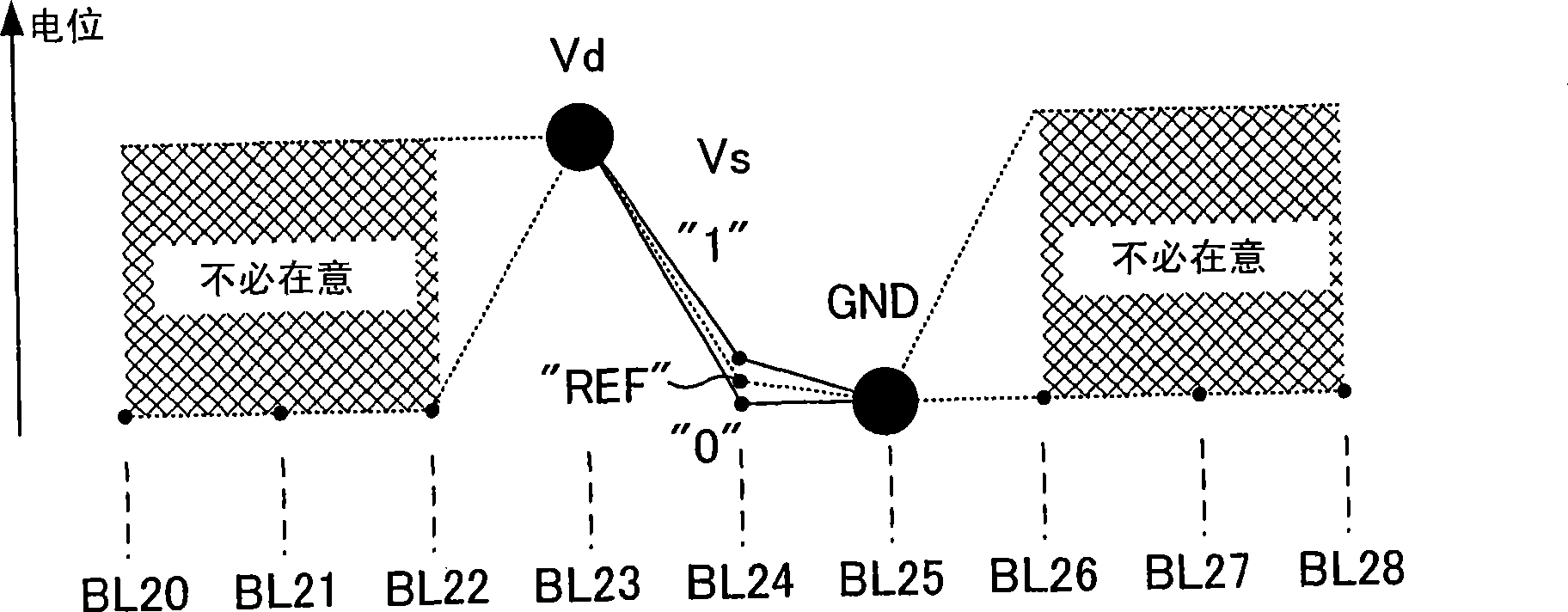
[0094] Figure 7 It is a diagram showing how the potential of the bit line near the memory cell 03 is read when the integration period ends in the present embodiment. Such as Figure 7 As shown, the bit line BL22 adjacent to the drain bit line BL23 on the side opposite to the source bit line BL24 is at ground potential.
[0095] If the bit line BL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com