Improved method for expanding and transforming jitter and modulating watermark
A technology of jitter modulation and expansion transformation, applied in image data processing, instrumentation, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of loss of carrier signal quality, the problem of amplitude scaling attack not being well solved, and not being flexible enough.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
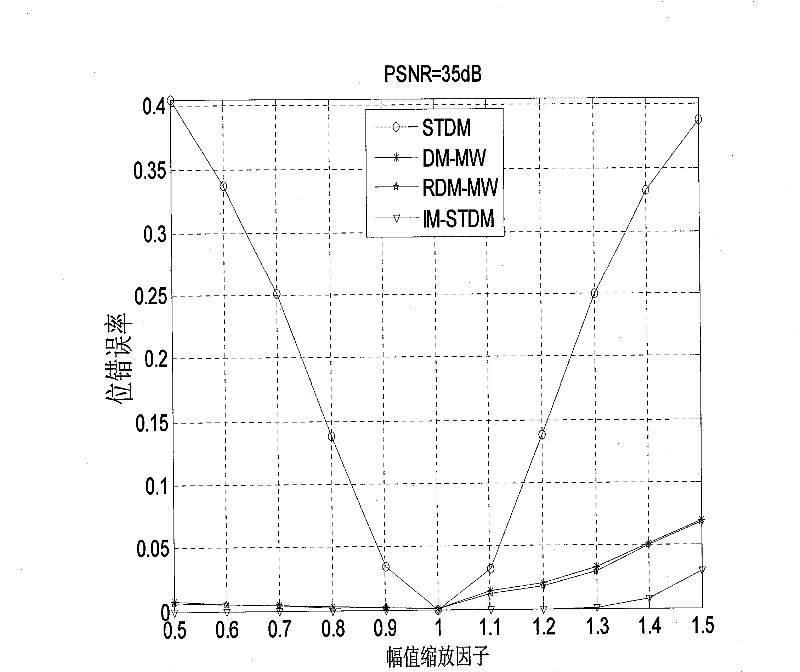
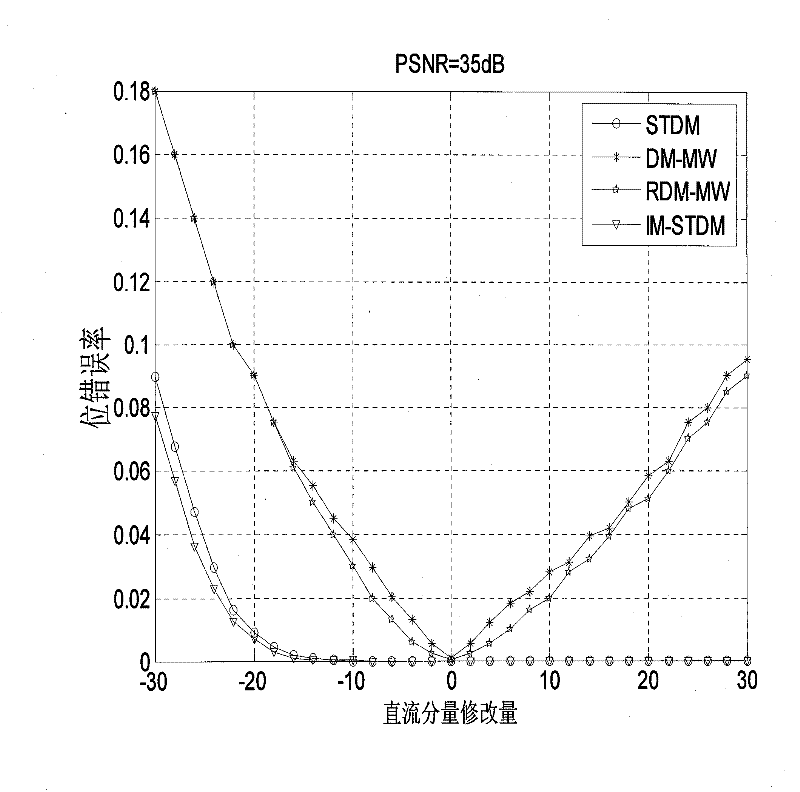
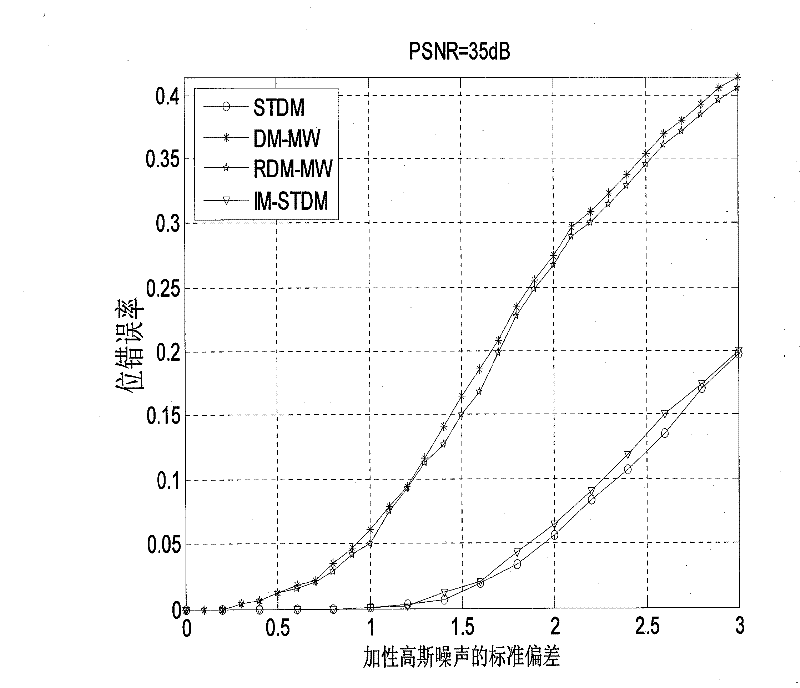
[0033] With watermark carrier A o For an image signal, an improved STDM watermark method is implemented. The watermark embedding process is as follows figure 1 As shown, including the following steps:
[0034] 1) From A o The block DCT (DCT: Discrete Cosine Transform) domain extracts the carrier signal x. Put A first o Divide into multiple non-overlapping sub-blocks, each block contains 8×8 pixels, and then perform DCT transformation on each block. Perform zigzag sorting on the 64 DCT coefficients in each block, and select 62 DCT coefficients between 3 and 64. Arrange all the extracted DCT coefficients into a large sequence as the carrier signal. The extracted carrier signal is shuffled in a random order, and the final carrier signal is generated as x, and its length is N. This step is implemented by the carrier signal extraction device.
[0035] 2) Express the information m to be embedded as a binary sequence b of length p, where each element b j ∈Ω, Ω={0,1}, j=1,...,p. This s...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The difference from Example 1 is that
[0080] In step 5 of the watermark embedding method, the method of calculating the feature sequence s. The DC component of each 8×8 image sub-block constitutes a vector, which has nothing to do with the watermarking process. In this embodiment, the average value of this vector is used, denoted as C00, to construct the characteristic sequence s. Specifically, the characteristic sequence s is taken as
[0081] s=C00I N
[0082] At the same time, in step 4 of the watermark detection method, the method of calculating the feature sequence s′ is also modified accordingly.
Embodiment 3
[0084] The difference from Example 1 is that
[0085] By removing the components along the watermark embedding direction from the carrier signal, a vector υ that has nothing to do with the watermark embedding process can be obtained. For x j , J=1,..., p, can be determined v j = x j - x j T uu / u T u . This embodiment uses each sub-vector v j The absolute value of the mean value of, constructs the characteristic sequence s. Specifically, the jth subvector s of the feature sequence s j Take as
[0086] In step 5 of the watermark embedding method, the method of calculating the feature sequence s. In this embodiment, the standard deviation of each sub-vector of the carrier signal is used to construct the characteristic sequence s. Let the function Var{·} denote the variance operator of the vector. Specifically, the jth subvector s of the feature sequence s j Take as
[0087] s j = Var { x j } I L
[0088] In s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com